Griseofulvin US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Griseofulvin. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Griseofulvin US Medical PG Question 1: You are taking care of a patient with renal failure secondary to anti-fungal therapy. The patient is a 66-year-old male being treated for cryptococcal meningitis. This drug has a variety of known side effects including acute febrile reactions to infusions, anemia, hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. What is the mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibition of squalene epoxidase
- B. Binding of the 50S subunit
- C. Pore formation secondary to ergosterol binding (Correct Answer)
- D. Disruption of microtubule formation
- E. Inhibition of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase
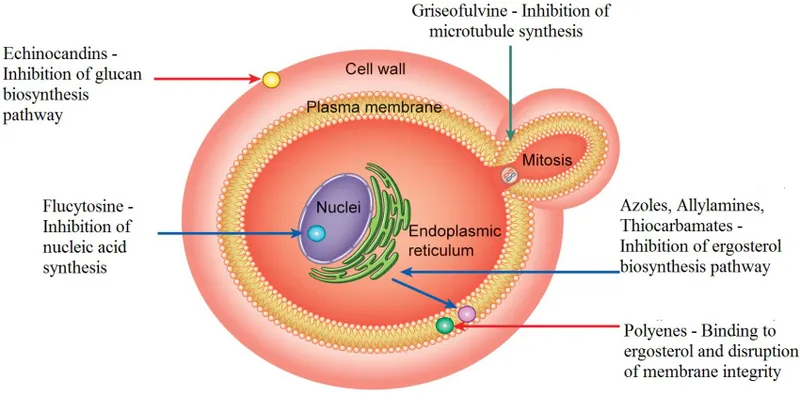
Griseofulvin Explanation: ***Pore formation secondary to ergosterol binding***
- This describes the mechanism of action of **amphotericin B**, the antifungal agent used for cryptococcal meningitis.
- Amphotericin B binds to **ergosterol** in the fungal cell membrane, leading to the formation of pores, disruption of membrane integrity, and ultimately cell death.
- The side effects described—**nephrotoxicity with renal failure, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia**—are classic adverse effects of amphotericin B due to its effect on renal tubular cells and electrolyte wasting.
*Inhibition of squalene epoxidase*
- This is the mechanism of action for **terbinafine**, an antifungal primarily used for dermatophyte infections (e.g., onychomycosis), not systemic infections like cryptococcal meningitis.
- Terbinafine inhibits ergosterol synthesis at an earlier step but does not cause the severe nephrotoxicity and electrolyte disturbances described.
*Binding of the 50S subunit*
- This mechanism of action is characteristic of **macrolide antibiotics** like azithromycin or clarithromycin, which are antibacterial agents, not antifungals.
- These drugs inhibit bacterial protein synthesis and are ineffective against fungal infections.
*Disruption of microtubule formation*
- This is the mechanism of action for **griseofulvin**, an antifungal drug used for dermatophyte infections of the skin, hair, and nails.
- Griseofulvin interferes with fungal cell division and is not used for life-threatening systemic infections like cryptococcal meningitis.
*Inhibition of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase*
- This mechanism is associated with **echinocandins** (e.g., caspofungin, micafungin), which inhibit fungal cell wall synthesis.
- While echinocandins are used for some systemic fungal infections (particularly Candida and Aspergillus), they do not typically cause the severe renal failure and electrolyte disturbances characteristic of amphotericin B.
Griseofulvin US Medical PG Question 2: A 58-year-old man with a 10-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension comes to the physician for a routine examination. Current medications include metformin and captopril. His pulse is 84/min and blood pressure is 120/75 mm Hg. His hemoglobin A1c concentration is 9.5%. The physician adds repaglinide to his treatment regimen. The mechanism of action of this agent is most similar to that of which of the following drugs?
- A. Linagliptin
- B. Glyburide (Correct Answer)
- C. Pioglitazone
- D. Miglitol
- E. Metformin
Griseofulvin Explanation: ***Glyburide***
- **Repaglinide** is a meglitinide, and **glyburide** is a sulfonylurea; both classes of drugs stimulate insulin release from pancreatic **beta cells** by closing ATP-sensitive potassium channels.
- This action leads to depolarization of the beta cell membrane, opening of **voltage-gated calcium channels**, and subsequent release of insulin from storage granules.
*Linagliptin*
- **Linagliptin** is a **dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor** that works by preventing the breakdown of incretins like GLP-1, thereby increasing postprandial insulin secretion and decreasing glucagon secretion.
- Its mechanism is distinct from repaglinide's direct stimulation of insulin release.
*Pioglitazone*
- **Pioglitazone** is a **thiazolidinedione** that acts by activating **peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-γ)** in adipose tissue, increasing insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues.
- This mechanism centers on improving insulin utilization rather than stimulating insulin secretion.
*Miglitol*
- **Miglitol** is an **alpha-glucosidase inhibitor** that delays carbohydrate absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, leading to a flatter postprandial glucose curve.
- Its action focuses on reducing glucose absorption, which is different from directly influencing insulin secretion or sensitivity.
*Metformin*
- **Metformin** is a biguanide that primarily reduces **hepatic glucose production** and improves insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissues.
- It does not directly affect insulin secretion from the pancreas, distinguishing it from repaglinide.
Griseofulvin US Medical PG Question 3: A 67-year-old man presents to his family physician’s office for a routine visit and to discuss a growth on his toenail that has been gradually enlarging for a month. He has a history of diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and hypertension and is on metformin, atorvastatin, and lisinopril. He admits to smoking 2 packs of cigarettes daily for the past 45 years. His blood pressure reading today is 132/88 mm Hg, heart rate is 78/min, respiration rate is 12/min and his temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F). On exam, the patient appears alert and in no apparent distress. Capillary refill is 3 seconds. Diminished dull and sharp sensations are present bilaterally in the lower extremities distal to the mid-tibial region. An image of the patient’s toenail is provided. A potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation of a nail clipping sample confirms the presence of hyphae. Which of the following treatment options will be most effective for this condition?
- A. Fluconazole
- B. Betamethasone + vitamin D analog
- C. Griseofulvin
- D. Terbinafine (Correct Answer)
- E. Cephalexin
Griseofulvin Explanation: ***Terbinafine***
- **Terbinafine** is a highly effective **antifungal medication** used to treat **onychomycosis**, a fungal infection of the nails, confirmed by the presence of hyphae in the KOH preparation.
- It works by inhibiting **squalene epoxidase**, an enzyme essential for fungal cell membrane synthesis, leading to fungicidal action.
*Fluconazole*
- While **fluconazole** is an antifungal medication, it is generally **less effective** than terbinafine for onychomycosis, especially for dermatophyte infections.
- It is often reserved for patients who cannot tolerate terbinafine or have contraindications to it, or for non-dermatophyte molds or yeast infections.
*Griseofulvin*
- **Griseofulvin** is an older antifungal agent that is **less effective** than newer options like terbinafine for onychomycosis and generally requires a much longer treatment course.
- Its use has largely been replaced by more potent and better-tolerated antifungals for nail infections.
*Betamethasone + vitamin D analog*
- This combination is a treatment for **psoriasis**, a chronic inflammatory skin condition that can affect nails, but it is **not effective** against fungal infections.
- The presence of **hyphae** confirmed by KOH preparation rules out psoriasis as the primary diagnosis and indicates a fungal etiology.
*Cephalexin*
- **Cephalexin** is an **antibiotic** used to treat bacterial infections and has **no activity** against fungal pathogens.
- It would be ineffective for onychomycosis, which is a fungal infection.
Griseofulvin US Medical PG Question 4: A 52-year-old woman presents to the emergency room complaining of chest pain. She reports a 4-hour history of dull substernal pain radiating to her jaw. Her history is notable for hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and alcohol abuse. She has a 30 pack-year smoking history and takes lisinopril and metformin but has an allergy to aspirin. Her temperature is 99.1°F (37.3°C), blood pressure is 150/90 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, and respirations are 22/min. Physical examination reveals a diaphoretic and distressed woman. An electrocardiogram reveals ST elevations in leads I, aVL, and V5-6. She is admitted with plans for immediate transport to the catheterization lab for stent placement. What is the mechanism of the next medication that should be given to this patient?
- A. Cyclooxygenase activator
- B. ADP receptor inhibitor (Correct Answer)
- C. Phosphodiesterase activator
- D. Thrombin inhibitor
- E. Vitamin K epoxide reductase inhibitor
Griseofulvin Explanation: ***ADP receptor inhibitor***
- This patient is experiencing an **ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)** as evidenced by ST elevations in leads I, aVL, and V5-6 (lateral wall infarction)
- **Dual antiplatelet therapy** is the standard of care for STEMI, typically consisting of aspirin plus a P2Y12 inhibitor (ADP receptor inhibitor)
- Since this patient has an **aspirin allergy**, an ADP receptor inhibitor such as **clopidogrel, ticagrelor, or prasugrel** becomes the critical next antiplatelet medication
- These agents **irreversibly or reversibly block the P2Y12 receptor** on platelets, preventing ADP-mediated platelet activation and aggregation
- This is essential for preventing further thrombotic complications during and after percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
*Cyclooxygenase activator*
- No cyclooxygenase activator exists in clinical practice for cardiovascular disease
- Aspirin works as a **cyclooxygenase inhibitor**, blocking COX-1 to prevent thromboxane A2 synthesis, but the patient is allergic to aspirin
- "Activating" cyclooxygenase would promote platelet aggregation, which is counterproductive in acute MI
*Phosphodiesterase activator*
- Phosphodiesterase activation would decrease cAMP/cGMP levels, which is not therapeutically beneficial
- **Phosphodiesterase inhibitors** (such as cilostazol or dipyridamole) can have antiplatelet effects by increasing cAMP, but they are not first-line agents for acute STEMI
- An activator would have the opposite and undesirable effect
*Thrombin inhibitor*
- Thrombin inhibitors (e.g., **bivalirudin, heparin**) are anticoagulants that prevent conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin
- While **anticoagulation is important in STEMI management**, it is used as adjunctive therapy alongside antiplatelet agents
- Given the aspirin allergy, the immediate priority is **antiplatelet therapy with an ADP receptor inhibitor**
- Anticoagulation would typically be given concurrently but is not "the next" critical medication in this specific context
*Vitamin K epoxide reductase inhibitor*
- Warfarin is a vitamin K epoxide reductase inhibitor used for chronic anticoagulation
- It has a **slow onset of action** (days) and is inappropriate for acute STEMI management
- It is used for long-term anticoagulation in conditions like atrial fibrillation or mechanical heart valves, not for acute coronary syndromes requiring rapid platelet inhibition
Griseofulvin US Medical PG Question 5: A 72-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician because she is concerned about the appearance of her toenails. Examination shows yellowish discoloration of all toenails on both feet. The edges of the toenails are lifted, and there is subungual debris. Potassium hydroxide preparation of scrapings from the nails shows multiple branching septate hyphae. Treatment with oral terbinafine is begun. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibition of squalene epoxidase (Correct Answer)
- B. Formation of pores in cell membrane
- C. Inhibition of β-glucan synthesis
- D. Interference with mitosis during metaphase
- E. Prevention of lanosterol to ergosterol conversion
Griseofulvin Explanation: ***Inhibition of squalene epoxidase***
- **Terbinafine** is an **allylamine** antifungal that inhibits the enzyme **squalene epoxidase**, an early step in fungal ergosterol synthesis
- This inhibition leads to the accumulation of **squalene**, which is toxic to the fungal cell, and a deficiency of **ergosterol**, disrupting cell membrane integrity and function
- Terbinafine is highly effective for **onychomycosis** (fungal nail infections) caused by dermatophytes
*Formation of pores in cell membrane*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **polyene antifungals** like **amphotericin B** and **nystatin**
- These drugs bind to **ergosterol** in the fungal cell membrane, creating pores that lead to leakage of intracellular contents and cell death
*Inhibition of β-glucan synthesis*
- This is the primary mechanism of action for **echinocandin** antifungals, such as **caspofungin**, **micafungin**, and **anidulafungin**
- These drugs inhibit **(1,3)-β-D-glucan synthase**, which is essential for the synthesis of glucan, a major component of the fungal cell wall
*Interference with mitosis during metaphase*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **griseofulvin**, another antifungal agent used for dermatophyte infections
- **Griseofulvin** interferes with **microtubule function**, disrupting mitotic spindle formation and preventing fungal cell division
*Prevention of lanosterol to ergosterol conversion*
- This mechanism is associated with **azole antifungals** (e.g., fluconazole, itraconazole), which inhibit fungal **cytochrome P450-dependent 14-α-demethylase**
- This enzyme is responsible for the conversion of **lanosterol** to **ergosterol**, leading to ergosterol depletion and accumulation of toxic sterol precursors
Griseofulvin US Medical PG Question 6: A potassium hydroxide preparation is conducted on a skin scraping of the hypopigmented area. Microscopy of the preparation shows long hyphae among clusters of yeast cells. Based on these findings, which of the following is the most appropriate pharmacotherapy?
- A. Topical corticosteroid
- B. Oral ketoconazole
- C. Topical selenium sulfide (Correct Answer)
- D. Topical nystatin
- E. Oral fluconazole
Griseofulvin Explanation: ***Topical selenium sulfide***
- The presence of **long hyphae** and **clusters of yeast cells** on KOH prep is characteristic of **tinea versicolor**, caused by *Malassezia furfur*.
- **Selenium sulfide** is a common and effective topical antifungal agent for tinea versicolor, available in shampoos and lotions.
*Topical corticosteroid*
- **Corticosteroids** have anti-inflammatory properties but do not treat fungal infections.
- Using corticosteroids alone would only mask symptoms and could potentially worsen the fungal infection.
*Oral ketoconazole*
- While **oral ketoconazole** is an antifungal, it is generally reserved for extensive or recalcitrant cases of tinea versicolor due to potential systemic side effects, such as **hepatotoxicity**.
- **Topical treatments** are preferred as first-line therapy for localized infections like this one.
*Topical nystatin*
- **Nystatin** is an antifungal agent primarily effective against *Candida* species.
- It is **not effective** against *Malassezia furfur*, the causative agent of tinea versicolor.
*Oral fluconazole*
- **Oral fluconazole** is an effective systemic antifungal used for various *Candida* and dermatophyte infections.
- Similar to oral ketoconazole, it is typically reserved for **widespread or recalcitrant cases** of tinea versicolor, with topical therapy being the preferred initial approach.
Griseofulvin US Medical PG Question 7: A 64-year-old woman comes to the emergency room because of a sudden weakness in her right arm and leg. She has atrial fibrillation, tinea unguium, gastroesophageal reflux disease, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia. Current medications include warfarin, enalapril, simvastatin, lansoprazole, hydrochlorothiazide, griseofulvin, and ginkgo biloba. Two weeks ago, she had an appointment with her podiatrist. Physical examination shows sagging of her right lower face and decreased muscle strength in her right upper and lower extremity. Babinski sign is positive on the right. Her prothrombin time is 14 seconds (INR = 1.5). Which of the following drugs is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's current condition?
- A. Ginkgo biloba
- B. Lansoprazole
- C. Enalapril
- D. Griseofulvin (Correct Answer)
- E. Simvastatin
Griseofulvin Explanation: ***Griseofulvin***
- Has been shown to **reduce the effectiveness of warfarin** by inducing hepatic enzymes, leading to a subtherapeutic INR and increased risk of thrombotic events like stroke.
- The patient's **INR of 1.5 is subtherapeutic** for atrial fibrillation, which normally requires an INR between 2.0 and 3.0 to prevent stroke.
*Ginkgo biloba*
- Is known to **increase the risk of bleeding** when taken with anticoagulants like warfarin, potentially leading to a higher INR and hemorrhagic stroke.
- In this case, the patient's **INR is subtherapeutic**, which points away from a bleeding diathesis caused by ginkgo biloba.
*Lansoprazole*
- While it can interact with warfarin, **proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)** typically **increase the INR** by inhibiting warfarin metabolism, increasing bleeding risk.
- The patient's **subtherapeutic INR** makes lansoprazole less likely to be the cause of the thrombotic event.
*Enalapril*
- As an **ACE inhibitor**, enalapril generally has **no significant direct interaction with warfarin** that would lead to a subtherapeutic INR or increased stroke risk in this way.
- It is primarily used for hypertension and heart failure, and its effects would not explain the observed subtherapeutic INR and thrombotic stroke.
*Simvastatin*
- Can **increase the effect of warfarin** by inhibiting its metabolism, leading to an **elevated INR** and increased bleeding risk.
- The patient's **low INR** suggests that simvastatin is not the cause of the subtherapeutic anticoagulation or stroke.
Griseofulvin US Medical PG Question 8: A 63-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. He feels well. He has a history of hypertension, atrial fibrillation, bipolar disorder, and osteoarthritis of the knees. Current medications include lisinopril, amiodarone, lamotrigine, and acetaminophen. He started amiodarone 6 months ago and switched from lithium to lamotrigine 4 months ago. The patient does not smoke. He drinks 1–4 beers per week. He does not use illicit drugs. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Serum
Na+ 137 mEq/L
K+ 4.2 mEq/L
Cl- 105 mEq/L
HCO3- 24 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 14 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.9 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 82 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 110 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 115 U/L
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Discontinue amiodarone (Correct Answer)
- B. Discontinue acetaminophen
- C. Follow-up laboratory results in 3 months
- D. Follow-up laboratory results in 6 months
- E. Decrease alcohol consumption
Griseofulvin Explanation: ***Discontinue amiodarone***
* The patient has elevated **AST** and **ALT** levels, suggestive of **drug-induced liver injury**. Amiodarone is a known cause of **hepatotoxicity**, which can occur even with normal baseline liver function.
* **Amiodarone-induced liver injury** can range from asymptomatic transaminase elevation to **fulminant hepatic failure**; therefore, discontinuing the drug is crucial to prevent further liver damage.
*Discontinue acetaminophen*
* Although **acetaminophen** can cause **hepatotoxicity** at high doses, the patient is likely taking it at therapeutic doses for osteoarthritis, as suggested by its use in routine care and the absence of overdose symptoms.
* The chronic nature of amiodarone use (6 months) and its well-established risk of **liver injury** make it a more probable cause of the elevated transaminases than **therapeutic-dose acetaminophen**.
*Follow-up laboratory results in 3 months*
* The current **liver enzyme elevations** (AST 110 U/L, ALT 115 U/L) are significant and indicate acute liver injury. Waiting 3 months for follow-up without intervention significantly risks further liver damage.
* Prompt identification and removal of the offending agent are necessary to prevent potentially irreversible **hepatic injury**.
*Follow-up laboratory results in 6 months*
* Delaying follow-up for 6 months is an inappropriate and potentially harmful approach given the current enzyme elevations. There is an immediate need to identify and address the cause of **liver injury**.
* Such a delay could lead to progression of **liver damage**, especially if the causative agent (e.g., amiodarone) continues to be administered.
*Decrease alcohol consumption*
* While excessive alcohol consumption can cause **elevated liver enzymes**, the patient’s intake of 1–4 beers per week is considered light to moderate and is unlikely to be the sole cause of these significant elevations.
* The presence of a known **hepatotoxic medication** (amiodarone) alongside the elevated enzymes makes the drug a much more probable cause than the patient's modest alcohol intake.
Griseofulvin US Medical PG Question 9: A 19-year-old South Asian male presents to the family physician concerned that he is beginning to go bald. He is especially troubled because his father and grandfather "went completely bald by the age of 25," and he is willing to try anything to prevent his hair loss. The family physician prescribes a medication that prevents the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone. Which of the following enzymes is inhibited by this medication?
- A. Cyclooxygenase 2
- B. Desmolase
- C. Aromatase
- D. cGMP phosphodiesterase
- E. 5-alpha-reductase (Correct Answer)
Griseofulvin Explanation: ***5-alpha-reductase***
- The medication described inhibits the conversion of **testosterone to dihydrotestosterone (DHT)**, which is catalyzed by the enzyme **5-alpha-reductase**.
- **Androgenetic alopecia** (male pattern baldness) is driven by DHT, and inhibiting this enzyme reduces DHT levels in the scalp, thereby slowing hair loss.
*Cyclooxygenase 2*
- **Cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2)** is involved in the synthesis of **prostaglandins** from arachidonic acid, mediating inflammation and pain.
- COX-2 inhibitors are used as anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g., celecoxib), not for male pattern baldness.
*Desmolase*
- **Cholesterol desmolase** (CYP11A1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the first committed step in **steroidogenesis**, converting cholesterol to pregnenolone.
- Inhibition of desmolase would affect the synthesis of all steroid hormones, not specifically target the conversion of testosterone to DHT for hair loss treatment.
*Aromatase*
- **Aromatase** is an enzyme responsible for converting androgens (like testosterone) into **estrogens**.
- Aromatase inhibitors are used in the treatment of estrogen-receptor positive breast cancer, not male pattern baldness.
*cGMP phosphodiesterase*
- **cGMP phosphodiesterase (PDE5)** is an enzyme that breaks down cyclic GMP (cGMP), which is involved in smooth muscle relaxation.
- PDE5 inhibitors (e.g., sildenafil) are used to treat **erectile dysfunction** and **pulmonary hypertension**, not hair loss.
Griseofulvin US Medical PG Question 10: A 59-year-old man comes to the physician because of a painful, burning red rash on his face and hands, which developed 30 minutes after going outside to do garden work. He wore a long-sleeved shirt and was exposed to direct sunlight for about 10 minutes. The patient is light-skinned and has a history of occasional sunburns when he does not apply sunscreen. The patient was diagnosed with small cell lung carcinoma 2 months ago and is currently undergoing chemotherapy. He is currently taking demeclocycline for malignancy-associated hyponatremia and amoxicillin for sinusitis. He has also had occasional back pain. He takes zolpidem and drinks 1–2 glasses of brandy before going to sleep every night. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for 20 years. His pulse is 72/min and his blood pressure is 120/75 mm Hg. Physical examination shows prominent erythema on his forehead, cheeks, and neck. Erythema and papular eruptions are seen on the dorsum of both hands. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Normal sunburn reaction
- B. Adverse reaction to amoxicillin
- C. Systemic lupus erythematosus
- D. Use of demeclocycline (Correct Answer)
- E. Uroporphyrin accumulation
Griseofulvin Explanation: ***Use of demeclocycline***
- The patient's acute, burning erythematous rash on sun-exposed areas (face, hands) after brief sun exposure is highly suggestive of **photosensitivity**.
- **Demeclocycline**, a tetracycline antibiotic, is a known cause of **phototoxic reactions**, making it the most likely culprit given his current medications.
*Normal sunburn reaction*
- A normal sunburn, while possible with brief exposure in a light-skinned individual, would typically take longer than **30 minutes** to develop a prominent, burning rash.
- The severity and rapid onset of symptoms are more indicative of a **phototoxic reaction** rather than a typical sunburn.
*Adverse reaction to amoxicillin*
- While amoxicillin can cause drug eruptions, they typically manifest as a **morbilliform rash** or **urticaria (hives)**, not a localized, burning rash primarily in sun-exposed areas.
- Amoxicillin is **not commonly associated** with photosensitivity.
*Systemic lupus erythematosus*
- SLE can cause photosensitive rashes (e.g., **malar rash**, discoid lesions), but these tend to be **chronic** or recurrent, and the acute, rapid onset of a burning sensation after brief exposure is less typical.
- Other systemic symptoms of SLE, such as **arthralgias, kidney involvement, or serositis**, are not described as the primary complaint.
*Uroporphyrin accumulation*
- **Porphyrias**, such as **porphyria cutanea tarda**, involve the accumulation of porphyrins (like uroporphyrin) leading to photosensitivity, blistering, and skin fragility.
- While it causes photosensitivity, the classic presentation often includes **blisters, hyperpigmentation, increased skin fragility, and hirsutism**, which are not described in this patient's acute presentation of a purely erythematous, burning rash.
More Griseofulvin US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.