Direct vasodilators US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Direct vasodilators. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Direct vasodilators US Medical PG Question 1: A 72-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of blurry vision for the past 3 days. He has also had 4 episodes of right-sided headaches over the past month. He has no significant past medical history. His father died of coronary artery disease at the age of 62 years. His temperature is 37.2°C (99°F), pulse is 94/min, and blood pressure is 232/128 mm Hg. Fundoscopy shows right-sided optic disc blurring and retinal hemorrhages. A medication is given immediately. Five minutes later, his pulse is 75/min and blood pressure is 190/105 mm Hg. Which of the following drugs was most likely administered?
- A. Nicardipine
- B. Hydralazine
- C. Nitroprusside
- D. Fenoldopam
- E. Labetalol (Correct Answer)
Direct vasodilators Explanation: ***Labetalol***
- This patient presents with **malignant hypertension** given the severely elevated blood pressure (232/128 mm Hg) and signs of **end-organ damage** (blurry vision, optic disc blurring, retinal hemorrhages suggesting hypertensive retinopathy, and new-onset headaches).
- **Labetalol** is a mixed alpha- and beta-blocker commonly used in hypertensive emergencies because of its **rapid onset of action** and ability to effectively lower blood pressure without causing significant reflex tachycardia. The decrease in pulse rate from 94/min to 75/min after administration is consistent with its beta-blocking effects.
*Nicardipine*
- **Nicardipine** is a dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker that primarily causes **vasodilation**, making it effective in hypertensive emergencies.
- While it would lower blood pressure, it typically causes **reflex tachycardia** due to vasodilation, which is not observed in this patient (pulse decreased).
*Hydralazine*
- **Hydralazine** is a direct arterial vasodilator often used in hypertensive emergencies, but it typically causes a more pronounced **reflex tachycardia** than calcium channel blockers.
- Its onset of action can also be less predictable, and its use is generally avoided if there's evidence of **coronary artery disease** due to the risk of increased myocardial oxygen demand.
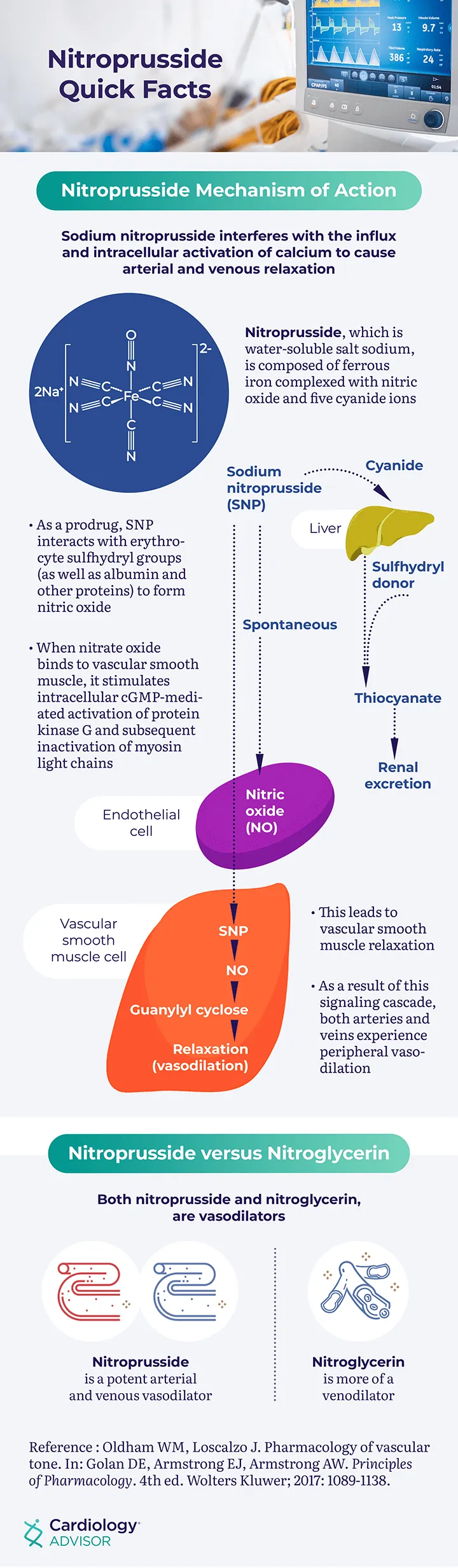
*Nitroprusside*
- **Nitroprusside** is a powerful balanced arterial and venous vasodilator, leading to a rapid and significant drop in blood pressure.
- It is known for causing **reflex tachycardia** and has a risk of **cyanide toxicity** with prolonged use, making its use in this scenario less ideal given the patient's existing elevated pulse.
*Fenoldopam*
- **Fenoldopam** is a dopamine-1 receptor agonist that causes vasodilation and improves renal blood flow, useful in hypertensive emergencies.
- Like other vasodilators, it can cause **reflex tachycardia** and may lead to increased intraocular pressure, which would be a concern in a patient with acute blurry vision.
Direct vasodilators US Medical PG Question 2: A 75 year-old gentleman presents to his general practitioner. He is currently being treated for hypertension and is on a multi-drug regimen. His current blood pressure is 180/100. The physician would like to begin treatment with minoxidil or hydralazine. Which of the following side effects is associated with administration of these drugs?
- A. Persistent cough
- B. Cyanosis in extremities
- C. Fetal renal toxicity
- D. Systemic volume loss
- E. Reflex tachycardia (Correct Answer)
Direct vasodilators Explanation: ***Reflex tachycardia***
- Both **minoxidil** and **hydralazine** are direct arterial vasodilators, causing a significant drop in **peripheral vascular resistance**.
- This vasodilation triggers a **baroreflex response**, leading to an increase in heart rate and **cardiac contractility** to maintain cardiac output, resulting in reflex tachycardia.
*Persistent cough*
- **Persistent cough** is a common side effect associated with **ACE inhibitors**, such as lisinopril or enalapril, due to the accumulation of **bradykinin**.
- This side effect is not typically seen with **minoxidil** or **hydralazine**, which act directly on vascular smooth muscle to cause vasodilation.
*Cyanosis in extremities*
- **Cyanosis** (bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes) usually indicates **hypoxemia** or poor peripheral perfusion.
- While sometimes associated with severe cardiogenic shock or specific drug toxicities like methemoglobinemia (not related to minoxidil or hydralazine), it is not a direct or typical side effect of these vasodilators.
*Fetal renal toxicity*
- **Fetal renal toxicity**, including **fetal renal dysfunction** and **oligohydramnios**, is a well-known risk associated with **ACE inhibitors** and **ARBs** during pregnancy.
- Neither **minoxidil** nor **hydralazine** are primarily linked to this specific fetal adverse effect, though hydralazine can be used in pregnancy for severe hypertension.
*Systemic volume loss*
- **Systemic volume loss** is usually caused by conditions like **dehydration**, excessive diuresis, or hemorrhage.
- While vasodilators can reduce blood pressure, they do not directly cause **systemic volume depletion**; rather, the reflex response to vasodilation can include fluid retention to counteract the blood pressure drop.
Direct vasodilators US Medical PG Question 3: A 55-year-old man presents to the emergency department complaining of mild vision changes, dizziness, and severe pain in the chest for the past hour. He has also been experiencing nausea since this morning and has already vomited twice. Past medical history includes poorly controlled type 2 diabetes and end-stage renal disease requiring dialysis. His blood pressure is 210/100 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 18/min. Ophthalmic examination of his eyes show papilledema and flame-shaped hemorrhages and he is diagnosed with hypertensive emergency. Treatment involves rapidly lowering his blood pressure, and he is started on intravenous sodium nitroprusside while emergent dialysis is arranged. Which of the following cardiac pressure-volume loops closely represents the action of the drug he has been administered, where blue represents before administration and purple represent after administration?
- A. Diagram B (Correct Answer)
- B. Diagram E
- C. Diagram A
- D. Diagram C
- E. Diagram D
Direct vasodilators Explanation: ***Diagram B***
- Sodium nitroprusside is a **balanced vasodilator**, meaning it reduces both **preload** (venous return) and **afterload** (arterial resistance).
- This typically results in a decrease in both **end-diastolic volume** (due to reduced preload) and **systolic pressure**/end-systolic volume (due to reduced afterload), as shown by the shift in Diagram B.
*Diagram E*
- This loop represents an increase in **contractility** and a decrease in **afterload**, which is not the primary action of nitroprusside.
- While nitroprusside causes vasodilation, it doesn't directly increase contractility; it primarily works by reducing the heart's workload.
*Diagram A*
- This diagram shows a significant increase in **preload** (increased end-diastolic volume) with a minimal change in afterload, which is inconsistent with sodium nitroprusside's action as a vasodilator.
- Nitroprusside would decrease preload rather than increase it.
*Diagram C*
- This loop depicts a significant increase in **afterload** (higher systolic pressure) and **preload** (increased end-diastolic volume), which is contrary to the effects of a vasodilator like sodium nitroprusside.
- Nitroprusside aims to lower blood pressure and reduce cardiac workload.
*Diagram D*
- This diagram illustrates a substantial increase in **contractility** with a relatively unchanged afterload, which is not the expected effect of sodium nitroprusside.
- Nitroprusside primarily acts on vascular smooth muscle to cause relaxation, not on myocardial contractility.
Direct vasodilators US Medical PG Question 4: A 55-year-old woman comes to the physician because of involuntary hand movements that improve with alcohol consumption. Physical examination shows bilateral hand tremors that worsen when the patient is asked to extend her arms out in front of her. The physician prescribes a medication that is associated with an increased risk of bronchospasms. This drug has which of the following immediate effects on the cardiovascular system?
Stroke volume | Heart rate | Peripheral vascular resistance
- A. ↓ ↓ ↓
- B. ↓ ↓ ↑ (Correct Answer)
- C. ↓ ↑ ↑
- D. ↑ ↑ ↑
- E. ↑ ↑ ↓
Direct vasodilators Explanation: ***↓ ↓ ↑***
- This patient likely has **essential tremor**, which is characterized by **bilateral hand tremors** that improve with alcohol and worsen with intention (postural tremor). The prescribed medication is a **beta-blocker** (e.g., propranolol), which is associated with an increased risk of bronchospasms due to blocking **beta-2 receptors** in the airways.
- Beta-blockers **decrease heart rate** (negative chronotropic effect) and **stroke volume** (negative inotropic effect) by blocking beta-1 receptors in the heart, reducing cardiac output.
- **Peripheral vascular resistance increases** acutely due to: (1) **unopposed alpha-1 adrenergic tone** in blood vessels (loss of beta-2 mediated vasodilation), and (2) baroreceptor-mediated reflex vasoconstriction in response to decreased cardiac output. This helps maintain blood pressure despite reduced cardiac output.
*↓ ↓ ↓*
- While beta-blockers decrease **heart rate** and **stroke volume**, peripheral vascular resistance does not decrease acutely. A decrease in all three parameters would cause severe hypotension.
- The loss of beta-2 receptor-mediated vasodilation and baroreceptor reflexes lead to increased, not decreased, peripheral vascular resistance.
*↓ ↑ ↑*
- Beta-blockers **decrease heart rate** through beta-1 blockade, not increase it. This is their primary cardiac mechanism of action.
- An increase in heart rate would be expected with sympathomimetic drugs or anticholinergics, not beta-blockers.
*↑ ↑ ↑*
- This combination indicates increased cardiovascular activity, which is the opposite effect of **beta-blockers**.
- Beta-blockers reduce heart rate and stroke volume by blocking beta-1 receptors; they do not increase these parameters.
- This pattern would suggest sympathetic activation or administration of an adrenergic agonist.
*↑ ↑ ↓*
- Beta-blockers **decrease** (not increase) both heart rate and stroke volume through beta-1 receptor blockade.
- While decreased peripheral vascular resistance occurs with vasodilators, beta-blockers acutely **increase** PVR due to unopposed alpha-adrenergic tone.
Direct vasodilators US Medical PG Question 5: A research team is studying the effects of a novel drug that was discovered to treat type 2 diabetes. In order to learn more about its effects, they follow patients who are currently taking the drug and determine whether there are adverse effects that exceed anticipated levels and may therefore be drug-related. They discover that the drug causes an excess of sudden cardiac death in 19 patients with renal failure out of 2 million total patients that are followed. Based on these results, an additional warning about this serious adverse effect is added to the investigator brochure for the drug. Which of the following clinical phase studies does this study most likely describe?
- A. Phase IV (Correct Answer)
- B. Phase II
- C. Phase V
- D. Phase III
- E. Phase I
Direct vasodilators Explanation: ***Phase IV***
- This study occurs **after a drug has been approved and marketed**, focusing on post-marketing surveillance for long-term safety, effectiveness, and real-world side effects in a large and diverse patient population.
- The discovery of a rare but serious adverse effect (sudden cardiac death) in a large patient population (2 million) after the drug is already in use is characteristic of a **Phase IV clinical trial**.
*Phase II*
- Phase II trials involve a **larger group of patients (hundreds)** and focus on evaluating the drug's effectiveness and further assessing safety in patients with the target condition.
- This phase is typically conducted **before widespread marketing** and would not involve 2 million patients.
*Phase V*
- There is **no widely recognized "Phase V"** in standard clinical trial terminology (Phases I-IV focus on drug development and post-marketing surveillance).
- This term is sometimes used informally to refer to **health economics and outcomes research** or implementation studies, which are not described in the scenario.
*Phase III*
- Phase III trials are large-scale studies involving **thousands of patients** to confirm effectiveness, monitor side effects, compare the drug to standard treatments, and collect information for safe use.
- While large, these trials are conducted **before regulatory approval** and marketing, and would not typically follow 2 million patients already taking the drug in the real world.
*Phase I*
- Phase I trials are the **first stage of human testing**, involving a small group of healthy volunteers (20-100) to assess safety, dosage, and pharmacokinetics.
- The primary goal is to determine if the drug is safe enough for further testing, not to identify rare adverse events in a large patient population.
Direct vasodilators US Medical PG Question 6: A 28-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0, at 32 weeks' gestation is admitted to the hospital for the management of elevated blood pressures. On admission, her pulse is 81/min, and blood pressure is 165/89 mm Hg. Treatment with an intravenous drug is initiated. Two days after admission, she has a headache and palpitations. Her pulse is 116/min and regular, and blood pressure is 124/80 mm Hg. Physical examination shows pitting edema of both lower extremities that was not present on admission. This patient most likely was given a drug that predominantly acts by which of the following mechanisms?
- A. Inhibition of β1, β2, and α1 receptors
- B. Inhibition of angiotensin II production
- C. Activation of α2 adrenergic receptors
- D. Inhibition of sodium reabsorption
- E. Direct dilation of the arterioles (Correct Answer)
Direct vasodilators Explanation: ***Direct dilation of the arterioles***
- The development of **headache**, **palpitations**, and **tachycardia** (pulse 116), along with a reduction in blood pressure (124/80 mm Hg) and new-onset **pitting edema**, suggests a direct arterial vasodilator like **hydralazine**.
- **Hydralazine reduces peripheral vascular resistance** by directly relaxing vascular smooth muscle, primarily in arterioles, leading to reflex tachycardia and fluid retention as compensatory mechanisms.
*Inhibition of β1, β2, and α1 receptors*
- Labetaolol, which is commonly used in pre-eclampsia and acts by inhibiting β1, β2, and α1 receptors, would typically lead to a **decrease in heart rate and sympathetic compensation**, not palpitations and increased pulse.
- While it lowers blood pressure, it would not typically cause **reflex tachycardia and new-onset edema** to this extent unless there is an underlying cardiac issue or overdose.
*Inhibition of angiotensin II production*
- Inhibitors of angiotensin II production (like ACE inhibitors or ARBs) are **contraindicated in pregnancy** due to their teratogenic effects, especially in the second and third trimesters.
- They typically do not cause **reflex tachycardia and palpitations** as primary side effects, but rather dry cough (ACE inhibitors) or hyperkalemia.
*Activation of α2 adrenergic receptors*
- **Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists** (e.g., methyldopa, clonidine) reduce sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system, leading to a **decrease in heart rate and blood pressure**.
- While effective for hypertension in pregnancy, they are more associated with **sedation and dry mouth** rather than palpitations and reflex tachycardia, and they do not typically cause significant peripheral edema.
*Inhibition of sodium reabsorption*
- Medications that inhibit sodium reabsorption are **diuretics**. While diuretics can help manage edema, they primarily lower blood pressure by reducing blood volume, and are not typically the immediate go-to for acute severe hypertension in pregnancy.
- Diuretics would **reduce edema**, not cause new-onset pitting edema, and would not typically cause reflex tachycardia as seen in this patient unless there is profound hypovolemia leading to a compensatory increase in heart rate.
Direct vasodilators US Medical PG Question 7: A 54-year-old African American male presents to the emergency department with 1 day history of severe headaches. He has a history of poorly controlled hypertension and notes he hasn't been taking his antihypertensive medications. His temperature is 100.1 deg F (37.8 deg C), blood pressure is 190/90 mmHg, pulse is 60/min, and respirations are 15/min. He is started on a high concentration sodium nitroprusside infusion and transferred to the intensive care unit. His blood pressure eventually improves over the next two days and his headache resolves, but he becomes confused and tachycardic. Labs reveal a metabolic acidosis. Which of the following is the best treatment?
- A. Sodium nitrite (Correct Answer)
- B. Bicarbonate
- C. Methylene blue
- D. Ethanol
- E. Glucagon
Direct vasodilators Explanation: ***Sodium nitrite***
- This patient is exhibiting symptoms of **cyanide toxicity** (confusion, tachycardia, metabolic acidosis) due to prolonged high-dose **sodium nitroprusside** infusion.
- Sodium nitrite works by inducing **methemoglobinemia**, which then binds to cyanide to form **cyanmethemoglobin**, thereby detoxifying the cyanide.
- **Note:** In clinical practice, sodium nitrite is typically combined with **sodium thiosulfate** (which converts cyanide to thiocyanate for renal excretion), and **hydroxocobalamin** is now preferred as first-line therapy. However, among the options listed, sodium nitrite is the most appropriate antidote.
*Bicarbonate*
- While metabolic acidosis is present, **bicarbonate** only addresses the symptom (acidosis) and does not treat the underlying cause of **cyanide poisoning**.
- Without addressing the cyanide, the acidosis will persist or worsen.
*Methylene blue*
- **Methylene blue** is used to treat **methemoglobinemia**, not cyanide toxicity.
- In this scenario, inducing methemoglobinemia with sodium nitrite is part of the treatment for cyanide poisoning, not reversing it.
*Ethanol*
- **Ethanol** is used to treat **methanol** or **ethylene glycol poisoning** by competitively inhibiting alcohol dehydrogenase.
- It has no role in the treatment of **cyanide toxicity**.
*Glucagon*
- **Glucagon** is primarily used to treat **beta-blocker overdose** or severe **hypoglycemia**.
- It does not have any therapeutic effect in cases of **cyanide poisoning**.
Direct vasodilators US Medical PG Question 8: A 61-year-old obese man with recently diagnosed hypertension returns to his primary care provider for a follow-up appointment and blood pressure check. He reports feeling well with no changes since starting his new blood pressure medication 1 week ago. His past medical history is noncontributory. Besides his blood pressure medication, he takes atorvastatin and a daily multivitamin. The patient reports a 25-pack-year smoking history and is a social drinker on weekends. Today his physical exam is normal. Vital signs and laboratory results are provided in the table.
Laboratory test
2 weeks ago Today
Blood pressure 159/87 mm Hg Blood pressure 164/90 mm Hg
Heart rate 90/min Heart rate 92/min
Sodium 140 mE/L Sodium 142 mE/L
Potassium 3.1 mE/L Potassium 4.3 mE/L
Chloride 105 mE/L Chloride 103 mE/L
Carbon dioxide 23 mE/L Carbon dioxide 22 mE/L
BUN 15 mg/dL BUN 22 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.80 mg/dL Creatinine 1.8 mg/dL
Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) shows a bilateral narrowing of renal arteries. Which of the following is most likely this patient's new medication that caused his acute renal failure?
- A. Clonidine
- B. Verapamil
- C. Hydralazine
- D. Captopril (Correct Answer)
- E. Hydrochlorothiazide
Direct vasodilators Explanation: ***Captopril***
- The patient has **bilateral renal artery stenosis** and develops **acute renal failure** after starting a new blood pressure medication. **ACE inhibitors** (like captopril) and **angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)** are nephrotoxic in such patients.
- In bilateral renal artery stenosis, the kidneys rely on **angiotensin II** to constrict the efferent arterioles, maintaining **glomerular filtration pressure**. ACE inhibitors block angiotensin II production, leading to a significant drop in glomerular filtration and acute kidney injury.
*Clonidine*
- Clonidine is an **alpha-2 adrenergic agonist** that lowers blood pressure by reducing sympathetic outflow from the central nervous system.
- It is **not directly nephrotoxic** and would not typically cause acute renal failure, especially in the context of renal artery stenosis.
*Verapamil*
- Verapamil is a **non-dihydropyridine calcium channel blocker** that reduces heart rate and blood pressure.
- While it can affect renal hemodynamics, it does not typically cause **acute renal failure** or have a contraindication in bilateral renal artery stenosis like ACE inhibitors.
*Hydralazine*
- Hydralazine is a **direct arterial vasodilator** that lowers blood pressure.
- It is **not associated with acute renal failure** in the setting of renal artery stenosis and would not acutely worsen kidney function.
*Hydrochlorothiazide*
- Hydrochlorothiazide is a **thiazide diuretic** that lowers blood pressure by increasing sodium and water excretion.
- While it can cause **prerenal azotemia** due to volume depletion, it does not directly lead to the severe acute renal failure seen with ACE inhibitors in bilateral renal artery stenosis.
Direct vasodilators US Medical PG Question 9: A 27-year-old G1P0 woman at 25 weeks estimated gestational age presents with a blood pressure of 188/99 mm Hg during a routine prenatal visit. She has no symptoms, except for a mild headache. The patient's heart rate is 78/min. An injectable antihypertensive along with a beta-blocker is administered, and her blood pressure returns to normal within a couple of hours. She is sent home with advice to continue the beta-blocker. The patient returns after a couple of weeks with joint pain in both of her knees and fatigue. A blood test for anti-histone antibodies is positive. Which of the following is the mechanism of action of the intravenous antihypertensive medication most likely used in this patient?
- A. Potassium channel activation
- B. Calcium channel antagonism
- C. Release endogenous nitric oxide
- D. Interference with action of inositol trisphosphate (IP3) on intracellular calcium release (Correct Answer)
- E. Inhibition of phosphodiesterase enzyme
Direct vasodilators Explanation: ***Interference with action of inositol trisphosphate (IP3) on intracellular calcium release***
- The clinical presentation of hypertension, especially during pregnancy, followed by **joint pain** and ** positive anti-histone antibodies**, strongly suggests **drug-induced lupus**.
- **Hydralazine** is a common cause of **drug-induced lupus** and acts by interfering with **IP3-mediated calcium release**, causing **vasodilatation**.
*Potassium channel activation*
- Medications like **minoxidil** and **diazoxide** activate potassium channels, leading to **hyperpolarization** and **vasorelaxation**.
- While effective antihypertensives, they are not typically associated with **drug-induced lupus**.
*Calcium channel antagonism*
- **Calcium channel blockers** (e.g., nifedipine, amlodipine) reduce intracellular calcium, leading to **smooth muscle relaxation**.
- These medications are generally safe in pregnancy but are not linked to **anti-histone antibody formation** or **drug-induced lupus**.
*Release endogenous nitrous oxide*
- **Nitrates** (e.g., nitroglycerin) release **nitric oxide**, which activates **guanylyl cyclase** and leads to **vasodilatation**.
- While used in hypertensive emergencies, they are not a common cause of **drug-induced lupus**.
*Inhibition of phosphodiesterase enzyme*
- **Phosphodiesterase inhibitors** (e.g., sildenafil) increase intracellular levels of **cAMP** or **cGMP**, leading to **vasodilatation**.
- These drugs are not the primary treatment for acute severe hypertension in pregnancy and do not typically cause **drug-induced lupus**.
Direct vasodilators US Medical PG Question 10: A 70-year-old man comes to the physician for the evaluation of pain, cramps, and tingling in his lower extremities over the past 6 months. The patient reports that the symptoms worsen with walking more than two blocks and are completely relieved by rest. Over the past 3 months, his symptoms have not improved despite his participating in supervised exercise therapy. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus. He had smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for the past 50 years, but quit 3 months ago. He does not drink alcohol. His current medications include metformin, atorvastatin, and aspirin. Examination shows loss of hair and decreased skin temperature in the lower legs. Femoral pulses are palpable; pedal pulses are absent. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
- A. Compression stockings
- B. Endarterectomy
- C. Bypass surgery
- D. Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty
- E. Administration of cilostazol (Correct Answer)
Direct vasodilators Explanation: ***Administration of cilostazol***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of **peripheral artery disease (PAD)**, including **intermittent claudication** (pain with exertion, relieved by rest), **loss of hair**, **decreased skin temperature**, and **absent pedal pulses**.
- **Cilostazol** is a phosphodiesterase inhibitor that improves walking distance and reduces symptoms of claudication by causing **vasodilation** and inhibiting **platelet aggregation**.
*Compression stockings*
- Compression stockings are primarily used for conditions like **venous insufficiency** or **lymphedema**, which involve problems with venous return or lymphatic drainage.
- They are **contraindicated** in patients with significant PAD because they can further occlude already compromised arterial flow and worsen tissue ischemia.
*Endarterectomy*
- **Endarterectomy** is a surgical procedure to remove plaque from the inner lining of an artery. It is indicated for **localized, severe arterial stenosis** and is more invasive than other revascularization options.
- While it can be considered for PAD, less invasive options are usually tried first, especially in a patient who has not yet received optimal medical therapy.
*Bypass surgery*
- **Bypass surgery** involves rerouting blood flow around a blocked artery using a graft (vein or synthetic material). It is a more invasive revascularization procedure for PAD with significant, extensive arterial occlusions.
- It is typically reserved for **severe symptoms** refractory to medical management and less invasive procedures, or for critical limb ischemia.
*Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty*
- **Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA)** is a minimally invasive procedure that uses a balloon to widen a narrowed artery, often with stent placement.
- It is an effective revascularization option for PAD but is generally considered after lifestyle modifications and pharmacotherapy (like cilostazol) have failed to improve symptoms sufficiently.
More Direct vasodilators US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.