Platinum compounds US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Platinum compounds. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Platinum compounds US Medical PG Question 1: A 67-year-old woman with advanced bladder cancer comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. She is currently undergoing chemotherapy with an agent that forms cross-links between DNA strands. Serum studies show a creatinine concentration of 2.1 mg/dL and a blood urea nitrogen concentration of 30 mg/dL. Urine dipstick of a clean-catch midstream specimen shows 2+ protein and 1+ glucose. Prior to initiation of chemotherapy, her laboratory values were within the reference range. In addition to hydration, administration of which of the following would most likely have prevented this patient's current condition?
- A. Leucovorin
- B. Amifostine (Correct Answer)
- C. Aprepitant
- D. Mesna
- E. Rasburicase
Platinum compounds Explanation: **Amifostine**
- This patient's symptoms (elevated creatinine and BUN, 2+ protein, 1+ glucose in urine) suggest **renal tubular damage**, specifically acute tubular necrosis, likely caused by a nephrotoxic chemotherapeutic agent.
- **Amifostine** is a cytoprotective agent that scavenges reactive oxygen species in local tissues, thereby reducing the nephrotoxic effects of **alkylating agents** like cisplatin, which forms cross-links between DNA strands.
*Leucovorin*
- **Leucovorin** (folinic acid) is used to rescue normal cells from the adverse effects of **methotrexate**, enhancing its excretion and reducing toxicity.
- It is not indicated for preventing kidney damage from DNA cross-linking agents.
*Aprepitant*
- **Aprepitant** is a neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor antagonist used to prevent **chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting**.
- It does not have protective effects against nephrotoxicity.
*Mesna*
- **Mesna** (2-mercaptoethane sulfonate sodium) is used to prevent **hemorrhagic cystitis** caused by acrolein, a toxic metabolite of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide.
- It does not prevent nephrotoxicity from other types of chemotherapy agents.
*Rasburicase*
- **Rasburicase** is a recombinant urate oxidase enzyme used to prevent or treat **tumor lysis syndrome** by converting uric acid to allantoin, which is more soluble and easily excreted.
- It is not used for preventing direct kidney damage from chemotherapeutic agents.
Platinum compounds US Medical PG Question 2: A 72-year-old man has been recently diagnosed with stage 3 squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. After the necessary laboratory workup, concurrent chemoradiation therapy has been planned. Radiation therapy is planned to take place over 7 weeks and he will receive radiation doses daily, Monday–Friday, in 2.0 Gy fractions. For concurrent chemotherapy, he will receive intravenous cisplatin at a dosage of 50 mg/m2 weekly for 7 weeks. Which of the following best explains the mechanism of action of the antineoplastic drug that the patient will receive?
- A. Free radical-mediated lipid peroxidation
- B. Inhibition of polymerization of tubulin
- C. Inhibition of topoisomerase 1
- D. Inhibition of topoisomerase 2
- E. Formation of interstrand DNA cross-links (Correct Answer)
Platinum compounds Explanation: ***Formation of interstrand DNA cross-links***
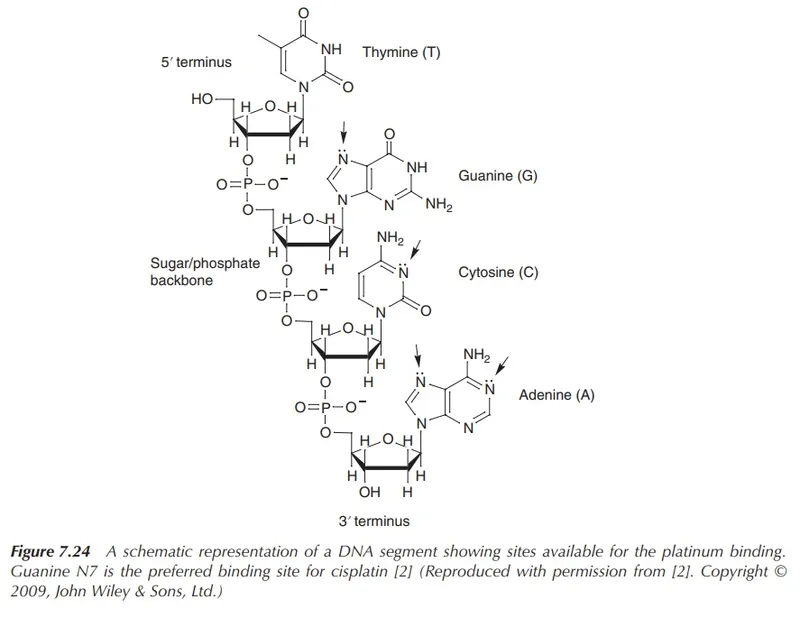
- **Cisplatin** is a **platinum-based chemotherapeutic agent** that acts by forming **interstrand and intrastrand DNA cross-links**.
- These cross-links interfere with **DNA replication and transcription**, leading to **DNA damage** and ultimately **apoptosis** in cancer cells.
*Free radical-mediated lipid peroxidation*
- While some chemotherapeutic agents, like **anthracyclines**, can induce **free radical formation** and subsequent damage, this is not the primary mechanism of action for cisplatin.
- **Lipid peroxidation** primarily affects cell membranes, whereas cisplatin's main target is DNA.
*Inhibition of polymerization of tubulin*
- This mechanism of action is characteristic of **vinca alkaloids** (e.g., vincristine, vinblastine) and **taxanes** (e.g., paclitaxel, docetaxel), which disrupt microtubule formation and function.
- Cisplatin does not target **tubulin polymerization**.
*Inhibition of topoisomerase 1*
- **Topoisomerase 1 inhibitors** such as **irinotecan** and **topotecan** prevent DNA unwinding by stabilizing the cleavable complex, leading to DNA breaks.
- This is not how cisplatin exerts its therapeutic effects.
*Inhibition of topoisomerase 2*
- **Topoisomerase 2 inhibitors** like **etoposide** and **doxorubicin** interfere with DNA replication and repair by preventing the religation of DNA strands.
- Cisplatin's mechanism is distinct from topoisomerase inhibition.
Platinum compounds US Medical PG Question 3: A 60-year-old female presents to her primary care physician complaining of bloating and fatigue over the past year. On examination, she has abdominal distension and ascites. Abdominal imaging reveals a mass-like lesion affecting the left ovary. A biopsy of the lesion demonstrates serous cystadenocarcinoma. She is subsequently started on a chemotherapeutic medication known to stabilize polymerized microtubules. Which of the following complications should this patient be monitored for following initiation of this medication?
- A. Peripheral neuropathy (Correct Answer)
- B. Pulmonary fibrosis
- C. Acoustic nerve damage
- D. Hemorrhagic cystitis
- E. Cardiotoxicity
Platinum compounds Explanation: ***Peripheral neuropathy***
- The chemotherapeutic medication described, which stabilizes **polymerized microtubules**, is likely a **taxane** (e.g., paclitaxel, docetaxel), often used for ovarian cancer.
- Taxanes are well-known to cause **dose-dependent peripheral neuropathy** due to their effects on microtubule dynamics in neuronal axons.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is a significant side effect associated with certain chemotherapeutic agents like **bleomycin** or **busulfan**, but not typically with taxanes.
- Monitoring for this would involve assessing breath sounds, oxygen saturation, and potentially imaging for interstitial changes.
*Acoustic nerve damage*
- **Acoustic nerve damage** and ototoxicity are characteristic side effects of **platinum-based chemotherapy agents** (e.g., cisplatin), which are also used in ovarian cancer but have a different mechanism of action than microtubule stabilizers.
- This typically manifests as **tinnitus** or **hearing loss**.
*Hemorrhagic cystitis*
- **Hemorrhagic cystitis** is a common and severe side effect of **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide**, alkylating agents, due to the accumulation of their metabolite **acrolein** in the bladder.
- It is not associated with microtubule-stabilizing agents like taxanes.
*Cardiotoxicity*
- **Cardiotoxicity**, including dilated cardiomyopathy, is a serious side effect primarily associated with **anthracyclines** (e.g., doxorubicin), which generate free radicals and damage cardiac myocytes.
- While some taxanes can cause cardiovascular effects, severe cardiotoxicity like that seen with anthracyclines is not their primary or most concerning side effect.
Platinum compounds US Medical PG Question 4: A 62-year-old woman presents to her oncologist to discuss the chemotherapy options for her newly diagnosed breast cancer. During the meeting, they discuss a drug that inhibits the breakdown of mitotic spindles in cells. Her oncologist explains that this will be more toxic to cancer cells because those cells are dividing more rapidly. Which of the following side effects is closely associated with the use of this chemotherapeutic agent?
- A. Photosensitivity
- B. Peripheral neuropathy (Correct Answer)
- C. Paralytic ileus
- D. Hemorrhagic cystitis
- E. Pulmonary fibrosis
Platinum compounds Explanation: ***Peripheral neuropathy***
- Drugs that inhibit the breakdown of **mitotic spindles** are **microtubule-targeting agents** (e.g., **taxanes** like paclitaxel/docetaxel, **vinca alkaloids** like vincristine/vinblastine).
- These agents interfere with **microtubule function** in neurons, leading to **axonal damage** and **peripheral neuropathy**.
- This is the **most characteristic and common dose-limiting toxicity** of microtubule inhibitors, affecting sensory and motor nerves (numbness, tingling, weakness in extremities).
*Photosensitivity*
- **Photosensitivity** is a common adverse effect associated with certain chemotherapeutic agents like **fluorouracil** (5-FU) or **methotrexate**, but is not linked to microtubule inhibitors.
- It involves an increased sensitivity to UV light, often manifesting as a rash or exaggerated sunburn.
*Paralytic ileus*
- **Paralytic ileus** can occur with **vinca alkaloids** (especially vincristine) due to autonomic neuropathy affecting the **enteric nervous system**.
- However, this is **less common** than peripheral neuropathy and occurs more specifically with vincristine rather than taxanes.
- **Peripheral neuropathy** is the more pervasive, dose-limiting, and universally characteristic side effect across all microtubule inhibitors.
*Hemorrhagic cystitis*
- **Hemorrhagic cystitis** is a classic side effect of **alkylating agents** like **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide**, which produce the toxic metabolite **acrolein**.
- It is prevented/managed with **mesna**, which inactivates acrolein.
- Not associated with microtubule inhibitors.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is a known side effect of certain chemotherapeutic drugs, most notably **bleomycin** and **busulfan**.
- This adverse effect is not associated with agents that target **mitotic spindle breakdown**.
Platinum compounds US Medical PG Question 5: A 65-year-old male presents to the physician after noticing gross blood with urination. He reports that this is not associated with pain. The patient smokes 1.5 packs per day for 45 years. Dipstick analysis is positive for blood, with 5 RBC per high-power field (HPF) on urinalysis. A cystoscopy is performed, which is significant for a lesion suspicious for malignancy. A biopsy was obtained, which is suggestive of muscle-invasive transitional cell carcinoma. Before radical cystectomy is performed, the patient is started on cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Which of the following is most likely associated with this chemotherapeutic drug?
- A. Cardiotoxicity
- B. Hemorrhagic cystitis
- C. Addition of mesna decreases drug toxicity
- D. Gentamicin enhances toxicity risk (Correct Answer)
- E. Myelosuppression
Platinum compounds Explanation: ***Gentamicin enhances toxicity risk***
- **Cisplatin** is a platinum-based chemotherapeutic agent with characteristic toxicities including **nephrotoxicity** (dose-limiting), **ototoxicity**, and **peripheral neuropathy**.
- **Gentamicin** is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that is also **nephrotoxic** and **ototoxic**.
- Concurrent use of gentamicin with cisplatin significantly **enhances the risk of both nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity** due to additive effects on renal tubular cells and cochlear hair cells.
- This is a **clinically important drug-drug interaction** that must be avoided or carefully monitored.
*Myelosuppression*
- While cisplatin can cause mild myelosuppression, this is **not its most characteristic or dose-limiting toxicity**.
- **Carboplatin** (another platinum agent) is much more associated with myelosuppression than cisplatin.
- Cisplatin's hallmark toxicities are **nephrotoxicity, ototoxicity, and neurotoxicity**.
*Cardiotoxicity*
- **Cardiotoxicity** is primarily associated with **anthracyclines** (e.g., doxorubicin, daunorubicin), not cisplatin.
- Anthracyclines cause dilated cardiomyopathy through free radical damage.
*Hemorrhagic cystitis*
- **Hemorrhagic cystitis** is a well-known side effect of **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide**, not cisplatin.
- This condition is caused by the metabolite **acrolein**, which irritates the bladder lining.
*Addition of mesna decreases drug toxicity*
- **Mesna** (2-mercaptoethane sulfonate sodium) is specifically used to prevent hemorrhagic cystitis caused by **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide** by binding and detoxifying acrolein.
- Mesna does **not mitigate cisplatin toxicity**; cisplatin toxicity is managed with **adequate hydration and saline diuresis** to protect the kidneys.
Platinum compounds US Medical PG Question 6: A 67-year-old woman who was diagnosed with cancer 2 months ago presents to her oncologist with a 6-day history of numbness and tingling in her hands and feet. She is concerned that these symptoms may be related to progression of her cancer even though she has been faithfully following her chemotherapy regimen. She is not currently taking any other medications and has never previously experienced these symptoms. On physical exam, she is found to have decreased sensation to pinprick and fine touch over hands, wrists, ankles, and feet. Furthermore, she is found to have decreased reflexes throughout. Her oncologist assures her that these symptoms are a side effect from her chemotherapy regimen rather than progression of the cancer. The drug most likely responsible for her symptoms has which of the following mechanisms?
- A. Alkylation of DNA
- B. Inhibit folate metabolism
- C. DNA strand breaking
- D. Inhibit microtubule formation (Correct Answer)
- E. Prevention of nucleotide synthesis
Platinum compounds Explanation: ***Inhibit microtubule formation***
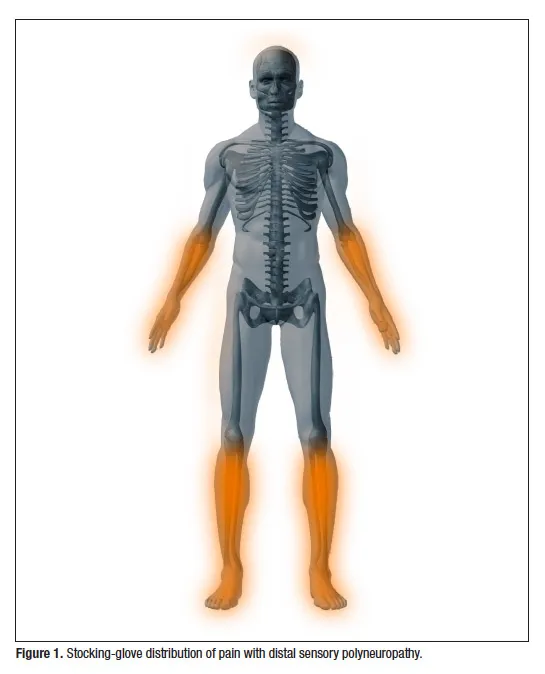
- The patient's symptoms of **numbness**, **tingling**, **decreased sensation** to pinprick and fine touch in a **stocking-glove distribution**, and **decreased reflexes** are characteristic of **peripheral neuropathy**.
- **Vinca alkaloids** (e.g., vincristine) and **taxanes** (e.g., paclitaxel, docetaxel) are chemotherapy agents that **inhibit microtubule formation**, and **peripheral neuropathy is their classic dose-limiting toxicity**.
- These agents are the **most strongly associated** with this specific adverse effect pattern among chemotherapy drugs.
*Alkylation of DNA*
- **Alkylating agents** (e.g., cyclophosphamide) and **platinum-based agents** (e.g., cisplatin, oxaliplatin) exert their cytotoxic effects by **cross-linking DNA strands**, preventing DNA replication and transcription.
- While **cisplatin and oxaliplatin can cause significant peripheral neuropathy**, the **microtubule inhibitors** (vinca alkaloids and taxanes) are **more classically associated** with this side effect and are the expected answer in this clinical context.
*Inhibit folate metabolism*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **antimetabolites** like **methotrexate**, which **inhibits dihydrofolate reductase**, thereby disrupting DNA synthesis.
- While methotrexate can have neurological side effects (particularly intrathecal administration causing neurotoxicity), **typical peripheral neuropathy is not its most common or direct adverse effect** related to this mechanism.
*DNA strand breaking*
- This mechanism is associated with agents like **etoposide** (a topoisomerase inhibitor) or **bleomycin** (which generates free radicals causing DNA strand breaks).
- While these drugs have various toxicities, they are **not typically associated with peripheral neuropathy** as their primary or most prominent side effect.
*Prevention of nucleotide synthesis*
- This is a broad mechanism shared by many **antimetabolites** (e.g., 5-fluorouracil, hydroxyurea, cytarabine) that interfere with the synthesis of purines or pyrimidines.
- While these agents can cause various adverse effects, **peripheral neuropathy is not a hallmark toxicity** as it is with drugs that target microtubules.
Platinum compounds US Medical PG Question 7: A 7-year-old girl presents with a low-grade fever, lethargy, and fatigue for the past week. The patient’s mother says she also complains of leg pain for the past couple of weeks. No significant past medical history. The patient was born at term via spontaneous transvaginal delivery with no complications. On physical examination, the patient shows generalized pallor. Cervical lymphadenopathy is present. A bone marrow biopsy is performed which confirms the diagnosis of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). The patient is started on a chemotherapy regimen consisting of vincristine, daunorubicin, L-asparaginase, and prednisolone for induction, followed by intrathecal methotrexate for maintenance. Following the 4th cycle of chemotherapy, she develops bilateral ptosis. Physical examination shows a normal pupillary reflex and eye movements. She is started on pyridoxine and pyridostigmine, and, in 7 days, she has complete resolution of the ptosis. Which of the following drugs is most likely associated with this patient’s adverse reaction?
- A. Methotrexate
- B. Daunorubicin
- C. Prednisolone
- D. Pyridoxine
- E. Vincristine (Correct Answer)
Platinum compounds Explanation: ***Vincristine***
- Vincristine is an **antimicrotubule agent** known for causing **peripheral neuropathy**, which can manifest as **cranial nerve palsies**, including ptosis from CN III involvement.
- Vincristine can cause **neuromuscular junction dysfunction** similar to myasthenia gravis, leading to muscle weakness including extraocular muscles.
- The response to **pyridostigmine** (an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor) confirms this mechanism, as it increases acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction.
- **Pyridoxine** (vitamin B6) is used for both prevention and treatment of vincristine-induced neuropathy.
*Methotrexate*
- Methotrexate is an **antifolate** that primarily causes **myelosuppression**, **mucositis**, and **hepatotoxicity**.
- While intrathecal methotrexate can cause neurotoxicity, it typically presents as **meningeal irritation**, **seizures**, or **leukoencephalopathy**, not isolated ptosis.
*Daunorubicin*
- Daunorubicin is an **anthracycline** antibiotic primarily known for **cardiotoxicity** and **myelosuppression**.
- It does not commonly cause **neurological side effects** like ptosis.
*Prednisolone*
- Prednisolone is a **corticosteroid** with side effects including **immunosuppression**, **hyperglycemia**, **osteoporosis**, and **mood changes**.
- It is not directly associated with **neuromuscular side effects** such as isolated ptosis.
*Pyridoxine*
- Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) is used for the **treatment** and **prevention** of vincristine-induced neuropathy, not its causation.
- The patient was started on pyridoxine to *resolve* the ptosis, indicating it is therapeutic for the vincristine-induced neurotoxicity.
Platinum compounds US Medical PG Question 8: A 67-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for a decline in his hearing that he noticed over the past week. The patient has a past medical history of hypertension and diabetes mellitus and was recently diagnosed with bladder cancer which is currently appropriately being treated. The patient is a hunter and often goes shooting in his spare time. His recent sick contacts include his grandson who is being treated with amoxicillin for ear pain. Physical exam is notable for decreased hearing bilaterally. The Weber test does not localize to either ear, and the Rinne test demonstrates air conduction is louder than bone conduction. Which of the following is the most likely etiology for this patient's hearing loss?
- A. Otitis externa
- B. Presbycusis
- C. Otosclerosis
- D. Medication regimen (Correct Answer)
- E. Otitis media
Platinum compounds Explanation: ***Medication regimen***
- The patient's history of bladder cancer treatment suggests recent exposure to **chemotherapeutic agents**, such as **cisplatin**, which are known to be **ototoxic**.
- A **sudden decline in hearing** over the past week points to an acute cause, such as drug-induced hearing loss.
*Otitis externa*
- This condition typically presents with **ear pain**, **pruritus**, and **discharge**, none of which are mentioned in the patient's presentation.
- The **Weber and Rinne test results** (normal AC > BC, no lateralization) are inconsistent with a conductive hearing loss typically associated with otitis externa.
*Presbycusis*
- **Presbycusis** is an age-related **sensorineural hearing loss** that typically develops **gradually over years**, not suddenly over a week.
- While the patient's age (67) is a risk factor, the acute onset makes this diagnosis less likely.
*Otosclerosis*
- **Otosclerosis** usually causes a **progressive conductive hearing loss**, often starting in young adulthood.
- The **Weber and Rinne test results** (normal AC > BC, no lateralization) are inconsistent with a conductive hearing loss.
*Otitis media*
- **Otitis media** typically presents with **ear pain**, **fullness**, and often **fever** or **discharge**, which are absent in this patient.
- The **Weber and Rinne test results** (normal AC > BC, no lateralization) are inconsistent with the conductive hearing loss that would be expected with otitis media.
Platinum compounds US Medical PG Question 9: A hospitalized 70-year-old woman, who recently underwent orthopedic surgery, develops severe thrombocytopenia of 40,000/mm3 during her 7th day of hospitalization. She has no other symptoms and has no relevant medical history. All of the appropriate post-surgery prophylactic measures had been taken. Her labs from the 7th day of hospitalization are shown here:
The complete blood count results are as follows:
Hemoglobin 13 g/dL
Hematocrit 38%
Leukocyte count 8,000/mm3
Neutrophils 54%
Bands 3%
Eosinophils 1%
Basophils 0%
Lymphocytes 33%
Monocytes 7%
Platelet count 40,000/mm3
The coagulation tests are as follows:
Partial thromboplastin time (activated) 85 seconds
Prothrombin time 63 seconds
Reticulocyte count 1.2%
Thrombin time < 2 seconds deviation from control
The lab results from previous days were within normal limits. What is the most likely cause of the thrombocytopenia?
- A. Thrombotic microangiopathy
- B. Myelodysplasia
- C. DIC
- D. Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (Correct Answer)
- E. Immune thrombocytopenia
Platinum compounds Explanation: **Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia**
- The development of **severe thrombocytopenia** (platelet count 40,000/mm3) between **days 5 and 10 of heparin therapy** (day 7 in this case, post-surgery implying heparin prophylaxis) is highly characteristic of **HIT**.
- **Prolonged PTT and PT** are seen due to **heparin's effect** on coagulation, even in the setting of HIT, and **thrombotic events** (though not explicitly stated as occurring, the risk is high) are a hallmark.
*Thrombotic microangiopathy*
- This condition typically presents with **microangiopathic hemolytic anemia** (fragmented red blood cells/schistocytes on blood smear) and **renal dysfunction**, none of which are mentioned here.
- Although it causes thrombocytopenia, the absence of **hemolysis** and **renal involvement** makes it less likely.
*Myelodysplasia*
- This is a bone marrow disorder causing **cytopenias** (low blood cell counts) in one or more cell lines, but it is a **chronic condition** that would not typically manifest acutely on the 7th day of hospitalization like this.
- It doesn't explain the **sudden drop in platelets** in the context of recent surgery and likely heparin exposure.
*DIC*
- **Disseminated intravascular coagulation** usually involves significant **consumption of clotting factors** and platelets, leading to both **bleeding and thrombosis**.
- While it causes thrombocytopenia and prolonged PT/PTT, the **absence of severe bleeding** or overwhelming sepsis/trauma, and the **isolated nature of the thrombocytopenia** (no significant drop in other cell lines or evidence of severe organ dysfunction), make it less likely than HIT in this context. The **normal thrombin time** is also atypical for DIC.
*Immune thrombocytopenia*
- **Immune thrombocytopenia (ITP)** is a diagnosis of exclusion and typically presents with **bleeding manifestations** and can be **acute or chronic**.
- While it causes isolated thrombocytopenia, the **timing of onset 7 days post-surgery and probable heparin exposure** makes HIT a much more specific and common diagnosis in this clinical scenario.
Platinum compounds US Medical PG Question 10: A 74-year-old female with a history of lung adenocarcinoma status post lobectomy, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, congestive heart failure, and diabetic nephropathy presents to clinic complaining of hearing loss. Over the last week, she has noticed that she has had difficulty hearing the telephone or the television. When sitting in a quiet room, she also has noticed a high-pitched ringing in her ears. She denies any vertigo or disequilibrium. Further review reveals ongoing dyspnea on exertion and worsening cough productive of whitish sputum for the last month. The patient was recently discharged from the hospital for a congestive heart failure exacerbation. She lives alone and keeps track of all her medications, but admits that sometimes she gets confused. She has a 20 pack-year tobacco history. Her home medications include aspirin, lisinopril, furosemide, short-acting insulin, and a long-acting ß-agonist inhaler. Two weeks ago she completed a course of salvage chemotherapy with docetaxel and cisplatin. Her tympanic membranes are clear and intact with no signs of trauma or impaction. Auditory testing reveals bilateral hearing impairment to a whispered voice. The Weber test is non-lateralizing. Rinne test is unrevealing.
Hemoglobin: 11.8 g/dL
Leukocyte count: 9,400/mm^3
Platelet count: 450,000/mm^3
Serum (Present visit):
Na+: 134 mEq/L
K+: 3.8 mEq/L
Cl-: 95 mEq/L
HCO3-: 30 mEq/L
BUN: 45 mg/dL
Creatinine: 2.1 mg/dL
Serum (1 month ago):
Na+: 135 mEq/L
K+: 4.6 mEq/L
Cl-: 102 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
BUN: 22 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.2 mg/dL
On follow up visit two weeks later, the patient's hearing has significantly improved. Which of the following is the most likely cause of her initial hearing loss?
- A. Cisplatin
- B. Furosemide (Correct Answer)
- C. Lisinopril
- D. Docetaxel
- E. Aspirin
Platinum compounds Explanation: ***Furosemide***
- The patient's **renal function has worsened** significantly, indicated by the rise in **BUN and creatinine**, making her more susceptible to **ototoxicity** from furosemide due to reduced drug clearance.
- Her recent discharge for **congestive heart failure exacerbation** suggests she was likely on higher doses or had increased exposure to furosemide during hospitalization.
- The **significant improvement in hearing within two weeks** is the key diagnostic feature, as **furosemide-induced ototoxicity is reversible** when the drug is discontinued or the dose is reduced, unlike other ototoxic agents.
- Loop diuretics like furosemide cause ototoxicity by disrupting the ionic balance in the endolymph of the inner ear, but this effect is typically **transient and reversible**.
*Cisplatin*
- **Cisplatin** is a known **ototoxic chemotherapy agent**, and its timing (two weeks post-treatment) fits with the onset of symptoms.
- However, cisplatin-induced ototoxicity is typically **irreversible and permanent**, involving destruction of the **outer hair cells** of the cochlea.
- The **rapid improvement in the patient's hearing** within two weeks makes cisplatin an unlikely cause, as its ototoxicity results in persistent, dose-dependent bilateral sensorineural hearing loss.
*Lisinopril*
- **Lisinopril**, an **ACE inhibitor**, is not associated with **ototoxicity** or hearing loss.
- Its primary mechanisms of action are related to **blood pressure regulation** and **cardiovascular remodeling**, with no direct known impact on auditory function.
*Docetaxel*
- **Docetaxel** is a **taxane chemotherapy drug** that can cause neurological side effects, including **peripheral neuropathy**, but it is not commonly associated with **ototoxicity** or hearing loss.
- The rapid resolution of hearing loss makes ototoxicity from docetaxel improbable.
*Aspirin*
- **Aspirin** can cause **reversible ototoxicity** (tinnitus and hearing loss), particularly at high doses (typically >3 g/day) in a condition called **salicylism**.
- However, the patient's hearing loss is more directly attributable to **furosemide** given the context of recent CHF exacerbation requiring aggressive diuretic therapy and worsening renal function that would increase furosemide levels.
More Platinum compounds US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.