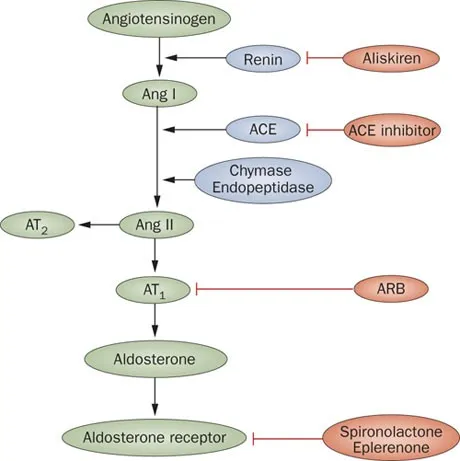
Angiotensin II receptor blockers US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Angiotensin II receptor blockers. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers US Medical PG Question 1: A 52-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. He feels well. His blood pressure is 125/70 mm Hg. His glomerular filtration rate is calculated to be 105 mL/min/1.73 m2 and glucose clearance is calculated to be 103 mL/min. This patient is most likely being treated with which of the following agents?
- A. Ifosfamide
- B. Acarbose
- C. Canagliflozin (Correct Answer)
- D. Glipizide
- E. Metformin
Angiotensin II receptor blockers Explanation: ***Canagliflozin***
- The key finding is that **glucose clearance (103 mL/min) approximately equals GFR (105 mL/min)**, indicating nearly complete failure of glucose reabsorption.
- **Canagliflozin** is an **SGLT2 inhibitor** that blocks the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 in the proximal tubule, preventing glucose reabsorption.
- This causes filtered glucose to be excreted in urine, resulting in **glucose clearance approaching GFR** - exactly what is seen in this patient.
- SGLT2 inhibitors are increasingly used as first-line agents in Type 2 Diabetes, especially with cardiovascular or renal benefits.
*Metformin*
- **Metformin** is a biguanide that decreases hepatic gluconeogenesis and increases peripheral insulin sensitivity.
- It does **NOT affect renal glucose handling** or glucose clearance, which would remain near zero in patients on metformin.
- The elevated glucose clearance in this patient rules out metformin monotherapy.
*Ifosfamide*
- **Ifosfamide** is an alkylating chemotherapy agent used for cancer treatment, not diabetes management.
- It can cause **Fanconi syndrome** (proximal tubule dysfunction) leading to glycosuria, but this would also cause decreased GFR, proteinuria, and electrolyte abnormalities.
- This patient's normal GFR and otherwise normal presentation makes ifosfamide-induced toxicity unlikely.
*Acarbose*
- **Acarbose** is an alpha-glucosidase inhibitor that slows carbohydrate absorption in the intestine.
- It works in the **GI tract**, not the kidneys, and does not affect glucose clearance.
- It would not explain the elevated renal glucose excretion seen here.
*Glipizide*
- **Glipizide** is a sulfonylurea that stimulates pancreatic insulin release.
- It does **NOT affect renal glucose handling** and would not cause elevated glucose clearance.
- The patient's glucose clearance pattern is inconsistent with sulfonylurea therapy.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers US Medical PG Question 2: A 75 year-old gentleman presents to his general practitioner. He is currently being treated for hypertension and is on a multi-drug regimen. His current blood pressure is 180/100. The physician would like to begin treatment with minoxidil or hydralazine. Which of the following side effects is associated with administration of these drugs?
- A. Persistent cough
- B. Cyanosis in extremities
- C. Fetal renal toxicity
- D. Systemic volume loss
- E. Reflex tachycardia (Correct Answer)
Angiotensin II receptor blockers Explanation: ***Reflex tachycardia***
- Both **minoxidil** and **hydralazine** are direct arterial vasodilators, causing a significant drop in **peripheral vascular resistance**.
- This vasodilation triggers a **baroreflex response**, leading to an increase in heart rate and **cardiac contractility** to maintain cardiac output, resulting in reflex tachycardia.
*Persistent cough*
- **Persistent cough** is a common side effect associated with **ACE inhibitors**, such as lisinopril or enalapril, due to the accumulation of **bradykinin**.
- This side effect is not typically seen with **minoxidil** or **hydralazine**, which act directly on vascular smooth muscle to cause vasodilation.
*Cyanosis in extremities*
- **Cyanosis** (bluish discoloration of the skin and mucous membranes) usually indicates **hypoxemia** or poor peripheral perfusion.
- While sometimes associated with severe cardiogenic shock or specific drug toxicities like methemoglobinemia (not related to minoxidil or hydralazine), it is not a direct or typical side effect of these vasodilators.
*Fetal renal toxicity*
- **Fetal renal toxicity**, including **fetal renal dysfunction** and **oligohydramnios**, is a well-known risk associated with **ACE inhibitors** and **ARBs** during pregnancy.
- Neither **minoxidil** nor **hydralazine** are primarily linked to this specific fetal adverse effect, though hydralazine can be used in pregnancy for severe hypertension.
*Systemic volume loss*
- **Systemic volume loss** is usually caused by conditions like **dehydration**, excessive diuresis, or hemorrhage.
- While vasodilators can reduce blood pressure, they do not directly cause **systemic volume depletion**; rather, the reflex response to vasodilation can include fluid retention to counteract the blood pressure drop.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers US Medical PG Question 3: An 81-year-old man is admitted to the hospital due to acute decompensated heart failure. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary artery disease, and congestive heart failure. Current medications include lisinopril, metformin, and low-dose aspirin. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 45 years. His temperature is 37.6°C (99.7°F), pulse is 105/min and regular, respirations are 21/min, and blood pressure is 103/64 mm Hg. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 13.7 g/dL
Leukocyte count 8200/mm3
Serum
Na+ 128 mEq/L
Cl- 98 mEq/L
K+ 4.9 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 58 mg/dL
Glucose 200 mg/dL
Creatinine 2.2 mg/dL
Which of the following changes in the medication regimen is most appropriate in this patient at this time?
- A. Begin vancomycin therapy
- B. Discontinue aspirin therapy
- C. Begin nitroprusside therapy
- D. Discontinue metformin therapy (Correct Answer)
- E. Begin hydrochlorothiazide therapy
Angiotensin II receptor blockers Explanation: ***Discontinue metformin therapy***
- The patient has **acute decompensated heart failure** with **acute kidney injury** (creatinine 2.2 mg/dL, BUN 58 mg/dL). Metformin is **contraindicated in acute kidney injury** due to the significantly increased risk of **lactic acidosis**.
- With renal failure, metformin excretion is impaired, leading to drug accumulation and dangerous elevations in lactic acid levels. **Immediate discontinuation** is critical to prevent this life-threatening complication.
- Current guidelines recommend avoiding metformin when eGFR <30 mL/min or creatinine >1.5 mg/dL in males.
*Begin vancomycin therapy*
- There is **no indication of bacterial infection** (normal leukocyte count 8200/mm³, only mild temperature elevation to 37.6°C, no localizing signs).
- Initiating broad-spectrum antibiotics like vancomycin without clear evidence of infection contributes to **antibiotic resistance** and potential adverse effects.
*Discontinue aspirin therapy*
- The patient has a history of **coronary artery disease** and **congestive heart failure**, making him high risk for acute coronary events.
- Aspirin provides crucial **antiplatelet therapy** for secondary prevention of cardiovascular events in this patient population and should be continued.
*Begin nitroprusside therapy*
- Nitroprusside is a potent vasodilator used in **hypertensive emergencies** or severe heart failure with elevated blood pressure.
- This patient currently has **hypotension** (BP 103/64 mm Hg), and nitroprusside would further lower blood pressure, potentially causing cardiovascular collapse and end-organ hypoperfusion.
*Begin hydrochlorothiazide therapy*
- While diuretics are used in heart failure, hydrochlorothiazide is a **thiazide diuretic** primarily effective with preserved renal function (eGFR >30 mL/min).
- This patient has **elevated creatinine (2.2 mg/dL)**, indicating acute kidney injury, which would significantly limit the efficacy of hydrochlorothiazide. **Loop diuretics** (furosemide) would be more appropriate if diuresis is needed in the setting of renal impairment.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers US Medical PG Question 4: A 52-year-old man with a history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia comes to the physician because of a 10-month history of substernal chest pain on exertion that is relieved with rest. His pulse is 82/min and blood pressure is 145/82 mm Hg. He is prescribed a drug that acts by forming free radical nitric oxide. The patient is most likely to experience which of the following adverse effects as a result of this drug?
- A. Pulsating headaches (Correct Answer)
- B. Erectile dysfunction
- C. Hypertensive urgency
- D. Lower extremity edema
- E. Nonproductive cough
Angiotensin II receptor blockers Explanation: ***Pulsating headaches***
- The drug described is likely **nitroglycerin** or another **nitrate**, which acts by releasing **nitric oxide (NO)** to cause **vasodilation**.
- **Vasodilation** in the cerebral vasculature is a common side effect of nitrates and can lead to **pulsating headaches**.
*Erectile dysfunction*
- **Erectile dysfunction** is not a direct adverse effect of nitrates; in fact, nitrates can be used to treat it, though their use with PDE5 inhibitors is contraindicated.
- This condition is more commonly associated with the underlying cardiovascular disease rather than the medication used to treat angina.
*Hypertensive urgency*
- **Nitrates** cause **vasodilation** and typically **lower blood pressure**, making **hypotension** (not hypertension) a potential side effect.
- **Hypertensive urgency** would indicate a sudden, severe elevation in blood pressure, which is antithetical to the drug's mechanism of action.
*Lower extremity edema*
- **Lower extremity edema** is generally not a direct side effect of nitrates; it is more commonly associated with conditions like **heart failure**, certain **calcium channel blockers**, or **venous insufficiency**.
- While vasodilation can sometimes lead to fluid shifts, edema is not a prominent or expected adverse effect of this class of drugs.
*Nonproductive cough*
- A **nonproductive cough** is a common side effect of **ACE inhibitors** (e.g., lisinopril), which act on the **renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system**.
- This symptom is not associated with **nitrates** because their mechanism of action is primarily through nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation, unrelated to the respiratory irritation seen with ACE inhibitors.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers US Medical PG Question 5: A 44-year-old man presents for a checkup. The patient says he has to urinate quite frequently but denies any dysuria or pain on urination. Past medical history is significant for diabetes mellitus type 2 and hypertension, both managed medically, as well as a chronic mild cough for the past several years. Current medications are metformin, aspirin, rosuvastatin, captopril, and furosemide. His vital signs are an irregular pulse of 74/min, a respiratory rate of 14/min, a blood pressure of 130/80 mm Hg, and a temperature of 36.7°C (98.0°F). His BMI is 32 kg/m2. On physical examination, there are visible jugular pulsations present in the neck bilaterally. Laboratory findings are significant for the following:
Glycated Hemoglobin (Hb A1c) 7.5%
Fasting Blood Glucose 120 mg/dL
Serum Electrolytes
Sodium 138 mEq/L
Potassium 3.9 mEq/L
Chloride 101 mEq/L
Serum Creatinine 1.3 mg/dL
Blood Urea Nitrogen 18 mg/dL
Which of the following is the next best step in the management of this patient?
- A. Replace captopril with valsartan.
- B. Stop furosemide.
- C. Stop metformin.
- D. Start rosiglitazone.
- E. Start exenatide. (Correct Answer)
Angiotensin II receptor blockers Explanation: ***Correct: Start exenatide.***
* The patient has **diabetes mellitus type 2** with an **HbA1c of 7.5%**, indicating suboptimal glycemic control despite being on metformin. Exenatide, a **GLP-1 receptor agonist**, helps improve glycemic control by increasing insulin secretion, decreasing glucagon secretion, and slowing gastric emptying.
* Given his BMI of **32 kg/m²**, exenatide is particularly beneficial as it also promotes **weight loss**, addressing an important comorbidity.
*Incorrect: Replace captopril with valsartan.*
* The patient is currently on captopril, an **ACE inhibitor**, for hypertension. Replacing it with valsartan, an **ARB**, is generally considered if the patient develops an ACE inhibitor-induced cough or angioedema.
* While the patient has a chronic cough, it's been present for several years, making a **long-standing smoker's cough or COPD more likely** than an ACE-inhibitor-induced cough, which usually resolves within a few weeks of stopping the drug. His blood pressure and renal function are stable on captopril.
*Incorrect: Stop furosemide.*
* The presence of **visible jugular pulsations** in the neck suggests **elevated central venous pressure**, which could indicate **fluid overload** or heart failure. Stopping a diuretic like furosemide in this context would likely worsen fluid retention.
* Furosemide is currently helping to manage the patient's fluid status, and discontinuing it could lead to **decompensation**, especially given the potential cardiac involvement hinted at by the jugular pulsations and irregular pulse.
*Incorrect: Stop metformin.*
* The patient's **HbA1c of 7.5%** indicates that his diabetes is **not well-controlled** on metformin alone, but this does not warrant stopping metformin, which is a first-line agent.
* Metformin should only be stopped in cases of severe renal impairment (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73m²), which is not indicated by his **creatinine of 1.3 mg/dL**, or other contraindications such as metabolic acidosis.
*Incorrect: Start rosiglitazone.*
* Rosiglitazone is a **thiazolidinedione (TZD)** that can improve insulin sensitivity and lower blood glucose. However, it is associated with side effects such as **weight gain** and **fluid retention**, which would be undesirable in this patient given his obesity and potential signs of fluid overload (jugular pulsations).
* Additionally, TZDs have been linked to an increased risk of **congestive heart failure**, a concern given his irregular pulse and jugular pulsations suggesting potential cardiac issues.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers US Medical PG Question 6: A 34-year-old man is being evaluated in an emergency clinic for dizziness and headache after a stressful event at work. He also reports that his face often becomes swollen and he occasionally has difficulty breathing during these spells. Family history is significant for his father who died of a stroke and his mother who often suffers from similar facial swelling. The patient’s blood pressure is 170/80 mm Hg. On physical examination, the patient appears well. Which of the following medications is most likely contraindicated in this patient?
- A. The patient has no contraindications.
- B. Enalapril (Correct Answer)
- C. Sulfadiazine
- D. Penicillin
- E. Losartan
Angiotensin II receptor blockers Explanation: **Enalapril**
- The patient's presentation with recurrent facial swelling, occasional difficulty breathing, and a family history of similar symptoms in his mother and stroke in his father is highly suggestive of **hereditary angioedema (HAE)**.
- **ACE inhibitors**, such as enalapril, are absolutely contraindicated in patients with HAE because they increase bradykinin levels, which can precipitate or worsen angioedema attacks.
*The patient has no contraindications.*
- The patient's history of recurrent angioedema episodes and a significant family history strongly suggest an underlying condition, likely HAE, which has clear contraindications for certain medications.
- Dismissing contraindications without further investigation into the cause of his angioedema would be unsafe and medically negligent.
*Sulfadiazine*
- **Sulfonamide antibiotics** are not directly contraindicated in HAE.
- While some individuals may have allergies to sulfa drugs, there is no specific link between sulfadiazine and triggering HAE attacks.
*Penicillin*
- Penicillin is a **beta-lactam antibiotic** and is not known to exacerbate or be contraindicated in hereditary angioedema.
- Allergic reactions to penicillin are common, but this is a Type I hypersensitivity, distinct from bradykinin-mediated angioedema.
*Losartan*
- **Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARBs)** like losartan generally do not significantly increase bradykinin levels and are typically considered a safer alternative to ACE inhibitors in patients who might develop ACE inhibitor–induced angioedema.
- While rare cases of ARB-induced angioedema have been reported, the risk is considerably lower than with ACE inhibitors, making it a less likely contraindication in this context.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers US Medical PG Question 7: A physician is choosing whether to prescribe losartan or lisinopril to treat hypertension in a 56-year-old male. Relative to losartan, one would expect treatment with lisinopril to produce which of the following changes in the circulating levels of these peptides?
- A. Aldosterone increase; bradykinin decrease
- B. Angiotensin II increase; bradykinin decrease
- C. Renin decrease; angiotensin I increase
- D. Bradykinin increase; angiotensin II decrease (Correct Answer)
- E. Renin decrease; angiotensin II increase
Angiotensin II receptor blockers Explanation: ***Bradykinin increase; angiotensin II decrease***
- **Lisinopril** is an **ACE inhibitor**, which directly blocks the conversion of **angiotensin I** to **angiotensin II**, leading to a decrease in circulating **angiotensin II** levels.
- ACE is also responsible for the breakdown of **bradykinin**, so inhibiting ACE with lisinopril will lead to an **increase in bradykinin** levels, contributing to vasodilation but also the characteristic cough.
*Aldosterone increase; bradykinin decrease*
- **Lisinopril** (an ACE inhibitor) decreases **angiotensin II**, which in turn leads to a **decrease in aldosterone** synthesis and release, not an increase.
- **Bradykinin** levels would increase due to ACE inhibition, as ACE is involved in its degradation.
*Angiotensin II increase; bradykinin decrease*
- **Lisinopril** directly inhibits the enzyme responsible for producing **angiotensin II**, thus leading to its **decrease**, not an increase.
- **Bradykinin** levels would increase because its degradation pathway (via ACE) is blocked, not decrease.
*Renin decrease; angiotensin I increase*
- **Lisinopril** reduces the negative feedback on **renin** release, leading to an **increase in renin** levels, not a decrease.
- While ACE is inhibited by lisinopril, this leads to an accumulation of its substrate, **angiotensin I**, resulting in an increase of angiotensin I.
*Renin decrease; angiotensin II increase*
- As an ACE inhibitor, lisinopril would lead to an **increase in renin** due to reduced negative feedback from angiotensin II, not a decrease.
- **Angiotensin II** levels would **decrease** because its production from angiotensin I is directly inhibited by lisinopril.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers US Medical PG Question 8: A 71-year-old African American man diagnosed with high blood pressure presents to the outpatient clinic. In the clinic, his blood pressure is 161/88 mm Hg with a pulse of 88/min. He has had similar blood pressure measurements in the past, and you initiate captopril. He presents back shortly after initiation with extremely swollen lips, tongue, and face. After captopril is discontinued, what is the most appropriate step for the management of his high blood pressure?
- A. Initiate a beta-blocker
- B. Switch to ramipril
- C. Initiate a thiazide diuretic (Correct Answer)
- D. Reinitiate captopril
- E. Initiate an ARB
Angiotensin II receptor blockers Explanation: ***Initiate a thiazide diuretic***
- The patient experienced **angioedema** after taking **captopril**, which is an **ACE inhibitor**. This is a life-threatening adverse effect, and it indicates that all **ACE inhibitors** should be avoided in the future.
- Due to the risk of angioedema, a different class of antihypertensive should be used. Given his African American ethnicity, a **thiazide diuretic** or **calcium channel blocker** would be an appropriate initial choice for monotherapy if hypertension is stage 1, or combination therapy if stage 2 hypertension, otherwise, a second agent, such as a **calcium channel blocker**, can be added.
*Initiate a beta-blocker*
- While beta-blockers are a class of antihypertensive drugs, they are generally not preferred as **first-line monotherapy** for **hypertension**, especially in older African American patients, unless there are specific comorbidities like heart failure or coronary artery disease.
- The most appropriate first-line choice after **ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema** would be a thiazide diuretic or calcium channel blocker, as per ACC/AHA guidelines for primary hypertension.
*Switch to ramipril*
- **Ramipril** is also an **ACE inhibitor**, and the patient experienced **angioedema** with **captopril** (another ACE inhibitor).
- Cross-reactivity and recurrence of angioedema are high with other ACE inhibitors, making this choice extremely dangerous and contraindicated.
*Reinitiate captopril*
- The patient developed **angioedema**, a severe and potentially fatal hypersensitivity reaction, to **captopril**.
- Reinitiating the same drug could lead to recurrent, and potentially more severe, angioedema and is therefore absolutely contraindicated.
*Initiate an ARB*
- **Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)**, while a different class from ACE inhibitors, act on the renin-angiotensin system and carry a **small but significant risk of cross-reactivity** leading to angioedema, especially in patients who have experienced it with an ACE inhibitor.
- Given the life-threatening nature of angioedema, it is generally recommended to avoid ARBs if a patient has a history of ACE inhibitor-induced angioedema.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers US Medical PG Question 9: A 28-year-old woman at 28 weeks gestation seeks evaluation at her obstetrician’s office with complaints of a severe headache, blurred vision, and vomiting for the past 2 days. Her pregnancy has been otherwise uneventful. The past medical history is unremarkable. The blood pressure is 195/150 mm Hg and the pulse is 88/min. On examination, moderate pitting edema is present in her ankles. The urinalysis is normal except for 3+ proteinuria. The obstetrician orders a complete blood count (CBC), liver function tests (LFTs), creatinine, and a coagulation profile. The obstetrician transfers her to the hospital by ambulance for expectant management. Which of the following medications would be most helpful for this patient?
- A. Olmesartan
- B. Lisinopril
- C. Nifedipine (Correct Answer)
- D. Hydrochlorothiazide
- E. Metoprolol
Angiotensin II receptor blockers Explanation: ***Nifedipine***
- The patient presents with **severe preeclampsia** (hypertension, proteinuria, and symptoms like headache and blurred vision), necessitating immediate **blood pressure reduction**. [1]
- **Nifedipine** is a **calcium channel blocker** that is effective and safe for acute blood pressure control in pregnancy, and is a first-line agent in this context. [1]
*Olmesartan*
- **Olmesartan** is an **angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB)**, which is **contraindicated in pregnancy** due to the risk of fetal renal toxicity and other adverse outcomes.
- ARBs can cause **fetal growth restriction**, oligohydramnios, and neonatal renal failure during the second and third trimesters.
*Lisinopril*
- **Lisinopril** is an **ACE inhibitor**, which, like ARBs, is **contraindicated in pregnancy** due to its teratogenic effects, particularly in the second and third trimesters.
- It can lead to **fetal renal dysfunction**, oligohydramnios, and other severe birth defects.
*Hydrochlorothiazide*
- **Hydrochlorothiazide** is a **thiazide diuretic**; while sometimes used in chronic hypertension in pregnancy, it is **not appropriate for acute, severe hypertension** in preeclampsia.
- Diuretics can reduce maternal intravascular volume, which is already compromised in preeclampsia, potentially worsening placental perfusion and fetal well-being.
*Metoprolol*
- **Metoprolol** is a **beta-blocker** sometimes used for chronic hypertension in pregnancy, but it may not be the optimal choice for **acute, severe hypertension** in preeclampsia.
- While generally considered safe, it can be associated with **fetal growth restriction** and **neonatal bradycardia** or hypoglycemia, and other agents like nifedipine or labetalol are often preferred for acute management.
Angiotensin II receptor blockers US Medical PG Question 10: A 27-year-old woman with no past medical history presents to her primary care provider because she has begun to experience color changes in her fingers on both hands in cold temperatures. She reports having had this problem for a few years, but with the weather getting colder this winter she has grown more concerned. She says that when exposed to cold her fingers turn white, blue, and eventually red. When the problem subsides she experiences pain in the affected fingers. She says that wearing gloves helps somewhat, but she continues to experience the problem. Inspection of the digits is negative for ulcerations. Which of the following is the next best step in treatment?
- A. Amlodipine (Correct Answer)
- B. Thoracic sympathectomy
- C. Phenylephrine
- D. Propranolol
- E. Sildenafil
Angiotensin II receptor blockers Explanation: ***Amlodipine***
- This patient exhibits classic symptoms of **Raynaud's phenomenon**, characterized by color changes (white, blue, red) in the digits upon cold exposure, followed by pain.
- **Calcium channel blockers** like **amlodipine** are the first-line pharmacologic treatment for Raynaud's, working by dilating peripheral arteries to improve blood flow.
*Thoracic sympathectomy*
- **Sympathectomy** is a surgical intervention reserved for **severe cases** of Raynaud's phenomenon that are refractory to medical therapy, especially when there is evidence of impending **ischemic damage** (e.g., ulcerations).
- This patient currently has a mild presentation without ulcerations, making surgery an overly aggressive initial treatment.
*Phenylephrine*
- **Phenylephrine** is an **alpha-1 adrenergic agonist** that causes **vasoconstriction**, primarily used as a decongestant or to raise blood pressure in hypotensive states.
- Administering a vasoconstrictor would **worsen** Raynaud's symptoms by further reducing blood flow to the digits.
*Propranolol*
- **Propranolol** is a **beta-blocker** that can potentially **worsen Raynaud's phenomenon** by causing unopposed alpha-adrenergic vasoconstriction, especially with non-selective agents.
- Beta-blockers are generally contraindicated in patients with Raynaud's, or should be used with extreme caution if absolutely necessary for another condition.
*Sildenafil*
- While **sildenafil** (a **phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor**) can cause vasodilation and has been used off-label for severe Raynaud's, it is typically considered a **second-line or adjunctive treatment** for refractory cases.
- **Calcium channel blockers** are the preferred initial pharmacologic therapy due to their proven efficacy and broader availability.
More Angiotensin II receptor blockers US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.