Antihypertensives

On this page
💊 The Antihypertensive Arsenal: Your Blood Pressure Command Center
Hypertension silently damages every organ system, yet you'll command an entire arsenal of drugs that intercept this cascade at multiple molecular checkpoints-from the renin-angiotensin axis to sympathetic outflow to vascular smooth muscle itself. You'll learn not just which agents lower pressure, but why specific patients demand specific strategies, how to combine drugs synergistically without triggering adverse effects, and how to make split-second decisions when blood pressure becomes a medical emergency. This lesson transforms pharmacology lists into a coherent battle plan, giving you the mechanistic insight and clinical judgment to protect your patients' hearts, kidneys, and brains for decades to come.
📌 Remember: ABCD - ACE inhibitors/ARBs, Beta-blockers, Calcium channel blockers, Diuretics represent the four cornerstone classes that form the foundation of modern hypertension management
The modern antihypertensive armamentarium encompasses 12 distinct drug classes, each targeting specific pathophysiological mechanisms underlying elevated blood pressure. Understanding these mechanisms transforms antihypertensive selection from memorization into logical therapeutic decision-making.
- RAAS Inhibitors (40% of prescriptions)
- ACE inhibitors: Block angiotensin II formation
- ARBs: Block angiotensin II receptors
- Direct renin inhibitors: Block renin activity
- Aldosterone antagonists: Block mineralocorticoid receptors
- Sympathetic Modulators (25% of prescriptions)
- Beta-blockers: Block β-adrenergic receptors
- Alpha-blockers: Block α1-adrenergic receptors
- Central alpha-2 agonists: Reduce sympathetic outflow
- Vascular Targets (20% of prescriptions)
- Calcium channel blockers: Block L-type calcium channels
- Direct vasodilators: Direct smooth muscle relaxation
- Volume Regulators (15% of prescriptions)
- Thiazide/thiazide-like diuretics: Block sodium reabsorption
- Loop diuretics: Block Na-K-2Cl cotransporter
- Potassium-sparing diuretics: Block epithelial sodium channels
| Drug Class | Primary Target | BP Reduction | Onset | Duration | First-Line Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE Inhibitors | ACE enzyme | 10-15 mmHg | 1-2 hours | 12-24 hours | ✓ |
| ARBs | AT1 receptors | 8-12 mmHg | 2-4 hours | 24 hours | ✓ |
| Thiazides | NCCT channels | 8-12 mmHg | 2-4 weeks | 12-24 hours | ✓ |
| CCBs | L-type Ca channels | 10-15 mmHg | 30 min-2 hours | 12-24 hours | ✓ |
| Beta-blockers | β-receptors | 8-12 mmHg | 1-2 hours | 12-24 hours | Limited |
💡 Master This: Each 10 mmHg reduction in systolic BP correlates with 20% reduction in cardiovascular events and 15% reduction in all-cause mortality-making precise antihypertensive selection a life-saving skill
Understanding antihypertensive pharmacology requires mastering not just individual drug mechanisms, but their synergistic interactions and complementary effects that enable optimal cardiovascular protection.
💊 The Antihypertensive Arsenal: Your Blood Pressure Command Center
⚙️ The RAAS Disruption Matrix: Blocking the Pressure Cascade
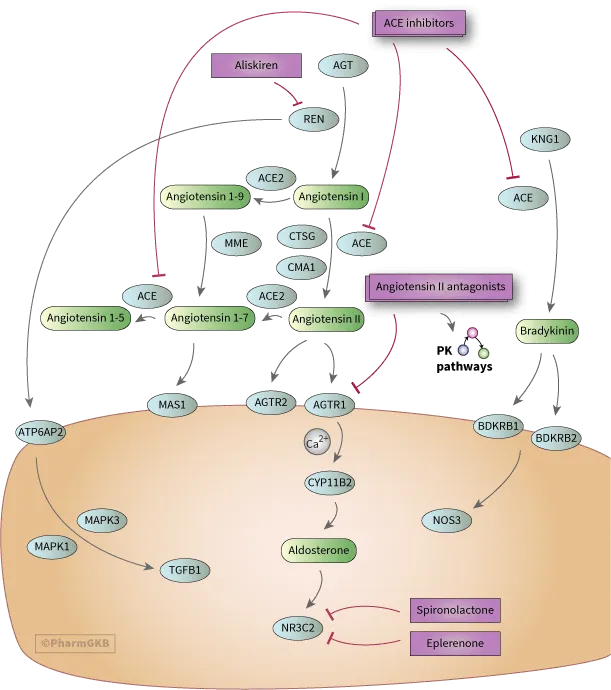
The RAAS cascade begins with renin release from juxtaglomerular cells, triggered by decreased renal perfusion, sympathetic stimulation, or reduced sodium delivery. Understanding each step reveals strategic intervention opportunities:
- Renin Level (Direct Renin Inhibitors)
- Aliskiren blocks renin directly
- Prevents angiotensinogen → angiotensin I conversion
- Plasma renin activity: ↓ 60-80%
- ACE Level (ACE Inhibitors)
- Block angiotensin I → angiotensin II conversion
- Prevent bradykinin degradation (beneficial + adverse effects)
- Angiotensin II levels: ↓ 85-90%
- Receptor Level (ARBs)
- Block AT1 receptor activation
- Preserve bradykinin (fewer side effects)
- AT1 receptor occupancy: >95% at therapeutic doses
- Aldosterone Level (MRAs)
- Block mineralocorticoid receptors
- Prevent sodium retention and potassium loss
- Aldosterone effect: ↓ 70-85%
📌 Remember: RAAS-4 - Renin (aliskiren), ACE (ACE-I), AT1 receptors (ARBs), Aldosterone (MRAs) represent the four strategic intervention points in the pressure cascade
| RAAS Target | Drug Examples | BP Reduction | K+ Effect | Cough Risk | Renal Protection |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Renin | Aliskiren | 8-12 mmHg | Minimal ↑ | <2% | Moderate |
| ACE | Lisinopril, Enalapril | 10-15 mmHg | Mild ↑ | 10-15% | Excellent |
| AT1 Receptor | Losartan, Valsartan | 8-12 mmHg | Mild ↑ | <2% | Excellent |
| Aldosterone | Spironolactone | 6-10 mmHg | Significant ↑ | <1% | Good |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: RAAS inhibitors demonstrate time-dependent efficacy-maximal cardiovascular benefits require 6-12 months of therapy, explaining why early discontinuation undermines long-term outcomes
💡 Master This: Combining RAAS inhibitors (ACE-I + ARB) increases hyperkalemia risk by 300% and acute kidney injury by 250% without additional cardiovascular benefit-a dangerous combination to avoid
Understanding RAAS pharmacology enables precise selection among the four intervention strategies, optimizing efficacy while minimizing adverse effects through mechanism-based decision making.
⚙️ The RAAS Disruption Matrix: Blocking the Pressure Cascade
🎯 The Sympathetic Shutdown Strategy: Taming the Fight-or-Flight Response
The sympathetic intervention hierarchy progresses from central nervous system modulation to peripheral receptor blockade:
- Central Alpha-2 Agonists (Brain stem control)
- Clonidine, methyldopa, guanfacine
- Reduce sympathetic outflow by 40-60%
- Onset: 30-60 minutes, Duration: 8-12 hours
- Primary use: Pregnancy (methyldopa), withdrawal syndromes
- Beta-Blockers (Cardiac + vascular effects)
- Selective (β1): Metoprolol, atenolol, bisoprolol
- Non-selective (β1+β2): Propranolol, nadolol, timolol
- Heart rate reduction: 15-25 beats/minute
- Cardiac output reduction: 20-30%
- Alpha-1 Blockers (Vascular smooth muscle)
- Doxazosin, prazosin, terazosin
- Peripheral resistance reduction: 25-35%
- Unique benefit: Improve BPH symptoms
- Mixed Alpha/Beta Blockers (Dual mechanism)
- Carvedilol, labetalol
- Combined effects: ↓ HR + ↓ peripheral resistance
- Superior outcomes in heart failure
📌 Remember: SCAB - Selective β1 (cardioselective), Central α2-agonists, Alpha-1 blockers, Beta-blockers (non-selective) represent the sympathetic modulation spectrum from central to peripheral
| Sympathetic Target | Selectivity | HR Effect | BP Reduction | Metabolic Effects | Special Indications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Central α2 | High | ↓ 15-25 bpm | 10-20 mmHg | Neutral | Pregnancy, ADHD |
| β1-Selective | Moderate | ↓ 15-20 bpm | 8-15 mmHg | Mild adverse | Post-MI, HF |
| β1+β2 Non-selective | Low | ↓ 20-30 bpm | 10-18 mmHg | Significant adverse | Migraine, anxiety |
| α1-Selective | High | Minimal | 8-12 mmHg | Favorable | BPH, PTSD |
| Mixed α/β | Variable | ↓ 10-15 bpm | 12-18 mmHg | Neutral | Heart failure |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Cardioselective beta-blockers lose selectivity at doses >100 mg metoprolol equivalent, potentially triggering bronchospasm in susceptible patients-dose escalation requires careful monitoring
💡 Master This: Abrupt beta-blocker withdrawal precipitates rebound hypertension and increased MI risk within 24-48 hours-always taper over 1-2 weeks to prevent catastrophic cardiovascular events
Understanding sympathetic pharmacology enables strategic selection among the diverse mechanisms, matching drug properties to patient characteristics while maximizing cardiovascular protection and minimizing adverse metabolic consequences.
🎯 The Sympathetic Shutdown Strategy: Taming the Fight-or-Flight Response
🔍 The Calcium Channel Choreography: Orchestrating Vascular Relaxation
The calcium channel architecture reveals 2 primary binding domains that determine drug selectivity and clinical effects:
- Dihydropyridine CCBs (Vascular-selective)
- Amlodipine, nifedipine, felodipine, clevidipine
- Vascular selectivity ratio: 100:1 (vascular:cardiac)
- Peripheral resistance reduction: 30-40%
- Reflex tachycardia: +10-20 bpm (short-acting forms)
- Primary indication: Hypertension, angina
- Non-Dihydropyridine CCBs (Cardiac-selective)
- Verapamil (phenylalkylamine), diltiazem (benzothiazepine)
- Cardiac selectivity ratio: 10:1 (cardiac:vascular)
- Heart rate reduction: 10-20 bpm
- AV conduction delay: PR interval ↑ 20-40 ms
- Primary indication: Arrhythmias, rate control
📌 Remember: DHP-V, Non-DHP-C - Dihydropyridines target Vascular smooth muscle, Non-Dihydropyridines target Cardiac tissue primarily
The pharmacokinetic profiles of CCBs determine their clinical applications and adverse effect patterns:
- Immediate-Release Formulations
- Onset: 15-30 minutes
- Duration: 4-8 hours
- Clinical use: Hypertensive emergencies (clevidipine, nicardipine)
- Risk: Precipitous BP drops, reflex tachycardia
- Extended-Release Formulations
- Onset: 2-4 hours
- Duration: 24 hours
- Clinical use: Chronic hypertension management
- Advantage: Smooth BP control, reduced side effects
| CCB Subclass | Prototype | Vascular:Cardiac Ratio | BP Reduction | HR Effect | Ankle Edema Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DHP | Amlodipine | 100:1 | 10-15 mmHg | ↑ 5-10 bpm | 15-20% |
| DHP | Nifedipine XL | 80:1 | 12-18 mmHg | ↑ 8-15 bpm | 10-15% |
| Phenylalkylamine | Verapamil | 1:10 | 8-12 mmHg | ↓ 10-15 bpm | <5% |
| Benzothiazepine | Diltiazem | 1:5 | 8-12 mmHg | ↓ 8-12 bpm | <5% |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: CCB-induced ankle edema results from arteriolar dilation without venodilation, creating capillary hydrostatic pressure imbalance-adding ACE inhibitors reduces edema incidence by 50-60% through venodilation
💡 Master This: Grapefruit juice inhibits CYP3A4 metabolism of CCBs, increasing drug levels by 200-300% and potentially causing dangerous hypotension-counsel patients to avoid grapefruit products
Understanding calcium channel pharmacology enables strategic selection between vascular-selective and cardiac-selective agents, optimizing therapeutic outcomes while minimizing mechanism-specific adverse effects through precise patient matching.
🔍 The Calcium Channel Choreography: Orchestrating Vascular Relaxation
⚖️ The Diuretic Precision Protocol: Mastering Volume and Electrolyte Balance
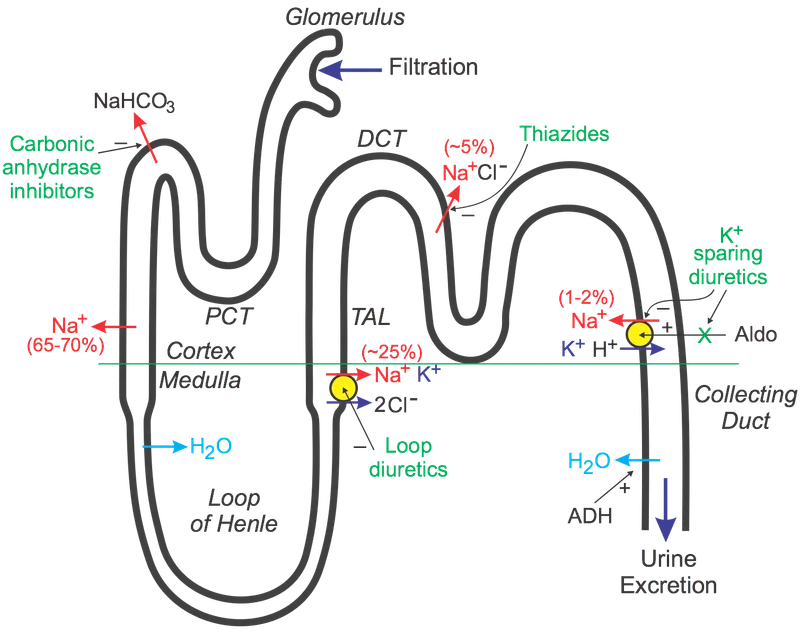
The nephron-based diuretic classification reveals 4 strategic intervention points with escalating potency:
- Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors (Proximal tubule)
- Acetazolamide: 5-10% sodium reabsorption blocked
- Volume effect: Mild, self-limiting
- Clinical use: Glaucoma, altitude sickness, metabolic alkalosis
- Electrolyte pattern: ↓ K+, ↓ HCO3-, ↑ Cl-
- Loop Diuretics (Thick ascending limb)
- Furosemide, bumetanide, torsemide: 20-25% sodium blocked
- Volume effect: Profound, dose-dependent
- Clinical use: Heart failure, pulmonary edema, CKD
- Electrolyte pattern: ↓ K+, ↓ Mg2+, ↓ Ca2+, ↑ uric acid
- Thiazide/Thiazide-like (Distal convoluted tubule)
- HCTZ, chlorthalidone, indapamide: 5-10% sodium blocked
- Volume effect: Moderate, sustained
- Clinical use: Hypertension (first-line), heart failure
- Electrolyte pattern: ↓ K+, ↓ Na+, ↑ Ca2+, ↑ glucose
- Potassium-Sparing (Collecting duct)
- Amiloride, triamterene, spironolactone: 2-3% sodium blocked
- Volume effect: Mild, K+-preserving
- Clinical use: Combination therapy, hyperaldosteronism
- Electrolyte pattern: ↑ K+, ↓ Na+, ↓ Mg2+ (spironolactone)
📌 Remember: CLOT - Carbonic anhydrase (proximal), Loop (thick ascending), Othiazide (distal), Triamterene/amiloride (collecting) represent the nephron progression of diuretic targets
| Diuretic Class | Nephron Site | Na+ Blockade | K+ Effect | Mg2+ Effect | Ca2+ Effect | Glucose Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbonic Anhydrase | Proximal | 5-10% | ↓ Mild | Minimal | Minimal | Minimal |
| Loop | Thick Ascending | 20-25% | ↓ Severe | ↓ Significant | ↓ Moderate | ↑ Mild |
| Thiazide | Distal | 5-10% | ↓ Moderate | ↓ Mild | ↑ Moderate | ↑ Significant |
| K-Sparing | Collecting | 2-3% | ↑ Risk | Variable | Minimal | Minimal |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Thiazide-induced hyponatremia occurs in 5-15% of elderly patients, typically within 2 weeks of initiation-monitor sodium levels closely in patients >65 years or with baseline sodium <135 mEq/L
💡 Master This: Loop diuretic resistance develops through nephron adaptation within 24-48 hours-overcome resistance by switching to continuous infusion or adding thiazide diuretics to block compensatory distal sodium reabsorption
Understanding diuretic pharmacology enables strategic nephron targeting while anticipating electrolyte consequences, optimizing volume management through mechanism-based selection and monitoring protocols.
⚖️ The Diuretic Precision Protocol: Mastering Volume and Electrolyte Balance
🔗 The Synergistic Integration Matrix: Advanced Combination Strategies
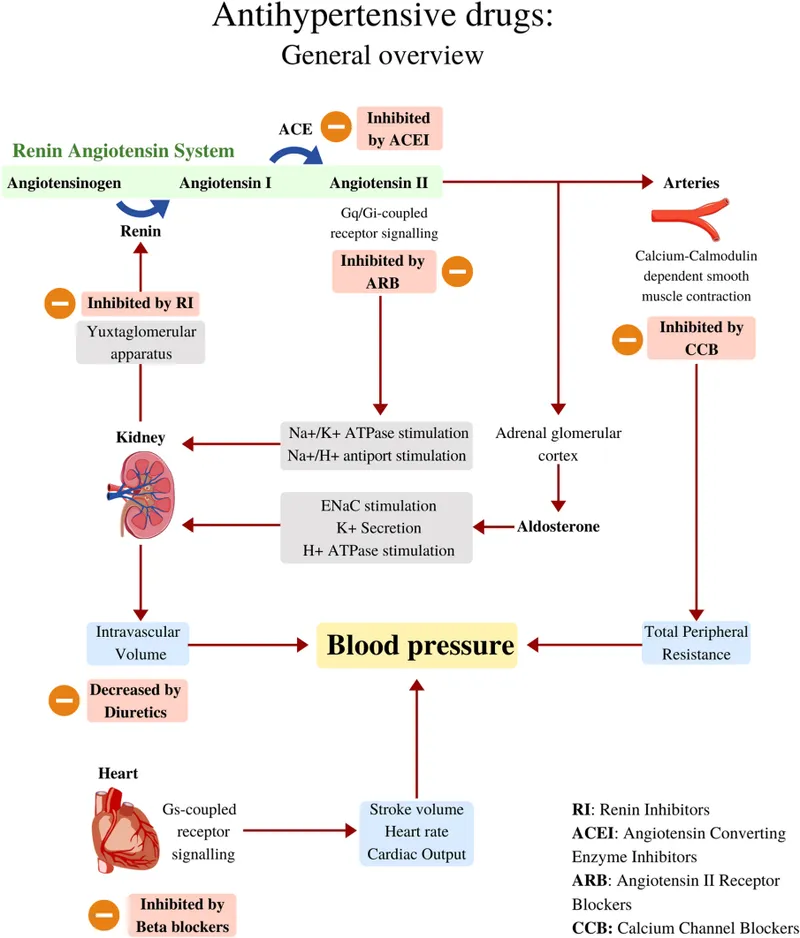
The combination therapy hierarchy progresses from complementary mechanisms to synergistic interactions:
- Preferred Combinations (Synergistic mechanisms)
- ACE-I/ARB + Thiazide: ↓ K+ loss, ↑ volume sensitivity
- ACE-I/ARB + CCB: ↓ ankle edema, ↑ renal protection
- CCB + Beta-blocker: ↓ reflex tachycardia, ↑ rate control
- Thiazide + K-sparing: ↓ hypokalemia, ↑ aldosterone blockade
- Rational Combinations (Additive effects)
- Beta-blocker + Thiazide: Complementary mechanisms
- Alpha-blocker + Beta-blocker: Dual sympathetic blockade
- Central agent + Peripheral agent: Central + peripheral effects
- Problematic Combinations (Dangerous interactions)
- ACE-I + ARB: ↑ hyperkalemia, ↑ AKI risk
- Beta-blocker + Non-DHP CCB: ↑ bradycardia, ↑ heart block
- Multiple K-sparing agents: ↑ severe hyperkalemia
📌 Remember: SMART combinations - Synergistic mechanisms, Minimal side effects, Additive efficacy, Reduced doses, Tolerance optimization guide successful antihypertensive pairing
The evidence base for specific combinations reveals superior cardiovascular outcomes beyond blood pressure reduction:
- ACE-I + Thiazide Combinations
- Cardiovascular events: ↓ 25-30% vs. monotherapy
- Stroke reduction: ↓ 35-40% (enhanced by thiazide)
- Heart failure prevention: ↓ 40-45% (ACE-I dominant)
- Renal protection: ↓ 30-35% progression to ESRD
- ARB + CCB Combinations
- Blood pressure control: 85-90% achieve target
- Ankle edema reduction: ↓ 50-60% vs. CCB alone
- Cardiovascular mortality: ↓ 20-25% in high-risk patients
- Diabetic nephropathy: ↓ 40% progression rate
| Combination Type | BP Reduction | CV Event Reduction | Tolerability | Cost Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE-I + Thiazide | 18-25 mmHg | 25-30% | Excellent | High |
| ARB + CCB | 20-28 mmHg | 20-25% | Excellent | Moderate |
| CCB + Beta-blocker | 15-22 mmHg | 15-20% | Good | Moderate |
| Thiazide + K-sparing | 12-18 mmHg | 15-20% | Good | High |
| Triple Therapy | 25-35 mmHg | 30-40% | Variable | Low |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Triple therapy (ACE-I/ARB + CCB + Thiazide) controls >95% of hypertensive patients, but requires careful monitoring for hyperkalemia (8-12% incidence) and acute kidney injury (3-5% risk)
💡 Master This: Resistant hypertension (uncontrolled on 3 drugs including diuretic) affects 10-15% of patients and requires aldosterone antagonist addition as fourth-line therapy, achieving control in 60-70% of resistant cases
Understanding combination pharmacology enables strategic drug pairing that leverages mechanistic synergy while avoiding dangerous interactions, optimizing both efficacy and safety through evidence-based selection protocols.
🔗 The Synergistic Integration Matrix: Advanced Combination Strategies
🎯 The Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid-Fire Decision Tools
📌 Remember: MATCH-BP - Mechanism to pathophysiology, Age-appropriate selection, Target organ protection, Comorbidity consideration, Heart rate effects, Blood pressure goals, Patient preferences guide optimal antihypertensive choice
Essential Clinical Decision Matrix:
- First-Line Monotherapy Selection
- Age <60: ACE-I/ARB preferred (renal protection)
- Age >60: Thiazide/CCB preferred (stroke prevention)
- Black patients: CCB/Thiazide preferred (enhanced efficacy)
- Diabetes: ACE-I/ARB mandatory (nephropathy prevention)
- Heart failure: ACE-I + Beta-blocker (mortality benefit)
- Post-MI: Beta-blocker + ACE-I (survival advantage)
Critical Contraindication Patterns:
| Drug Class | Absolute Contraindications | Relative Contraindications | Monitoring Requirements |
|---|---|---|---|
| ACE-I/ARB | Pregnancy, bilateral RAS | CKD (Cr >3.0), K+ >5.5 | Cr, K+ at 1-2 weeks |
| Beta-blockers | Severe asthma, 2nd/3rd° AV block | COPD, PVD, diabetes | HR, glucose, symptoms |
| CCB | None absolute | Severe AS, acute MI | Ankle edema, gingival hyperplasia |
| Thiazides | Anuria, severe hyponatremia | Gout, diabetes, CKD | Na+, K+, glucose, uric acid |
💡 Master This: White coat hypertension affects 15-30% of patients-confirm with 24-hour ambulatory monitoring or home BP measurements before initiating therapy to avoid unnecessary treatment and adverse effects
Rapid Reference Thresholds:
- Target BP: <130/80 mmHg (most patients), <140/90 mmHg (age >65)
- Hyperkalemia risk: K+ >5.5 mEq/L (hold RAAS inhibitors)
- Acute kidney injury: Creatinine ↑ >30% from baseline
- Combination therapy: Required when monotherapy fails to achieve <140/90 mmHg
- Resistant hypertension: Uncontrolled on 3 drugs including diuretic at optimal doses
Understanding antihypertensive mastery requires integrating pharmacological knowledge with clinical decision-making frameworks that optimize patient-specific outcomes while preventing predictable adverse events through systematic monitoring and adjustment protocols.
🎯 The Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid-Fire Decision Tools
Practice Questions: Antihypertensives
Test your understanding with these related questions
An investigator is comparing the risk of adverse effects among various antiarrhythmic medications. One of the drugs being studied primarily acts by blocking the outward flow of K+ during myocyte repolarization. Further investigation shows that the use of this drug is associated with a lower rate of ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation, and torsades de pointes when compared to similar drugs. Which of the following drugs is most likely being studied?












