Flucytosine US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Flucytosine. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
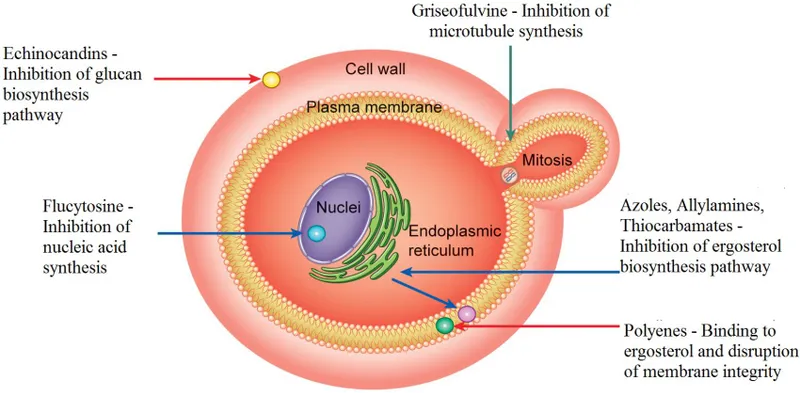
Flucytosine US Medical PG Question 1: You are taking care of a patient with renal failure secondary to anti-fungal therapy. The patient is a 66-year-old male being treated for cryptococcal meningitis. This drug has a variety of known side effects including acute febrile reactions to infusions, anemia, hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. What is the mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibition of squalene epoxidase
- B. Binding of the 50S subunit
- C. Pore formation secondary to ergosterol binding (Correct Answer)
- D. Disruption of microtubule formation
- E. Inhibition of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase
Flucytosine Explanation: ***Pore formation secondary to ergosterol binding***
- This describes the mechanism of action of **amphotericin B**, the antifungal agent used for cryptococcal meningitis.
- Amphotericin B binds to **ergosterol** in the fungal cell membrane, leading to the formation of pores, disruption of membrane integrity, and ultimately cell death.
- The side effects described—**nephrotoxicity with renal failure, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia**—are classic adverse effects of amphotericin B due to its effect on renal tubular cells and electrolyte wasting.
*Inhibition of squalene epoxidase*
- This is the mechanism of action for **terbinafine**, an antifungal primarily used for dermatophyte infections (e.g., onychomycosis), not systemic infections like cryptococcal meningitis.
- Terbinafine inhibits ergosterol synthesis at an earlier step but does not cause the severe nephrotoxicity and electrolyte disturbances described.
*Binding of the 50S subunit*
- This mechanism of action is characteristic of **macrolide antibiotics** like azithromycin or clarithromycin, which are antibacterial agents, not antifungals.
- These drugs inhibit bacterial protein synthesis and are ineffective against fungal infections.
*Disruption of microtubule formation*
- This is the mechanism of action for **griseofulvin**, an antifungal drug used for dermatophyte infections of the skin, hair, and nails.
- Griseofulvin interferes with fungal cell division and is not used for life-threatening systemic infections like cryptococcal meningitis.
*Inhibition of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase*
- This mechanism is associated with **echinocandins** (e.g., caspofungin, micafungin), which inhibit fungal cell wall synthesis.
- While echinocandins are used for some systemic fungal infections (particularly Candida and Aspergillus), they do not typically cause the severe renal failure and electrolyte disturbances characteristic of amphotericin B.
Flucytosine US Medical PG Question 2: An 18-year old college freshman presents to his university clinic because he has not been feeling well for the past two weeks. He has had a persistent headache, occasional cough, and chills without rigors. The patient’s vital signs are normal and physical exam is unremarkable. His radiograph shows patchy interstitial lung infiltrates and he is diagnosed with atypical pneumonia. The patient is prescribed azithromycin and takes his medication as instructed. Despite adherence to his drug regimen, he returns to the clinic one week later because his symptoms have not improved. The organism responsible for this infection is likely resistant to azithromycin through which mechanism?
- A. Mutation in topoisomerase II
- B. Methylation of ribosomal binding site
- C. Presence of a beta-lactamase
- D. Decreased binding to RNA polymerase
- E. Insertion of drug efflux pumps (Correct Answer)
Flucytosine Explanation: ***Insertion of drug efflux pumps***
- **Azithromycin** is a macrolide antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the **50S ribosomal subunit**.
- In **Mycoplasma pneumoniae** (the most common cause of atypical pneumonia in young adults), the **most common** mechanism of macrolide resistance is through **efflux pumps**, particularly the **mef genes**.
- These efflux pumps actively transport macrolides out of the bacterial cell, reducing intracellular drug concentration and conferring resistance.
- This mechanism is responsible for the majority of macrolide-resistant *M. pneumoniae* isolates worldwide.
*Methylation of ribosomal binding site*
- **Methylation** of the ribosomal binding site (specifically the **23S rRNA** via erm genes) does prevent azithromycin from binding effectively.
- While this is a valid macrolide resistance mechanism seen in organisms like *Streptococcus pneumoniae* and *Streptococcus pyogenes*, it is **less common** in *Mycoplasma pneumoniae*.
- Efflux pumps (mef) are the predominant mechanism in *M. pneumoniae* resistant strains.
*Mutation in topoisomerase II*
- **Topoisomerase II** (DNA gyrase) is the target of **fluoroquinolone antibiotics**, not macrolides.
- Mutations in this enzyme lead to resistance against fluoroquinolones, such as **ciprofloxacin**.
*Presence of a beta-lactamase*
- **Beta-lactamase enzymes** inactivate **beta-lactam antibiotics** (e.g., penicillin, cephalosporins) by hydrolyzing their beta-lactam ring.
- Additionally, *Mycoplasma pneumoniae* **lacks a cell wall**, making it inherently resistant to all beta-lactam antibiotics regardless of beta-lactamase production.
*Decreased binding to RNA polymerase*
- **RNA polymerase** is the target for antibiotics like **rifampin**, which inhibits bacterial transcription.
- Decreased binding to RNA polymerase would lead to rifampin resistance, not azithromycin resistance.
Flucytosine US Medical PG Question 3: A 13-year-old Caucasian male presents with his father to the pediatrician’s office complaining of left lower thigh pain. He reports slowly progressive pain over the distal aspect of his left thigh over the past three months. He denies any recent trauma to the area. His temperature is 100.9°F (38.3°C). On exam, there is swelling and tenderness overlying the inferior aspect of the left femoral diaphysis. Laboratory evaluation is notable for an elevated white blood cell (WBC) count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). Biopsy of the lesion demonstrates sheets of monotonous small round blue cells with minimal cytoplasm. He is diagnosed and started on a medication that inhibits transcription by intercalating into DNA at the transcription initiation complex. Which of the following adverse events will this patient be at highest risk for following initiation of this medication?
- A. Peripheral neuropathy
- B. Bone marrow suppression (Correct Answer)
- C. Gingival hyperplasia
- D. Pulmonary fibrosis
- E. Hemorrhagic cystitis
Flucytosine Explanation: ***Bone marrow suppression***
- The medication described, which inhibits transcription by intercalating into DNA at the transcription initiation complex, is likely **dactinomycin (actinomycin D)**.
- **Bone marrow suppression** is a common and severe adverse effect of dactinomycin, leading to issues like **neutropenia** and **thrombocytopenia**.
*Peripheral neuropathy*
- This is a common side effect of **vinca alkaloids** (e.g., vincristine, vinblastine) and **taxanes**, which are not described by the mechanism of action given.
- Dactinomycin does not typically cause significant peripheral neuropathy.
*Gingival hyperplasia*
- **Gingival hyperplasia** is a known side effect of medications such as **cyclosporine**, **phenytoin**, and **calcium channel blockers** like nifedipine.
- It is not associated with dactinomycin.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- This is a serious adverse effect of certain chemotherapeutic agents like **bleomycin** and **busulfan**, and other drugs like **amiodarone** and **methotrexate**.
- Dactinomycin is not primarily associated with pulmonary fibrosis.
*Hemorrhagic cystitis*
- **Hemorrhagic cystitis** is a classic adverse effect of **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide**, caused by the metabolite **acrolein**.
- This adverse event is prevented by co-administration of **MESNA**, and is not a common side effect of dactinomycin.
Flucytosine US Medical PG Question 4: You are treating a neonate with meningitis using ampicillin and a second antibiotic, X, that is known to cause ototoxicity. What is the mechanism of antibiotic X?
- A. It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex
- B. It binds the 30S ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex (Correct Answer)
- C. It binds the 30S ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation
- D. It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits peptidyltransferase
- E. It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation
Flucytosine Explanation: ***It binds the 30s ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex***
- The second antibiotic, X, is likely an **aminoglycoside**, such as **gentamicin** or **amikacin**, which are commonly used in combination with ampicillin for neonatal meningitis and are known to cause ototoxicity.
- Aminoglycosides exert their bactericidal effect by **irreversibly binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit**, thereby **inhibiting the formation of the initiation complex** and leading to misreading of mRNA.
*It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **linezolid**, which targets the 50S ribosomal subunit to prevent the formation of the initiation complex.
- While linezolid can cause side effects, **ototoxicity** is less commonly associated with it compared to aminoglycosides, and it is not a primary drug for neonatal meningitis alongside ampicillin.
*It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits peptidyltransferase*
- This is the mechanism of action for **chloramphenicol**, which inhibits **peptidyltransferase** activity on the 50S ribosomal subunit, preventing peptide bond formation.
- Although chloramphenicol can cause **ototoxicity** and **aplastic anemia**, its use in neonates is limited due to the risk of **Gray Baby Syndrome**.
*It binds the 30s ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation*
- This describes the mechanism of action of **tetracyclines**, which reversibly bind to the 30S ribosomal subunit and prevent the attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA, thereby inhibiting protein synthesis.
- Tetracyclines are **contraindicated in neonates** due to their potential to cause **tooth discoloration** and **bone growth inhibition**, and ototoxicity is not their primary adverse effect.
*It binds the 50s ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation*
- This mechanism of reversibly inhibiting translocation by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit is characteristic of **macrolides** (e.g., erythromycin, azithromycin) and **clindamycin**.
- While some macrolides can cause **transient ototoxicity**, they are not typically the second antibiotic of choice for neonatal meningitis in combination with ampicillin, and clindamycin's side effect profile is different.
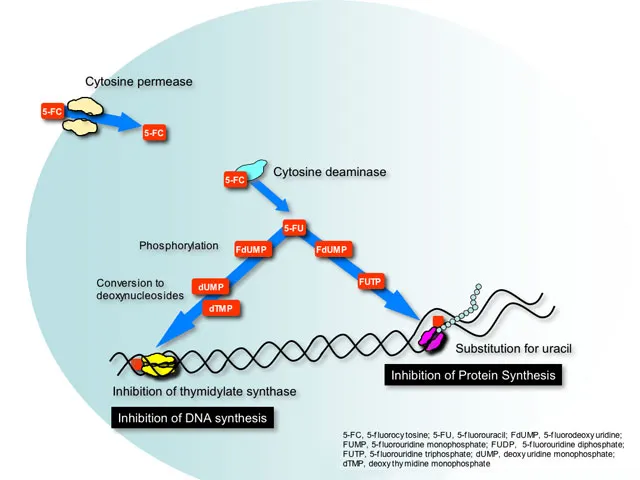
Flucytosine US Medical PG Question 5: A 71-year-old man with colon cancer presents to his oncologist because he has been experiencing photosensitivity with his current chemotherapeutic regimen. During the conversation, they decide that his symptoms are most likely a side effect of the 5-fluorouracil he is currently taking and decide to replace it with another agent. The patient is curious why some organs appear to be especially resistant to chemotherapy whereas others are particularly susceptible to chemotherapy. Which of the following cell types would be most resistant to chemotherapeutic agents?
- A. Cardiac myocytes (Correct Answer)
- B. Hematopoietic cells
- C. Liver hepatocytes
- D. Enterocytes
- E. Hair follicle cells
Flucytosine Explanation: ***Cardiac myocytes***
- **Cardiac myocytes** are highly differentiated, **terminally differentiated cells** that rarely divide, making them inherently resistant to chemotherapeutic agents which primarily target rapidly dividing cells.
- Their **low mitotic activity** means they are less susceptible to agents that interfere with DNA replication, cell division, or other cell cycle-dependent processes.
*Hematopoietic cells*
- **Hematopoietic cells** in the bone marrow are among the most **rapidly dividing cells** in the body, making them extremely susceptible to chemotherapy.
- Damage to these cells leads to **myelosuppression**, a common and serious side effect of chemotherapy.
*Liver hepatocytes*
- **Hepatocytes** have a **moderate proliferative capacity**, allowing for regeneration, but they are still more susceptible to chemotherapy than terminally differentiated cells.
- While they can regenerate, they are particularly vulnerable to hepatotoxic chemotherapy agents due to their role in **drug metabolism** and detoxification.
*Enterocytes*
- **Enterocytes** of the small intestine lining have a **very high turnover rate**, making them highly sensitive to chemotherapeutic agents.
- This sensitivity explains common side effects like **mucositis**, diarrhea, and nausea due to damage to the intestinal lining.
*Hair follicle cells*
- **Hair follicle cells** are also characterized by their rapid division and high metabolic activity, which makes them very vulnerable to chemotherapy.
- Damage to these cells leads to **alopecia** (hair loss), a well-known side effect of many chemotherapeutic regimens.
Flucytosine US Medical PG Question 6: A 60-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of blood in his urine, lower abdominal pain, and a burning sensation while micturating. Five months ago, he was diagnosed with high-grade non-Hodgkin lymphoma and a deep vein thrombosis of his right popliteal vein. His medications include polychemotherapy every 3 weeks and a daily subcutaneous dose of low molecular weight heparin. The last cycle of chemotherapy was 2 weeks ago. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 94/min, and blood pressure is 110/76 mm Hg. Examination shows bilateral axillary and inguinal lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly, and mild suprapubic tenderness. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.2 g/dL
Leukocytes 4,300/mm3
Platelet count 145,000/mm3
Partial thromboplastin time 55 seconds
Prothrombin time 11 seconds (INR=1)
Urine
RBCs 50–55/hpf
RBC casts negative
WBCs 7/hpf
Epithelial cells 5/hpf
Bacteria occasional
Administration of which of the following is most likely to have prevented this patient's current condition?
- A. Ciprofloxacin
- B. Palifermin
- C. Mercaptoethane sulfonate (Correct Answer)
- D. Protamine sulfate
- E. Dexrazoxane
Flucytosine Explanation: ***Mercaptoethane sulfonate***
- The patient's symptoms of **hematuria**, **lower abdominal pain**, and **dysuria** in the context of recent chemotherapy strongly suggest **hemorrhagic cystitis**. This is a known side effect of cyclophosphamide (or ifosfamide), which is often part of polychemotherapy for lymphoma.
- **Mercaptoethane sulfonate (MESNA)** is a chemoprotectant specifically used to detoxify the urotoxic metabolites (acrolein) of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide, thereby preventing hemorrhagic cystitis.
*Ciprofloxacin*
- **Ciprofloxacin** is an antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections, particularly urinary tract infections. While the patient has some WBCs and occasional bacteria in his urine, his primary condition is most likely drug-induced hemorrhagic cystitis, not a bacterial UTI that would be prevented by ciprofloxacin.
- The context of recent chemotherapy points away from a primary bacterial infection as the cause of hematuria.
*Palifermin*
- **Palifermin** is a recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor used to prevent and treat **oral mucositis**, a common side effect of chemotherapy and radiation.
- It does not have any protective effect against hemorrhagic cystitis.
*Protamine sulfate*
- **Protamine sulfate** is used to reverse the anticoagulant effects of **heparin** and **low molecular weight heparin (LMWH)**. While the patient is on LMWH, the hematuria is more likely due to chemotherapy-induced cystitis rather than LMWH overdose, as his platelet count is reasonable and he has no other signs of widespread bleeding attributable to LMWH.
- Administering protamine sulfate would not prevent hemorrhagic cystitis.
*Dexrazoxane*
- **Dexrazoxane** is a cardioprotective agent used to reduce the incidence and severity of **anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity** (e.g., from doxorubicin).
- It does not prevent or treat hemorrhagic cystitis caused by cyclophosphamide or ifosfamide.
Flucytosine US Medical PG Question 7: A pharmaceutical company is studying a new drug that inhibits the glucose transporter used by intestinal enterocytes to absorb glucose into the body. The drug was designed such that it would act upon the glucose transporter similarly to how cyanide acts upon cytochrome proteins. During pre-clinical studies, the behavior of this drug on the activity of the glucose transporter is examined. Specifically, enterocyte cells are treated with the drug and then glucose is added to the solution at a concentration that saturates the activity of the transporter. The transport velocity and affinity of the transporters under these conditions are then measured. Compared to the untreated state, which of the following changes would most likely be seen in these transporters after treatment?
- A. Unchanged Km and decreased Vmax (Correct Answer)
- B. Unchanged Km and unchanged Vmax
- C. Increased Km and unchanged Vmax
- D. Increased Km and decreased Vmax
- E. Decreased Km and decreased Vmax
Flucytosine Explanation: ***Unchanged Km and decreased Vmax***
- The drug functions similarly to **cyanide**, which works as a **noncompetitive inhibitor** by binding irreversibly to a site other than the active site
- **Noncompetitive inhibition** results in a **decreased Vmax** (maximum transport velocity) because fewer active transporters are available, but the **Km (substrate affinity) remains unchanged** as the binding affinity of the remaining active transporters is unaffected
- This is the expected pattern when glucose is added at saturating concentrations in the presence of an irreversible noncompetitive inhibitor
*Unchanged Km and unchanged Vmax*
- This would imply no significant effect of the drug on the glucose transporter, which contradicts the drug's design as an inhibitor
- An unaffected Vmax suggests that the maximum transport rate is maintained, and an unchanged Km indicates unaltered affinity—neither of which aligns with the action of a noncompetitive inhibitor
*Increased Km and unchanged Vmax*
- An **increased Km** signifies a **decreased affinity** of the transporter for glucose, which is characteristic of **competitive inhibition**
- An **unchanged Vmax** means the maximum transport rate is still achievable at high substrate concentrations, as competitive inhibitors can be overcome by saturating substrate concentrations
- This pattern does not match the cyanide-like irreversible noncompetitive inhibitor described
*Increased Km and decreased Vmax*
- This pattern suggests **mixed inhibition** or **uncompetitive inhibition**, where both Km and Vmax are affected
- While Vmax is appropriately decreased, the increase in Km indicates reduced affinity, which is not the primary mechanism for a cyanide-like noncompetitive inhibitor that binds irreversibly to a separate site
*Decreased Km and decreased Vmax*
- A **decreased Km** would imply an **increased affinity** of the transporter for glucose, which is not expected from an inhibitor designed to reduce overall transport
- Although Vmax is appropriately decreased, the change in Km does not fit the typical profile of a noncompetitive inhibitor acting in a cyanide-like manner
Flucytosine US Medical PG Question 8: A 31-year-old female receives a kidney transplant for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). Three weeks later, the patient experiences acute, T-cell mediated rejection of the allograft and is given sirolimus. Which of the following are side effects of this medication?
- A. Nephrotoxicity, hypertension
- B. Hyperlipidemia, thrombocytopenia (Correct Answer)
- C. Nephrotoxicity, gingival hyperplasia
- D. Pancreatitis
- E. Cytokine release syndrome, hypersensitivity reaction
Flucytosine Explanation: ***Hyperlipidemia, thrombocytopenia***
- **Sirolimus** (rapamycin) is an **mTOR inhibitor** commonly used in transplant immunology, which frequently causes **hyperlipidemia** (elevated cholesterol and triglycerides) and **thrombocytopenia** (low platelet count).
- Other common side effects include **myelosuppression** (leukopenia, anemia), **mouth ulcers**, and **impaired wound healing**.
*Nephrotoxicity, hypertension*
- **Nephrotoxicity** and **hypertension** are more characteristic side effects of **calcineurin inhibitors** like **tacrolimus** and **cyclosporine**, which are also used in transplant immunosuppression but have a different mechanism of action than sirolimus.
- While sirolimus can indirectly affect kidney function, it is generally considered less nephrotoxic than calcineurin inhibitors.
*Nephrotoxicity, gingival hyperplasia*
- **Gingival hyperplasia** is a hallmark side effect of **cyclosporine**, a calcineurin inhibitor, along with **hirsutism** and **nephrotoxicity**.
- Sirolimus does not typically cause gingival hyperplasia.
*Pancreatitis*
- While some immunosuppressants can rarely cause pancreatitis, it is not a common or characteristic side effect of **sirolimus**.
- **Azathioprine** is more frequently associated with pancreatitis among immunosuppressive agents.
*Cytokine release syndrome, hypersensitivity reaction*
- **Cytokine release syndrome** and acute **hypersensitivity reactions** are more often associated with **monoclonal antibodies** (e.g., **basiliximab**, **daclizumab**) used for induction therapy or treatment of acute rejection, particularly within hours or days of administration.
- Sirolimus is less likely to cause these immediate severe reactions.
Flucytosine US Medical PG Question 9: A 58-year-old woman comes to the physician for evaluation of worsening fatigue for 1 week. She also has a 1-year history of hand pain and stiffness. Four months ago, she started a new medication for these symptoms. Medications used prior to that included ibuprofen, prednisone, and hydroxychloroquine. Examination shows a subcutaneous nodule on her left elbow and old joint destruction with Boutonniere deformity. Her hemoglobin concentration is 10.1 g/dL, leukocyte count is 3400/mm3, and platelet count is 101,000/mm3. Methylmalonic acid levels are normal. Which of the following could have prevented this patient's laboratory abnormalities?
- A. Vitamin B12
- B. Vitamin B6
- C. Amifostine
- D. 2-Mercaptoethanesulfonate
- E. Leucovorin (Correct Answer)
Flucytosine Explanation: **Leucovorin**
- The patient's pancytopenia (anemia, leukopenia, and thrombocytopenia) in the context of rheumatoid arthritis treatment points towards **methotrexate toxicity** as the cause.
- **Leucovorin (folinic acid)** is often co-administered with methotrexate or used as a rescue therapy to prevent or counteract its adverse effects by providing an alternative source of folate, bypassing the dihydrofolate reductase inhibition.
*Vitamin B12*
- While **vitamin B12 deficiency** can cause anemia and pancytopenia, the patient's normal **methylmalonic acid levels** rule out this possibility.
- B12 deficiency is typically associated with **macrocytic anemia** and neurological symptoms, which are not explicitly mentioned as the primary concern here.
*Vitamin B6*
- **Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)** deficiency can lead to microcytic anemia, but it is not typically associated with the comprehensive pancytopenia observed here, nor is it related to methotrexate toxicity.
- It is crucial for **heme synthesis** and can be deficient in conditions like alcoholism.
*Amifostine*
- **Amifostine** is a cytoprotective agent used to prevent nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity associated with certain chemotherapy agents like **cisplatin**, and also to reduce xerostomia in head and neck radiation.
- It is not indicated for the prevention of methotrexate-induced myelosuppression.
*2-Mercaptoethanesulfonate*
- **2-Mercaptoethanesulfonate (Mesna)** is a uroprotectant used to prevent hemorrhagic cystitis caused by **oxazaphosphorine chemotherapeutic agents** like cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide.
- It has no role in preventing the hematologic toxicity of methotrexate.
Flucytosine US Medical PG Question 10: A 29-year-old female presents to her gynecologist complaining of a painful rash around her genitals. She has multiple sexual partners and uses condoms intermittently. Her last STD screen one year ago was negative. On examination, she has bilateral erosive vesicles on her labia majora and painful inguinal lymphadenopathy. She is started on an oral medication that requires a specific thymidine kinase for activation. Which of the following adverse effects is associated with this drug?
- A. Photosensitivity
- B. Deafness
- C. Renal failure (Correct Answer)
- D. Gingival hyperplasia
- E. Pulmonary fibrosis
Flucytosine Explanation: ***Renal failure***
- The patient's symptoms (painful genital rash, erosive vesicles, inguinal lymphadenopathy) are highly suggestive of **herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection**, likely genital herpes.
- The drug described is an antiviral agent like **acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir**, which require **viral thymidine kinase** for activation and are known to cause **renal impairment** (nephrotoxicity) as an adverse effect, especially with high doses or in dehydrated patients due to crystal nephropathy.
*Photosensitivity*
- **Photosensitivity** is a common side effect of some antibiotics (e.g., tetracyclines, sulfonamides), diuretics (e.g., thiazides), and antifungals, but it is **not a prominent adverse effect of acyclovir or its derivatives**.
- While theoretical, it is not a clinically significant or frequently observed adverse effect associated with the class of antiviral drugs used for HSV.
*Deafness*
- **Ototoxicity**, leading to deafness or hearing loss, is a well-known adverse effect of certain classes of drugs, such as **aminoglycoside antibiotics** (e.g., gentamicin) and **loop diuretics** (e.g., furosemide).
- It is **not an adverse effect** associated with antiviral medications like acyclovir.
*Gingival hyperplasia*
- **Gingival hyperplasia** (overgrowth of gum tissue) is a recognized side effect of specific medications including **phenytoin** (an anticonvulsant), **cyclosporine** (an immunosuppressant), and **calcium channel blockers** (e.g., nifedipine, amlodipine).
- This adverse effect is **not associated with antiviral drugs** used to treat herpes simplex.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is a serious adverse effect linked to various drugs like **amiodarone** (an antiarrhythmic), **bleomycin** (a chemotherapeutic agent), **methotrexate** (an immunosuppressant/chemotherapeutic), and **nitrofurantoin** (an antibiotic).
- **Antiviral medications for HSV** do not typically cause pulmonary fibrosis.
More Flucytosine US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.