Vinca alkaloids and taxanes US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Vinca alkaloids and taxanes. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old man presents with a 1-week history of progressive diplopia followed by numbness and tingling in his hands and feet, some weakness in his extremities, and occasional difficulty swallowing. He was recently diagnosed with Hodgkin's lymphoma and started on a chemotherapeutic regimen that included bleomycin, doxorubicin, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone. He denies fever, recent viral illness, or vaccination. On neurological examination, he has bilateral ptosis. His bilateral pupils are 5 mm in diameter and poorly responsive to light and accommodation. He has a bilateral facial weakness and his gag reflex is reduced. Motor examination using the Medical Research Council scale reveals a muscle strength of 4/5 in the proximal muscles of upper extremities bilaterally and 2/5 in distal muscles. In his lower extremities, hip muscles are mildly weak bilaterally, and he has bilateral foot drop. Deep tendon reflexes are absent. Sensory examination reveals a stocking-pattern loss to all sensory modalities in the lower extremities up to the middle of his shins. A brain MRI is normal. Lumbar puncture is unremarkable. His condition can be explained by a common adverse effect of which of the following drugs?
- A. Doxorubicin
- B. Bleomycin
- C. Cyclophosphamide
- D. Prednisone
- E. Vincristine (Correct Answer)
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes Explanation: ***Vincristine***
- The patient's symptoms of **progressive diplopia**, **numbness and tingling**, **weakness (especially distal foot drop)**, **cranial nerve palsies (ptosis, facial weakness, reduced gag reflex)**, and **absent deep tendon reflexes (areflexia)**, along with a **stocking-glove sensory loss**, are highly indicative of **vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy**.
- **Vincristine** is a vinca alkaloid commonly used in Hodgkin's lymphoma treatment known for its **neurotoxicity**, primarily affecting **sensory and motor peripheral nerves** and **cranial nerves**.
*Doxorubicin*
- **Doxorubicin** is an anthracycline known for its **cardiotoxicity**, which can lead to **dilated cardiomyopathy** and **congestive heart failure**.
- It does not typically cause the prominent **peripheral neuropathy** and **cranial nerve deficits** observed in this patient.
*Bleomycin*
- **Bleomycin** is an antitumor antibiotic primarily associated with **pulmonary toxicity**, including **fibrosis and pneumonitis**.
- It does not cause significant **neurological side effects** like polyneuropathy.
*Cyclophosphamide*
- **Cyclophosphamide** is an alkylating agent known for its side effects such as **hemorrhagic cystitis**, **bone marrow suppression**, and **gonadal dysfunction**.
- It generally does not cause **peripheral neuropathy** or **cranial nerve palsies** as its primary toxicity.
*Prednisone*
- **Prednisone** is a corticosteroid that can cause a wide range of side effects including **hyperglycemia**, **immunosuppression**, **osteoporosis**, and **myopathy (proximal weakness)** with prolonged use.
- While it can cause some muscle weakness, it does not typically present with the **distal nerve involvement**, **sensory loss**, **diplopia**, and **areflexia** seen in this patient.
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes US Medical PG Question 2: A 57-year-old woman with non-small cell lung cancer comes to the physician 4 weeks after her tumor was resected. She takes no medications. The physician starts her on a treatment regimen that includes vinblastine. This treatment puts the patient at highest risk for which of the following?
- A. Pulmonary embolism
- B. Invasive fungal infection (Correct Answer)
- C. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- D. Pulmonary fibrosis
- E. Heart failure
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes Explanation: ***Invasive fungal infection***
- Vinblastine is an **antimitotic chemotherapy agent** that, like other chemotherapeutic agents, can cause **myelosuppression**.
- **Myelosuppression** (particularly **neutropenia**) severely compromises the immune system, making patients highly susceptible to **opportunistic infections**, including invasive fungal infections.
*Pulmonary embolism*
- While cancer itself is a risk factor for **venous thromboembolism**, including pulmonary embolism, vinblastine itself **does not directly increase the risk** more than other chemotherapy agents.
- The highest risk with vinblastine specifically relates to its impact on bone marrow.
*Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy*
- This is a rare, severe opportunistic infection of the brain caused by the **JC virus**, primarily seen in patients with **severe immunosuppression**, such as those with HIV/AIDS or on chronic immunosuppressive therapy (e.g., natalizumab).
- While chemotherapy can cause immunosuppression, PML is not the most common or highest specific risk directly associated with vinblastine or its immediate, acute side effects compared to myelosuppression and opportunistic infections.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is a known side effect of certain chemotherapeutic agents like **bleomycin** and **busulfan**, but it is **not a primary or common adverse effect of vinblastine**.
- The side effect profile of vinblastine primarily involves myelosuppression, neurotoxicity, and gastrointestinal effects.
*Heart failure*
- **Cardiotoxicity leading to heart failure** is a significant concern with certain chemotherapy drugs, particularly **anthracyclines** (e.g., doxorubicin) and some tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
- **Vinblastine is not typically associated with cardiotoxicity or heart failure** as a primary or high-risk adverse effect.
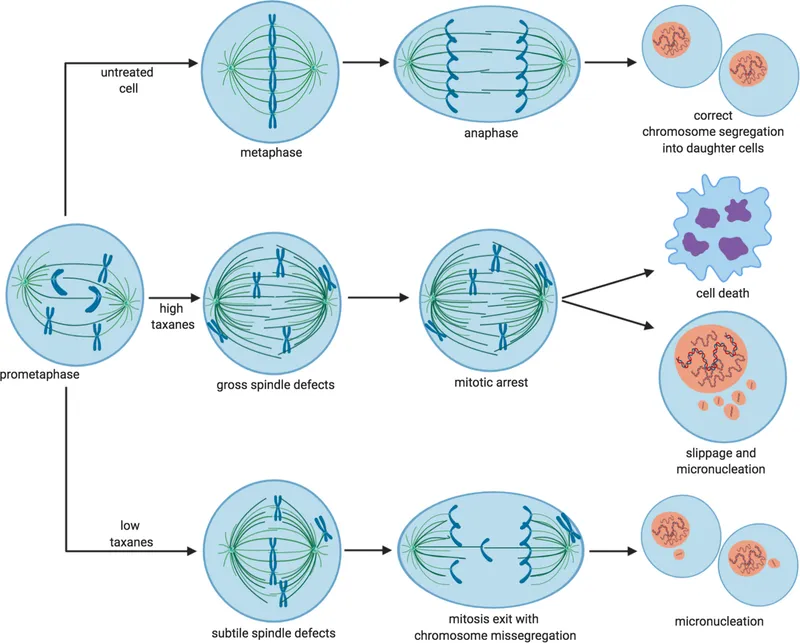
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes US Medical PG Question 3: A 60-year-old female presents to her primary care physician complaining of bloating and fatigue over the past year. On examination, she has abdominal distension and ascites. Abdominal imaging reveals a mass-like lesion affecting the left ovary. A biopsy of the lesion demonstrates serous cystadenocarcinoma. She is subsequently started on a chemotherapeutic medication known to stabilize polymerized microtubules. Which of the following complications should this patient be monitored for following initiation of this medication?
- A. Peripheral neuropathy (Correct Answer)
- B. Pulmonary fibrosis
- C. Acoustic nerve damage
- D. Hemorrhagic cystitis
- E. Cardiotoxicity
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes Explanation: ***Peripheral neuropathy***
- The chemotherapeutic medication described, which stabilizes **polymerized microtubules**, is likely a **taxane** (e.g., paclitaxel, docetaxel), often used for ovarian cancer.
- Taxanes are well-known to cause **dose-dependent peripheral neuropathy** due to their effects on microtubule dynamics in neuronal axons.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is a significant side effect associated with certain chemotherapeutic agents like **bleomycin** or **busulfan**, but not typically with taxanes.
- Monitoring for this would involve assessing breath sounds, oxygen saturation, and potentially imaging for interstitial changes.
*Acoustic nerve damage*
- **Acoustic nerve damage** and ototoxicity are characteristic side effects of **platinum-based chemotherapy agents** (e.g., cisplatin), which are also used in ovarian cancer but have a different mechanism of action than microtubule stabilizers.
- This typically manifests as **tinnitus** or **hearing loss**.
*Hemorrhagic cystitis*
- **Hemorrhagic cystitis** is a common and severe side effect of **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide**, alkylating agents, due to the accumulation of their metabolite **acrolein** in the bladder.
- It is not associated with microtubule-stabilizing agents like taxanes.
*Cardiotoxicity*
- **Cardiotoxicity**, including dilated cardiomyopathy, is a serious side effect primarily associated with **anthracyclines** (e.g., doxorubicin), which generate free radicals and damage cardiac myocytes.
- While some taxanes can cause cardiovascular effects, severe cardiotoxicity like that seen with anthracyclines is not their primary or most concerning side effect.
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes US Medical PG Question 4: An 84-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of lower back pain and lower extremity weakness for 3 weeks. Over the past week, he has also found it increasingly difficult to urinate. He has a history of prostate cancer, for which he underwent radical prostatectomy 8 years ago. His prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level was undetectable until a routine follow-up visit last year, when it began to increase from 0.8 ng/mL to its present value of 64.3 ng/mL (N < 4). An MRI of the spine shows infiltrative vertebral lesions with a collapse of the L5 vertebral body, resulting in cord compression at L4–L5. The patient receives one dose of intravenous dexamethasone and subsequently undergoes external beam radiation. Which of the following cellular changes is most likely to occur as a result of this treatment?
- A. Intercalation of neighbouring DNA base pairs
- B. Disruption of microtubule assembly
- C. Formation of DNA crosslinks
- D. Generation of hydroxyl radicals (Correct Answer)
- E. Formation of pyrimidine dimers
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes Explanation: ***Generation of hydroxyl radicals***
- **External beam radiation** primarily causes cellular damage through the **ionization of water molecules**, leading to the formation of highly reactive **hydroxyl radicals**.
- These radicals directly damage **DNA**, proteins, and cell membranes, leading to **cell death or apoptosis**, especially in rapidly dividing cells like cancer cells.
*Intercalation of neighbouring DNA base pairs*
- This mechanism is characteristic of certain **chemotherapeutic agents** (e.g., **doxorubicin**, **daunorubicin**) that insert themselves between stacked DNA base pairs.
- This process distorts the DNA helix, interfering with replication and transcription, but it is **not the primary mechanism of radiation therapy**.
*Disruption of microtubule assembly*
- **Microtubule inhibitors** (e.g., **vincristine**, **paclitaxel**) disrupt the formation or disassembly of microtubules, which are essential for cell division and intracellular transport.
- While this is a common mechanism of action for some **chemotherapeutic drugs**, it is **not how radiation therapy works**.
*Formation of DNA crosslinks*
- **Alkylating agents** (e.g., **cyclophosphamide**, **cisplatin**) form covalent bonds within or between DNA strands, creating crosslinks that prevent DNA replication and transcription.
- Though highly damaging to DNA, this is a distinct mechanism of action typically associated with **chemotherapy**, not direct radiation.
*Formation of pyrimidine dimers*
- **Ultraviolet (UV) radiation** causes the formation of **pyrimidine dimers** (e.g., thymine dimers) in DNA.
- This type of DNA damage is characteristic of UV light exposure and is **not the primary mechanism of action for external beam radiation therapy**, which uses higher-energy ionizing radiation.
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes US Medical PG Question 5: A 7-year-old boy presents to an urgent care clinic from his friend’s birthday party after experiencing trouble breathing. His father explains that the patient had eaten peanut butter at the party, and soon after, he developed facial flushing and began scratching his face and neck. This has never happened before but his father says that they have avoided peanuts and peanut butter in the past because they were worried about their son having an allergic reaction. The patient has no significant medical history and takes no medications. His blood pressure is 94/62 mm Hg, heart rate is 125/min, and respiratory rate is 22/min. On physical examination, his lips are edematous and he has severe audible stridor. Of the following, which type of hypersensitivity reaction is this patient experiencing?
- A. Type II hypersensitivity reaction
- B. Type III hypersensitivity reaction
- C. Type I hypersensitivity reaction (Correct Answer)
- D. Type IV hypersensitivity reaction
- E. Combined type I and type III hypersensitivity reactions
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes Explanation: ***Type I hypersensitivity reaction***
- This patient is experiencing **anaphylaxis** due to **peanut exposure**, a classic example of a **Type I hypersensitivity reaction**. This involves **IgE-mediated mast cell and basophil degranulation**, releasing histamines and other inflammatory mediators.
- The symptoms like **facial flushing, itching, angioedema (edematous lips), stridor (upper airway obstruction), tachycardia**, and potentially **hypotension** (blood pressure 94/62 mmHg in a child suggests relative hypotension) are all consistent with a severe systemic allergic reaction.
*Type II hypersensitivity reaction*
- Type II hypersensitivity involves **antibody-mediated cytotoxicity**, where **IgG or IgM antibodies** bind to antigens on cell surfaces, leading to cell destruction.
- This type of reaction typically manifests as **hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia**, or **Goodpasture syndrome**, which are distinct from the patient's acute allergic presentation.
*Type III hypersensitivity reaction*
- Type III hypersensitivity is characterized by the formation of **immune complexes** (antigen-antibody complexes) that deposit in tissues, leading to inflammation and tissue damage.
- Conditions like **serum sickness, lupus nephritis**, or **Arthus reaction** are examples of Type III reactions and do not fit the acute, IgE-mediated symptoms seen in this patient.
*Type IV hypersensitivity reaction*
- Type IV hypersensitivity is a **delayed-type hypersensitivity** reaction mediated by **T-cells**, not antibodies. It takes 24-72 hours to develop.
- Examples include **contact dermatitis (e.g., poison ivy)**, **tuberculin skin test reactions**, or **graft rejection**, which are much slower and have different mechanisms than the immediate anaphylactic response described.
*Combined type I and type III hypersensitivity reactions*
- While some complex immune conditions might involve multiple types of hypersensitivity over time, the patient's acute, rapid-onset symptoms after peanut ingestion are overwhelmingly characteristic of a **primary Type I hypersensitivity reaction**.
- There is no clinical evidence in this presentation to suggest the involvement of **immune complex deposition** (Type III) in addition to the immediate IgE-mediated response.
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes US Medical PG Question 6: Antituberculosis treatment is started. Two months later, the patient comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. The patient feels well. She reports that she has had tingling and bilateral numbness of her feet for the past 6 days. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Her lips are dry, scaly, and slightly swollen. Neurologic examination shows decreased sensation to pinprick and light touch over her feet, ankles, and the distal portion of her calves. Laboratory studies show:
Leukocyte count 7400 /mm3
RBC count 2.9 million/mm3
Hemoglobin 10.8 g/dL
Hematocrit 30.1%
Mean corpuscular volume 78 fL
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin 24.2 pg/cell
Platelet count 320,000/mm3
Serum
Glucose 98 mg/dL
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 44 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 52 U/L
Administration of which of the following is most likely to have prevented this patient's neurological symptoms?
- A. Interferon beta
- B. Iron
- C. Vitamin B12
- D. Vitamin E
- E. Pyridoxine (Correct Answer)
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes Explanation: ***Pyridoxine***
- The patient is experiencing **peripheral neuropathy** (tingling, numbness in feet) and **cheilosis** (dry, scaly, swollen lips), which are characteristic side effects of **isoniazid** (an antituberculosis drug).
- Isoniazid interferes with **pyridoxine (vitamin B6)** metabolism, leading to its deficiency, which can be prevented by co-administering **pyridoxine** with isoniazid.
*Interferon beta*
- **Interferon beta** is primarily used in the treatment of **multiple sclerosis** to reduce the frequency and severity of relapses by modulating the immune system.
- It is not related to the metabolic pathways or side effects of antituberculosis medications and would not prevent these neurologic symptoms.
*Iron*
- The patient's mild microcytic anemia (low Hb, low MCV, low MCH) could suggest **iron deficiency**, but this is not the primary cause of her neurological symptoms.
- While iron supplementation would address the anemia, it would not prevent the **isoniazid-induced peripheral neuropathy** or cheilosis.
*Vitamin B12*
- **Vitamin B12 deficiency** can cause peripheral neuropathy and anemia, often **macrocytic anemia**, but the patient here has **microcytic anemia** and cheilosis.
- Furthermore, the symptoms are characteristic of **isoniazid-induced pyridoxine deficiency** occurring during antituberculosis treatment, rather than an underlying B12 deficiency.
*Vitamin E*
- **Vitamin E deficiency** can cause neurological symptoms, including neuropathy and ataxia, due to its role as an **antioxidant** protecting nerve membranes.
- However, there is no direct link between antituberculosis drugs like isoniazid and vitamin E deficiency, and supplementation would not prevent the specific neurological symptoms seen here.
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes US Medical PG Question 7: A 1-year-old boy presents to the emergency department with weakness and a change in his behavior. His parents state that they first noticed the change in his behavior this morning and it has been getting worse. They noticed the patient was initially weak in his upper body and arms, but now he won’t move his legs with as much strength or vigor as he used to. Physical exam is notable for bilateral ptosis with a sluggish pupillary response, a very weak sucking and gag reflex, and shallow respirations. The patient is currently drooling and his diaper is dry. The parents state he has not had a bowel movement in over 1 day. Which of the following is the pathophysiology of this patient’s condition?
- A. Lower motor neuron destruction in the anterior horn
- B. Antibodies against postsynaptic nicotinic cholinergic ion channels
- C. Blockade of presynaptic acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction (Correct Answer)
- D. Autoantibodies against the presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels
- E. Autoimmune demyelination of peripheral nerves
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes Explanation: ***Blockade of presynaptic acetylcholine release at the neuromuscular junction***
- The patient's symptoms, including **descending flaccid paralysis** (starting in the upper body and progressing downwards), **ptosis**, **sluggish pupillary response**, **weak suck/gag reflex**, **shallow respirations**, **drooling**, and **constipation**, are classic for **infant botulism**.
- **Infant botulism** is caused by the **botulinum toxin** produced by *Clostridium botulinum*, which **inhibits acetylcholine exocytosis** at the neuromuscular junction.
*Lower motor neuron destruction in the anterior horn*
- This describes conditions like **poliomyelitis**, which causes **asymmetric flaccid paralysis** and spares extraocular and bulbar muscles.
- The patient's presentation of **symmetric, descending paralysis** with prominent **bulbar involvement** (ptosis, weak suck/gag, sluggish pupils) is inconsistent with anterior horn cell destruction.
*Antibodies against postsynaptic nicotinic cholinergic ion channels*
- This is the pathophysiology of **myasthenia gravis**, which causes fluctuating muscle weakness that **worsens with activity** and improves with rest.
- While it can cause ptosis and bulbar weakness, it typically does not present with the rapid, progressive descending paralysis, absent gag reflex, or pupillary sluggishness seen in this infant.
*Autoantibodies against the presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels*
- This is characteristic of **Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome (LEMS)**, which causes proximal muscle weakness and often improves with repeated muscle activation (unlike myasthenia gravis).
- LEMS is rare in infants and typically associated with malignancy in adults; the patient's symptoms are more consistent with a neurotoxin.
*Autoimmune demyelination of peripheral nerves*
- This is the hallmark of **Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)**, which typically presents with **ascending paralysis** (weakness starting in the legs and moving upwards) and **areflexia**.
- The patient's **descending paralysis** and prominent **bulbar/autonomic symptoms** (pupil changes, constipation) are not typical for GBS.
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes US Medical PG Question 8: A 57-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his son for odd behavior. The patient and his son had planned to go on a hike today. On the drive up to the mountain, the patient began acting strangely which prompted the patient's son to bring him in. The patient has a past medical history of constipation, seasonal allergies, alcohol abuse, and IV drug abuse. His current medications include diphenhydramine, metoprolol, and disulfiram. The patient's son states he has been with the patient all morning and has only seen him take his over the counter medications and eat breakfast. His temperature is 102.0°F (38.9°C), blood pressure is 147/102 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. The patient appears uncomfortable. Physical exam is notable for tachycardia. The patient's skin appears dry, red, and flushed, and he is confused and not responding to questions appropriately. Which of the following is the best treatment for this patient's condition?
- A. Naloxone
- B. IV fluids, thiamine, and dextrose
- C. Physostigmine (Correct Answer)
- D. Atropine
- E. Neostigmine
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes Explanation: ***Physostigmine***
- The patient's symptoms (fever, tachycardia, hypertension, dry flushed skin, confusion, and agitation) are classic for **anticholinergic toxicity**, likely caused by **diphenhydramine**.
- **Physostigmine** is a reversible **acetylcholinesterase inhibitor** that crosses the blood-brain barrier, effectively counteracting both peripheral and central anticholinergic effects.
*Naloxone*
- **Naloxone** is used to reverse **opioid overdose**, which typically presents with **respiratory depression** and miosis, not seen here.
- While the patient has a history of IV drug abuse, the clinical picture does not align with opioid intoxication.
*IV fluids, thiamine, and dextrose*
- This combination is standard empirical treatment for altered mental status in patients with suspected **alcohol abuse** or **nutritional deficiencies**.
- While the patient has a history of alcohol abuse, his primary presentation points more specifically to anticholinergic toxicity.
*Atropine*
- **Atropine** is an **anticholinergic agent**; administering it would worsen the patient's already present anticholinergic toxicity.
- It is used to treat cholinergic crises, such as organophosphate poisoning, by blocking acetylcholine receptors.
*Neostigmine*
- **Neostigmine** is an **acetylcholinesterase inhibitor** but does **not cross the blood-brain barrier**, meaning it would only address peripheral cholinergic effects and not the patient's central nervous system symptoms like confusion.
- It is often used for myasthenia gravis or reversal of neuromuscular blockade.
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes US Medical PG Question 9: A 27-year-old male arrives to your walk-in clinic complaining of neck pain. He reports that the discomfort began two hours ago, and now he feels like he can’t move his neck. He also thinks he is having hot flashes, but he denies dyspnea or trouble swallowing. The patient’s temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 124/76 mmHg, pulse is 112/min, and respirations are 14/min with an oxygen saturation of 99% O2 on room air. You perform a physical exam of the patient's neck, and you note that his neck is rigid and flexed to the left. You are unable to passively flex or rotate the patient's neck to the right. There is no airway compromise. The patient's past medical history is significant for asthma, and he was also recently diagnosed with schizophrenia. The patient denies current auditory or visual hallucinations. He appears anxious, but his speech is organized and appropriate. Which of the following is the best initial step in management?
- A. Propranolol
- B. Diphenhydramine (Correct Answer)
- C. Lorazepam
- D. Dantrolene
- E. Change medication to clozapine
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes Explanation: ***Diphenhydramine***
- The patient is presenting with acute **cervical dystonia**, likely an **acute extrapyramidal symptom (EPS)** induced by antipsychotic medication, given his recent schizophrenia diagnosis.
- **Anticholinergic medications** like diphenhydramine are the first-line treatment for acute dystonia as they block muscarinic receptors and restore dopamine-acetylcholine balance in the basal ganglia.
*Propranolol*
- Propranolol, a **beta-blocker**, is primarily used for managing **akathisia**, another common EPS characterized by restlessness.
- It would not be effective for acute dystonia, which involves sustained muscle contractions.
*Lorazepam*
- Lorazepam, a **benzodiazepine**, can be used as an adjunct or alternative for acute dystonia, especially if anticholinergics are ineffective or contraindicated.
- However, **diphenhydramine** is generally preferred as the initial agent due to its direct anticholinergic action.
*Dantrolene*
- Dantrolene is a **direct skeletal muscle relaxant** and is the primary treatment for **neuroleptic malignant syndrome (NMS)**, a severe EPS with fever, altered mental status, and severe muscle rigidity.
- This patient's presentation of isolated dystonia with normal vital signs does not fit the criteria for NMS.
*Change medication to clozapine*
- While clozapine has a lower risk of inducing EPS and is effective for refractory schizophrenia, changing chronic medication is not an appropriate initial step for an acute dystonic reaction.
- The immediate priority is to alleviate the acute symptoms, and only then consider long-term medication adjustments in consultation with a psychiatrist.
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes US Medical PG Question 10: A 50-year-old woman presents with acute onset fever and chills for the past hour. She mentions earlier in the day she felt blue, so she took some St. John’s wort because she was told by a friend that it helps with depression. Past medical history is significant for hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and depression managed medically with captopril, metformin, and fluoxetine. She has no history of allergies. Her pulse is 130/min, the respiratory rate is 18/min, the blood pressure is 176/92 mm Hg, and the temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F). On physical examination, the patient is profusely diaphoretic and extremely irritable when asked questions. Oriented x 3. The abdomen is soft and nontender with no hepatosplenomegaly. Increased bowel sounds are heard in the abdomen. Deep tendon reflexes are 3+ bilaterally and clonus is elicited. The sensation is decreased in the feet bilaterally. Mydriasis is present. Fingerstick glucose is 140 mg/dL. An ECG shows sinus tachycardia but is otherwise normal. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s condition?
- A. Sepsis
- B. Anaphylactic reaction
- C. Diabetic ketoacidosis
- D. Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
- E. Serotonin syndrome (Correct Answer)
Vinca alkaloids and taxanes Explanation: ***Serotonin syndrome***
- The patient's presentation with **fever, diaphoresis, hypertension, tachycardia, hyperreflexia, clonus, mydriasis**, and **agitation** after combining an **SSRI (fluoxetine)** with **St. John's wort** (a serotonin-enhancing herbal supplement) is highly characteristic of serotonin syndrome.
- This condition results from excessive serotonergic activity in the central and peripheral nervous system.
*Sepsis*
- While **fever, chills, and tachycardia** can be indicators of sepsis, the presence of specific neurological and neuromuscular signs like **hyperreflexia, clonus, and mydriasis** points away from it.
- The patient's **irritable state and normal mental orientation** is less typical for severe sepsis, which often involves altered mental status.
*Anaphylactic reaction*
- **Anaphylaxis** presents with rapid onset of symptoms such as **urticaria, angioedema, bronchospasm, and hypotension**, which are not observed in this patient.
- There is no history of allergen exposure, and the prominent neurological symptoms are not typical of anaphylaxis.
*Diabetic ketoacidosis*
- **DKA** is characterized by **hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and ketonemia**, often presenting with Kussmaul respirations and fruity breath odor.
- The patient's **fingerstick glucose (140 mg/dL)** is not significantly elevated, and there is no mention of deep, rapid breathing or other DKA-specific symptoms.
*Neuroleptic malignant syndrome*
- **NMS** is typically associated with exposure to **dopamine antagonists (antipsychotics)** and is characterized by **severe muscle rigidity, hyperthermia, altered mental status, and autonomic instability.**
- While some symptoms overlap, this patient's history of St. John's wort and fluoxetine points to increased serotonin, and the specific neuromuscular findings like clonus are more indicative of serotonin syndrome.
More Vinca alkaloids and taxanes US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.