Antimetabolites US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Antimetabolites. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
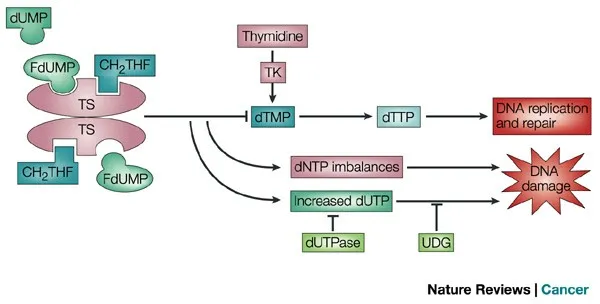
Antimetabolites US Medical PG Question 1: A 54-year-old woman with metastatic breast cancer comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. She had a mastectomy 6 months ago and received chemotherapy with doxorubicin and paclitaxel. A CT scan of the chest shows new metastases in the lungs and liver. Adjuvant therapy is initiated with a drug that inhibits the formation of deoxythymidine monophosphate and results in the accumulation of deoxyuridine triphosphate. The patient is advised to avoid folic acid supplementation while receiving this drug in order to prevent the toxic effects of this drug. Which of the following drugs was most likely given?
- A. Leflunomide
- B. Capecitabine (Correct Answer)
- C. Mycophenolate mofetil
- D. Hydroxyurea
- E. Azathioprine
Antimetabolites Explanation: Capecitabine
- Capecitabine is a **prodrug of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)**, which inhibits **thymidylate synthase**, thereby blocking the formation of **deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP)** from deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) [1], [2].
- This leads to the accumulation of **deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP)** and depletion of deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP), disrupting DNA synthesis [2].
- The instruction to avoid **folic acid supplementation** is important because excessive folate can potentially reduce the drug's efficacy by providing alternative pathways for nucleotide synthesis, though leucovorin (folinic acid) is sometimes given WITH 5-FU to enhance its binding to thymidylate synthase in certain chemotherapy regimens [1], [2].
- Commonly used in **metastatic breast cancer** and colorectal cancer [3].
*Hydroxyurea*
- Inhibits **ribonucleotide reductase**, preventing the conversion of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides needed for DNA synthesis.
- Affects all deoxyribonucleotides (not specifically dTMP), and does not cause dUTP accumulation.
- Used in **sickle cell disease**, chronic myeloid leukemia, and polycythemia vera.
*Mycophenolate mofetil*
- An **immunosuppressant** that inhibits **inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH)**, blocking de novo **guanine nucleotide synthesis**.
- Does not affect thymidylate synthase or pyrimidine metabolism.
- Used to prevent **organ transplant rejection** and in autoimmune diseases.
*Leflunomide*
- An **immunosuppressant** that inhibits **dihydroorotate dehydrogenase**, blocking de novo **pyrimidine synthesis** at an earlier step than thymidylate synthase.
- Does not specifically inhibit dTMP formation or cause dUTP accumulation.
- Primarily used in **rheumatoid arthritis**.
*Azathioprine*
- An **immunosuppressant** that acts as a prodrug for 6-mercaptopurine, interfering with **purine synthesis** (adenine and guanine pathways).
- Does not affect pyrimidine metabolism or thymidylate synthase.
- Used in transplant recipients and autoimmune diseases.
Antimetabolites US Medical PG Question 2: A 67-year-old woman with advanced bladder cancer comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. She is currently undergoing chemotherapy with an agent that forms cross-links between DNA strands. Serum studies show a creatinine concentration of 2.1 mg/dL and a blood urea nitrogen concentration of 30 mg/dL. Urine dipstick of a clean-catch midstream specimen shows 2+ protein and 1+ glucose. Prior to initiation of chemotherapy, her laboratory values were within the reference range. In addition to hydration, administration of which of the following would most likely have prevented this patient's current condition?
- A. Leucovorin
- B. Amifostine (Correct Answer)
- C. Aprepitant
- D. Mesna
- E. Rasburicase
Antimetabolites Explanation: **Amifostine**
- This patient's symptoms (elevated creatinine and BUN, 2+ protein, 1+ glucose in urine) suggest **renal tubular damage**, specifically acute tubular necrosis, likely caused by a nephrotoxic chemotherapeutic agent.
- **Amifostine** is a cytoprotective agent that scavenges reactive oxygen species in local tissues, thereby reducing the nephrotoxic effects of **alkylating agents** like cisplatin, which forms cross-links between DNA strands.
*Leucovorin*
- **Leucovorin** (folinic acid) is used to rescue normal cells from the adverse effects of **methotrexate**, enhancing its excretion and reducing toxicity.
- It is not indicated for preventing kidney damage from DNA cross-linking agents.
*Aprepitant*
- **Aprepitant** is a neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor antagonist used to prevent **chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting**.
- It does not have protective effects against nephrotoxicity.
*Mesna*
- **Mesna** (2-mercaptoethane sulfonate sodium) is used to prevent **hemorrhagic cystitis** caused by acrolein, a toxic metabolite of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide.
- It does not prevent nephrotoxicity from other types of chemotherapy agents.
*Rasburicase*
- **Rasburicase** is a recombinant urate oxidase enzyme used to prevent or treat **tumor lysis syndrome** by converting uric acid to allantoin, which is more soluble and easily excreted.
- It is not used for preventing direct kidney damage from chemotherapeutic agents.
Antimetabolites US Medical PG Question 3: A 24-year-old woman of Ashkenazi Jewish descent presents with recurrent bloody diarrhea and abdominal pain. She says she feels well otherwise. Review of systems is significant for a 4 kg weight loss over the past month. Physical examination is significant for multiple aphthous oral ulcers. Colonoscopy reveals a cobblestone pattern of lesions of the mucosa of the intestinal wall with skip lesions involving the terminal ileum and colon. The patient is informed of the diagnosis and medication to treat her condition is prescribed. On a follow-up visit 6 weeks later, the patient presents with non-productive cough, chest pain, dyspnea on exertion, and worsening oral lesions. A chest radiograph reveals a diffuse interstitial pattern. Which of the following enzymes is inhibited by the medication most likely prescribed for her initial diagnosis?
- A. Thymidine kinase
- B. DNA polymerase
- C. Dihydrofolate reductase (Correct Answer)
- D. Hypoxanthine guanine-phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT)
- E. Thymidylate synthase
Antimetabolites Explanation: ***Dihydrofolate reductase***
- The patient's initial symptoms (recurrent **bloody diarrhea**, **abdominal pain**, **weight loss**, **oral ulcers**, **cobblestone pattern** of lesions in the sigmoid colon) are highly suggestive of **Crohn's disease**. The patient's **Ashkenazi Jewish descent** is also a risk factor for Crohn's disease.
- The worsening oral lesions, cough, chest pain, and **diffuse interstitial pattern** on chest radiograph 6 weeks later are classic signs of **methotrexate toxicity**. Methotrexate, a common treatment for Crohn's disease, inhibits **dihydrofolate reductase**, an enzyme essential for **folate metabolism** and **DNA synthesis**.
*Thymidine kinase*
- **Thymidine kinase** is an enzyme involved in the salvage pathway of pyrimidine synthesis. It is typically inhibited by antiviral drugs like **acyclovir** and **ganciclovir**, which are not used for Crohn's disease.
- Inhibition of thymidine kinase is not associated with the lung and oral toxicities seen in this patient.
*DNA polymerase*
- **DNA polymerase** is crucial for DNA replication and repair. Drugs inhibiting DNA polymerase, such as some **antivirals** (e.g., foscarnet) and **chemotherapeutics** (e.g., cytarabine), are not primary treatments for Crohn's disease.
- Inhibition of DNA polymerase does not directly lead to the specific constellation of symptoms observed from methotrexate toxicity.
*Hypoxanthine guanine-phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT)*
- **HGPRT** is an enzyme central to the purine salvage pathway. Its deficiency leads to **Lesch-Nyhan syndrome**.
- While some immunosuppressants like **azathioprine** and **mercaptopurine** act as purine analogs and affect purine metabolism, they do not directly inhibit HGPRT and do not typically cause the acute pulmonary toxicity seen with methotrexate.
*Thymidylate synthase*
- **Thymidylate synthase** is an enzyme involved in the synthesis of pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotides, particularly dTMP, which is essential for DNA synthesis. It is a target for some **chemotherapeutic agents** like **5-fluorouracil**.
- While methotrexate indirectly affects thymidylate synthesis by depleting folate precursors, its direct mechanism of action is the inhibition of **dihydrofolate reductase**, not thymidylate synthase itself, and 5-fluorouracil toxicity differs from the presented symptoms.
Antimetabolites US Medical PG Question 4: A 9-month-old boy is brought to the pediatrician because he cannot sit on his own without support and has involuntary movements. He was born vaginally with no complications at full term. There is no history of consanguinity among parents. On physical examination, it was noticed that he is a stunted infant with generalized hypotonia and severe generalized dystonic movements. The mother says that she has noticed the presence of orange sand in his diapers many times. Laboratory evaluation revealed elevated uric acid levels in both blood and urine. Which of the following enzymes is deficient in this patient?
- A. Ribonucleotide reductase
- B. Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase
- C. Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase
- D. Dihydrofolate reductase
- E. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (Correct Answer)
Antimetabolites Explanation: ***Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT)***
- The clinical presentation describes classic **Lesch-Nyhan syndrome**: developmental delay, dystonia, hyperuricemia, and orange crystals (uric acid) in diapers.
- Lesch-Nyhan syndrome is caused by **deficiency of HGPRT**, an enzyme in the **purine salvage pathway**.
- HGPRT normally converts hypoxanthine to IMP and guanine to GMP, recycling purine bases.
- Without HGPRT, purines cannot be salvaged and are degraded to uric acid, causing hyperuricemia.
- Treatment includes allopurinol (xanthine oxidase inhibitor) to reduce uric acid production.
- X-linked recessive inheritance affects males primarily.
*Ribonucleotide reductase*
- This enzyme converts ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides for DNA synthesis.
- Not involved in purine salvage or degradation pathways.
- Deficiency would affect DNA synthesis globally, not specifically purine metabolism.
*Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase*
- Converts IMP to XMP in the de novo purine synthesis pathway.
- Inhibited by mycophenolate (immunosuppressant), not deficient in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
*Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase*
- Enzyme in de novo pyrimidine synthesis pathway.
- Deficiency causes orotic aciduria with megaloblastic anemia and developmental delay, but not hyperuricemia or dystonia.
*Dihydrofolate reductase*
- Essential for tetrahydrofolate synthesis, required for purine and pyrimidine synthesis.
- Target of methotrexate, not deficient in this condition.
Antimetabolites US Medical PG Question 5: A 60-year-old female presents to her gynecologist with bloating, abdominal discomfort, and fatigue. She has a history of hypertension and takes hydrochlorothiazide. Physical exam reveals ascites and right adnexal tenderness. Initial imaging reveals a mass in the right ovary and eventual biopsy of the mass reveals ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma. She is started on a chemotherapeutic agent with plans for surgical resection. Soon after starting the medication, she develops dysuria and hematuria. Laboratory analysis of her urine is notable for the presence of a cytotoxic metabolite. Which of the following mechanisms of action is consistent with the medication in question?
- A. Folate analog
- B. Microtubule inhibitor
- C. DNA alkylating agent (Correct Answer)
- D. Platinum-based DNA cross-linking agent
- E. BRAF inhibitor
Antimetabolites Explanation: ***DNA alkylating agent***
- Cyclophosphamide is a **DNA alkylating agent** commonly used in the treatment of ovarian cancer. It is metabolized to **acrolein**, a cytotoxic metabolite that causes **hemorrhagic cystitis**, presenting as dysuria and hematuria.
- DNA alkylating agents exert their cytotoxic effects by forming **covalent bonds** with DNA, leading to DNA damage, cross-linking, and subsequent inhibition of DNA replication and transcription, ultimately inducing **apoptosis** in rapidly dividing cancer cells.
*Folate analog*
- Folate analogs like **methotrexate** inhibit **dihydrofolate reductase**, interfering with DNA synthesis by depleting tetrahydrofolate, a crucial cofactor for nucleotide synthesis.
- While they are chemotherapeutic agents, they do not typically cause hemorrhagic cystitis; their common side effects include **myelosuppression**, mucositis, and hepatotoxicity.
*Microtubule inhibitor*
- Microtubule inhibitors such as **paclitaxel** and **vincristine** interfere with microtubule formation or breakdown, disrupting cell division (mitosis).
- Common side effects include **neuropathy** and myelosuppression, but not hemorrhagic cystitis.
*Platinum-based DNA cross-linking agent*
- Platinum-based drugs like **cisplatin** and **carboplatin** are often used for ovarian cancer and cause nephrotoxicity, neurotoxicity, and ototoxicity.
- They form **DNA adducts and interstrand cross-links**, inhibiting DNA replication and transcription, but do not directly cause acrolein-induced hemorrhagic cystitis.
*BRAF inhibitor*
- BRAF inhibitors (e.g., **vemurafenib**) are **targeted therapies** used in cancers with specific mutations, such as BRAF-mutated melanoma.
- They inhibit the BRAF kinase in the MAPK signaling pathway, and while effective in specific contexts, they are not typically associated with hemorrhagic cystitis.
Antimetabolites US Medical PG Question 6: A 32-year-old female presents to her gynecologist complaining of heavy and irregular vaginal bleeding. One month ago, she underwent a dilation and curettage procedure to remove a hydatidiform mole. On examination, her uterus appears enlarged. Serum ß-hCG is highly elevated. Biopsy of her uterus reveals avillous proliferation of cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts. She is eventually diagnosed with choriocarcinoma and initiates treatment with a medication known to affect folate metabolism. Which of the following complications should this patient most likely be monitored for following initiation of the medication?
- A. Hemorrhagic cystitis
- B. Pulmonary fibrosis
- C. Peripheral neuropathy
- D. Cardiotoxicity
- E. Bone marrow suppression (Correct Answer)
Antimetabolites Explanation: ***Bone marrow suppression***
- The medication affecting folate metabolism used for choriocarcinoma is **methotrexate**, a folate antagonist that inhibits dihydrofolate reductase.
- **Myelosuppression (bone marrow suppression)** is the **most common and clinically significant dose-limiting toxicity** of methotrexate, manifesting as pancytopenia with decreased white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets.
- Patients on methotrexate require **routine complete blood count (CBC) monitoring** before and during treatment to detect myelosuppression early.
- Other important methotrexate toxicities include hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and mucositis, but bone marrow suppression is the primary concern requiring close monitoring.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- While methotrexate can rarely cause pulmonary toxicity, it typically presents as **acute pneumonitis** (hypersensitivity reaction) rather than chronic fibrosis.
- Pulmonary toxicity occurs in <10% of patients and is more commonly associated with chronic low-dose methotrexate use (e.g., for rheumatoid arthritis) than high-dose chemotherapy.
- This is not the most likely complication requiring routine monitoring.
*Hemorrhagic cystitis*
- **Hemorrhagic cystitis** is a characteristic complication of **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide**, not methotrexate.
- It results from toxic metabolite (acrolein) accumulation in the bladder and can be prevented with hydration and mesna.
*Peripheral neuropathy*
- **Peripheral neuropathy** is typically associated with **vinca alkaloids** (vincristine, vinblastine) and **taxanes** (paclitaxel, docetaxel), which disrupt microtubule function.
- Methotrexate does not cause peripheral neuropathy as a primary toxicity.
*Cardiotoxicity*
- **Cardiotoxicity**, including dilated cardiomyopathy, is a well-known dose-dependent complication of **anthracyclines** (doxorubicin, daunorubicin).
- Methotrexate is not associated with direct cardiac toxicity.
Antimetabolites US Medical PG Question 7: A 62-year-old woman presents to her oncologist to discuss the chemotherapy options for her newly diagnosed breast cancer. During the meeting, they discuss a drug that inhibits the breakdown of mitotic spindles in cells. Her oncologist explains that this will be more toxic to cancer cells because those cells are dividing more rapidly. Which of the following side effects is closely associated with the use of this chemotherapeutic agent?
- A. Photosensitivity
- B. Peripheral neuropathy (Correct Answer)
- C. Paralytic ileus
- D. Hemorrhagic cystitis
- E. Pulmonary fibrosis
Antimetabolites Explanation: ***Peripheral neuropathy***
- Drugs that inhibit the breakdown of **mitotic spindles** are **microtubule-targeting agents** (e.g., **taxanes** like paclitaxel/docetaxel, **vinca alkaloids** like vincristine/vinblastine).
- These agents interfere with **microtubule function** in neurons, leading to **axonal damage** and **peripheral neuropathy**.
- This is the **most characteristic and common dose-limiting toxicity** of microtubule inhibitors, affecting sensory and motor nerves (numbness, tingling, weakness in extremities).
*Photosensitivity*
- **Photosensitivity** is a common adverse effect associated with certain chemotherapeutic agents like **fluorouracil** (5-FU) or **methotrexate**, but is not linked to microtubule inhibitors.
- It involves an increased sensitivity to UV light, often manifesting as a rash or exaggerated sunburn.
*Paralytic ileus*
- **Paralytic ileus** can occur with **vinca alkaloids** (especially vincristine) due to autonomic neuropathy affecting the **enteric nervous system**.
- However, this is **less common** than peripheral neuropathy and occurs more specifically with vincristine rather than taxanes.
- **Peripheral neuropathy** is the more pervasive, dose-limiting, and universally characteristic side effect across all microtubule inhibitors.
*Hemorrhagic cystitis*
- **Hemorrhagic cystitis** is a classic side effect of **alkylating agents** like **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide**, which produce the toxic metabolite **acrolein**.
- It is prevented/managed with **mesna**, which inactivates acrolein.
- Not associated with microtubule inhibitors.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is a known side effect of certain chemotherapeutic drugs, most notably **bleomycin** and **busulfan**.
- This adverse effect is not associated with agents that target **mitotic spindle breakdown**.
Antimetabolites US Medical PG Question 8: An 18-month-old boy is brought to the physician because of walking difficulties. His mother says that he cannot walk unless he is supported. She has also noted orange, sandy residues in his diapers. Over the past year, she has frequently caught him pulling his toenails and chewing the tips of his fingers. Examination shows scarring of his fingertips. Muscle tone is decreased in the upper and lower extremities. He cannot pick up and hold small objects between the tips of the index finger and the thumb. The most appropriate pharmacotherapy for this patient's condition inhibits which of the following conversions?
- A. Hypoxanthine to inosine monophosphate
- B. Adenosine to inosine
- C. Ornithine to citrulline
- D. Orotate to uridine monophosphate
- E. Xanthine to urate (Correct Answer)
Antimetabolites Explanation: ***Xanthine to urate***
- The patient's symptoms (developmental delay, self-mutilation, hypotonia, orange sandy residues in diapers) are classic for **Lesch-Nyhan syndrome**, which is caused by a deficiency of **hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT)**.
- This deficiency leads to increased production of uric acid; the most appropriate pharmacotherapy is **allopurinol**, which inhibits **xanthine oxidase**, thereby blocking the conversion of xanthine to urate and reducing uric acid levels.
*Hypoxanthine to inosine monophosphate*
- This conversion is part of the **salvage pathway** catalyzed by **HGPRT**, which is deficient in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
- Inhibiting this step would worsen the underlying deficiency and is not a therapeutic strategy for this condition.
*Adenosine to inosine*
- This conversion is catalyzed by **adenosine deaminase (ADA)**. A deficiency in ADA leads to **severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID)**, not Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
- While ADA deficiency involves purine metabolism, its clinical presentation and treatment are distinct.
*Ornithine to citrulline*
- This step is part of the **urea cycle**, catalyzed by **ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC)**.
- Deficiency in OTC results in **hyperammonemia** and neurological symptoms, but not the specific features of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome like self-mutilation or hyperuricemia.
*Orotate to uridine monophosphate*
- This conversion is involved in **pyrimidine synthesis**, catalyzed by **uridine monophosphate synthase**.
- A defect in this pathway leads to **orotic aciduria**, characterized by megaloblastic anemia and growth retardation, which is different from the presentation of Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
Antimetabolites US Medical PG Question 9: A 67-year-old woman who was diagnosed with cancer 2 months ago presents to her oncologist with a 6-day history of numbness and tingling in her hands and feet. She is concerned that these symptoms may be related to progression of her cancer even though she has been faithfully following her chemotherapy regimen. She is not currently taking any other medications and has never previously experienced these symptoms. On physical exam, she is found to have decreased sensation to pinprick and fine touch over hands, wrists, ankles, and feet. Furthermore, she is found to have decreased reflexes throughout. Her oncologist assures her that these symptoms are a side effect from her chemotherapy regimen rather than progression of the cancer. The drug most likely responsible for her symptoms has which of the following mechanisms?
- A. Alkylation of DNA
- B. Inhibit folate metabolism
- C. DNA strand breaking
- D. Inhibit microtubule formation (Correct Answer)
- E. Prevention of nucleotide synthesis
Antimetabolites Explanation: ***Inhibit microtubule formation***
- The patient's symptoms of **numbness**, **tingling**, **decreased sensation** to pinprick and fine touch in a **stocking-glove distribution**, and **decreased reflexes** are characteristic of **peripheral neuropathy**.
- **Vinca alkaloids** (e.g., vincristine) and **taxanes** (e.g., paclitaxel, docetaxel) are chemotherapy agents that **inhibit microtubule formation**, and **peripheral neuropathy is their classic dose-limiting toxicity**.
- These agents are the **most strongly associated** with this specific adverse effect pattern among chemotherapy drugs.
*Alkylation of DNA*
- **Alkylating agents** (e.g., cyclophosphamide) and **platinum-based agents** (e.g., cisplatin, oxaliplatin) exert their cytotoxic effects by **cross-linking DNA strands**, preventing DNA replication and transcription.
- While **cisplatin and oxaliplatin can cause significant peripheral neuropathy**, the **microtubule inhibitors** (vinca alkaloids and taxanes) are **more classically associated** with this side effect and are the expected answer in this clinical context.
*Inhibit folate metabolism*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **antimetabolites** like **methotrexate**, which **inhibits dihydrofolate reductase**, thereby disrupting DNA synthesis.
- While methotrexate can have neurological side effects (particularly intrathecal administration causing neurotoxicity), **typical peripheral neuropathy is not its most common or direct adverse effect** related to this mechanism.
*DNA strand breaking*
- This mechanism is associated with agents like **etoposide** (a topoisomerase inhibitor) or **bleomycin** (which generates free radicals causing DNA strand breaks).
- While these drugs have various toxicities, they are **not typically associated with peripheral neuropathy** as their primary or most prominent side effect.
*Prevention of nucleotide synthesis*
- This is a broad mechanism shared by many **antimetabolites** (e.g., 5-fluorouracil, hydroxyurea, cytarabine) that interfere with the synthesis of purines or pyrimidines.
- While these agents can cause various adverse effects, **peripheral neuropathy is not a hallmark toxicity** as it is with drugs that target microtubules.
Antimetabolites US Medical PG Question 10: A 50-year-old woman presents to the clinic with joint pain that has persisted for the last 2 months. She reports having intermittently swollen, painful hands bilaterally. She adds that when she wakes up in the morning, her hands are stiff and do not loosen up until an hour later. The pain tends to improve with movement. Physical examination is significant for warm, swollen, tender proximal interphalangeal joints, metacarpophalangeal joints, and wrists bilaterally. Laboratory results are positive for rheumatoid factor (4-fold greater than the upper limit of normal (ULN)) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (anti-CCP) antibodies (3-fold greater than ULN). CRP and ESR are elevated. Plain X-rays of the hand joints show periarticular osteopenia and bony erosions. She was started on the first-line drug for her condition which inhibits dihydrofolate reductase. Which medication was this patient started on?
- A. Hydroxyurea
- B. Allopurinol
- C. Methotrexate (Correct Answer)
- D. 5-fluorouracil
- E. Leflunomide
Antimetabolites Explanation: ***Methotrexate***
- The patient's clinical presentation (symmetrical polyarthritis, morning stiffness, elevated inflammatory markers, positive **rheumatoid factor**, and **anti-CCP antibodies**) is classic for **rheumatoid arthritis (RA)**.
- **Methotrexate** is the **first-line disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD)** for RA and acts by inhibiting **dihydrofolate reductase**, thereby interfering with purine and pyrimidine synthesis.
*Hydroxyurea*
- **Hydroxyurea** is an antineoplastic agent that works by inhibiting **ribonucleotide reductase**, not dihydrofolate reductase.
- It is primarily used in conditions like **myeloproliferative disorders** (e.g., chronic myeloid leukemia, polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia) and **sickle cell disease**, not rheumatoid arthritis.
*Allopurinol*
- **Allopurinol** is a **xanthine oxidase inhibitor** used to reduce **uric acid production** in conditions like **gout and tumor lysis syndrome**.
- It is not indicated for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, nor does it inhibit dihydrofolate reductase.
*5-fluorouracil*
- **5-fluorouracil** is a **pyrimidine analog** that inhibits **thymidylate synthase** (after being metabolized to 5-FdUMP), primarily used in **chemotherapy for various cancers**, especially gastrointestinal malignancies.
- It does not inhibit dihydrofolate reductase and is not used to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
*Leflunomide*
- **Leflunomide** is another DMARD used for rheumatoid arthritis, but it inhibits **dihydroorotate dehydrogenase**, an enzyme involved in *de novo pyrimidine synthesis*, not dihydrofolate reductase.
- While it is a treatment for RA, it is not the medication that acts specifically by inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase.
More Antimetabolites US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.