Alkylating agents US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Alkylating agents. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Alkylating agents US Medical PG Question 1: A 72-year-old man has been recently diagnosed with stage 3 squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. After the necessary laboratory workup, concurrent chemoradiation therapy has been planned. Radiation therapy is planned to take place over 7 weeks and he will receive radiation doses daily, Monday–Friday, in 2.0 Gy fractions. For concurrent chemotherapy, he will receive intravenous cisplatin at a dosage of 50 mg/m2 weekly for 7 weeks. Which of the following best explains the mechanism of action of the antineoplastic drug that the patient will receive?
- A. Free radical-mediated lipid peroxidation
- B. Inhibition of polymerization of tubulin
- C. Inhibition of topoisomerase 1
- D. Inhibition of topoisomerase 2
- E. Formation of interstrand DNA cross-links (Correct Answer)
Alkylating agents Explanation: ***Formation of interstrand DNA cross-links***
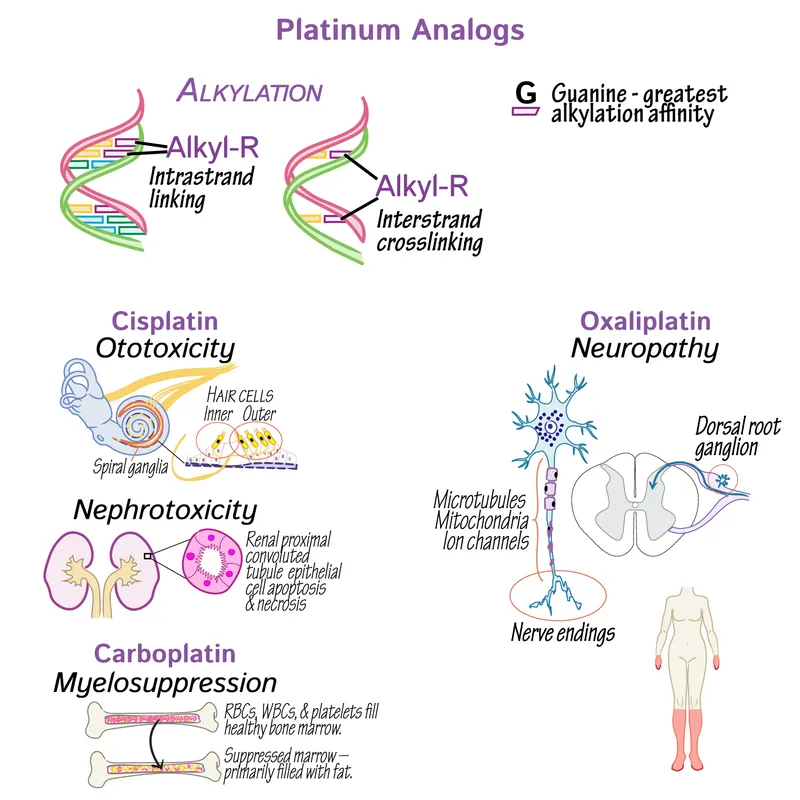
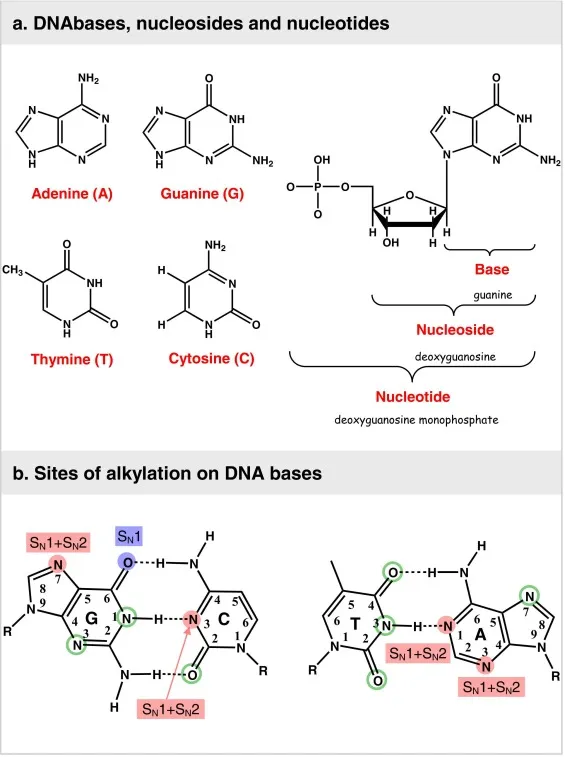
- **Cisplatin** is a **platinum-based chemotherapeutic agent** that acts by forming **interstrand and intrastrand DNA cross-links**.
- These cross-links interfere with **DNA replication and transcription**, leading to **DNA damage** and ultimately **apoptosis** in cancer cells.
*Free radical-mediated lipid peroxidation*
- While some chemotherapeutic agents, like **anthracyclines**, can induce **free radical formation** and subsequent damage, this is not the primary mechanism of action for cisplatin.
- **Lipid peroxidation** primarily affects cell membranes, whereas cisplatin's main target is DNA.
*Inhibition of polymerization of tubulin*
- This mechanism of action is characteristic of **vinca alkaloids** (e.g., vincristine, vinblastine) and **taxanes** (e.g., paclitaxel, docetaxel), which disrupt microtubule formation and function.
- Cisplatin does not target **tubulin polymerization**.
*Inhibition of topoisomerase 1*
- **Topoisomerase 1 inhibitors** such as **irinotecan** and **topotecan** prevent DNA unwinding by stabilizing the cleavable complex, leading to DNA breaks.
- This is not how cisplatin exerts its therapeutic effects.
*Inhibition of topoisomerase 2*
- **Topoisomerase 2 inhibitors** like **etoposide** and **doxorubicin** interfere with DNA replication and repair by preventing the religation of DNA strands.
- Cisplatin's mechanism is distinct from topoisomerase inhibition.
Alkylating agents US Medical PG Question 2: A 71-year-old man with colorectal cancer comes to the physician for follow-up examination after undergoing a sigmoid colectomy. The physician recommends adjuvant chemotherapy with an agent that results in single-stranded DNA breaks. This chemotherapeutic agent most likely has an effect on which of the following enzymes?
- A. DNA polymerase III
- B. Topoisomerase I (Correct Answer)
- C. Helicase
- D. Telomerase
- E. Topoisomerase II
Alkylating agents Explanation: ***Topoisomerase I***
- **Topoisomerase I** creates **single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) breaks** to relieve torsional stress during DNA replication and transcription.
- Many chemotherapeutic agents, such as camptothecin and its derivatives (e.g., irinotecan, topotecan), target topoisomerase I, leading to DNA damage and apoptosis in cancer cells.
*DNA polymerase III*
- **DNA polymerase III** is primarily involved in bacterial DNA replication, synthesizing new DNA strands in a 5' to 3' direction.
- While essential for bacterial survival, it is not the target of chemotherapeutic agents that induce single-stranded DNA breaks in human cells.
*Helicase*
- **Helicase** is responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix during replication and transcription, separating the two strands.
- While its function is critical for DNA processes, it does not directly create DNA breaks as its primary mechanism of action.
*Telomerase*
- **Telomerase** is an enzyme that maintains telomere length at the ends of chromosomes, particularly active in cancer cells.
- Inhibitors of telomerase aim to shorten telomeres, leading to cellular senescence or apoptosis, but they do not primarily cause single-stranded DNA breaks.
*Topoisomerase II*
- **Topoisomerase II** creates **double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) breaks** to untangle and decatenate DNA.
- Though also a target for chemotherapy (e.g., etoposide, doxorubicin), its mechanism involves double-stranded breaks, not single-stranded breaks as specified in the question.
Alkylating agents US Medical PG Question 3: A 60-year-old female presents to her primary care physician complaining of bloating and fatigue over the past year. On examination, she has abdominal distension and ascites. Abdominal imaging reveals a mass-like lesion affecting the left ovary. A biopsy of the lesion demonstrates serous cystadenocarcinoma. She is subsequently started on a chemotherapeutic medication known to stabilize polymerized microtubules. Which of the following complications should this patient be monitored for following initiation of this medication?
- A. Peripheral neuropathy (Correct Answer)
- B. Pulmonary fibrosis
- C. Acoustic nerve damage
- D. Hemorrhagic cystitis
- E. Cardiotoxicity
Alkylating agents Explanation: ***Peripheral neuropathy***
- The chemotherapeutic medication described, which stabilizes **polymerized microtubules**, is likely a **taxane** (e.g., paclitaxel, docetaxel), often used for ovarian cancer.
- Taxanes are well-known to cause **dose-dependent peripheral neuropathy** due to their effects on microtubule dynamics in neuronal axons.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is a significant side effect associated with certain chemotherapeutic agents like **bleomycin** or **busulfan**, but not typically with taxanes.
- Monitoring for this would involve assessing breath sounds, oxygen saturation, and potentially imaging for interstitial changes.
*Acoustic nerve damage*
- **Acoustic nerve damage** and ototoxicity are characteristic side effects of **platinum-based chemotherapy agents** (e.g., cisplatin), which are also used in ovarian cancer but have a different mechanism of action than microtubule stabilizers.
- This typically manifests as **tinnitus** or **hearing loss**.
*Hemorrhagic cystitis*
- **Hemorrhagic cystitis** is a common and severe side effect of **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide**, alkylating agents, due to the accumulation of their metabolite **acrolein** in the bladder.
- It is not associated with microtubule-stabilizing agents like taxanes.
*Cardiotoxicity*
- **Cardiotoxicity**, including dilated cardiomyopathy, is a serious side effect primarily associated with **anthracyclines** (e.g., doxorubicin), which generate free radicals and damage cardiac myocytes.
- While some taxanes can cause cardiovascular effects, severe cardiotoxicity like that seen with anthracyclines is not their primary or most concerning side effect.
Alkylating agents US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-month history of progressive back pain. He has also had a 5-kg (11-lb) weight loss over the past 3 months. His only medications are a daily multivitamin and ibuprofen, which he takes daily for the back pain. Physical examination shows tenderness to palpation over the lower spine and the left iliac crest. His hemoglobin concentration is 9.3 g/dL, his serum calcium concentration is 12 mg/dL, and his serum creatinine concentration is 2.1 mg/dL. A bone marrow biopsy shows 21% plasma cells. A diagnosis of multiple myeloma is established. In preparation for an autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, the patient receives a myeloablative treatment regimen that includes busulfan. Which of the following drugs acts via a similar mechanism of action to busulfan?
- A. Etoposide
- B. Vemurafenib
- C. Vincristine
- D. Cytarabine
- E. Lomustine (Correct Answer)
Alkylating agents Explanation: ***Lomustine***
- Both **busulfan** and **lomustine** are **alkylating agents**. They act by transferring **alkyl groups** to DNA, leading to cross-linking of DNA strands and inhibition of DNA synthesis and function.
- This **DNA damage** results in cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, particularly in rapidly dividing cells like cancer cells.
*Etoposide*
- **Etoposide** is a **topoisomerase II inhibitor** that prevents DNA relegation after strand breaks, leading to DNA damage and cell death.
- While it also targets DNA, its mechanism is distinct from the alkylation process of busulfan.
*Vemurafenib*
- **Vemurafenib** is a **BRAF kinase inhibitor** used in melanoma treatment. It specifically targets the **BRAF V600E mutation**.
- Its mechanism involves blocking signal transduction pathways critical for cell proliferation, rather than directly damaging DNA.
*Vincristine*
- **Vincristine** is a **vinca alkaloid** that acts as a **microtubule inhibitor**, preventing the formation of the **mitotic spindle** during cell division.
- This leads to metaphase arrest and apoptosis, a mechanism fundamentally different from DNA alkylation.
*Cytarabine*
- **Cytarabine** is an **antimetabolite**, specifically a **pyrimidine analog**, that inhibits **DNA polymerase**.
- It gets incorporated into DNA, leading to chain termination and inhibition of DNA synthesis and repair, making its action different from direct DNA alkylation.
Alkylating agents US Medical PG Question 5: A 32-year-old female presents to her gynecologist complaining of heavy and irregular vaginal bleeding. One month ago, she underwent a dilation and curettage procedure to remove a hydatidiform mole. On examination, her uterus appears enlarged. Serum ß-hCG is highly elevated. Biopsy of her uterus reveals avillous proliferation of cytotrophoblasts and syncytiotrophoblasts. She is eventually diagnosed with choriocarcinoma and initiates treatment with a medication known to affect folate metabolism. Which of the following complications should this patient most likely be monitored for following initiation of the medication?
- A. Hemorrhagic cystitis
- B. Pulmonary fibrosis
- C. Peripheral neuropathy
- D. Cardiotoxicity
- E. Bone marrow suppression (Correct Answer)
Alkylating agents Explanation: ***Bone marrow suppression***
- The medication affecting folate metabolism used for choriocarcinoma is **methotrexate**, a folate antagonist that inhibits dihydrofolate reductase.
- **Myelosuppression (bone marrow suppression)** is the **most common and clinically significant dose-limiting toxicity** of methotrexate, manifesting as pancytopenia with decreased white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets.
- Patients on methotrexate require **routine complete blood count (CBC) monitoring** before and during treatment to detect myelosuppression early.
- Other important methotrexate toxicities include hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and mucositis, but bone marrow suppression is the primary concern requiring close monitoring.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- While methotrexate can rarely cause pulmonary toxicity, it typically presents as **acute pneumonitis** (hypersensitivity reaction) rather than chronic fibrosis.
- Pulmonary toxicity occurs in <10% of patients and is more commonly associated with chronic low-dose methotrexate use (e.g., for rheumatoid arthritis) than high-dose chemotherapy.
- This is not the most likely complication requiring routine monitoring.
*Hemorrhagic cystitis*
- **Hemorrhagic cystitis** is a characteristic complication of **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide**, not methotrexate.
- It results from toxic metabolite (acrolein) accumulation in the bladder and can be prevented with hydration and mesna.
*Peripheral neuropathy*
- **Peripheral neuropathy** is typically associated with **vinca alkaloids** (vincristine, vinblastine) and **taxanes** (paclitaxel, docetaxel), which disrupt microtubule function.
- Methotrexate does not cause peripheral neuropathy as a primary toxicity.
*Cardiotoxicity*
- **Cardiotoxicity**, including dilated cardiomyopathy, is a well-known dose-dependent complication of **anthracyclines** (doxorubicin, daunorubicin).
- Methotrexate is not associated with direct cardiac toxicity.
Alkylating agents US Medical PG Question 6: A 33-year-old man with recently diagnosed testicular cancer visits his oncologist to discuss the treatment plan. His left testicle was removed after a thorough workup of a lump. A pelvic CT showed no enlarged lymph nodes and a simple orchiectomy and pelvic lymph node dissection was completed. The final diagnosis was stage IB non-seminoma testicular cancer (pT2N0M0). A combination of different chemotherapeutic medications is recommended including bleomycin, etoposide, and cisplatin. Each of the antineoplastic drugs has a different mechanism of action targeting cancer cells. What is the primary mechanism of action of bleomycin in cancer treatment?
- A. Direct DNA strand cleavage (Correct Answer)
- B. Ribonucleotide reductase inhibition
- C. RNA polymerase inhibition
- D. Topoisomerase II inhibition
- E. DNA polymerase inhibition
Alkylating agents Explanation: ***Direct DNA strand cleavage***
- Bleomycin is a **cytotoxic antibiotic** that induces DNA damage by generating **free radicals**, leading to **single and double-strand DNA breaks**.
- This mechanism primarily occurs in the **G2 and M phases** of the cell cycle, inhibiting DNA synthesis and cell division.
*Ribonucleotide reductase inhibition*
- This is the primary mechanism of action for drugs like **hydroxyurea**, which prevents the conversion of **ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides**, thereby impairing DNA synthesis.
- Bleomycin does not act by inhibiting this enzyme.
*RNA polymerase inhibition*
- This mechanism is associated with drugs such as **dactinomycin (actinomycin D)**, which intercalates into DNA and blocks RNA synthesis.
- Bleomycin's action is more direct in causing DNA damage rather than inhibiting RNA transcription.
*Topoisomerase II inhibition*
- Drugs like **etoposide** and **doxorubicin** are topoisomerase II inhibitors, which prevent DNA unwinding and re-ligation, leading to DNA breaks and cell death.
- While etoposide is used in the same regimen, this is not the mechanism of action for bleomycin.
*DNA polymerase inhibition*
- This is the mechanism of action for certain **antimetabolites** and **nucleoside analogs**, such as **cytarabine** or **gemcitabine**, which interfere with DNA replication by blocking DNA polymerase.
- Bleomycin's action is distinct, involving direct oxidative cleavage of DNA.
Alkylating agents US Medical PG Question 7: A 55-year-old male with a 60 pack-year smoking history presents to his oncologist for ongoing management of his recently diagnosed small cell lung cancer. His oncologist discusses several options and decides to start the chemotherapeutic medication, etoposide. The patient is warned that one side effect of this drug is myelosuppression so he should be vigilant for development of any infectious symptoms. The beneficial effect of this drug in treating cancer is most likely due to which of the following effects?
- A. DNA intercalation
- B. Crosslinking of DNA
- C. Stabilization of microtubules
- D. Alkylation of DNA
- E. Inhibition of supercoil relaxation (Correct Answer)
Alkylating agents Explanation: ***Inhibition of supercoil relaxation***
- **Etoposide** is a **topoisomerase II inhibitor**, preventing DNA uncoiling and replication, thus causing DNA strand breaks and **apoptosis** in rapidly dividing cancer cells.
- This mechanism specifically targets the enzyme responsible for managing the topological state of DNA, a crucial process during cell division.
*DNA intercalation*
- **DNA intercalation** involves drugs inserting themselves between the base pairs of DNA, distorting its structure and inhibiting replication and transcription (e.g., **doxorubicin**).
- This is not the primary mechanism of action for **etoposide**, which directly interferes with topoisomerase II enzymes.
*Crosslinking of DNA*
- **Crosslinking of DNA** involves forming covalent bonds within or between DNA strands, preventing DNA replication and transcription (e.g., **cisplatin**, **cyclophosphamide**).
- While effective in chemotherapy, this mechanism is characteristic of **alkylating agents** and is distinct from how etoposide operates.
*Stabilization of microtubules*
- **Stabilization of microtubules** (e.g., **paclitaxel**, **docetaxel**) or destabilization (e.g., **vincristine**, **vinblastine**) are mechanisms of **microtubule-targeting agents** that disrupt cell division.
- **Etoposide** does not primarily affect microtubules but rather targets **DNA topoisomerases**.
*Alkylation of DNA*
- **Alkylation of DNA** involves the addition of an alkyl group to DNA bases, leading to DNA damage, miscoding, and ultimately cell death.
- This mechanism is typical of **alkylating agents** like **cyclophosphamide** and **busulfan**, but it is not the primary mode of action for **etoposide**.
Alkylating agents US Medical PG Question 8: A 67-year-old woman with advanced bladder cancer comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. She is currently undergoing chemotherapy with an agent that forms cross-links between DNA strands. Serum studies show a creatinine concentration of 2.1 mg/dL and a blood urea nitrogen concentration of 30 mg/dL. Urine dipstick of a clean-catch midstream specimen shows 2+ protein and 1+ glucose. Prior to initiation of chemotherapy, her laboratory values were within the reference range. In addition to hydration, administration of which of the following would most likely have prevented this patient's current condition?
- A. Leucovorin
- B. Amifostine (Correct Answer)
- C. Aprepitant
- D. Mesna
- E. Rasburicase
Alkylating agents Explanation: **Amifostine**
- This patient's symptoms (elevated creatinine and BUN, 2+ protein, 1+ glucose in urine) suggest **renal tubular damage**, specifically acute tubular necrosis, likely caused by a nephrotoxic chemotherapeutic agent.
- **Amifostine** is a cytoprotective agent that scavenges reactive oxygen species in local tissues, thereby reducing the nephrotoxic effects of **alkylating agents** like cisplatin, which forms cross-links between DNA strands.
*Leucovorin*
- **Leucovorin** (folinic acid) is used to rescue normal cells from the adverse effects of **methotrexate**, enhancing its excretion and reducing toxicity.
- It is not indicated for preventing kidney damage from DNA cross-linking agents.
*Aprepitant*
- **Aprepitant** is a neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor antagonist used to prevent **chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting**.
- It does not have protective effects against nephrotoxicity.
*Mesna*
- **Mesna** (2-mercaptoethane sulfonate sodium) is used to prevent **hemorrhagic cystitis** caused by acrolein, a toxic metabolite of cyclophosphamide and ifosfamide.
- It does not prevent nephrotoxicity from other types of chemotherapy agents.
*Rasburicase*
- **Rasburicase** is a recombinant urate oxidase enzyme used to prevent or treat **tumor lysis syndrome** by converting uric acid to allantoin, which is more soluble and easily excreted.
- It is not used for preventing direct kidney damage from chemotherapeutic agents.
Alkylating agents US Medical PG Question 9: A 67-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for a decline in his hearing that he noticed over the past week. The patient has a past medical history of hypertension and diabetes mellitus and was recently diagnosed with bladder cancer which is currently appropriately being treated. The patient is a hunter and often goes shooting in his spare time. His recent sick contacts include his grandson who is being treated with amoxicillin for ear pain. Physical exam is notable for decreased hearing bilaterally. The Weber test does not localize to either ear, and the Rinne test demonstrates air conduction is louder than bone conduction. Which of the following is the most likely etiology for this patient's hearing loss?
- A. Otitis externa
- B. Presbycusis
- C. Otosclerosis
- D. Medication regimen (Correct Answer)
- E. Otitis media
Alkylating agents Explanation: ***Medication regimen***
- The patient's history of bladder cancer treatment suggests recent exposure to **chemotherapeutic agents**, such as **cisplatin**, which are known to be **ototoxic**.
- A **sudden decline in hearing** over the past week points to an acute cause, such as drug-induced hearing loss.
*Otitis externa*
- This condition typically presents with **ear pain**, **pruritus**, and **discharge**, none of which are mentioned in the patient's presentation.
- The **Weber and Rinne test results** (normal AC > BC, no lateralization) are inconsistent with a conductive hearing loss typically associated with otitis externa.
*Presbycusis*
- **Presbycusis** is an age-related **sensorineural hearing loss** that typically develops **gradually over years**, not suddenly over a week.
- While the patient's age (67) is a risk factor, the acute onset makes this diagnosis less likely.
*Otosclerosis*
- **Otosclerosis** usually causes a **progressive conductive hearing loss**, often starting in young adulthood.
- The **Weber and Rinne test results** (normal AC > BC, no lateralization) are inconsistent with a conductive hearing loss.
*Otitis media*
- **Otitis media** typically presents with **ear pain**, **fullness**, and often **fever** or **discharge**, which are absent in this patient.
- The **Weber and Rinne test results** (normal AC > BC, no lateralization) are inconsistent with the conductive hearing loss that would be expected with otitis media.
Alkylating agents US Medical PG Question 10: A 28-year-old gravida-2-para-1 at 12 weeks gestation presents for a prenatal visit. Over the past week, she has felt increasingly tired, even after waking up in the morning. She is vegan and avoids all animal products. She was diagnosed with Graves’ disease 6 months ago. Before conception, methimazole was switched to propylthiouracil (PTU). Other medications include folic acid and a multivitamin. The vital signs include: temperature 37.1℃ (98.8℉), pulse 72/min, respiratory rate 12/min, and blood pressure 110/75 mm Hg. The conjunctivae and nail beds are pale. Petechiae are present over the distal lower extremities. The pelvic examination reveals a uterus consistent in size with a 12-week gestation. Examination of the neck, lungs, heart, and abdomen shows no abnormalities. The laboratory studies show the following:
Laboratory test
Hemoglobin 9.0 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume 90 μm3
Leukocyte count 4,000/mm3
Segmented neutrophils 55%
Lymphocytes 40%
Platelet count 110,000/mm3
Serum
Thyroid-stimulating hormone 0.1 μU/mL
Thyroxine (T-4) 8 μg/dL
Lactate dehydrogenase 60 U/L
Total bilirubin 0.5 mg/dL
Iron 100 μg/dL
Ferritin 110 ng/mL
Total iron-binding capacity 250 μg/dL
Which of the following best explains these findings?
- A. Excess antithyroid medication
- B. Drug-induced marrow failure (Correct Answer)
- C. Vitamin B12 deficiency
- D. Hemodilution of pregnancy
- E. Autoimmune hemolysis
Alkylating agents Explanation: **Drug-induced marrow failure**
- The patient's **pancytopenia** (low hemoglobin, leukocytes, and platelets) along with petechiae, in the context of **propylthiouracil (PTU)** use, strongly suggests drug-induced bone marrow suppression. PTU is known to cause agranulocytosis and, less commonly, aplastic anemia.
- The **normal thyroid hormone levels** (TSH 0.1 μU/mL, T4 8 μg/dL) indicate that her Graves' disease is adequately controlled, but the hematological changes are severe enough to point towards a drug-related adverse effect rather than thyroid dysfunction.
*Excess antithyroid medication*
- While excess antithyroid medication like PTU can lead to **hypothyroidism**, the patient's low TSH (though near normal during pregnancy due to hCG effects) and normal T4 indicate she is **not hypothyroid**.
- Hypothyroidism does not directly cause **pancytopenia** or petechiae, which are observed in this case.
*Vitamin B12 deficiency*
- **Vitamin B12 deficiency** typically causes **macrocytic anemia** (high MCV), and sometimes pancytopenia. However, this patient has a **normal MCV (90 μm3)**.
- Although the patient is vegan, she is taking a multivitamin and folic acid, and iron studies are normal, making B12 deficiency less likely given the MCV.
*Hemodilution of pregnancy*
- **Physiologic hemodilution** in pregnancy can cause a *mild drop* in hemoglobin and hematocrit and a *slight decrease* in platelet count but typically does not lead to **leukopenia** or significant thrombocytopenia with petechiae.
- The degree of *pancytopenia* observed here is beyond what would be expected from normal hemodilution.
*Autoimmune hemolysis*
- **Autoimmune hemolysis** would primarily cause **anemia** and potentially elevated bilirubin and LDH due to red blood cell destruction, but it does **not explain the leukopenia or thrombocytopenia** (pancytopenia).
- The patient's bilirubin and LDH are normal, making significant hemolysis unlikely.
More Alkylating agents US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.