Antifungal spectrum of activity US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Antifungal spectrum of activity. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Antifungal spectrum of activity US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old HIV-positive male presents to his primary care physician complaining of decreased libido. He reports that he has been unable to maintain an erection for the past two weeks. He has never encountered this problem before. He was hospitalized four weeks ago for cryptococcal meningitis and has been on long-term antifungal therapy since then. His CD4 count is 400 cells/mm^3 and viral load is 5,000 copies/ml. He was previously non-compliant with HAART but since his recent infection, he has been more consistent with its use. His past medical history is also notable for hypertension, major depressive disorder, and alcohol abuse. He takes lisinopril and sertraline. His temperature is 98.6°F (37°C), blood pressure is 120/85 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 18/min. The physician advises the patient that side effects like decreased libido may manifest due to a drug with which of the following mechanisms of action?
- A. Inhibition of beta-glucan synthesis
- B. Formation of pores in cell membrane
- C. Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis (Correct Answer)
- D. Disruption of microtubule formation
- E. Inhibition of pyrimidine synthesis
Antifungal spectrum of activity Explanation: ***Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis***
- The patient was recently treated for **cryptococcal meningitis** and is likely on an **azole antifungal**, such as fluconazole or itraconazole, for long-term therapy.
- Azole antifungals inhibit **14-alpha-demethylase**, an enzyme crucial for **ergosterol synthesis**, and are known to cause endocrine side effects like **decreased libido** and **erectile dysfunction** due to their impact on steroid hormone synthesis.
*Inhibition of beta-glucan synthesis*
- This mechanism of action belongs to **echinocandins** (e.g., caspofungin, micafungin), which inhibit the synthesis of **1,3-beta-D-glucan**, a key component of the fungal cell wall.
- Echinocandins are typically used for *Candida* infections and are generally not associated with significant endocrine side effects like decreased libido or erectile dysfunction.
*Formation of pores in cell membrane*
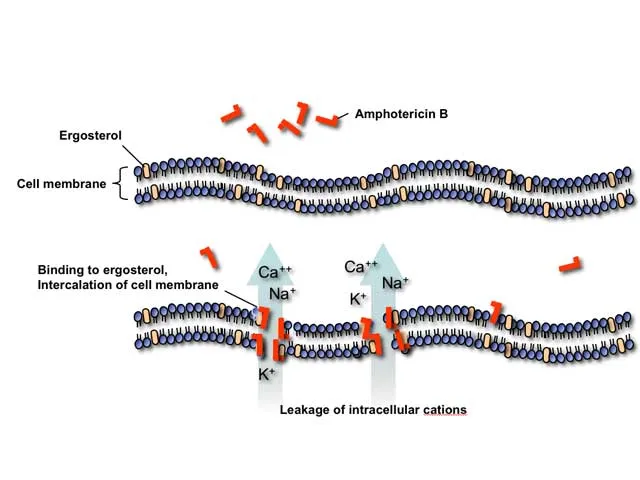
- This is the mechanism of action for **polyene antifungals** like **amphotericin B** and **nystatin**, which bind to ergosterol in the fungal cell membrane, creating pores and leading to cell lysis.
- While effective against *Cryptococcus*, amphotericin B is primarily used for acute, severe infections due to its significant toxicity, including nephrotoxicity, and is not typically used for long-term maintenance in this context with libido as the main symptom.
*Disruption of microtubule formation*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **griseofulvin**, an antifungal primarily used for dermatophyte infections of the skin and nails.
- It interferes with **microtubule function** and inhibits fungal mitosis, but it is not used for systemic fungal infections like cryptococcal meningitis, nor is it commonly associated with decreased libido.
*Inhibition of pyrimidine synthesis*
- This mechanism belongs to **flucytosine**, which is converted to **5-fluorouracil** within fungal cells, inhibiting DNA and RNA synthesis.
- Flucytosine is typically used in combination with amphotericin B for severe cryptococcal infections, but it is not known to cause decreased libido as a common or prominent side effect.
Antifungal spectrum of activity US Medical PG Question 2: A 45-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of pain in his mouth and throat and difficulty swallowing. He has a history of COPD, for which he takes theophylline and inhaled budesonide-formoterol. Physical examination shows white patches on the tongue and buccal mucosa that can be scraped off easily. Appropriate pharmacotherapy is initiated. One week later, he returns because of nausea, palpitations, and anxiety. His pulse is 110/min and regular. Physical examination shows a tremor in both hands. Which of the following drugs was most likely prescribed?
- A. Amphotericin B
- B. Griseofulvin
- C. Terbinafine
- D. Fluconazole (Correct Answer)
- E. Nystatin
Antifungal spectrum of activity Explanation: ***Fluconazole***
- Fluconazole is a potent **CYP450 inhibitor**, specifically **CYP2C9 and CYP3A4**, which can significantly increase the levels of drugs metabolized by these enzymes, such as **theophylline**.
- The patient's symptoms of nausea, palpitations, anxiety, tremor, and tachycardia are consistent with **theophylline toxicity**, which would be exacerbated by co-administration with fluconazole.
*Amphotericin B*
- Amphotericin B is a powerful antifungal, but its primary side effects include **nephrotoxicity**, **infusion-related reactions** (fever, chills, rigors), and **electrolyte disturbances**, not theophylline toxicity.
- It is typically reserved for **severe systemic fungal infections** and is not a first-line treatment for uncomplicated **oral candidiasis**.
*Griseofulvin*
- Griseofulvin is used to treat **dermatophyte infections** (tinea infections) and is not active against *Candida*.
- Its main side effects include **gastrointestinal upset**, **headache**, and **photosensitivity**, and it does not significantly interact with theophylline.
*Terbinafine*
- Terbinafine is an allylamine antifungal primarily used for **dermatophyte infections**, particularly **onychomycosis**, and is not effective for candidiasis.
- While it can cause liver enzyme elevation, it does not typically lead to theophylline toxicity or the constellation of symptoms described.
*Nystatin*
- Nystatin is a **topical or oral non-absorbable antifungal** used for superficial candidal infections, including oral thrush.
- It is not absorbed systemically, so it has **virtually no drug interactions** or systemic side effects, and therefore would not cause theophylline toxicity.
Antifungal spectrum of activity US Medical PG Question 3: A 57-year-old florist presents to his family physician with nodular lesions on his right hand and forearm. He explains that he got pricked by a rose thorn on his right "pointer finger" where the first lesions appeared, and the other lesions then began to appear in an ascending manner. The physician prescribed a medication and warned him of gynecomastia as a side effect if taken for long periods of time. Which of the following is the mechanism of action of the medication?
- A. Inhibits squalene epoxidase
- B. Binds to ergosterol, forming destructive pores in cell membrane
- C. Disrupts microtubule function
- D. Inhibits ergosterol synthesis (Correct Answer)
- E. Inhibits formation of beta glucan
Antifungal spectrum of activity Explanation: ***Inhibits ergosterol synthesis***
- The clinical presentation of **nodular lesions** on the hand and forearm in an **ascending manner** after a rose thorn prick is characteristic of **sporotrichosis**, caused by *Sporothrix schenckii*.
- **Itraconazole** is the treatment of choice for sporotrichosis, and it works by **inhibiting ergosterol synthesis** via the inhibition of **lanosterol 14-alpha-demethylase**. Gynecomastia is a known side effect of long-term itraconazole use.
*Inhibits squalene epoxidase*
- This is the mechanism of action of **terbinafine**, another antifungal agent.
- While terbinafine is used for some fungal infections, it is **not the first-line treatment for sporotrichosis** and is not typically associated with gynecomastia as a common side effect.
*Binds to ergosterol, forming destructive pores in cell membrane*
- This describes the mechanism of action of **amphotericin B** and **nystatin**.
- Amphotericin B is used for severe systemic fungal infections, but sporotrichosis typically responds well to oral itraconazole, and amphotericin B is reserved for severe or disseminated cases.
*Disrupts microtubule function*
- This is the mechanism of action of **griseofulvin**, an antifungal agent primarily used for dermatophyte infections of the skin, hair, and nails.
- It is **not effective against *Sporothrix schenckii*** and is not associated with the clinical scenario described.
*Inhibits formation of beta glucan*
- This is the mechanism of action of **echinocandins** (e.g., caspofungin, micafungin, anidulafungin).
- Echinocandins are effective against *Candida* and *Aspergillus* species but have **limited activity against dimorphic fungi** like *Sporothrix schenckii*.
Antifungal spectrum of activity US Medical PG Question 4: A 26-year-old female with AIDS (CD4 count: 47) presents to the emergency department in severe pain. She states that over the past week she has been fatigued and has had a progressively worse headache and fever. These symptoms have failed to remit leading her to seek care in the ED. A lumbar puncture is performed which demonstrates an opening pressure of 285 mm H2O, increased lymphocytes, elevated protein, and decreased glucose. The emergency physician subsequently initiates treatment with IV amphotericin B and PO flucytosine. What additional treatment in the acute setting may be warranted in this patient?
- A. Serial lumbar punctures (Correct Answer)
- B. Fluconazole
- C. Mannitol
- D. Chloramphenicol
- E. Acetazolamide
Antifungal spectrum of activity Explanation: **Serial lumbar punctures**
- The elevated opening pressure (285 mm H2O) indicates **increased intracranial pressure (ICP)**, which is common in cryptococcal meningitis and can be life-threatening.
- Serial lumbar punctures can help to **reduce ICP** and relieve symptoms, improving outcomes in patients with cryptococcal meningitis.
*Fluconazole*
- Fluconazole is used for **maintenance therapy** to prevent relapse after the acute phase of cryptococcal meningitis has been controlled.
- It is generally **not recommended for initial acute treatment** in severe cases due to its fungistatic nature, making it less effective than the combination of amphotericin B and flucytosine.
*Mannitol*
- Mannitol is an **osmotic diuretic** sometimes used to acutely *reduce* ICP in cases of cerebral edema.
- While effective in some situations, it is **not the primary treatment for increased ICP** in cryptococcal meningitis, where repeated LPs are preferred to remove infected CSF and directly reduce pressure.
*Chloramphenicol*
- Chloramphenicol is an **antibiotic** primarily used to treat bacterial infections, not fungal infections.
- It has **no role in the treatment of fungal meningitis** caused by *Cryptococcus neoformans*.
*Acetazolamide*
- Acetazolamide is a **carbonic anhydrase inhibitor** that can reduce CSF production, thereby *reducing* ICP.
- While it can be used in some cases of elevated ICP, routine use in cryptococcal meningitis is **not standard practice**, and serial LPs are generally the preferred method for managing dangerously high ICP in this context due to their immediate efficacy.
Antifungal spectrum of activity US Medical PG Question 5: A 25-year-old man visits a local clinic while volunteering abroad to rebuild homes after a natural disaster. He reports that he has been experiencing an intermittent rash on his feet for several weeks that is associated with occasional itching and burning. He states that he has been working in wet conditions in work boots and often does not get a chance to remove them until just before going to bed. On physical exam, there is diffuse erythema and maceration of the webspaces between his toes. He starts taking a medication. Two days later, he experiences severe nausea and vomiting after drinking alcohol. Which of the following is the mechanism of action of the drug most likely prescribed in this case?
- A. Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
- B. Inhibition of steroid synthesis
- C. Inhibition of DNA synthesis
- D. Cell arrest at metaphase
- E. Disruption of fungal cell membrane
- F. Cell arrest at metaphase (Correct Answer)
Antifungal spectrum of activity Explanation: ***Cell arrest at metaphase***
- The patient's clinical presentation (intermittent rash, itching, burning on feet, erythema and maceration of toe webspaces, prolonged wet conditions in work boots) is characteristic of **tinea pedis** (athlete's foot), a dermatophyte fungal infection.
- The **disulfiram-like reaction** (severe nausea and vomiting after alcohol consumption) is a classic adverse effect of **griseofulvin**, an oral antifungal commonly used for dermatophyte infections including tinea pedis.
- **Griseofulvin's mechanism of action**: Interferes with fungal **microtubule function** by disrupting the mitotic spindle, causing **cell cycle arrest at metaphase** and inhibiting fungal cell division.
- Griseofulvin also disrupts nucleic acid synthesis and inhibits fungal mitosis, making it fungistatic against dermatophytes.
*Disruption of fungal cell membrane*
- This mechanism describes **azole antifungals** (ketoconazole, fluconazole, clotrimazole) which inhibit ergosterol synthesis, and **polyene antifungals** (amphotericin B, nystatin) which bind to ergosterol.
- While azoles can also cause disulfiram-like reactions (particularly ketoconazole), the mechanism of cell arrest at metaphase is more specific to griseofulvin, which is the first-line oral agent for tinea pedis in many cases.
- **Allylamines** (terbinafine) also disrupt the membrane by inhibiting squalene epoxidase but do not cause disulfiram-like reactions.
*Inhibition of steroid synthesis*
- This describes **azole antifungals** that inhibit fungal **ergosterol synthesis** (a steroid component of fungal cell membranes) by blocking 14-α-demethylase.
- While ketoconazole can cause disulfiram-like reactions, the question stem points more specifically to griseofulvin given the classic presentation and reaction pattern.
*Inhibition of DNA synthesis*
- This mechanism describes **flucytosine** (5-FC), a pyrimidine analog that inhibits fungal DNA and RNA synthesis.
- Flucytosine is used primarily for systemic mycoses (Cryptococcus, Candida) in combination with amphotericin B, not for dermatophyte infections like tinea pedis.
- It does not cause disulfiram-like reactions with alcohol.
*Inhibition of cell wall synthesis*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **antibacterial agents** (penicillins, cephalosporins, vancomycin) that target bacterial peptidoglycan cell walls.
- While fungi have cell walls made of chitin and glucans, and **echinocandins** (caspofungin, micafungin) inhibit fungal cell wall synthesis by blocking β-1,3-glucan synthase, these agents are used for invasive candidiasis and aspergillosis, not tinea pedis.
- Echinocandins do not cause disulfiram-like reactions.
Antifungal spectrum of activity US Medical PG Question 6: A 32-year-old woman presents with three-days of vaginal burning, itching, and pain with intercourse. She is in a monogamous relationship with her husband and has an intrauterine device for contraception. Her past medical history is unremarkable, except for recently being treated with antibiotics for sinusitis. Pelvic exam is remarkable for vulvar excoriations, vaginal wall edema, and thick, white discharge in the vault. Wet mount with KOH staining reveals budding filaments with pseudohyphae and hyphae. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment?
- A. Voriconazole
- B. Posaconazole
- C. Metronidazole
- D. Itraconazole
- E. Fluconazole (Correct Answer)
Antifungal spectrum of activity Explanation: ***Fluconazole***
- The patient's symptoms (vaginal burning, itching, pain with intercourse, thick, white discharge) and **wet mount findings (budding filaments with pseudohyphae and hyphae)** are classic for **vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC)**, often precipitated by recent antibiotic use.
- **Fluconazole** is a highly effective and commonly prescribed oral antifungal for uncomplicated VVC due to its convenience and excellent therapeutic profile.
*Voriconazole*
- **Voriconazole** is a broad-spectrum triazole antifungal primarily used for invasive fungal infections, such as **invasive aspergillosis** and candidemia, and is not a first-line treatment for uncomplicated VVC.
- Its use is typically reserved for more severe or refractory systemic fungal infections, and it has a more significant side effect profile than fluconazole.
*Posaconazole*
- **Posaconazole** is another extended-spectrum triazole antifungal primarily used for the prophylaxis and treatment of **invasive fungal infections** in immunocompromised patients, particularly those unresponsive to other antifungals.
- It is not indicated for the treatment of uncomplicated vulvovaginal candidiasis.
*Metronidazole*
- **Metronidazole** is an antibiotic and antiprotozoal agent used to treat bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis, both of which are common causes of vaginitis.
- It is **ineffective against fungal infections**, and the patient's symptoms and wet mount findings rule out bacterial vaginosis and trichomoniasis.
*Itraconazole*
- **Itraconazole** is an antifungal drug effective against superficial and systemic fungal infections, but it is typically used for more severe or recurrent VVC, or in cases of non-albicans Candida species.
- While effective, **fluconazole** is generally preferred as the first-line oral treatment for uncomplicated VVC due to its single-dose efficacy and established safety profile for this indication.
Antifungal spectrum of activity US Medical PG Question 7: A 45-year-old man presents to the emergency department with difficulties swallowing food. He states that he experiences pain when he attempts to swallow his medications or when he drinks water. He reveals that he was diagnosed with HIV infection five years ago. He asserts that he has been taking his antiretroviral regimen, including emtricitabine, rilpivirine, and tenofovir. His temperature is 98°F (37°C), blood pressure is 100/60 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 22/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. His physical exam is notable for a clear oropharynx, no lymphadenopathy, and a normal cardiac and pulmonary exam. No rashes are noted throughout his body. His laboratory results are displayed below:
Hemoglobin: 12 g/dL
Hematocrit: 37 %
Leukocyte count: 8,000/mm^3 with normal differential
Platelet count: 160,000/mm^3
Serum:
Na+: 138 mEq/L
Cl-: 108 mEq/L
K+: 3.5 mEq/L
HCO3-: 26 mEq/L
BUN: 35 mg/dL
Glucose: 108 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.1 mg/dL
CD4+ count: 90/mm^3
HIV viral load: 59,000 copies/mL
What is the best next step in management?
- A. Fluconazole (Correct Answer)
- B. Nystatin
- C. Oral swab and microscopy
- D. Methylprednisolone
- E. Esophageal endoscopy and biopsy
Antifungal spectrum of activity Explanation: ***Fluconazole***
- The patient's **odynophagia**, low **CD4+ count**, and high **HIV viral load** are highly suggestive of **esophageal candidiasis**.
- **Fluconazole** is the initial empiric treatment of choice for suspected esophageal candidiasis in HIV-positive patients, given its high efficacy and good tolerability.
*Nystatin*
- **Nystatin** is typically used for **oral candidiasis (thrush)**, which presents with white plaques in the mouth.
- The patient has a **clear oropharynx** and **odynophagia**, indicating esophageal involvement, for which nystatin is less effective.
*Oral swab and microscopy*
- While an **oral swab** can confirm oral candidiasis, it is not sufficient for diagnosing **esophageal candidiasis**.
- Given the patient's symptoms of odynophagia and high clinical suspicion in an immunocompromised patient, empiric treatment is preferred over initial diagnostic testing for uncomplicated esophageal candidiasis.
*Methylprednisolone*
- **Methylprednisolone** is a corticosteroid used to reduce inflammation and is not indicated for the treatment of **candidal infections**.
- Using corticosteroids in an immunocompromised patient with an active opportunistic infection could worsen his condition.
*Esophageal endoscopy and biopsy*
- **Esophageal endoscopy and biopsy** are typically reserved for patients who **fail empiric antifungal therapy** or present with **atypical symptoms** not consistent with candidiasis.
- Given the clear clinical picture, initial empiric treatment with fluconazole is the standard first step.
Antifungal spectrum of activity US Medical PG Question 8: A 41-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of fatigue, cough, and a 4.5-kg (10-lb) weight loss. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. He appears emaciated. A chest x-ray shows a calcified nodule in the left lower lobe and left hilar lymphadenopathy. The physician initiates therapy for the condition and informs him that he will have to return for monthly ophthalmologic examination for the next 2 months. These examinations are most likely to evaluate the patient for an adverse effect of a drug with which of the following mechanisms of action?
- A. Impaired synthesis of mycolic acids
- B. Impaired protein synthesis due to binding to 50S ribosomes
- C. Impaired production of hemozoin from heme
- D. Impaired synthesis of cell wall polysaccharides (Correct Answer)
- E. Impaired protein synthesis due to binding to 30S ribosomes
Antifungal spectrum of activity Explanation: ***Impaired synthesis of cell wall polysaccharides***
- The patient's clinical presentation (fatigue, cough, weight loss, calcified nodule, hilar lymphadenopathy) is classic for **tuberculosis**.
- The requirement for **monthly ophthalmologic examinations** is pathognomonic for **ethambutol** therapy, as this drug causes **optic neuritis** (decreased visual acuity, red-green color blindness).
- **Ethambutol** inhibits **arabinosyl transferase**, which impairs the synthesis of **arabinogalactan**, a key polysaccharide component of the mycobacterial cell wall.
- Due to the risk of optic neuritis, patients on ethambutol require baseline and monthly ophthalmologic monitoring, especially during the first 2 months of therapy.
*Impaired synthesis of mycolic acids*
- This describes the mechanism of **isoniazid (INH)**, a first-line anti-TB drug that inhibits mycolic acid synthesis.
- The main adverse effects of isoniazid are **peripheral neuropathy** (prevented with pyridoxine/vitamin B6) and **hepatotoxicity**, not optic neuritis.
- Isoniazid does not require routine ophthalmologic monitoring.
*Impaired protein synthesis due to binding to 50S ribosomes*
- This mechanism describes **macrolides** (e.g., clarithromycin, azithromycin) and **chloramphenicol**.
- While macrolides may be used for atypical mycobacterial infections, they are not first-line TB therapy and do not cause optic neuritis requiring monthly eye exams.
*Impaired protein synthesis due to binding to 30S ribosomes*
- This mechanism describes **aminoglycosides** (e.g., streptomycin) and **tetracyclines**.
- While streptomycin is a second-line anti-TB drug, its main adverse effects are **ototoxicity** (hearing loss, vestibular dysfunction) and **nephrotoxicity**, not optic neuritis.
- These drugs do not require ophthalmologic monitoring.
*Impaired production of hemozoin from heme*
- This is the mechanism of **chloroquine** and **hydroxychloroquine**, which are antimalarial drugs.
- While chloroquine can cause retinopathy requiring ophthalmologic monitoring, this patient has **tuberculosis**, not malaria.
- The clinical scenario (calcified lung nodule, hilar lymphadenopathy) and TB treatment context make this mechanism incorrect for this case.
Antifungal spectrum of activity US Medical PG Question 9: A 72-year-old woman with type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician because she is concerned about the appearance of her toenails. Examination shows yellowish discoloration of all toenails on both feet. The edges of the toenails are lifted, and there is subungual debris. Potassium hydroxide preparation of scrapings from the nails shows multiple branching septate hyphae. Treatment with oral terbinafine is begun. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibition of squalene epoxidase (Correct Answer)
- B. Formation of pores in cell membrane
- C. Inhibition of β-glucan synthesis
- D. Interference with mitosis during metaphase
- E. Prevention of lanosterol to ergosterol conversion
Antifungal spectrum of activity Explanation: ***Inhibition of squalene epoxidase***
- **Terbinafine** is an **allylamine** antifungal that inhibits the enzyme **squalene epoxidase**, an early step in fungal ergosterol synthesis
- This inhibition leads to the accumulation of **squalene**, which is toxic to the fungal cell, and a deficiency of **ergosterol**, disrupting cell membrane integrity and function
- Terbinafine is highly effective for **onychomycosis** (fungal nail infections) caused by dermatophytes
*Formation of pores in cell membrane*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **polyene antifungals** like **amphotericin B** and **nystatin**
- These drugs bind to **ergosterol** in the fungal cell membrane, creating pores that lead to leakage of intracellular contents and cell death
*Inhibition of β-glucan synthesis*
- This is the primary mechanism of action for **echinocandin** antifungals, such as **caspofungin**, **micafungin**, and **anidulafungin**
- These drugs inhibit **(1,3)-β-D-glucan synthase**, which is essential for the synthesis of glucan, a major component of the fungal cell wall
*Interference with mitosis during metaphase*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **griseofulvin**, another antifungal agent used for dermatophyte infections
- **Griseofulvin** interferes with **microtubule function**, disrupting mitotic spindle formation and preventing fungal cell division
*Prevention of lanosterol to ergosterol conversion*
- This mechanism is associated with **azole antifungals** (e.g., fluconazole, itraconazole), which inhibit fungal **cytochrome P450-dependent 14-α-demethylase**
- This enzyme is responsible for the conversion of **lanosterol** to **ergosterol**, leading to ergosterol depletion and accumulation of toxic sterol precursors
Antifungal spectrum of activity US Medical PG Question 10: A 46-year-old man with HIV infection comes to the physician because of a 1-week history of severe retrosternal pain while swallowing. He has not been compliant with his antiretroviral drug regimen. His CD4+ T-lymphocyte count is 98/mm3 (N ≥ 500). Endoscopy shows white plaques in the esophagus. The most appropriate immediate treatment is a drug that inhibits which of the following enzymes?
- A. DNA polymerase
- B. Hydrogen-potassium ATPase
- C. Cytochrome p450 enzymes (Correct Answer)
- D. Phospholipase A2
- E. Squalene epoxidase
Antifungal spectrum of activity Explanation: ***Cytochrome P450 enzymes***
- The patient's symptoms (retrosternal pain on swallowing, white plaques on endoscopy) and severely low **CD4+ count (98/mm³)** are highly suggestive of **esophageal candidiasis**, a common opportunistic infection in AIDS.
- **Fluconazole**, an azole antifungal, is the **first-line treatment** for esophageal candidiasis and works by inhibiting **14α-demethylase (lanosterol demethylase)**, a fungal **cytochrome P450 enzyme**.
- This inhibition prevents the conversion of lanosterol to ergosterol, disrupting **fungal cell membrane synthesis** and leading to fungal cell death.
*Squalene epoxidase*
- **Terbinafine** and **naftifine** (allylamine antifungals) inhibit squalene epoxidase in the ergosterol synthesis pathway.
- These agents are primarily used for **dermatophyte infections** (onychomycosis, tinea) and have **poor activity against Candida species**.
- They are not appropriate for treating esophageal candidiasis.
*DNA polymerase*
- Inhibitors of **DNA polymerase**, such as acyclovir or ganciclovir, are used to treat **herpesvirus infections** (HSV, CMV).
- While herpes esophagitis can occur in immunocompromised patients, it typically presents with **punched-out ulcers**, not white plaques.
*Hydrogen-potassium ATPase*
- **Proton pump inhibitors** (PPIs) target hydrogen-potassium ATPase in gastric parietal cells to reduce **acid secretion**.
- These are used to treat **GERD** or **peptic ulcers**, which do not present with white plaques on endoscopy.
- While PPIs may provide symptomatic relief, they do not treat the underlying fungal infection.
*Phospholipase A2*
- Phospholipase A2 inhibitors are used as **anti-inflammatory agents**, as PLA2 releases arachidonic acid, a precursor to inflammatory mediators.
- These drugs have no role in treating fungal infections like esophageal candidiasis.
More Antifungal spectrum of activity US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.
 -D-glucan synthase inhibition in the fungal cell wall)
-D-glucan synthase inhibition in the fungal cell wall)
