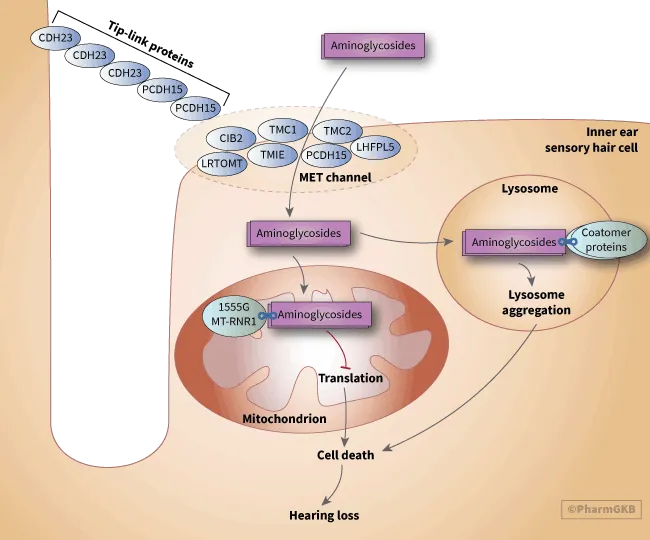
Aminoglycosides US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Aminoglycosides. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Aminoglycosides US Medical PG Question 1: You are taking care of a patient with renal failure secondary to anti-fungal therapy. The patient is a 66-year-old male being treated for cryptococcal meningitis. This drug has a variety of known side effects including acute febrile reactions to infusions, anemia, hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia. What is the mechanism of action of this drug?
- A. Inhibition of squalene epoxidase
- B. Binding of the 50S subunit
- C. Pore formation secondary to ergosterol binding (Correct Answer)
- D. Disruption of microtubule formation
- E. Inhibition of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase
Aminoglycosides Explanation: ***Pore formation secondary to ergosterol binding***
- This describes the mechanism of action of **amphotericin B**, the antifungal agent used for cryptococcal meningitis.
- Amphotericin B binds to **ergosterol** in the fungal cell membrane, leading to the formation of pores, disruption of membrane integrity, and ultimately cell death.
- The side effects described—**nephrotoxicity with renal failure, hypokalemia, and hypomagnesemia**—are classic adverse effects of amphotericin B due to its effect on renal tubular cells and electrolyte wasting.
*Inhibition of squalene epoxidase*
- This is the mechanism of action for **terbinafine**, an antifungal primarily used for dermatophyte infections (e.g., onychomycosis), not systemic infections like cryptococcal meningitis.
- Terbinafine inhibits ergosterol synthesis at an earlier step but does not cause the severe nephrotoxicity and electrolyte disturbances described.
*Binding of the 50S subunit*
- This mechanism of action is characteristic of **macrolide antibiotics** like azithromycin or clarithromycin, which are antibacterial agents, not antifungals.
- These drugs inhibit bacterial protein synthesis and are ineffective against fungal infections.
*Disruption of microtubule formation*
- This is the mechanism of action for **griseofulvin**, an antifungal drug used for dermatophyte infections of the skin, hair, and nails.
- Griseofulvin interferes with fungal cell division and is not used for life-threatening systemic infections like cryptococcal meningitis.
*Inhibition of 1,3-beta-glucan synthase*
- This mechanism is associated with **echinocandins** (e.g., caspofungin, micafungin), which inhibit fungal cell wall synthesis.
- While echinocandins are used for some systemic fungal infections (particularly Candida and Aspergillus), they do not typically cause the severe renal failure and electrolyte disturbances characteristic of amphotericin B.
Aminoglycosides US Medical PG Question 2: A 60-year-old man with a history of coronary artery disease and hyperlipidemia presents to his internist for a follow-up visit 3 weeks after visiting an urgent care center for symptoms of cough, fever, and difficulty breathing. He had been prescribed erythromycin in addition to his usual regimen of rosuvastatin and aspirin. With which potential side effect or interaction should the internist be most concerned?
- A. Myalgia due to decreased rosuvastatin metabolism in the presence of erythromycin (Correct Answer)
- B. Gastric bleeding due to decreased aspirin metabolism in the presence of erythromycin
- C. Unstable angina due to decreased rosuvastatin metabolism in the presence of erythromycin
- D. Tinnitus due to decreased aspirin metabolism in the presence of erythromycin
- E. Metabolic acidosis due to decreased aspirin metabolism in the presence of erythromycin
Aminoglycosides Explanation: ***Myalgia due to decreased rosuvastatin metabolism in the presence of erythromycin***
- **Rosuvastatin** is metabolized by **CYP3A4** to a lesser extent, but it's also a substrate for **organic anion transporting polypeptide (OATP) 1B1**. **Erythromycin** is a potent **CYP3A4 inhibitor** and can also inhibit **OATP1B1**.
- Inhibition of rosuvastatin metabolism/transport by erythromycin can lead to increased serum concentrations of rosuvastatin, increasing the risk of **statin-induced myopathy** and **rhabdomyolysis**, a severe adverse effect characterized by **myalgia**.
*Gastric bleeding due to decreased aspirin metabolism in the presence of erythromycin*
- **Aspirin's metabolism** is primarily through hydrolysis to salicylic acid; erythromycin does not significantly affect this pathway.
- Gastric bleeding with aspirin is related to its **antiplatelet effects** and direct gastrointestinal irritation, not typically altered metabolism by erythromycin.
*Unstable angina due to decreased rosuvastatin metabolism in the presence of erythromycin*
- While **rosuvastatin levels** might increase, leading to myalgia, this interaction does not directly cause **unstable angina**.
- Unstable angina is a cardiac event related to **coronary artery disease progression** or plaque rupture, not typically a direct drug-drug interaction with erythromycin and rosuvastatin.
*Tinnitus due to decreased aspirin metabolism in the presence of erythromycin*
- **Tinnitus** is a known side effect of **aspirin toxicity**, particularly at high doses (salicylism).
- Erythromycin does not significantly alter aspirin metabolism in a way that would lead to increased aspirin levels and associated tinnitus.
*Metabolic acidosis due to decreased aspirin metabolism in the presence of erythromycin*
- **Metabolic acidosis** can occur with **high-dose aspirin poisoning** (salicylate poisoning).
- There is no known direct interaction between erythromycin and aspirin metabolism that would lead to clinically significant changes in aspirin levels sufficient to cause metabolic acidosis.
Aminoglycosides US Medical PG Question 3: A 37-year-old woman with a history of anorectal abscesses complains of pain in the perianal region. Physical examination reveals mild swelling, tenderness, and erythema of the perianal skin. She is prescribed oral ampicillin and asked to return for follow-up. Two days later, the patient presents with a high-grade fever, syncope, and increased swelling. Which of the following would be the most common mechanism of resistance leading to the failure of antibiotic therapy in this patient?
- A. Intrinsic absence of a target site for the drug
- B. Use of an altered metabolic pathway
- C. Production of beta-lactamase enzyme (Correct Answer)
- D. Altered structural target for the drug
- E. Drug efflux pump
Aminoglycosides Explanation: ***Production of beta-lactamase enzyme***
- The patient's symptoms of a rapidly worsening infection despite ampicillin treatment suggest the presence of a **beta-lactamase producing organism**. Ampicillin is a **beta-lactam antibiotic** that is inactivated by these enzymes.
- Anorectal abscesses and rapidly progressing soft tissue infections are often caused by **polymicrobial flora**, including staphylococci and enterococci, many of which can produce **beta-lactamase**.
*Intrinsic absence of a target site for the drug*
- While some bacteria inherently lack the target site for certain drugs (e.g., mycoplasma lacking a cell wall, thus being resistant to beta-lactams), this is less likely to be the **most common mechanism of acquired resistance** leading to treatment failure in a typical perianal infection.
- The rapid progression and failed initial treatment point towards an **acquired mechanism of resistance** rather than an intrinsic one.
*Use of an altered metabolic pathway*
- This mechanism, such as altered **folate synthesis pathways** in resistance to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, is less common as the primary mechanism for ampicillin resistance.
- Ampicillin's mechanism of action primarily targets the **bacterial cell wall**, not a metabolic pathway in the same way.
*Altered structural target for the drug*
- This involves modifications to the **penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs)**, which are the targets of beta-lactam antibiotics like ampicillin. While a valid mechanism (e.g., in MRSA), the **production of beta-lactamase** is generally a more widespread and common cause of ampicillin failure, especially in infections involving mixed flora from the perianal region.
- Given the abrupt failure of ampicillin, **beta-lactamase inactivation** is a more immediate and common cause than a rapid mutational change in PBPs.
*Drug efflux pump*
- **Efflux pumps** actively remove antibiotics from the bacterial cell, contributing to resistance against various drug classes.
- While efflux pumps can play a role, the dominant mechanism for resistance to **ampicillin** in many common perianal pathogens is the **enzymatic degradation by beta-lactamases**.
Aminoglycosides US Medical PG Question 4: An investigator is studying the chemical structure of antibiotics and its effect on bacterial growth. He has synthesized a simple beta-lactam antibiotic and has added a bulky side chain to the molecule that inhibits the access of bacterial enzymes to the beta-lactam ring. The synthesized drug will most likely be appropriate for the treatment of which of the following conditions?
- A. Folliculitis (Correct Answer)
- B. Nocardiosis
- C. Atypical pneumonia
- D. Erythema migrans
- E. Otitis media
Aminoglycosides Explanation: ***Folliculitis***
- The bulky side chain provides **steric hindrance** that prevents **staphylococcal beta-lactamases** from accessing and degrading the **beta-lactam ring**.
- This modification creates an **anti-staphylococcal penicillin** (similar to methicillin, nafcillin, or oxacillin), which is effective against **methicillin-sensitive *Staphylococcus aureus* (MSSA)**.
- **Folliculitis** is most commonly caused by *S. aureus*, making this modified beta-lactam an appropriate treatment choice for MSSA-related folliculitis.
- The bulky side chain specifically protects against the **penicillinase** (beta-lactamase) produced by staphylococci.
*Otitis media*
- Otitis media is commonly caused by beta-lactamase-producing organisms like *Haemophilus influenzae* and *Moraxella catarrhalis*.
- However, the beta-lactamases produced by these gram-negative organisms are **not inhibited by bulky side chains** alone.
- Treatment of beta-lactamase-producing *H. influenzae* and *M. catarrhalis* requires **beta-lactamase inhibitors** (such as clavulanic acid combined with amoxicillin), not steric hindrance.
- The mechanism of protection differs: beta-lactamase inhibitors **suicide inhibitors** that bind to the enzyme, whereas bulky side chains provide **physical blocking**.
*Nocardiosis*
- Nocardiosis is caused by *Nocardia* species, which are **aerobic actinomycetes**.
- These bacteria are typically treated with **sulfonamides** (trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole) for prolonged periods.
- Beta-lactam antibiotics are generally not first-line treatment, as *Nocardia* species often show intrinsic resistance or require specific antibiotic combinations.
*Atypical pneumonia*
- Atypical pneumonia is caused by organisms like *Mycoplasma pneumoniae*, *Chlamydophila pneumoniae*, and *Legionella pneumophila*.
- These organisms lack a **peptidoglycan cell wall**, which is the target of all **beta-lactam antibiotics**.
- Beta-lactams (regardless of modifications) are completely ineffective against atypical pneumonia pathogens.
- Treatment requires **macrolides** (azithromycin), **tetracyclines** (doxycycline), or **fluoroquinolones**.
*Erythema migrans*
- Erythema migrans is the characteristic rash of early **Lyme disease**, caused by *Borrelia burgdorferi*.
- While *Borrelia* is sensitive to certain beta-lactam antibiotics (amoxicillin, ceftriaxone), it does **not produce beta-lactamases**.
- The bulky side chain modification is unnecessary for treating *Borreria* infections, as there is no beta-lactamase to protect against.
- Standard treatment uses doxycycline, amoxicillin, or ceftriaxone—not anti-staphylococcal penicillins.
Aminoglycosides US Medical PG Question 5: An investigator is studying the genetic profile of an isolated pathogen that proliferates within macrophages. The pathogen contains sulfatide on the surface of its cell wall to prevent fusion of the phagosome and lysosome. She finds that some of the organisms under investigation have mutations in a gene that encodes the enzyme required for synthesis of RNA from a DNA template. The mutations are most likely to reduce the therapeutic effect of which of the following drugs?
- A. Pyrazinamide
- B. Ethambutol
- C. Rifampin (Correct Answer)
- D. Streptomycin
- E. Levofloxacin
Aminoglycosides Explanation: ***Rifampin***
- **Rifampin** specifically targets bacterial **DNA-dependent RNA polymerase**, inhibiting **RNA synthesis**. Mutations in the gene encoding this enzyme would directly reduce rifampin's binding and effectiveness.
- The description of the pathogen thriving within macrophages and using **sulfatide to evade lysosomal fusion** strongly suggests **Mycobacterium tuberculosis**, a bacterium for which rifampin is a cornerstone treatment.
*Pyrazinamide*
- **Pyrazinamide** is a prodrug that, once converted to **pyrazinoid acid**, disrupts **mycobacterial membrane potential** and metabolism. Its primary target is not RNA synthesis.
- Its efficacy is pH-dependent and it acts optimally in acidic environments, such as within macrophages, but mutations affecting RNA synthesis would not directly compromise its action.
*Ethambutol*
- **Ethambutol** inhibits **arabinosyl transferase**, an enzyme essential for the synthesis of the **mycobacterial cell wall component arabinogalactan**.
- Its mechanism of action is distinct from RNA synthesis, thus mutations affecting RNA polymerase would not impact its efficacy.
*Streptomycin*
- **Streptomycin** is an **aminoglycoside antibiotic** that binds to the **30S ribosomal subunit**, inhibiting bacterial **protein synthesis**.
- This mechanism is unrelated to DNA-dependent RNA polymerase, so mutations in RNA synthesis enzymes would not affect streptomycin's action.
*Levofloxacin*
- **Levofloxacin** is a **fluoroquinolone antibiotic** that inhibits **bacterial DNA gyrase (topoisomerase II)** and **topoisomerase IV**, thereby blocking DNA replication and transcription.
- While it affects processes related to DNA, its direct target is not the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase enzyme itself, distinguishing it from rifampin's specific mechanism.
Aminoglycosides US Medical PG Question 6: A 77-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department from her nursing home because she was found down overnight. On presentation she was found to be delirious and was unable to answer questions. Chart review shows that she is allergic to cephalosporins. Her temperature is 102.2°F (39°C), blood pressure is 105/52 mmHg, pulse is 94/min, and respirations are 23/min. Physical exam reveals a productive cough. A metabolic panel is obtained with the following results:
Serum:
Na+: 135 mEq/L
Cl-: 95 mEq/L
K+: 4 mEq/L
HCO3-: 19 mEq/L
BUN: 40 mg/dL
Creatinine: 2.5 mg/dL
Glucose: 150 mg/dL
Based on these findings two different drugs are started empirically. Gram stain on a blood sample is performed showing the presence of gram-positive organisms on all samples. One of the drugs is subsequently stopped. The drug that was most likely stopped has which of the following characteristics?
- A. Resistance conveyed through acetylation
- B. Associated with red man syndrome
- C. Single-ringed ß-lactam structure (Correct Answer)
- D. Causes discolored teeth in children
- E. Accumulates inside bacteria via O2-dependent uptake
Aminoglycosides Explanation: ***Single-ringed ß-lactam structure***
- The patient presents with **sepsis** due to **pneumonia** likely caused by **gram-positive organisms**. Given a cephalosporin allergy, **aztreonam** (a monobactam) would be an initial empirical antibiotic choice to cover gram-negative bacteria, alongside a drug for gram-positive coverage (like vancomycin).
- Since the **blood cultures** confirmed **gram-positive organisms**, the drug covering gram-negative bacteria (aztreonam) would be stopped. Aztreonam is characterized by its **single-ringed β-lactam structure**.
*Resistance conveyed through acetylation*
- This mechanism of resistance is typical of **aminoglycosides** (e.g., gentamicin) and **chloramphenicol**.
- Aminoglycosides were unlikely to be one of the empirically started drugs, as they are often used in combination with β-lactams, and this patient has a cephalosporin allergy.
*Associated with red man syndrome*
- **Red man syndrome** is a common adverse effect associated with **vancomycin** administration, especially with rapid infusion.
- Vancomycin would likely be continued, as it effectively targets gram-positive organisms, including **MRSA**, and is a suitable alternative given the cephalosporin allergy.
*Causes discolored teeth in children*
- This is a characteristic side effect of **tetracyclines** (e.g., doxycycline), which are contraindicated in young children and pregnant women due to their effects on bone and teeth development.
- Tetracyclines are not typically first-line empiric therapy for severe pneumonia or sepsis, especially in an elderly patient.
*Accumulates inside bacteria via O2-dependent uptake*
- This describes the mechanism of uptake for **aminoglycosides**. Their entry into bacteria is an **energy-dependent process** requiring oxygen.
- As mentioned, aminoglycosides are less likely to be the initial drug stopped in this scenario, as they target gram-negative bacteria.
Aminoglycosides US Medical PG Question 7: A scientist is studying the mechanisms by which bacteria become resistant to antibiotics. She begins by obtaining a culture of vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis and conducts replicate plating experiments. In these experiments, colonies are inoculated onto a membrane and smeared on 2 separate plates, 1 containing vancomycin and the other with no antibiotics. She finds that all of the bacterial colonies are vancomycin resistant because they grow on both plates. She then maintains the bacteria in liquid culture without vancomycin while she performs her other studies. Fifteen generations of bacteria later, she conducts replicate plating experiments again and finds that 20% of the colonies are now sensitive to vancomycin. Which of the following mechanisms is the most likely explanation for why these colonies have become vancomycin sensitive?
- A. Point mutation
- B. Gain of function mutation
- C. Viral infection
- D. Plasmid loss (Correct Answer)
- E. Loss of function mutation
Aminoglycosides Explanation: ***Plasmid loss***
- The initial **vancomycin resistance** in *Enterococcus faecalis* is often mediated by genes located on **plasmids**, which are extrachromosomal DNA.
- In the absence of selective pressure (vancomycin), bacteria that lose the plasmid (and thus the resistance genes) have a **growth advantage** over those that retain the energetically costly plasmid, leading to an increase in sensitive colonies over generations.
*Point mutation*
- A **point mutation** typically involves a change in a single nucleotide and could lead to loss of resistance if it occurred in a gene conferring resistance.
- However, since there was no selective pressure for loss of resistance, it is less likely that 20% of the population would acquire such a specific point mutation to revert resistance.
*Gain of function mutation*
- A **gain of function mutation** would imply that the bacteria acquired a *new* advantageous trait, not the *loss* of resistance.
- This type of mutation would not explain why some colonies became sensitive to vancomycin after the drug was removed.
*Viral infection*
- **Viral infection** (bacteriophages) can transfer genes through transduction or cause bacterial lysis, but it's not the primary mechanism for a widespread reversion of resistance in the absence of antibiotic pressure.
- It would not explain the observed increase in vancomycin-sensitive colonies due to evolutionary pressure.
*Loss of function mutation*
- While a **loss of function mutation** in a gene conferring resistance could lead to sensitivity, it's generally less likely to explain a 20% shift without selective pressure than **plasmid loss**.
- Plasmids are often unstable and are easily lost in the absence of selection, whereas a specific gene mutation causing loss of function would need to arise and become prevalent in the population.
Aminoglycosides US Medical PG Question 8: You are treating a neonate with meningitis using ampicillin and a second antibiotic, X, that is known to cause ototoxicity. What is the mechanism of antibiotic X?
- A. It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex
- B. It binds the 30S ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex (Correct Answer)
- C. It binds the 30S ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation
- D. It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits peptidyltransferase
- E. It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation
Aminoglycosides Explanation: ***It binds the 30s ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex***
- The second antibiotic, X, is likely an **aminoglycoside**, such as **gentamicin** or **amikacin**, which are commonly used in combination with ampicillin for neonatal meningitis and are known to cause ototoxicity.
- Aminoglycosides exert their bactericidal effect by **irreversibly binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit**, thereby **inhibiting the formation of the initiation complex** and leading to misreading of mRNA.
*It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **linezolid**, which targets the 50S ribosomal subunit to prevent the formation of the initiation complex.
- While linezolid can cause side effects, **ototoxicity** is less commonly associated with it compared to aminoglycosides, and it is not a primary drug for neonatal meningitis alongside ampicillin.
*It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits peptidyltransferase*
- This is the mechanism of action for **chloramphenicol**, which inhibits **peptidyltransferase** activity on the 50S ribosomal subunit, preventing peptide bond formation.
- Although chloramphenicol can cause **ototoxicity** and **aplastic anemia**, its use in neonates is limited due to the risk of **Gray Baby Syndrome**.
*It binds the 30s ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation*
- This describes the mechanism of action of **tetracyclines**, which reversibly bind to the 30S ribosomal subunit and prevent the attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA, thereby inhibiting protein synthesis.
- Tetracyclines are **contraindicated in neonates** due to their potential to cause **tooth discoloration** and **bone growth inhibition**, and ototoxicity is not their primary adverse effect.
*It binds the 50s ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation*
- This mechanism of reversibly inhibiting translocation by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit is characteristic of **macrolides** (e.g., erythromycin, azithromycin) and **clindamycin**.
- While some macrolides can cause **transient ototoxicity**, they are not typically the second antibiotic of choice for neonatal meningitis in combination with ampicillin, and clindamycin's side effect profile is different.
Aminoglycosides US Medical PG Question 9: An investigator is studying a strain of bacteria that retains a blue color after crystal violet dye and acetone are applied. The bacteria are inoculated in a petri dish containing hypotonic saline. After the addition of an antibiotic, the bacteria swell and rupture. This antibiotic most likely belongs to which of the following classes?
- A. Macrolide
- B. Cephalosporin (Correct Answer)
- C. Sulfonamide
- D. Fluoroquinolone
- E. Tetracycline
Aminoglycosides Explanation: ***Cephalosporin***
- This scenario describes a **Gram-positive bacterium** (retains blue color) which, after antibiotic treatment, swells and lyses in a hypotonic solution. This indicates a defect in the **peptidoglycan cell wall**.
- **Cephalosporins** are **β-lactam antibiotics** that inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis by interfering with **peptidoglycan cross-linking**, leading to osmotic lysis in hypotonic environments.
*Macrolide*
- Macrolides like **azithromycin** and **erythromycin** inhibit bacterial **protein synthesis** by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit.
- They do not directly target the cell wall, so they would not cause immediate osmotic lysis in this manner.
*Sulfonamide*
- Sulfonamides inhibit bacterial **folic acid synthesis** by acting as a competitive inhibitor of dihydropteroate synthase, disrupting DNA and RNA production.
- Their mechanism of action does not involve direct cell wall disruption or osmotic lysis.
*Fluoroquinolone*
- Fluoroquinolones interfere with bacterial **DNA replication and transcription** by inhibiting **DNA gyrase** and **topoisomerase IV**.
- This class of antibiotics does not primarily target the cell wall, and therefore would not lead to prompt osmotic swelling and rupture.
*Tetracycline*
- Tetracyclines inhibit bacterial **protein synthesis** by binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit, preventing the attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA.
- They do not affect the cell wall, so they would not cause the observed osmotic lysis.
Aminoglycosides US Medical PG Question 10: A 56-year-old man presents with breathlessness and altered mental status. The patient’s daughter says that he has been having high fever and cough for the last 3 days. Past medical history is significant for a recent hospitalization 5 days ago, following a successful coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG). In the post-operative period, he was in an intensive care unit (ICU) for 6 days, including 12 hours on mechanical ventilation. Current medications are aspirin and rosuvastatin. The patient’s daughter mentions that he has had anaphylactic reactions to penicillin in the past. His temperature is 39.4°C (103°F), pulse rate is 110/min, blood pressure is 104/78 mm Hg, and respiratory rate is 30/min. On physical examination, the patient is confused and disoriented and shows signs of respiratory distress and cyanosis. On chest auscultation, there is crepitus in the right lung. The patient is immediately started on oxygen therapy, intravenous fluids, and supportive care. After the collection of appropriate samples for bacteriological culture, treatment with empirical intravenous antibiotics are started. After 24 hours of treatment, the microbiology results indicate Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. Antibiotic therapy is changed to a combination of aztreonam and tobramycin. Which of the following best describes the rationale for choosing this antibiotic combination?
- A. Broad-spectrum coverage against anaerobes by adding tobramycin to aztreonam
- B. Synergism of aztreonam with tobramycin (Correct Answer)
- C. Reduction of the side-effects of both aztreonam and tobramycin
- D. Broad-spectrum coverage against gram-positive cocci by adding tobramycin to aztreonam
- E. Effective combination of a bactericidal and a bacteriostatic antimicrobial against Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Aminoglycosides Explanation: ***Synergism of aztreonam with tobramycin***
- This combination provides a **synergistic effect** against *Pseudomonas aeruginosa*, meaning their combined action is greater than the sum of their individual effects.
- Aztreonam is a **monobactam** that targets gram-negative bacteria, and tobramycin is an **aminoglycoside**; their co-administration often enhances bactericidal activity and helps overcome resistance.
*Broad-spectrum coverage against anaerobes by adding tobramycin to aztreonam*
- Tobramycin is an **aminoglycoside** primarily effective against aerobic gram-negative bacteria and has **no significant activity against anaerobes**.
- Aztreonam also **lacks activity against anaerobic bacteria**, making this option incorrect.
*Reduction of the side-effects of both aztreanam and tobramycin*
- Both aztreonam and tobramycin have distinct side effects, including **nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity** for tobramycin.
- Combining them, especially tobramycin, generally **increases the risk of side effects** rather than reducing them, necessitating careful monitoring.
*Broad-spectrum coverage against gram-positive cocci by adding tobramycin to aztreonam*
- Aztreonam has a **narrow spectrum** focusing on gram-negative bacteria, and **lacks activity against gram-positive cocci**.
- Tobramycin (an aminoglycoside) also has **limited activity against gram-positive cocci** when used alone, and adding it to aztreonam does not significantly broaden coverage in this regard.
*Effective combination of a bactericidal and a bacteriostatic antimicrobial against Pseudomonas aeruginosa*
- Both aztreonam (a beta-lactam) and tobramycin (an aminoglycoside) are **bactericidal antibiotics**, meaning they kill bacteria.
- This option is incorrect because it inaccurately categorizes one of the drugs as bacteriostatic; the combination consists of two bactericidal agents.
More Aminoglycosides US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.