Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines US Medical PG Question 1: An 8-year-old girl is brought to the emergency room for a 6-hour history of fever, sore throat, and difficulty swallowing. Physical examination shows pooling of oral secretions and inspiratory stridor. Lateral x-ray of the neck shows thickening of the epiglottis and aryepiglottic folds. Throat culture with chocolate agar shows small, gram-negative coccobacilli. The patient's brother is started on the recommended antibiotic for chemoprophylaxis. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibition of the 50S ribosomal subunit
- B. Inhibition of prokaryotic topoisomerase II
- C. Inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase (Correct Answer)
- D. Inhibition of the 30S ribosomal subunit
- E. Inhibition of peptidoglycan crosslinking
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines Explanation: ***Inhibition of DNA-dependent RNA-polymerase***
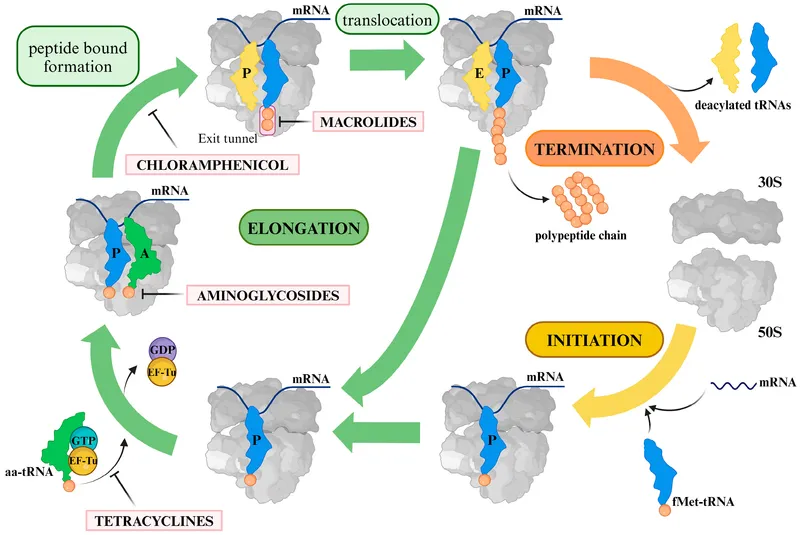
- The clinical picture strongly suggests **epiglottitis** caused by *Haemophilus influenzae type b* (Hib), characterized by **fever, sore throat, difficulty swallowing, pooling of oral secretions, inspiratory stridor**, and **epiglottic thickening** on X-ray.
- **Rifampin** is the recommended antibiotic for chemoprophylaxis in close contacts of Hib patients; its primary mechanism of action is to inhibit bacterial **DNA-dependent RNA polymerase**, thereby preventing **mRNA synthesis**.
*Inhibition of the 50S ribosomal subunit*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **macrolides** (e.g., azithromycin, erythromycin) and **clindamycin**, which are not the primary choice for Hib chemoprophylaxis.
- These drugs prevent **protein synthesis** by interfering with translocation or peptide bond formation on the larger ribosomal subunit.
*Inhibition of prokaryotic topoisomerase II*
- This is the mechanism of action for **fluoroquinolones** (e.g., ciprofloxacin), which are typically reserved for specific infections due to potential side effects in children.
- Fluoroquinolones interfere with **DNA replication** and **transcription** by preventing DNA unwinding and supercoiling.
*Inhibition of the 30S ribosomal subunit*
- This mechanism is associated with **tetracyclines** and **aminoglycosides** (e.g., doxycycline, gentamicin).
- These antibiotics block **protein synthesis** by preventing tRNA attachment or causing misreading of mRNA.
*Inhibition of peptidoglycan crosslinking*
- This describes the mechanism of **beta-lactam antibiotics** (e.g., penicillin, amoxicillin, cephalosporins), which inhibit bacterial **cell wall synthesis**.
- While some beta-lactams are used to treat Hib infections, they are not the primary drug for **chemoprophylaxis**.
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines US Medical PG Question 2: A 37-year-old woman with a history of anorectal abscesses complains of pain in the perianal region. Physical examination reveals mild swelling, tenderness, and erythema of the perianal skin. She is prescribed oral ampicillin and asked to return for follow-up. Two days later, the patient presents with a high-grade fever, syncope, and increased swelling. Which of the following would be the most common mechanism of resistance leading to the failure of antibiotic therapy in this patient?
- A. Intrinsic absence of a target site for the drug
- B. Use of an altered metabolic pathway
- C. Production of beta-lactamase enzyme (Correct Answer)
- D. Altered structural target for the drug
- E. Drug efflux pump
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines Explanation: ***Production of beta-lactamase enzyme***
- The patient's symptoms of a rapidly worsening infection despite ampicillin treatment suggest the presence of a **beta-lactamase producing organism**. Ampicillin is a **beta-lactam antibiotic** that is inactivated by these enzymes.
- Anorectal abscesses and rapidly progressing soft tissue infections are often caused by **polymicrobial flora**, including staphylococci and enterococci, many of which can produce **beta-lactamase**.
*Intrinsic absence of a target site for the drug*
- While some bacteria inherently lack the target site for certain drugs (e.g., mycoplasma lacking a cell wall, thus being resistant to beta-lactams), this is less likely to be the **most common mechanism of acquired resistance** leading to treatment failure in a typical perianal infection.
- The rapid progression and failed initial treatment point towards an **acquired mechanism of resistance** rather than an intrinsic one.
*Use of an altered metabolic pathway*
- This mechanism, such as altered **folate synthesis pathways** in resistance to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, is less common as the primary mechanism for ampicillin resistance.
- Ampicillin's mechanism of action primarily targets the **bacterial cell wall**, not a metabolic pathway in the same way.
*Altered structural target for the drug*
- This involves modifications to the **penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs)**, which are the targets of beta-lactam antibiotics like ampicillin. While a valid mechanism (e.g., in MRSA), the **production of beta-lactamase** is generally a more widespread and common cause of ampicillin failure, especially in infections involving mixed flora from the perianal region.
- Given the abrupt failure of ampicillin, **beta-lactamase inactivation** is a more immediate and common cause than a rapid mutational change in PBPs.
*Drug efflux pump*
- **Efflux pumps** actively remove antibiotics from the bacterial cell, contributing to resistance against various drug classes.
- While efflux pumps can play a role, the dominant mechanism for resistance to **ampicillin** in many common perianal pathogens is the **enzymatic degradation by beta-lactamases**.
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines US Medical PG Question 3: A 39-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with a high fever, cough, and malaise. One week ago, he returned from a vacation to Hawaii where he went waterskiing with his family. Three days before presentation, he started experiencing intermittent abdominal pain, which was followed by flu-like symptoms, itchiness in his eyes, and photosensitivity. On presentation, his temperature is 103°F (39.4°C), blood pressure is 114/72 mmHg, pulse is 105/min, and respirations are 18/min. Physical exam reveals conjunctivitis and mild jaundice. Which of the following treatments could be used to treat this patient's condition?
- A. Ganciclovir
- B. Metronidazole
- C. Doxycycline (Correct Answer)
- D. Vancomycin
- E. Azithromycin
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines Explanation: ***Doxycycline***
- The patient's symptoms (fever, cough, malaise, abdominal pain, **conjunctival suffusion** presenting as conjunctivitis, jaundice) after waterskiing in Hawaii are highly suggestive of **leptospirosis**, an infection caused by *Leptospira* bacteria.
- **Doxycycline** is the recommended treatment for mild to moderate leptospirosis, while severe cases (Weil's disease with jaundice) may require intravenous penicillin G or ceftriaxone.
- The biphasic illness pattern and water exposure history are classic features of this spirochete infection.
*Ganciclovir*
- **Ganciclovir** is an antiviral medication primarily used to treat **cytomegalovirus (CMV)** infections, especially in immunocompromised patients.
- The clinical picture presented does not align with typical CMV infection, which is often asymptomatic or causes mono-like symptoms without the water exposure history.
*Metronidazole*
- **Metronidazole** is an antibiotic effective against **anaerobic bacteria** and certain parasites (e.g., *Giardia*, *Trichomonas*).
- It is not indicated for the treatment of leptospirosis, which is caused by a spirochete requiring tetracyclines or beta-lactams.
*Vancomycin*
- **Vancomycin** is an antibiotic used for treating serious infections caused by **Gram-positive bacteria**, particularly **methicillin-resistant *Staphylococcus aureus* (MRSA)** or *Clostridioides difficile*.
- It is not effective against *Leptospira* species, which are spirochetes.
*Azithromycin*
- **Azithromycin** is a macrolide antibiotic effective against a range of bacterial infections, including **atypical pneumonia** and some sexually transmitted infections.
- While azithromycin has some activity against leptospirosis, **doxycycline** or penicillin-based antibiotics are strongly preferred as first-line treatment with better evidence base.
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines US Medical PG Question 4: A 42-year-old woman with a history of multiple sclerosis and recurrent urinary tract infections comes to the emergency department because of flank pain and fever. Her temperature is 38.8°C (101.8°F). Examination shows left-sided costovertebral angle tenderness. She is admitted to the hospital and started on intravenous vancomycin. Three days later, her symptoms have not improved. Urine culture shows growth of Enterococcus faecalis. Which of the following best describes the most likely mechanism of antibiotic resistance in this patient?
- A. Increased efflux across bacterial cell membranes
- B. Production of beta-lactamase
- C. Alteration of penicillin-binding proteins
- D. Alteration of peptidoglycan synthesis (Correct Answer)
- E. Alteration of ribosomal targets
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines Explanation: ***Alteration of peptidoglycan synthesis***
- **Vancomycin** targets the **D-Ala-D-Ala terminus** on the peptidoglycan precursor, preventing cross-linking during bacterial cell wall synthesis.
- **Vancomycin resistance in Enterococcus faecalis** occurs through acquisition of resistance genes (vanA, vanB) that encode enzymes modifying the peptidoglycan precursor from **D-Ala-D-Ala to D-Ala-D-Lac**.
- This structural change reduces vancomycin's binding affinity by approximately 1000-fold, rendering the antibiotic ineffective.
- The mechanism directly involves **alteration of the peptidoglycan synthesis pathway**, specifically the terminal amino acid residues of the pentapeptide precursor.
*Increased efflux across bacterial cell membranes*
- This mechanism involves **efflux pumps that actively transport antibiotics out of the bacterial cell**, reducing intracellular concentration.
- While efflux pumps contribute to resistance for antibiotics like **tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones, and macrolides**, this is not the primary mechanism of vancomycin resistance in Enterococcus.
*Production of beta-lactamase*
- **Beta-lactamase enzymes** hydrolyze the **beta-lactam ring** of antibiotics like **penicillins and cephalosporins**, rendering them inactive.
- **Vancomycin is a glycopeptide antibiotic, not a beta-lactam**, so its efficacy is not affected by beta-lactamase production.
*Alteration of ribosomal targets*
- This mechanism confers resistance to antibiotics that target **bacterial ribosomes** to inhibit protein synthesis, such as **macrolides, aminoglycosides, and tetracyclines**.
- **Vancomycin acts on cell wall synthesis**, not protein synthesis, so alteration of ribosomal targets is not relevant to vancomycin resistance.
*Alteration of penicillin-binding proteins*
- **Penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs)** are the targets of **beta-lactam antibiotics** (penicillins, cephalosporins, carbapenems).
- Alterations in PBPs cause resistance to beta-lactams, not to vancomycin.
- **Vancomycin does not interact with PBPs**; it binds directly to the D-Ala-D-Ala terminus of peptidoglycan precursors in the cell wall.
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines US Medical PG Question 5: An investigator is studying the chemical structure of antibiotics and its effect on bacterial growth. He has synthesized a simple beta-lactam antibiotic and has added a bulky side chain to the molecule that inhibits the access of bacterial enzymes to the beta-lactam ring. The synthesized drug will most likely be appropriate for the treatment of which of the following conditions?
- A. Folliculitis (Correct Answer)
- B. Nocardiosis
- C. Atypical pneumonia
- D. Erythema migrans
- E. Otitis media
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines Explanation: ***Folliculitis***
- The bulky side chain provides **steric hindrance** that prevents **staphylococcal beta-lactamases** from accessing and degrading the **beta-lactam ring**.
- This modification creates an **anti-staphylococcal penicillin** (similar to methicillin, nafcillin, or oxacillin), which is effective against **methicillin-sensitive *Staphylococcus aureus* (MSSA)**.
- **Folliculitis** is most commonly caused by *S. aureus*, making this modified beta-lactam an appropriate treatment choice for MSSA-related folliculitis.
- The bulky side chain specifically protects against the **penicillinase** (beta-lactamase) produced by staphylococci.
*Otitis media*
- Otitis media is commonly caused by beta-lactamase-producing organisms like *Haemophilus influenzae* and *Moraxella catarrhalis*.
- However, the beta-lactamases produced by these gram-negative organisms are **not inhibited by bulky side chains** alone.
- Treatment of beta-lactamase-producing *H. influenzae* and *M. catarrhalis* requires **beta-lactamase inhibitors** (such as clavulanic acid combined with amoxicillin), not steric hindrance.
- The mechanism of protection differs: beta-lactamase inhibitors **suicide inhibitors** that bind to the enzyme, whereas bulky side chains provide **physical blocking**.
*Nocardiosis*
- Nocardiosis is caused by *Nocardia* species, which are **aerobic actinomycetes**.
- These bacteria are typically treated with **sulfonamides** (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole) for prolonged periods.
- Beta-lactam antibiotics are generally not first-line treatment, as *Nocardia* species often show intrinsic resistance or require specific antibiotic combinations.
*Atypical pneumonia*
- Atypical pneumonia is caused by organisms like *Mycoplasma pneumoniae*, *Chlamydophila pneumoniae*, and *Legionella pneumophila*.
- These organisms lack a **peptidoglycan cell wall**, which is the target of all **beta-lactam antibiotics**.
- Beta-lactams (regardless of modifications) are completely ineffective against atypical pneumonia pathogens.
- Treatment requires **macrolides** (azithromycin), **tetracyclines** (doxycycline), or **fluoroquinolones**.
*Erythema migrans*
- Erythema migrans is the characteristic rash of early **Lyme disease**, caused by *Borrelia burgdorferi*.
- While *Borrelia* is sensitive to certain beta-lactam antibiotics (amoxicillin, ceftriaxone), it does **not produce beta-lactamases**.
- The bulky side chain modification is unnecessary for treating *Borreria* infections, as there is no beta-lactamase to protect against.
- Standard treatment uses doxycycline, amoxicillin, or ceftriaxone—not anti-staphylococcal penicillins.
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines US Medical PG Question 6: An 18-year old college freshman presents to his university clinic because he has not been feeling well for the past two weeks. He has had a persistent headache, occasional cough, and chills without rigors. The patient’s vital signs are normal and physical exam is unremarkable. His radiograph shows patchy interstitial lung infiltrates and he is diagnosed with atypical pneumonia. The patient is prescribed azithromycin and takes his medication as instructed. Despite adherence to his drug regimen, he returns to the clinic one week later because his symptoms have not improved. The organism responsible for this infection is likely resistant to azithromycin through which mechanism?
- A. Mutation in topoisomerase II
- B. Methylation of ribosomal binding site
- C. Presence of a beta-lactamase
- D. Decreased binding to RNA polymerase
- E. Insertion of drug efflux pumps (Correct Answer)
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines Explanation: ***Insertion of drug efflux pumps***
- **Azithromycin** is a macrolide antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis by binding to the **50S ribosomal subunit**.
- In **Mycoplasma pneumoniae** (the most common cause of atypical pneumonia in young adults), the **most common** mechanism of macrolide resistance is through **efflux pumps**, particularly the **mef genes**.
- These efflux pumps actively transport macrolides out of the bacterial cell, reducing intracellular drug concentration and conferring resistance.
- This mechanism is responsible for the majority of macrolide-resistant *M. pneumoniae* isolates worldwide.
*Methylation of ribosomal binding site*
- **Methylation** of the ribosomal binding site (specifically the **23S rRNA** via erm genes) does prevent azithromycin from binding effectively.
- While this is a valid macrolide resistance mechanism seen in organisms like *Streptococcus pneumoniae* and *Streptococcus pyogenes*, it is **less common** in *Mycoplasma pneumoniae*.
- Efflux pumps (mef) are the predominant mechanism in *M. pneumoniae* resistant strains.
*Mutation in topoisomerase II*
- **Topoisomerase II** (DNA gyrase) is the target of **fluoroquinolone antibiotics**, not macrolides.
- Mutations in this enzyme lead to resistance against fluoroquinolones, such as **ciprofloxacin**.
*Presence of a beta-lactamase*
- **Beta-lactamase enzymes** inactivate **beta-lactam antibiotics** (e.g., penicillin, cephalosporins) by hydrolyzing their beta-lactam ring.
- Additionally, *Mycoplasma pneumoniae* **lacks a cell wall**, making it inherently resistant to all beta-lactam antibiotics regardless of beta-lactamase production.
*Decreased binding to RNA polymerase*
- **RNA polymerase** is the target for antibiotics like **rifampin**, which inhibits bacterial transcription.
- Decreased binding to RNA polymerase would lead to rifampin resistance, not azithromycin resistance.
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines US Medical PG Question 7: An experimental drug, ES 62, is being studied. It prohibits the growth of vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. It is highly lipid-soluble. The experimental design is dependent on a certain plasma concentration of the drug. The target plasma concentration is 100 mmol/dL. Which of the following factors is most important for calculating the appropriate loading dose?
- A. Volume of distribution (Correct Answer)
- B. Half-life of the drug
- C. Therapeutic index
- D. Clearance of the drug
- E. Rate of administration
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines Explanation: **Volume of distribution**
- The **loading dose** is primarily determined by the desired **plasma concentration** and the **volume of distribution (Vd)**, as it reflects how extensively a drug is distributed in the body.
- The formula for loading dose is: Loading Dose = (Target Plasma Concentration × Vd).
*Half-life of the drug*
- The **half-life** is crucial for determining the **dosing interval** and the time it takes to reach **steady-state concentrations**, not the initial loading dose.
- It reflects the rate at which the drug is eliminated from the body.
*Therapeutic index*
- The **therapeutic index** is a measure of a drug's relative safety, indicating the ratio between the **toxic dose** and the **effective dose**.
- While important for drug safety, it does not directly determine the magnitude of the loading dose itself.
*Clearance of the drug*
- **Clearance** is the rate at which the drug is removed from the body and is a primary determinant of the **maintenance dose** required to sustain a desired plasma concentration.
- It does not directly calculate the initial loading dose needed to achieve an immediate target concentration.
*Rate of administration*
- The **rate of administration** (e.g., infusion rate) primarily influences how quickly the drug reaches its target concentration, but not the total quantity of drug needed for the initial loading dose.
- It affects the kinetics of how the loading dose achieves the target concentration, rather than defining the dose amount.
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines US Medical PG Question 8: A 30-year-old female with a history of epilepsy becomes pregnant. Her epilepsy has been well controlled by taking a medication that inhibits GABA transaminase and blocks voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels. Her obstetrician informs her that her epilepsy medication has been shown to have teratogenic effects. Of the following, which teratogenic effect is this woman's medication most likely to cause?
- A. Limb defects
- B. Neural tube defect (Correct Answer)
- C. Renal damage
- D. Ebstein's anomaly
- E. Discolored teeth
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines Explanation: ***Neural tube defect***
- The medication described, which **inhibits GABA transaminase** and has multiple mechanisms including effects on voltage-gated channels, is **valproic acid** (valproate).
- **Valproic acid** is the antiepileptic drug with the **highest risk of neural tube defects** (e.g., spina bifida), with an incidence of approximately 1-2% when taken during pregnancy.
- This teratogenic effect occurs primarily during the first trimester and is believed to be due to interference with **folate metabolism** and **histone deacetylase inhibition**, which are crucial for proper neural tube closure.
- Folic acid supplementation is recommended for women of childbearing age taking valproate.
*Limb defects*
- **Limb defects** (e.g., phocomelia, limb reduction defects) are classically associated with **thalidomide** exposure during early pregnancy.
- While **phenytoin** (fetal hydantoin syndrome) can cause limb abnormalities including hypoplastic nails and distal phalanges, this is not the primary teratogenic concern with valproic acid.
*Renal damage*
- **Fetal renal damage** can be caused by medications such as **ACE inhibitors**, **ARBs**, and **NSAIDs** when taken during pregnancy.
- This is not a characteristic teratogenic effect of valproic acid or other antiepileptic medications.
*Ebstein's anomaly*
- **Ebstein's anomaly**, a congenital heart defect characterized by apical displacement of the tricuspid valve, is most notably associated with **lithium exposure** during the first trimester of pregnancy.
- This cardiac anomaly is not typically linked to valproic acid or other anticonvulsant medications.
*Discolored teeth*
- **Discolored teeth** (yellow-brown staining) and enamel hypoplasia are classic adverse effects of **tetracycline antibiotics** when administered during pregnancy (second and third trimesters) or early childhood.
- This effect is not associated with antiepileptic medications.
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines US Medical PG Question 9: A 3-year-old girl is brought to the physician for a well-child visit. Her father is concerned about the color and strength of her teeth. He says that most of her teeth have had stains since the time that they erupted. She also has a limp when she walks. Examination shows brownish-gray discoloration of the teeth. She has lower limb length discrepancy; her left knee-to-ankle length is 4 cm shorter than the right. Which of the following drugs is most likely to have been taken by this child's mother when she was pregnant?
- A. Tetracycline (Correct Answer)
- B. Gentamicin
- C. Ciprofloxacin
- D. Trimethoprim
- E. Chloramphenicol
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines Explanation: ***Tetracycline***
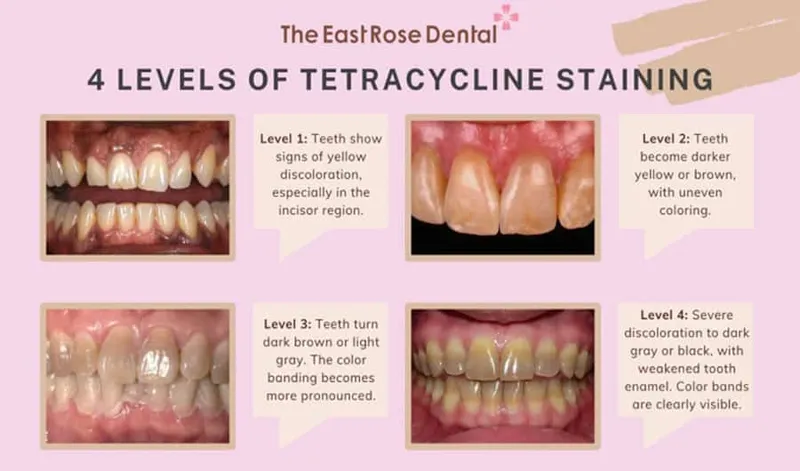
- **Tetracycline** exposure during tooth development (in utero or early childhood) can cause **permanent brownish-gray discoloration** and enamel hypoplasia due to its deposition in dentin and enamel.
- The drug's affinity for **calcium** can also interfere with bone growth and development, potentially leading to **skeletal abnormalities** like limb length discrepancies if exposure occurs during critical periods of growth.
*Gentamicin*
- **Gentamicin** is an **aminoglycoside antibiotic** primarily associated with **ototoxicity** (hearing loss) and **nephrotoxicity** (kidney damage) if taken during pregnancy.
- It does not typically cause dental discoloration or skeletal growth issues in the fetus.
*Ciprofloxacin*
- **Ciprofloxacin** is a **fluoroquinolone antibiotic** that, in children, has been linked to **cartilage damage** and arthropathy, thus generally avoided in pregnancy and childhood.
- It is not associated with dental staining or limb length discrepancies.
*Trimethoprim*
- **Trimethoprim** is an **antifolate antibiotic** that, particularly when combined with sulfamethoxazole, is known to pose a risk of **neural tube defects** if taken in the first trimester.
- It does not cause dental discoloration or skeletal growth abnormalities.
*Chloramphenicol*
- **Chloramphenicol** is primarily associated with **"Gray Baby Syndrome"** in neonates due to its effects on mitochondrial function and immature liver conjugation.
- It does not cause dental discoloration or skeletal issues like the limb length discrepancy described.
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines US Medical PG Question 10: A 35-year-old woman visits the office with complaints of yellowish vaginal discharge and increased urinary frequency for a week. She also complains of pain during urination. Past medical history is irrelevant. She admits to having multiple sexual partners in the past few months. Physical examination is within normal limits except for lower abdominal tenderness. Urine culture yields Chlamydia trachomatis. What is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Acyclovir
- B. Doxycycline (Correct Answer)
- C. Metronidazole
- D. Clindamycin
- E. Boric acid
Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines Explanation: ***Doxycycline***
- **Doxycycline** is a recommended first-line treatment for **Chlamydia trachomatis** infections (along with azithromycin).
- A 7-day course of **doxycycline 100 mg orally twice daily** is highly effective in eradicating the infection.
- **Alternative:** Azithromycin 1 g PO single dose is also first-line and may be preferred for compliance.
*Acyclovir*
- **Acyclovir** is an antiviral medication used to treat **herpes simplex virus (HSV)** infections.
- It is ineffective against **bacterial infections** like Chlamydia.
*Metronidazole*
- **Metronidazole** is an antibiotic primarily used for **anaerobic bacterial** and **parasitic infections** (e.g., bacterial vaginosis, trichomoniasis).
- It is not effective against **Chlamydia trachomatis**.
*Clindamycin*
- **Clindamycin** is an antibiotic effective against a range of **bacterial infections**, including some anaerobic bacteria.
- However, it is not a recommended treatment for **Chlamydia trachomatis** infections.
*Boric acid*
- **Boric acid** is an antifungal agent primarily used for treating **recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis** (yeast infections).
- It has no role in treating **bacterial infections** like Chlamydia.
More Tetracyclines and glycylcyclines US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.