Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old HIV-positive male presents to his primary care physician complaining of decreased libido. He reports that he has been unable to maintain an erection for the past two weeks. He has never encountered this problem before. He was hospitalized four weeks ago for cryptococcal meningitis and has been on long-term antifungal therapy since then. His CD4 count is 400 cells/mm^3 and viral load is 5,000 copies/ml. He was previously non-compliant with HAART but since his recent infection, he has been more consistent with its use. His past medical history is also notable for hypertension, major depressive disorder, and alcohol abuse. He takes lisinopril and sertraline. His temperature is 98.6°F (37°C), blood pressure is 120/85 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 18/min. The physician advises the patient that side effects like decreased libido may manifest due to a drug with which of the following mechanisms of action?
- A. Inhibition of beta-glucan synthesis
- B. Formation of pores in cell membrane
- C. Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis (Correct Answer)
- D. Disruption of microtubule formation
- E. Inhibition of pyrimidine synthesis
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) Explanation: ***Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis***
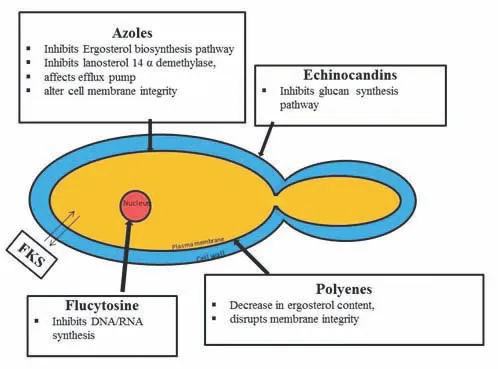
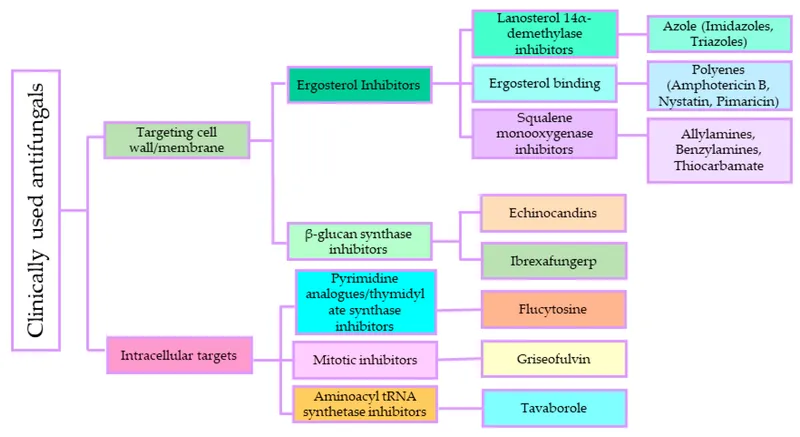
- The patient was recently treated for **cryptococcal meningitis** and is likely on an **azole antifungal**, such as fluconazole or itraconazole, for long-term therapy.
- Azole antifungals inhibit **14-alpha-demethylase**, an enzyme crucial for **ergosterol synthesis**, and are known to cause endocrine side effects like **decreased libido** and **erectile dysfunction** due to their impact on steroid hormone synthesis.
*Inhibition of beta-glucan synthesis*
- This mechanism of action belongs to **echinocandins** (e.g., caspofungin, micafungin), which inhibit the synthesis of **1,3-beta-D-glucan**, a key component of the fungal cell wall.
- Echinocandins are typically used for *Candida* infections and are generally not associated with significant endocrine side effects like decreased libido or erectile dysfunction.
*Formation of pores in cell membrane*
- This is the mechanism of action for **polyene antifungals** like **amphotericin B** and **nystatin**, which bind to ergosterol in the fungal cell membrane, creating pores and leading to cell lysis.
- While effective against *Cryptococcus*, amphotericin B is primarily used for acute, severe infections due to its significant toxicity, including nephrotoxicity, and is not typically used for long-term maintenance in this context with libido as the main symptom.
*Disruption of microtubule formation*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **griseofulvin**, an antifungal primarily used for dermatophyte infections of the skin and nails.
- It interferes with **microtubule function** and inhibits fungal mitosis, but it is not used for systemic fungal infections like cryptococcal meningitis, nor is it commonly associated with decreased libido.
*Inhibition of pyrimidine synthesis*
- This mechanism belongs to **flucytosine**, which is converted to **5-fluorouracil** within fungal cells, inhibiting DNA and RNA synthesis.
- Flucytosine is typically used in combination with amphotericin B for severe cryptococcal infections, but it is not known to cause decreased libido as a common or prominent side effect.
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) US Medical PG Question 2: A 46-year-old man with HIV infection comes to the physician because of a 1-week history of severe retrosternal pain while swallowing. He has not been compliant with his antiretroviral drug regimen. His CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 98/mm3 (N ≥ 500). Endoscopy shows white plaques in the esophagus. The most appropriate immediate treatment is a drug that inhibits which of the following enzymes?
- A. DNA polymerase
- B. Hydrogen-potassium ATPase
- C. Cytochrome p450 enzymes (Correct Answer)
- D. Phospholipase A2
- E. Squalene epoxidase
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) Explanation: ***Cytochrome P450 enzymes***
- The patient's symptoms (retrosternal pain on swallowing, white plaques on endoscopy) and severely low **CD4+ count (98/mm³)** are highly suggestive of **esophageal candidiasis**, a common opportunistic infection in AIDS.
- **Fluconazole**, an azole antifungal, is the **first-line treatment** for esophageal candidiasis and works by inhibiting **14α-demethylase (lanosterol demethylase)**, a fungal **cytochrome P450 enzyme**.
- This inhibition prevents the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol, disrupting **fungal cell membrane synthesis** and leading to fungal cell death.
*Squalene epoxidase*
- **Terbinafine** and **naftifine** (allylamine antifungals) inhibit squalene epoxidase in the ergosterol synthesis pathway.
- These agents are primarily used for **dermatophyte infections** (onychomycosis, tinea) and have **poor activity against Candida species**.
- They are not appropriate for treating esophageal candidiasis.
*DNA polymerase*
- Inhibitors of **DNA polymerase**, such as acyclovir or ganciclovir, are used to treat **herpesvirus infections** (HSV, CMV).
- While herpes esophagitis can occur in immunocompromised patients, it typically presents with **punched-out ulcers**, not white plaques.
*Hydrogen-potassium ATPase*
- **Proton pump inhibitors** (PPIs) target hydrogen-potassium ATPase in gastric parietal cells to reduce **acid secretion**.
- These are used to treat **GERD** or **peptic ulcers**, which do not present with white plaques on endoscopy.
- While PPIs may provide symptomatic relief, they do not treat the underlying fungal infection.
*Phospholipase A2*
- Phospholipase A2 inhibitors are used as **anti-inflammatory agents**, as PLA2 releases arachidonic acid, a precursor to inflammatory mediators.
- These drugs have no role in treating fungal infections like esophageal candidiasis.
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) US Medical PG Question 3: An epidemiologist is evaluating the efficacy of Noxbinle in preventing HCC deaths at the population level. A clinical trial shows that over 5 years, the mortality rate from HCC was 25% in the control group and 15% in patients treated with Noxbinle 100 mg daily. Based on this data, how many patients need to be treated with Noxbinle 100 mg to prevent, on average, one death from HCC?
- A. 20
- B. 73
- C. 10 (Correct Answer)
- D. 50
- E. 100
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) Explanation: ***10***
- The **number needed to treat (NNT)** is calculated by first finding the **absolute risk reduction (ARR)**.
- **ARR** = Risk in control group - Risk in treatment group = 25% - 15% = **10%** (or 0.10).
- **NNT = 1 / ARR** = 1 / 0.10 = **10 patients**.
- This means that **10 patients must be treated with Noxbinle to prevent one death from HCC** over 5 years.
*20*
- This would result from an ARR of 5% (1/0.05 = 20), which is not supported by the data.
- May arise from miscalculating the risk difference or incorrectly halving the actual ARR.
*73*
- This value does not correspond to any standard calculation of NNT from the given mortality rates.
- May result from confusion with other epidemiological measures or calculation error.
*50*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 2% (1/0.02 = 50), which significantly underestimates the actual risk reduction.
- Could result from incorrectly calculating the difference as a proportion rather than absolute percentage points.
*100*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 1% (1/0.01 = 100), grossly underestimating the treatment benefit.
- May result from confusing ARR with relative risk reduction or other calculation errors.
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) US Medical PG Question 4: A 76-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. One week ago, he was prescribed azithromycin for acute bacterial sinusitis. He has a history of atrial fibrillation treated with warfarin and metoprolol. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Compared to one month ago, laboratory studies show a mild increase in INR. Which of the following best explains this patient's laboratory finding?
- A. Drug-induced hepatotoxicity
- B. Depletion of intestinal flora
- C. Inhibition of cytochrome p450 (Correct Answer)
- D. Increased gastrointestinal absorption of warfarin
- E. Increased non-protein bound warfarin fraction
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) Explanation: ***Inhibition of cytochrome p450***
- **Azithromycin**, while a weaker inhibitor compared to erythromycin and clarithromycin, **does inhibit CYP3A4 and other cytochrome P450 enzymes** to a clinically significant degree.
- This inhibition **reduces warfarin metabolism**, leading to increased warfarin levels and **enhanced anticoagulant effect**, manifesting as an **increased INR**.
- This pharmacokinetic interaction is well-documented and is the **primary mechanism** for azithromycin-warfarin interaction.
*Depletion of intestinal flora*
- The theory that antibiotics deplete **vitamin K-producing gut bacteria** leading to increased warfarin effect is a **common misconception**.
- Humans obtain vitamin K primarily from **dietary sources** (leafy greens, vegetable oils), not from gut bacterial synthesis; intestinal bacteria contribute minimally to vitamin K stores.
- This mechanism has been **debunked** in modern pharmacology literature and does not explain antibiotic-warfarin interactions.
*Drug-induced hepatotoxicity*
- While hepatotoxicity can impair **clotting factor synthesis** and increase INR, **azithromycin** rarely causes significant liver injury.
- The presentation shows only a **mild INR increase** one week after starting therapy, without other signs of liver dysfunction.
- This acute, mild change is more consistent with a **pharmacokinetic drug interaction** than hepatotoxicity.
*Increased gastrointestinal absorption of warfarin*
- **Warfarin** has high oral bioavailability (~100%) under normal conditions.
- **Azithromycin** does not enhance the **gastrointestinal absorption** of warfarin.
- This mechanism is not supported by pharmacological evidence for this drug interaction.
*Increased non-protein bound warfarin fraction*
- Displacement of warfarin from **plasma protein binding sites** can transiently increase free drug.
- However, **azithromycin** does not significantly displace warfarin from **albumin**.
- This mechanism does not explain the sustained INR elevation seen with azithromycin therapy.
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) US Medical PG Question 5: A 32-year-old woman presents with three-days of vaginal burning, itching, and pain with intercourse. She is in a monogamous relationship with her husband and has an intrauterine device for contraception. Her past medical history is unremarkable, except for recently being treated with antibiotics for sinusitis. Pelvic exam is remarkable for vulvar excoriations, vaginal wall edema, and thick, white discharge in the vault. Wet mount with KOH staining reveals budding filaments with pseudohyphae and hyphae. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
- A. Voriconazole
- B. Posaconazole
- C. Metronidazole
- D. Itraconazole
- E. Fluconazole (Correct Answer)
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) Explanation: ***Fluconazole***
- The patient's symptoms (vaginal burning, itching, pain with intercourse, thick, white discharge) and **wet mount findings (budding filaments with pseudohyphae and hyphae)** are classic for **vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC)**, often precipitated by recent antibiotic use.
- **Fluconazole** is a highly effective and commonly prescribed oral antifungal for uncomplicated VVC due to its convenience and excellent therapeutic profile.
*Voriconazole*
- **Voriconazole** is a broad-spectrum triazole antifungal primarily used for invasive fungal infections, such as **invasive aspergillosis** and candidemia, and is not a first-line treatment for uncomplicated VVC.
- Its use is typically reserved for more severe or refractory systemic fungal infections, and it has a more significant side effect profile than fluconazole.
*Posaconazole*
- **Posaconazole** is another extended-spectrum triazole antifungal primarily used for the prophylaxis and treatment of **invasive fungal infections** in immunocompromised patients, particularly those unresponsive to other antifungals.
- It is not indicated for the treatment of uncomplicated vulvovaginal candidiasis.
*Metronidazole*
- **Metronidazole** is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal agent used to treat bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis, both of which are common causes of vaginitis.
- It is **ineffective against fungal infections**, and the patient's symptoms and wet mount findings rule out bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis.
*Itraconazole*
- **Itraconazole** is an antifungal drug effective against superficial and systemic fungal infections, but it is typically used for more severe or recurrent VVC, or in cases of non-albicans Candida species.
- While effective, **fluconazole** is generally preferred as the first-line oral treatment for uncomplicated VVC due to its single-dose efficacy and established safety profile for this indication.
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) US Medical PG Question 6: A 72-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician because she is concerned about the appearance of her toenails. Examination shows yellowish discoloration of all toenails on both feet. The edges of the toenails are lifted, and there is subungual debris. Potassium hydroxide preparation of scrapings from the nails shows multiple branching septate hyphae. Treatment with oral terbinafine is begun. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibition of squalene epoxidase (Correct Answer)
- B. Formation of pores in cell membrane
- C. Inhibition of β-glucan synthesis
- D. Interference with mitosis during metaphase
- E. Prevention of lanosterol to ergosterol conversion
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) Explanation: ***Inhibition of squalene epoxidase***
- **Terbinafine** is an **allylamine** antifungal that inhibits the enzyme **squalene epoxidase**, an early step in fungal ergosterol synthesis
- This inhibition leads to the accumulation of **squalene**, which is toxic to the fungal cell, and a deficiency of **ergosterol**, disrupting cell membrane integrity and function
- Terbinafine is highly effective for **onychomycosis** (fungal nail infections) caused by dermatophytes
*Formation of pores in cell membrane*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **polyene antifungals** like **amphotericin B** and **nystatin**
- These drugs bind to **ergosterol** in the fungal cell membrane, creating pores that lead to leakage of intracellular contents and cell death
*Inhibition of β-glucan synthesis*
- This is the primary mechanism of action for **echinocandin** antifungals, such as **caspofungin**, **micafungin**, and **anidulafungin**
- These drugs inhibit **(1,3)-β-D-glucan synthase**, which is essential for the synthesis of glucan, a major component of the fungal cell wall
*Interference with mitosis during metaphase*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **griseofulvin**, another antifungal agent used for dermatophyte infections
- **Griseofulvin** interferes with **microtubule function**, disrupting mitotic spindle formation and preventing fungal cell division
*Prevention of lanosterol to ergosterol conversion*
- This mechanism is associated with **azole antifungals** (e.g., fluconazole, itraconazole), which inhibit fungal **cytochrome P450-dependent 14-α-demethylase**
- This enzyme is responsible for the conversion of **lanosterol** to **ergosterol**, leading to ergosterol depletion and accumulation of toxic sterol precursors
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) US Medical PG Question 7: A 24-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 4-hour history of headaches, nausea, and vomiting. During this time, she has also had recurrent dizziness and palpitations. The symptoms started while she was at a friend's birthday party, where she had one beer. One week ago, the patient was diagnosed with a genitourinary infection and started on antimicrobial therapy. She has no history of major medical illness. Her pulse is 106/min and blood pressure is 102/73 mm Hg. Physical examination shows facial flushing and profuse sweating. The patient is most likely experiencing adverse effects caused by treatment for an infection with which of the following pathogens?
- A. Candida albicans
- B. Chlamydia trachomatis
- C. Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- D. Herpes simplex virus
- E. Trichomonas vaginalis (Correct Answer)
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) Explanation: ***Trichomonas vaginalis***
- The patient's symptoms (headache, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, palpitations, facial flushing, sweating) after consuming alcohol while on antimicrobial therapy for a genitourinary infection are characteristic of a **disulfiram-like reaction**.
- **Metronidazole**, a common treatment for *Trichomonas vaginalis* infection, is known to cause a disulfiram-like reaction when combined with alcohol, due to inhibition of **acetaldehyde dehydrogenase**.
*Candida albicans*
- Genitourinary infections with *Candida albicans* (e.g., vulvovaginal candidiasis) are typically treated with **antifungal medications** like fluconazole, which do not cause disulfiram-like reactions with alcohol.
- While symptoms like headache can occur with some antifungals, the constellation of flushing, palpitations, and nausea after a single beer strongly points away from this pathogen.
*Chlamydia trachomatis*
- *Chlamydia trachomatis* is commonly treated with **azithromycin** or **doxycycline**, neither of which are associated with disulfiram-like reactions to alcohol.
- The patient's symptoms are specific to alcohol interaction with certain antimicrobials, not typical side effects of these antibiotics.
*Neisseria gonorrhoeae*
- Infections with *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* are usually treated with **ceftriaxone** (often with azithromycin), which also do not cause disulfiram-like reactions.
- The clinical presentation after alcohol consumption is inconsistent with the typical adverse effects of these treatments.
*Herpes simplex virus*
- Genitourinary infections caused by herpes simplex virus are treated with **antiviral medications** such as acyclovir or valacyclovir.
- These antiviral drugs do not cause disulfiram-like reactions when ingested with alcohol.
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) US Medical PG Question 8: A 55-year-old male presents to his primary care physician for a normal check-up. He has a history of atrial fibrillation for which he takes metoprolol and warfarin. During his last check-up, his international normalized ratio (INR) was 2.5. He reports that he recently traveled to Mexico for a business trip where he developed a painful red rash on his leg. He was subsequently prescribed an unknown medication by a local physician. The rash resolved after a few days and he currently feels well. His temperature is 98.6°F (37°C), blood pressure is 130/80 mmHg, pulse is 95/min, and respirations are 18/min. Laboratory analysis reveals that his current INR is 4.5. Which of the following is the most likely medication this patient took while in Mexico?
- A. Griseofulvin
- B. Rifampin
- C. St. John’s wort
- D. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (Correct Answer)
- E. Phenobarbital
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) Explanation: ***Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole***
- **Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole** is a potent inhibitor of **CYP2C9**, the primary enzyme responsible for metabolizing **warfarin**, leading to significantly increased INR and bleeding risk.
- The patient's **elevated INR (4.5)** from a previous stable level of 2.5 strongly suggests an interaction with a medication that inhibits warfarin metabolism, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole is a common culprit.
- TMP-SMX is commonly used to treat **cellulitis** and other skin infections, which aligns with the clinical presentation of a painful red rash.
*Griseofulvin*
- **Griseofulvin** is an antifungal agent that acts as a **CYP inducer**, which would *increase* warfarin metabolism and lead to a *decreased* INR, not the elevated INR seen in this patient.
- While it could treat fungal skin infections (e.g., tinea), it would cause the opposite effect on warfarin levels.
*Rifampin*
- **Rifampin** is a strong **CYP inducer**, meaning it would *increase* warfarin metabolism and thus *decrease* INR, leading to a higher risk of clotting, which is the opposite of what is seen in this patient.
- It is often used for tuberculosis or serious bacterial infections, not typically for a simple skin rash.
*St. John's wort*
- **St. John's wort** is a known **CYP inducer**, similar to rifampin, and would lead to a *decrease* in warfarin levels and INR.
- It is an herbal supplement primarily used for depression and would not typically be prescribed by a physician for a rash.
*Phenobarbital*
- **Phenobarbital** is a potent **CYP inducer**, which would *accelerate* warfarin metabolism and result in a *decreased* INR, increasing the risk of thrombosis.
- It is an anticonvulsant and sedative, not a medication typically prescribed for a rash.
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) US Medical PG Question 9: A 59-year-old man comes to the physician because of a painful, burning red rash on his face and hands, which developed 30 minutes after going outside to do garden work. He wore a long-sleeved shirt and was exposed to direct sunlight for about 10 minutes. The patient is light-skinned and has a history of occasional sunburns when he does not apply sunscreen. The patient was diagnosed with small cell lung carcinoma 2 months ago and is currently undergoing chemotherapy. He is currently taking demeclocycline for malignancy-associated hyponatremia and amoxicillin for sinusitis. He has also had occasional back pain. He takes zolpidem and drinks 1–2 glasses of brandy before going to sleep every night. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for 20 years. His pulse is 72/min and his blood pressure is 120/75 mm Hg. Physical examination shows prominent erythema on his forehead, cheeks, and neck. Erythema and papular eruptions are seen on the dorsum of both hands. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Normal sunburn reaction
- B. Adverse reaction to amoxicillin
- C. Systemic lupus erythematosus
- D. Use of demeclocycline (Correct Answer)
- E. Uroporphyrin accumulation
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) Explanation: ***Use of demeclocycline***
- The patient's acute, burning erythematous rash on sun-exposed areas (face, hands) after brief sun exposure is highly suggestive of **photosensitivity**.
- **Demeclocycline**, a tetracycline antibiotic, is a known cause of **phototoxic reactions**, making it the most likely culprit given his current medications.
*Normal sunburn reaction*
- A normal sunburn, while possible with brief exposure in a light-skinned individual, would typically take longer than **30 minutes** to develop a prominent, burning rash.
- The severity and rapid onset of symptoms are more indicative of a **phototoxic reaction** rather than a typical sunburn.
*Adverse reaction to amoxicillin*
- While amoxicillin can cause drug eruptions, they typically manifest as a **morbilliform rash** or **urticaria (hives)**, not a localized, burning rash primarily in sun-exposed areas.
- Amoxicillin is **not commonly associated** with photosensitivity.
*Systemic lupus erythematosus*
- SLE can cause photosensitive rashes (e.g., **malar rash**, discoid lesions), but these tend to be **chronic** or recurrent, and the acute, rapid onset of a burning sensation after brief exposure is less typical.
- Other systemic symptoms of SLE, such as **arthralgias, kidney involvement, or serositis**, are not described as the primary complaint.
*Uroporphyrin accumulation*
- **Porphyrias**, such as **porphyria cutanea tarda**, involve the accumulation of porphyrins (like uroporphyrin) leading to photosensitivity, blistering, and skin fragility.
- While it causes photosensitivity, the classic presentation often includes **blisters, hyperpigmentation, increased skin fragility, and hirsutism**, which are not described in this patient's acute presentation of a purely erythematous, burning rash.
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) US Medical PG Question 10: A 39-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of fatigue, decreased sexual desire, and difficulty achieving an erection. He has no past medical history except for a traumatic brain injury he sustained in a motor vehicle accident 4 months ago. At that time, neuroimaging studies showed no abnormalities. Physical examination shows bilateral gynecomastia and a thin white nipple discharge. Decreased production of which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's current condition?
- A. Gonadotropin-releasing hormone
- B. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone
- C. Luteinizing hormone
- D. Growth hormone
- E. Dopamine (Correct Answer)
Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) Explanation: ***Dopamine***
- The patient's symptoms (fatigue, decreased sexual desire, erectile dysfunction, gynecomastia, galactorrhea) following a **traumatic brain injury (TBI)** are indicative of **hypopituitarism**, specifically affecting dopamine's inhibitory control over prolactin.
- **Dopamine** is produced in the hypothalamus and tonically inhibits **prolactin secretion** from the anterior pituitary; a decrease in dopamine can lead to elevated prolactin, causing the observed symptoms.
*Gonadotropin-releasing hormone*
- While TBI can cause **hypogonadism** due to GnRH deficiency, this would primarily lead to decreased LH/FSH and subsequent low testosterone, causing sexual dysfunction but not necessarily **galactorrhea** or **gynecomastia**.
- Decreased GnRH would result in low levels of LH and FSH, but the direct cause of gynecomastia and nipple discharge in this case is likely **hyperprolactinemia**.
*Thyrotropin-releasing hormone*
- TRH stimulates TSH release; a deficiency would lead to **central hypothyroidism** (fatigue, cold intolerance, weight gain), but it does not directly explain **gynecomastia** or **galactorrhea**.
- While TRH can stimulate prolactin secretion, a primary TRH deficiency would more prominently feature symptoms of hypothyroidism, which are not mentioned as the primary concern.
*Luteinizing hormone*
- A decrease in LH would lead to **decreased testosterone production** and symptoms like low sexual desire and erectile dysfunction. However, it does not directly cause **galactorrhea** or **gynecomastia** as seen in this patient.
- LH primarily acts on Leydig cells to produce testosterone; while low testosterone can cause gynecomastia, the nipple discharge points more strongly to **hyperprolactinemia**.
*Growth hormone*
- Growth hormone deficiency in adults can cause fatigue, decreased muscle mass, and central obesity but is not typically associated with **gynecomastia** or **galactorrhea**.
- A decrease in GH does not explain the breast-related symptoms observed in this patient.
More Azoles (imidazoles and triazoles) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.