Antifungals

On this page
🧬 The Antifungal Arsenal: Your Molecular Weapons Cache
Fungal infections kill more people annually than malaria or tuberculosis, yet they remain medicine's quiet epidemic-often misdiagnosed, inadequately treated, and increasingly resistant to our limited drug arsenal. You'll master the molecular mechanisms that distinguish fungal cells from human ones, learn to recognize clinical patterns from superficial mycoses to life-threatening systemic infections, and develop evidence-based treatment algorithms that account for resistance patterns and patient-specific factors. By integrating pharmacology, microbiology, and clinical reasoning, you'll transform antifungals from a confusing drug class into precision weapons you can deploy confidently across every practice setting.
📌 Remember: FAME-G for antifungal classes - Flucytosine, Azoles, Morpholines, Echinocandins, Griseofulvin. Each targets different fungal vulnerabilities with distinct resistance patterns.
The therapeutic landscape spans from superficial dermatophyte infections requiring weeks of topical therapy to life-threatening invasive mycoses demanding months of systemic treatment. Mortality rates for untreated invasive candidiasis exceed 40%, while invasive aspergillosis approaches 90% without appropriate therapy.
-
Polyenes (Amphotericin B formulations)
- Target: Ergosterol membrane binding
- Spectrum: Broadest antifungal activity (>95% of pathogenic fungi)
- Toxicity: Nephrotoxicity in 80% of patients
- Conventional amphotericin: 25-30% nephrotoxicity
- Lipid formulations: 10-15% nephrotoxicity reduction
-
Azoles (Imidazoles and Triazoles)
- Target: 14α-demethylase enzyme inhibition
- Resistance: 15-20% of Candida species show reduced susceptibility
- Drug interactions: Major CYP450 inhibition affecting >50 medications
- Fluconazole: Moderate CYP2C9/CYP3A4 inhibition
- Voriconazole: Potent CYP2C19/CYP3A4 inhibition
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Voriconazole levels vary 10-fold between patients due to genetic polymorphisms in CYP2C19. Therapeutic drug monitoring is essential-target trough levels 1-5.5 mg/L for efficacy without toxicity.
| Drug Class | Mechanism | Spectrum | Resistance Rate | Key Toxicity | Monitoring Required |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyenes | Membrane pore formation | Universal | <5% | Nephrotoxicity (80%) | Creatinine daily |
| Triazoles | Ergosterol synthesis ↓ | Broad | 15-20% | Hepatotoxicity (25%) | LFTs, drug levels |
| Echinocandins | β-glucan synthesis ↓ | Candida/Aspergillus | 5-10% | Minimal | None routine |
| Flucytosine | DNA/RNA synthesis ↓ | Limited | 20-30% | Bone marrow (15%) | CBC, levels |
| Terbinafine | Squalene epoxidase ↓ | Dermatophytes | <5% | Hepatotoxicity (rare) | LFTs monthly |
The emergence of multidrug-resistant Candida auris represents a paradigm shift in antifungal resistance, with 90% of isolates showing fluconazole resistance and 30% demonstrating echinocandin resistance. This pathogen's ability to persist on surfaces for weeks and spread rapidly through healthcare facilities has elevated antifungal stewardship from optional to essential.
Connect these foundational principles through mechanism-based targeting to understand how molecular precision translates into clinical outcomes.
🧬 The Antifungal Arsenal: Your Molecular Weapons Cache
⚔️ Mechanism Mastery: The Cellular Battlefield
📌 Remember: MEGA-P for antifungal targets - Membrane (polyenes), Ergosterol synthesis (azoles), Glucan synthesis (echinocandins), Antimetabolite (flucytosine), Protein synthesis (some topicals). Each represents a different vulnerability in fungal cellular architecture.
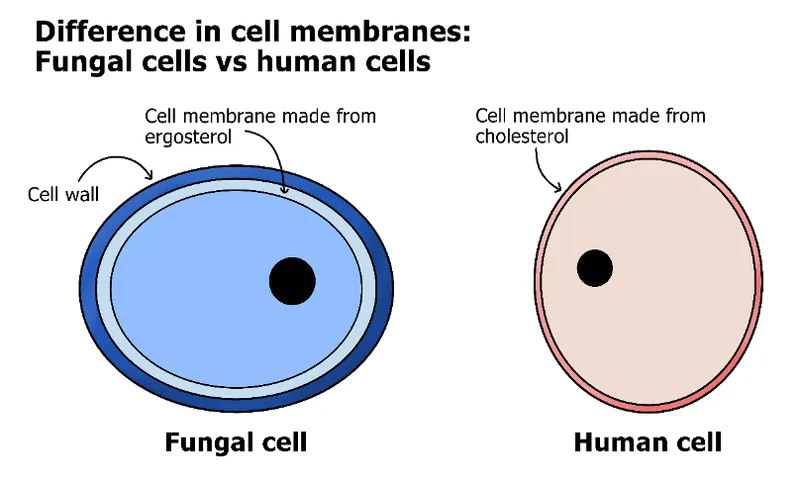
Polyene Mechanism: Membrane Warfare Amphotericin B binds directly to ergosterol in fungal membranes, forming transmembrane pores that allow critical ions and small molecules to leak out. The drug's higher affinity for ergosterol versus cholesterol (10:1 ratio) provides selectivity, though this margin explains the significant toxicity profile.
- Pore Formation Kinetics
- Initial binding: <30 seconds at therapeutic concentrations
- Pore assembly: 8-10 amphotericin molecules per functional pore
- Ion leakage: K+ efflux within 2-5 minutes leads to cell death
- Critical threshold: >50% intracellular K+ loss
- Irreversible damage: >70% membrane disruption
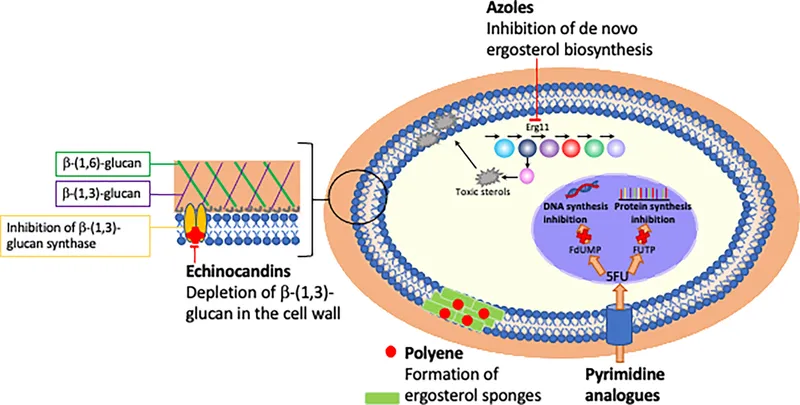
Azole Mechanism: Enzymatic Precision Azoles inhibit 14α-demethylase (CYP51), the rate-limiting enzyme in ergosterol biosynthesis. This creates ergosterol depletion and accumulation of toxic sterol intermediates that disrupt membrane function and cell division.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Azole resistance often involves CYP51 mutations that reduce drug binding affinity by 10-100 fold. Point mutations at positions Y132 and K143 are particularly common in resistant Candida species.
- Enzymatic Inhibition Patterns
- Fluconazole: Competitive inhibition, Ki = 0.1-1 μM
- Voriconazole: Mixed inhibition, Ki = 0.05-0.5 μM
- Itraconazole: Non-competitive inhibition, Ki = 0.01-0.1 μM
- Lower Ki values indicate higher potency
- Resistance emerges when Ki increases >10-fold
| Mechanism | Target | Selectivity Ratio | Time to Effect | Resistance Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyenes | Ergosterol binding | 10:1 vs cholesterol | 2-5 minutes | <5% |
| Azoles | CYP51 enzyme | 100:1 vs human CYP | 4-24 hours | 15-20% |
| Echinocandins | β-glucan synthase | Absent in humans | 1-4 hours | 5-10% |
| Flucytosine | Cytosine deaminase | 100:1 vs human | 12-24 hours | 20-30% |
| Terbinafine | Squalene epoxidase | 1000:1 vs human | 24-48 hours | <5% |
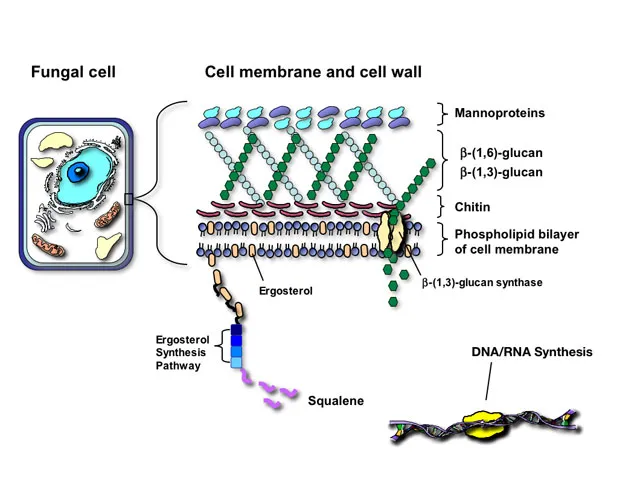
Echinocandin Mechanism: Wall Destruction Echinocandins inhibit β-1,3-glucan synthase, preventing synthesis of the primary structural component of fungal cell walls. Since humans lack cell walls entirely, this mechanism offers exceptional selectivity with minimal toxicity.
The non-competitive inhibition pattern means echinocandins maintain activity even against azole-resistant strains, making them first-line therapy for invasive candidiasis. However, FKS gene mutations encoding glucan synthase can confer resistance, particularly in Candida glabrata.
Connect these molecular mechanisms through resistance pattern analysis to understand how fungi adapt and evolve countermeasures.
⚔️ Mechanism Mastery: The Cellular Battlefield
🎯 Clinical Command Center: Pattern Recognition Mastery
📌 Remember: SCRIPT for antifungal selection - Site of infection, Culture results, Renal function, Immune status, Prior therapy, Toxicity profile. Each factor narrows therapeutic options and guides optimal drug choice.
Pattern 1: Invasive Candidiasis Recognition When you see candidemia in ICU patients, think echinocandin first-line therapy. The 2016 IDSA guidelines recommend echinocandins over fluconazole due to superior outcomes in critically ill patients and coverage of azole-resistant species.
- High-Risk Indicators for Echinocandin Selection
- ICU admission with APACHE II score >15
- Prior azole exposure within 30 days
- Candida glabrata or C. krusei isolation
- Hemodynamic instability requiring vasopressors
- Mortality reduction: 15-20% with echinocandins vs fluconazole
- Time to clearance: 2-3 days faster with echinocandins
Pattern 2: CNS Fungal Infection Approach When you see CNS symptoms with fungal risk factors, think fluconazole or amphotericin for CNS penetration. Most echinocandins have poor CNS penetration (<10% CSF levels), making them inappropriate for meningitis.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Fluconazole achieves 70-80% of serum concentrations in CSF, making it ideal for Cryptococcus maintenance therapy. Voriconazole penetrates CNS well but requires therapeutic drug monitoring due to variable metabolism.
- CNS Penetration Rankings
- Excellent (>50% CSF penetration): Fluconazole, flucytosine
- Good (20-50% CSF penetration): Voriconazole, amphotericin
- Poor (<20% CSF penetration): Itraconazole, echinocandins
- Cryptococcal meningitis: Amphotericin + flucytosine induction
- Candida CNS: Amphotericin or high-dose fluconazole
Pattern 3: Renal Dysfunction Modifications When you see creatinine >2.0 mg/dL, think echinocandin or azole alternatives to amphotericin. Nephrotoxicity occurs in 80% of amphotericin recipients, with 25% developing severe kidney injury.
- Renal-Safe Antifungal Hierarchy
- First choice: Echinocandins (no dose adjustment needed)
- Second choice: Azoles (hepatic metabolism, minimal renal impact)
- Avoid: Conventional amphotericin (unless life-threatening infection)
- Lipid amphotericin formulations: 50% reduction in nephrotoxicity
- Echinocandins: <5% incidence of renal dysfunction
| Clinical Scenario | First-Line Choice | Alternative | Avoid | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICU Candidemia | Echinocandin | Fluconazole | Amphotericin | Resistance coverage |
| CNS Infection | Fluconazole | Amphotericin | Echinocandin | CNS penetration |
| Renal Dysfunction | Echinocandin | Azoles | Amphotericin | Nephrotoxicity |
| Liver Disease | Echinocandin | Amphotericin | Azoles | Hepatotoxicity |
| Neutropenia | Amphotericin | Voriconazole | Fluconazole | Broad spectrum |
Pattern 4: Drug Interaction Alerts When you see patients on warfarin, phenytoin, or cyclosporine, think echinocandin to avoid azole interactions. Azoles inhibit CYP450 enzymes, causing dangerous drug accumulation and toxicity.
- High-Risk Drug Interactions with Azoles
- Warfarin: 2-5 fold INR elevation risk
- Phenytoin: 50% reduction in azole levels
- Cyclosporine: 2-3 fold increase in levels
- Statins: Rhabdomyolysis risk with simvastatin/lovastatin
- Fluconazole: Moderate CYP2C9/CYP3A4 inhibition
- Voriconazole: Potent CYP2C19/CYP3A4 inhibition
Connect these recognition patterns through resistance surveillance to understand how local epidemiology shapes optimal therapy choices.
🎯 Clinical Command Center: Pattern Recognition Mastery
🔬 Resistance Intelligence: The Evolutionary Arms Race
📌 Remember: FARMS for resistance mechanisms - Flux pumps (efflux), Alteration of targets, Reduced uptake, Metabolic bypass, Stress responses. Each represents a different evolutionary strategy fungi use to survive antifungal pressure.
Azole Resistance: The CYP51 Mutations Azole resistance primarily involves point mutations in the CYP51 gene encoding 14α-demethylase. These mutations reduce drug binding affinity while preserving enzyme function, allowing fungi to maintain ergosterol synthesis despite drug presence.
- Critical Resistance Mutations
- Y132F substitution: 10-50 fold fluconazole resistance
- K143R substitution: 5-20 fold pan-azole resistance
- G464S substitution: 100+ fold fluconazole resistance
- ERG11 overexpression: 5-10 fold resistance across azoles
- Candida albicans: 15% clinical isolates show azole resistance
- Candida glabrata: 25% isolates demonstrate reduced susceptibility
Echinocandin Resistance: The FKS Mutations Echinocandin resistance involves FKS gene mutations that alter the β-glucan synthase enzyme structure. These mutations cluster in "hot spot" regions and confer cross-resistance to all echinocandins.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: FKS mutations occur in <5% of Candida species overall, but reach 15% in C. glabrata after echinocandin exposure. Prior echinocandin therapy increases resistance risk 8-fold within 30 days.
- Species-Specific Resistance Patterns
- Candida krusei: Intrinsic fluconazole resistance (>90% of isolates)
- Candida glabrata: Acquired azole resistance (25% of isolates)
- Candida auris: Multidrug resistance (90% azole, 30% echinocandin)
- Aspergillus fumigatus: Triazole resistance (5-10% globally, >20% in Netherlands)
- Environmental azole use in agriculture drives A. fumigatus resistance
- TR34/L98H mutations confer pan-triazole resistance
| Species | Azole Resistance | Echinocandin Resistance | Amphotericin Resistance | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C. albicans | 5-15% | <5% | <1% | Moderate concern |
| C. glabrata | 15-25% | 5-15% | <5% | High concern |
| C. krusei | >90% (intrinsic) | <5% | <5% | Predictable |
| C. auris | 85-95% | 25-35% | 5-15% | Critical threat |
| A. fumigatus | 5-20% | N/A | <5% | Regional variation |
Biofilm-Associated Resistance Fungal biofilms create physical barriers that reduce drug penetration by 100-1000 fold. The extracellular matrix binds antifungals, preventing therapeutic concentrations from reaching embedded organisms.
- Biofilm Resistance Mechanisms
- Matrix binding: 50-90% drug sequestration in biofilm
- Persister cells: 1-5% of cells enter dormant state
- Efflux pump upregulation: 10-100 fold increased expression
- Metabolic changes: Reduced growth decreases drug susceptibility
- Central venous catheters: 80% of candidemia involves biofilm
- Device removal: Essential for biofilm-associated infections
Surveillance and Stewardship Antifungal stewardship programs reduce resistance emergence by 30-50% through optimized drug selection, dosing, and duration. Real-time surveillance identifies resistance trends before they become endemic.
Connect resistance intelligence through combination therapy strategies to understand how drug synergy overcomes individual resistance mechanisms.
🔬 Resistance Intelligence: The Evolutionary Arms Race
⚖️ Therapeutic Precision: Evidence-Based Treatment Algorithms
📌 Remember: OPTIMAL for treatment selection - Organism identification, Patient stability, Tissue penetration, Immune status, Monitoring requirements, Adverse effects, Length of therapy. Each factor influences drug choice and dosing strategy.
Invasive Candidiasis: The Echinocandin Era The 2016 IDSA guidelines established echinocandins as first-line therapy for invasive candidiasis in non-neutropenic patients. This recommendation reflects superior outcomes in critically ill patients and excellent coverage of azole-resistant species.
- Echinocandin Selection Criteria
- ICU patients: Caspofungin 70mg loading, then 50mg daily
- Azole-resistant risk: Prior azole exposure within 30 days
- Severe illness: APACHE II >15 or vasopressor requirement
- Species coverage: C. glabrata, C. krusei intrinsic resistance
- Mortality benefit: 15% reduction vs fluconazole in ICU patients
- Time to clearance: 1-2 days faster than azoles
Step-Down Therapy Protocol Transition from echinocandin to fluconazole when clinical stability achieved and susceptibility confirmed. This approach reduces costs by 60-70% while maintaining efficacy.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: De-escalation criteria include hemodynamic stability for 48 hours, negative blood cultures, and fluconazole MIC ≤2 mg/L. Continue echinocandin for C. glabrata or C. krusei regardless of clinical improvement.
- Fluconazole Transition Guidelines
- Clinical stability: No vasopressors for 48 hours
- Microbiological clearance: Negative cultures × 2
- Susceptibility confirmed: MIC ≤2 mg/L for fluconazole
- Species appropriate: Not C. glabrata or C. krusei
- Cost savings: $200-400 per day with fluconazole step-down
- Equivalent outcomes: No mortality difference when criteria met
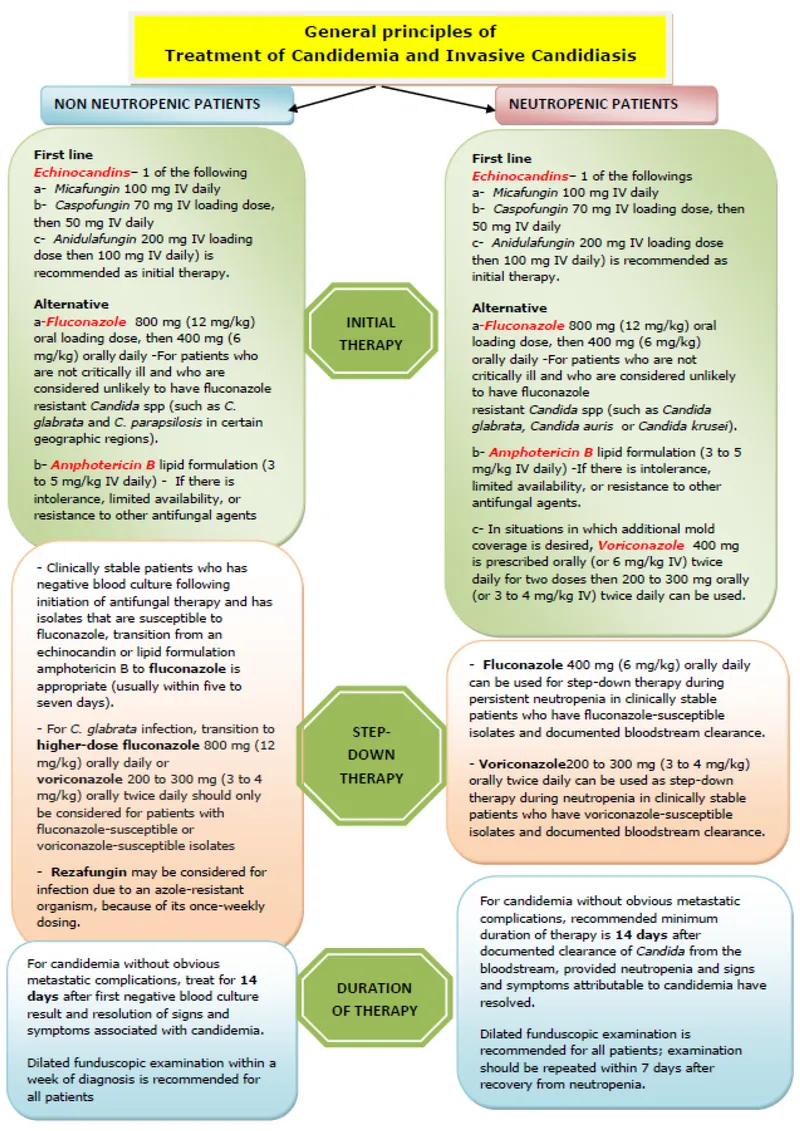
Invasive Aspergillosis: Voriconazole Supremacy Voriconazole remains first-line therapy for invasive aspergillosis based on superior survival compared to amphotericin B. The AspICU study demonstrated 20% mortality reduction with voriconazole in ICU patients.
- Voriconazole Dosing Protocol
- Loading dose: 6 mg/kg IV every 12 hours × 2 doses
- Maintenance: 4 mg/kg IV every 12 hours
- Oral transition: 200-300 mg every 12 hours
- TDM target: Trough 1-5.5 mg/L for efficacy without toxicity
- Genetic polymorphisms: CYP2C19 variants affect metabolism
- Poor metabolizers: 10-fold higher drug levels
| Indication | First-Line Therapy | Alternative | Duration | Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Invasive Candidiasis | Echinocandin | Fluconazole | 14 days post-clearance | Daily CBC, BMP |
| Invasive Aspergillosis | Voriconazole | Amphotericin | 6-12 weeks | TDM, LFTs weekly |
| Cryptococcal Meningitis | AmB + Flucytosine | Fluconazole | 10 weeks total | Creatinine, CBC |
| Mucormycosis | Amphotericin | Posaconazole | Until resolution | Creatinine daily |
| Empirical Therapy | Echinocandin | Amphotericin | Until pathogen ID | Organ function |
Combination Therapy Strategies Combination antifungal therapy shows synergistic effects in specific scenarios, particularly salvage therapy for resistant organisms or severe infections with high mortality risk.
- Evidence-Based Combinations
- Amphotericin + flucytosine: Cryptococcal meningitis induction
- Voriconazole + echinocandin: Salvage aspergillosis therapy
- Amphotericin + azole: Mucormycosis combination therapy
- Echinocandin + azole: Resistant Candida infections
- Synergy mechanisms: Different targets prevent resistance
- Mortality benefit: 10-15% in salvage scenarios
Duration and Monitoring Protocols Treatment duration depends on infection site, immune status, and clinical response. Premature discontinuation increases relapse rates by 30-50%, while prolonged therapy increases resistance risk.
Connect therapeutic precision through advanced monitoring strategies to understand how real-time adjustments optimize outcomes.
⚖️ Therapeutic Precision: Evidence-Based Treatment Algorithms
🔗 Integration Nexus: Multi-System Antifungal Mastery
📌 Remember: SYSTEMS for integrated antifungal care - Susceptibility testing, Yield optimization, Synergy evaluation, TDM protocols, End-organ protection, Monitoring strategies, Stewardship principles. Each component contributes to therapeutic success.
Pharmacogenomic Integration Genetic polymorphisms in CYP450 enzymes create 10-100 fold variations in antifungal metabolism between patients. CYP2C19 genotyping for voriconazole therapy enables personalized dosing that improves efficacy while reducing toxicity.
- CYP2C19 Phenotype Impact on Voriconazole
- Extensive metabolizers (70% population): Standard dosing appropriate
- Intermediate metabolizers (20% population): 25% dose reduction needed
- Poor metabolizers (5% population): 50% dose reduction required
- Ultra-rapid metabolizers (5% population): Higher doses or alternative drug
- Therapeutic failure: 40% in ultra-rapid metabolizers with standard dosing
- Toxicity risk: 60% in poor metabolizers without dose adjustment
Biomarker-Guided Therapy β-D-glucan and galactomannan levels guide treatment decisions and monitor therapeutic response. Serial measurements predict treatment success 5-7 days before clinical improvement becomes apparent.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: β-D-glucan levels >80 pg/mL suggest invasive fungal infection with 85% sensitivity. Declining levels during therapy predict successful treatment, while rising levels indicate treatment failure or resistance.
- Biomarker Monitoring Protocols
- β-D-glucan: Weekly monitoring during therapy
- Galactomannan: Twice weekly for aspergillosis
- Cryptococcal antigen: Monthly for CNS infections
- Candida mannan: Adjunctive for candidemia diagnosis
- Therapeutic response: 50% decline in biomarkers within 2 weeks
- Treatment failure: Rising levels despite appropriate therapy
Immune Reconstitution Considerations Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) occurs in 10-25% of patients with recovering immune function during antifungal therapy. This paradoxical worsening requires anti-inflammatory therapy rather than antifungal intensification.
- IRIS Risk Factors and Management
- High-risk populations: HIV patients starting ART, neutropenia recovery
- Timing: 2-8 weeks after immune recovery begins
- Clinical presentation: Worsening symptoms despite microbiological improvement
- Management: Corticosteroids plus continued antifungal therapy
- Incidence: 25% in cryptococcal meningitis with ART initiation
- Mortality impact: 15% increase if IRIS not recognized
Organ-Specific Optimization Different anatomical sites require tailored approaches based on drug penetration, local immune function, and anatomical barriers. CNS infections demand drugs with excellent blood-brain barrier penetration, while endocarditis requires prolonged therapy with fungicidal agents.
| Infection Site | Preferred Agent | Penetration | Duration | Special Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNS | Fluconazole | 70-80% CSF | 10-12 weeks | High-dose for Candida |
| Endocarditis | Amphotericin | Variable | 6+ weeks | Valve replacement often needed |
| Osteoarticular | Fluconazole | Good bone | 6-12 months | Surgical debridement |
| Intra-abdominal | Echinocandin | Excellent | 2-4 weeks | Source control essential |
| Urinary | Fluconazole | 90% urine | 2 weeks | Amphotericin for resistant |
Antifungal Stewardship Integration Prospective audit and feedback programs reduce inappropriate antifungal use by 40-60% while improving outcomes. Real-time decision support systems integrate resistance data, patient factors, and guidelines to optimize therapy selection.
- Stewardship Program Components
- Prospective review: 48-72 hour therapy evaluation
- Biomarker integration: β-D-glucan to guide empirical therapy
- Resistance surveillance: Monthly antibiograms by unit
- Education programs: Quarterly updates on resistance trends
- Cost reduction: 30-50% decrease in antifungal expenditure
- Outcome improvement: 20% reduction in treatment failures
Emerging Therapeutic Strategies Immunomodulatory therapy combined with antifungals shows promise for severe infections in immunocompromised hosts. Interferon-γ and granulocyte transfusions enhance host defenses while antifungals control pathogen burden.
Connect integration principles through rapid reference frameworks to create practical tools for immediate clinical application.
🔗 Integration Nexus: Multi-System Antifungal Mastery
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Your Rapid-Fire Reference
📌 Remember: RAPID for emergency antifungal decisions - Resistance patterns, Allergies/interactions, Penetration requirements, Immune status, Dose adjustments. These five factors determine optimal therapy in <2 minutes.
Essential Antifungal Arsenal
- First-Line Choices by Indication
- ICU Candidemia: Caspofungin 70mg → 50mg daily
- CNS Cryptococcus: AmB 0.7mg/kg + Flucytosine 25mg/kg q6h
- Invasive Aspergillosis: Voriconazole 6mg/kg q12h × 2, then 4mg/kg q12h
- Neutropenic Fever: Caspofungin 70mg → 50mg daily
- Mortality reduction: 15-25% with appropriate first-line therapy
- Time to response: 3-5 days faster with optimal selection
⭐ Clinical Pearl: "The 48-hour rule" - If no clinical improvement within 48 hours of appropriate antifungal therapy, consider resistance testing, combination therapy, or surgical intervention. Delayed response increases mortality by 10% per day.
Critical Drug Levels and Thresholds
- Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Targets
- Voriconazole trough: 1-5.5 mg/L (efficacy without toxicity)
- Flucytosine level: 25-100 mg/L (avoid bone marrow toxicity)
- Itraconazole trough: >0.5 mg/L for systemic infections
- Posaconazole trough: >1.0 mg/L for prophylaxis, >1.25 mg/L for treatment
- Sub-therapeutic levels: 40% treatment failure rate
- Supra-therapeutic levels: 60% toxicity incidence
💡 Master This: Voriconazole levels >5.5 mg/L cause hepatotoxicity and visual disturbances in >50% of patients. Levels <1.0 mg/L result in treatment failure in >40% of invasive aspergillosis cases.
| Clinical Scenario | Drug of Choice | Dose | Duration | Key Monitoring |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICU Candidemia | Caspofungin | 70mg → 50mg daily | 14d post-clearance | CBC, LFTs |
| Azole-Resistant Candida | Amphotericin B | 0.6-1.0 mg/kg daily | Until susceptible | Creatinine, K+, Mg+ |
| CNS Aspergillosis | Voriconazole | 6mg/kg q12h × 2 → 4mg/kg q12h | 12+ weeks | TDM, LFTs |
| Mucormycosis | Amphotericin B | 1.0-1.5 mg/kg daily | Until resolution | Creatinine daily |
| Empirical Neutropenia | Caspofungin | 70mg → 50mg daily | Until ANC >500 | CBC, fungal markers |
- Red Flag Resistance Patterns
- C. krusei: Always fluconazole-resistant (intrinsic)
- C. auris: 90% azole-resistant, 30% echinocandin-resistant
- A. fumigatus: TR34/L98H = pan-triazole resistance
- Prior azole exposure: 8-fold increased resistance risk
- Breakthrough infections: >80% resistance likelihood
- Geographic hotspots: Netherlands (20% A. fumigatus resistance)
Emergency Antifungal Protocols
- Severe Sepsis with Fungal Risk
- Immediate: Caspofungin 70mg IV within 1 hour
- Blood cultures: 2 sets before antifungal administration
- Biomarkers: β-D-glucan, galactomannan if available
- Source control: Remove catheters within 24 hours
- Mortality benefit: 20% reduction with early appropriate therapy
- Golden hour: Each hour delay increases mortality 6%
⭐ Clinical Pearl: "Source control saves lives" - Central line removal within 24 hours reduces candidemia mortality by 25%. Surgical debridement is essential for osteoarticular and deep tissue infections.
Toxicity Management Quick Reference
- Amphotericin Nephrotoxicity Prevention
- Pre-hydration: 500mL NS before each dose
- Electrolyte monitoring: Daily K+, Mg+, creatinine
- Dose adjustment: Hold if creatinine doubles
- Lipid formulations: 50% nephrotoxicity reduction
- Risk factors: Age >65, baseline CKD, concurrent nephrotoxins
- Recovery: 80% of patients recover baseline function
This arsenal provides the foundation for expert-level antifungal decision-making across all clinical scenarios, from routine infections to life-threatening emergencies.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Your Rapid-Fire Reference
Practice Questions: Antifungals
Test your understanding with these related questions
You are taking care of a patient with renal failure secondary to anti-fungal therapy. The patient is a 66-year-old male being treated for cryptococcal meningitis. This drug has a variety of known side effects including acute febrile reactions to infusions, anemia, hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. What is the mechanism of action of this drug?













