Vaccines

On this page
💉 The Immunological Arsenal: Vaccine Mastery Fundamentals
Vaccines represent humanity's most successful medical intervention, preventing millions of deaths annually by training immune systems to recognize threats before they strike. You'll master how vaccines work at the molecular level, distinguish normal immune responses from true adverse reactions, and integrate population-level strategies with individual patient care. This lesson builds your clinical reasoning from immunological mechanisms through diagnostic frameworks to evidence-based management, equipping you to confidently counsel patients, recognize complications, and contribute to public health protection. By connecting bench science to bedside decisions, you'll understand not just what vaccines do, but why they succeed and occasionally fail.
Vaccines represent humanity's most successful public health intervention, preventing 2-3 million deaths annually and achieving >95% efficacy against targeted diseases. The immunological precision required for vaccine development parallels surgical expertise - each component must function flawlessly to achieve protective immunity.
Vaccine Classification Architecture
-
Live Attenuated Vaccines
- Weakened but viable pathogens that replicate in host
- Single dose often provides lifelong immunity (>90% protection)
- Examples: MMR, varicella, rotavirus, intranasal influenza
- Contraindicated in immunocompromised patients
- Require 2-8°C storage (cold chain critical)
- Can cause mild disease in 1-5% of recipients
-
Inactivated Vaccines
- Killed pathogens or purified components
- Multiple doses required for optimal protection (2-4 doses)
- Examples: IPV, hepatitis A, influenza (injectable), rabies
- Safe for immunocompromised individuals
- More stable storage requirements
- Booster doses needed every 5-10 years
-
Subunit/Conjugate Vaccines
- Purified antigens or polysaccharides linked to proteins
- Enhanced immunogenicity through carrier protein conjugation
- Examples: Hib, pneumococcal, meningococcal, HPV
- Overcome T-independent immune responses
- Effective in children <2 years old
- Require 3-4 primary doses for protection
📌 Remember: LIVE vaccines - Lifelong immunity, Immunocompromised contraindication, Viral replication, Excellent single-dose protection
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Live vaccines must be given simultaneously or ≥4 weeks apart to prevent immune interference. Inactivated vaccines can be administered at any interval without compromising efficacy.
| Vaccine Type | Doses Required | Duration of Immunity | Immunocompromised Use | Storage Temp | Efficacy Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Live Attenuated | 1-2 | Lifelong (>20 years) | Contraindicated | 2-8°C | 90-98% |
| Inactivated | 2-4 primary + boosters | 5-10 years | Safe | 2-8°C | 85-95% |
| Subunit | 3-4 primary + boosters | 3-5 years | Safe | 2-8°C | 80-90% |
| mRNA | 2 primary + boosters | 6-12 months | Safe | -70°C to 2-8°C | 90-95% |
| Viral Vector | 1-2 | 6-24 months | Caution | 2-8°C | 70-85% |
Understanding vaccine fundamentals enables precise immunization strategies that protect individual patients while contributing to population-level herd immunity thresholds of 85-95% for most vaccine-preventable diseases.
💉 The Immunological Arsenal: Vaccine Mastery Fundamentals
🧬 Immunological Engineering: The Molecular Vaccine Machinery
The Immunological Cascade Architecture
-
Antigen Processing Phase (0-6 hours)
- Dendritic cells capture vaccine antigens at injection site
- Pattern recognition receptors identify pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- Antigen processing occurs via proteasomal degradation
- MHC Class I presentation for CD8+ T cells
- MHC Class II presentation for CD4+ T cells
- Cross-presentation enables both pathways simultaneously
-
Adaptive Immune Activation (1-7 days)
- T helper cells differentiate into Th1, Th2, or Th17 subsets
- B cell activation requires dual signals: antigen binding + T cell help
- Germinal center formation in lymph nodes within 5-7 days
- Somatic hypermutation increases antibody affinity 100-1000x
- Class switching produces IgG, IgA, or IgE antibodies
- Memory cell generation peaks at 14-21 days
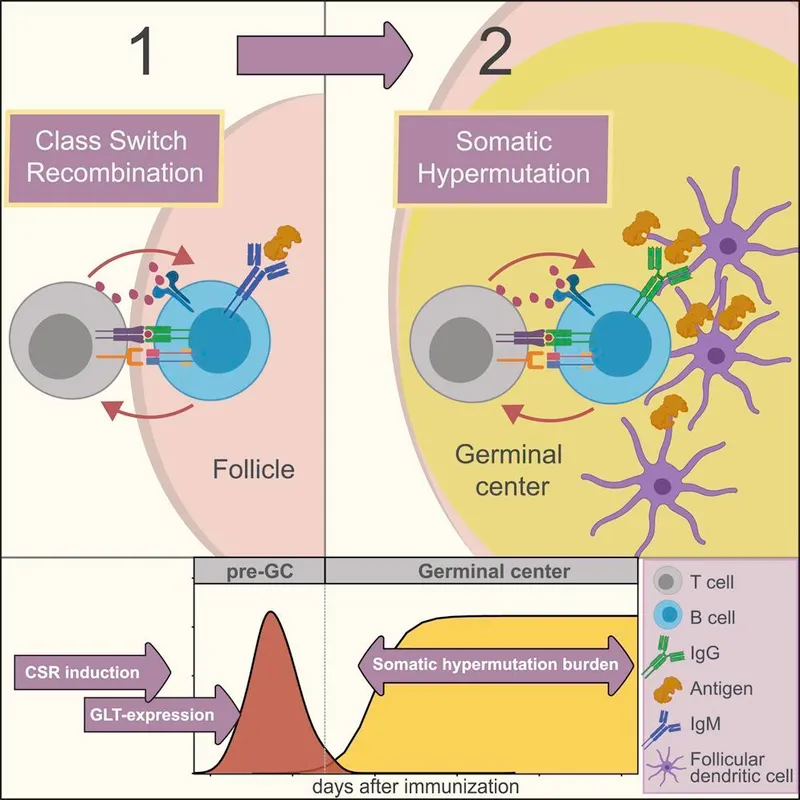
📌 Remember: AIMS for vaccine response - Antigen processing, Innate activation, Memory formation, Specific antibodies
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Peak antibody responses occur 2-4 weeks post-vaccination, which is why serological testing should be performed ≥4 weeks after immunization to assess vaccine response accurately.
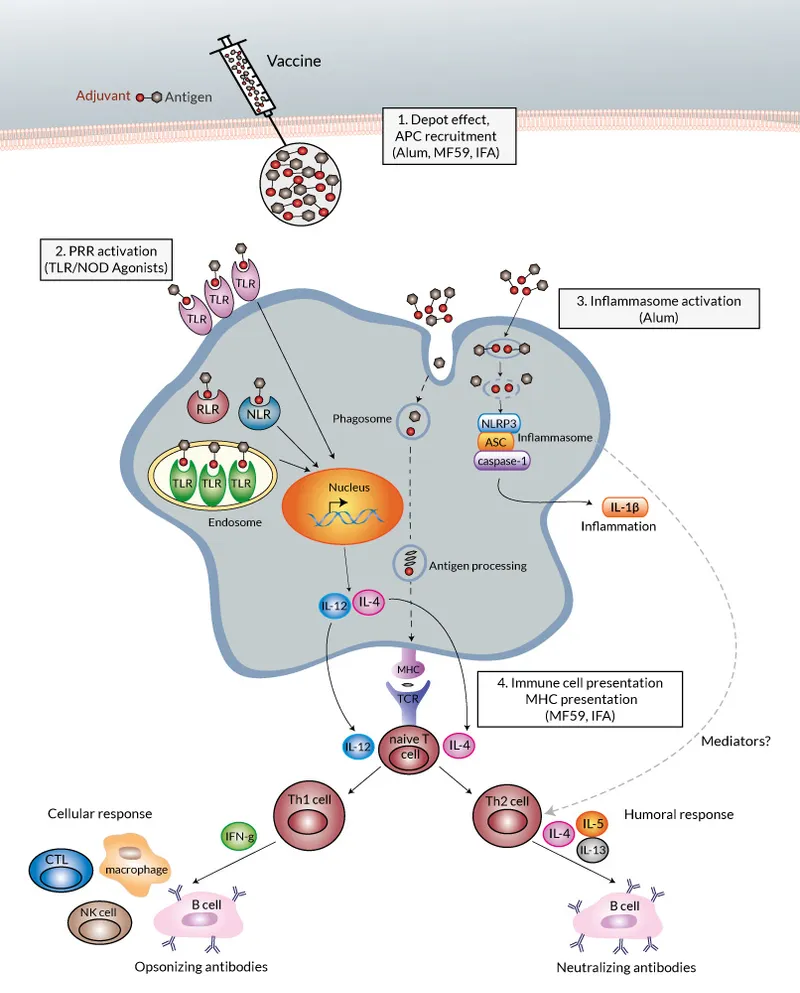
Adjuvant Mechanisms and Enhancement
-
Aluminum-based Adjuvants (Alum, AS04)
- Create depot effect prolonging antigen exposure
- Activate NLRP3 inflammasome pathway
- Enhance Th2 responses and antibody production
- Used in >80% of inactivated vaccines
- Increase antibody titers 5-10 fold
- Local reactions in 10-20% of recipients
-
Oil-in-Water Emulsions (MF59, AS03)
- Stimulate innate immune cell recruitment
- Enhance cross-reactive immunity
- Enable antigen dose sparing (reduce by 50-75%)
- Particularly effective in elderly populations
- Improve seroconversion rates by 15-25%
- Used in pandemic influenza vaccines
| Adjuvant Type | Mechanism | Immune Response | Vaccines Used | Enhancement Factor |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum salts | Depot + NLRP3 | Th2/Antibody | Hepatitis B, DTaP | 5-10x antibody |
| MF59 emulsion | Cell recruitment | Th1/Th2 balanced | Influenza | 3-5x antibody |
| AS04 (Alum + MPL) | TLR4 + NLRP3 | Th1/Antibody | HPV, Hepatitis B | 10-20x antibody |
| CpG oligonucleotides | TLR9 activation | Th1/CTL | Hepatitis B | 5-15x cellular |
| Liposomes | Antigen delivery | Balanced | Experimental | 3-8x response |
Understanding immunological mechanisms enables prediction of vaccine efficacy, optimal timing of booster doses, and rational design of immunization schedules that maximize protective immunity while minimizing adverse events.
🧬 Immunological Engineering: The Molecular Vaccine Machinery
🎯 Clinical Recognition Mastery: Vaccine Response Patterns
Normal Vaccine Response Patterns
-
Immediate Phase (0-30 minutes)
- Injection site pain in 80-90% of recipients
- Mild erythema and swelling <2 cm diameter
- Systemic reactions rare (<1%) except anaphylaxis
- Monitor for 15 minutes post-vaccination
- Vasovagal reactions in 1-3% of adolescents
- True anaphylaxis occurs in 1 per million doses
-
Early Immune Response (1-3 days)
- Low-grade fever <38.5°C in 10-15% of recipients
- Mild systemic symptoms: fatigue, headache, myalgia
- Local reactions peak at 24-48 hours
- Injection site induration <5 cm considered normal
- Lymphadenopathy in 5-10% of recipients
- Symptoms resolve spontaneously within 72 hours
-
Peak Immune Response (7-21 days)
- Live vaccine reactions may occur 7-21 days post-vaccination
- Mild rash with MMR vaccine in 5% of recipients
- Transient thrombocytopenia 1 per 30,000 MMR doses
- Febrile seizures 1 per 3,000-4,000 MMR doses
- Parotid swelling mimicking mumps in <1%
- Arthralgia in 25% of adult women receiving rubella vaccine
📌 Remember: FEVER pattern recognition - First 24h (inactivated), Early week (live vaccines), Very rare (>39°C), Evaluate other causes, Resolves spontaneously
"See This, Think That" Clinical Correlations
-
When you see: Fever >39°C within 24 hours of vaccination
- Think: Concurrent illness, not vaccine reaction
- Action: Investigate other infectious causes
- Evidence: Vaccine-induced fever typically <38.5°C and delayed
-
When you see: Extensive limb swelling after 4th or 5th DTaP dose
- Think: Extensive limb swelling (ELS) - benign reaction
- Action: Symptomatic treatment, complete series
- Evidence: Occurs in 2-3% of children, resolves in 24-72 hours
-
When you see: Shoulder pain persisting >48 hours post-vaccination
- Think: Shoulder injury related to vaccine administration (SIRVA)
- Action: Anti-inflammatory treatment, physiotherapy referral
- Evidence: Results from injection too high in deltoid muscle
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Temporal association doesn't prove causation. Most events occurring within 48 hours of vaccination are coincidental illnesses, especially in children with high baseline infection rates.
| Clinical Presentation | Vaccine Association | Timing | Frequency | Management |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fever <38.5°C | Likely related | 6-24 hours | 10-15% | Symptomatic |
| Fever >39°C | Unlikely related | Any time | <1% | Investigate |
| Local swelling <5cm | Normal response | 24-48 hours | 20-30% | Reassurance |
| Extensive limb swelling | DTaP-related | 24-72 hours | 2-3% | Symptomatic |
| Febrile seizure | MMR-related | 7-14 days | 0.03% | Supportive |
Developing pattern recognition skills enables confident vaccine safety counseling, appropriate adverse event reporting, and evidence-based clinical decision-making that maintains vaccine confidence while ensuring patient safety.
🎯 Clinical Recognition Mastery: Vaccine Response Patterns
🔬 Differential Diagnosis Framework: Vaccine Reactions vs. Disease
Systematic Discrimination Criteria
-
Temporal Relationship Analysis
- Inactivated vaccines: Reactions within 24-48 hours
- Live vaccines: Reactions 7-21 days post-vaccination
- Concurrent illness: No temporal pattern with vaccination
- Incubation periods for common infections: 2-14 days
- Seasonal illness patterns independent of vaccination timing
- Multiple family members affected suggests infectious cause
-
Clinical Pattern Recognition
- Vaccine reactions: Stereotyped presentations with known frequencies
- Natural disease: Variable presentations with progressive symptoms
- Coincidental illness: Typical disease patterns unrelated to vaccination
- Vaccine reactions rarely cause high fever >39°C
- Progressive symptoms suggest infectious etiology
- Bilateral vs. unilateral presentations differ by cause
High-Yield Discrimination Patterns
| Clinical Feature | Vaccine Reaction | Natural Disease | Concurrent Illness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fever onset | 6-24h (inactivated) | Variable (2-14d) | Independent timing |
| Fever pattern | Low-grade, brief | High, sustained | Typical for pathogen |
| Rash characteristics | Sparse, transient | Dense, progressive | Pathogen-specific |
| Systemic symptoms | Mild, self-limited | Severe, progressive | Variable severity |
| Laboratory findings | Normal/mild changes | Pathogen-specific | Diagnostic patterns |
- Vaccine rash: Sparse, <10 lesions, no cough/coryza
- Natural measles: Dense rash, Koplik spots, respiratory symptoms
- Timing: Vaccine rash 7-12 days, measles 10-14 days incubation
- Vaccine rash non-contagious vs. measles highly contagious
- Fever with vaccine rash <38.5°C vs. measles >39°C
- Duration: vaccine 1-2 days vs. measles 5-7 days
- Varicella Vaccine vs. Natural Chickenpox
- Vaccine lesions: <50 lesions, mostly maculopapular
- Natural varicella: >250 lesions, vesicular progression
- Distribution: Vaccine lesions localized vs. varicella generalized
- Vaccine lesions rarely vesiculate or crust
- Transmission risk minimal with vaccine lesions
- Severity: vaccine mild vs. natural moderate-severe
📌 Remember: MILD vaccine reactions - Minimal fever, Isolated symptoms, Limited duration, Distinct timing pattern
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Vaccine-strain virus detection by PCR can confirm vaccine-related illness, but most vaccine reactions are clinical diagnoses based on characteristic patterns and timing.
Evidence-Based Assessment Framework
-
Brighton Collaboration Criteria
- Standardized case definitions for vaccine adverse events
- Levels of diagnostic certainty based on clinical evidence
- Used for global vaccine safety surveillance
- Level 1: Definite case with laboratory confirmation
- Level 2: Probable case with clinical criteria
- Level 3: Possible case with limited evidence
-
WHO Causality Assessment
- Consistent temporal relationship with vaccination
- Known adverse event for specific vaccine
- Biological plausibility of mechanism
- Alternative explanations systematically excluded
- Dechallenge/rechallenge evidence when available
- Literature consistency with reported cases
💡 Master This: Systematic causality assessment prevents both over-attribution of coincidental events to vaccines and under-recognition of genuine adverse events. Most events are temporally associated but not causally related.
Mastering differential diagnosis frameworks enables confident clinical assessment, appropriate adverse event reporting, and evidence-based counseling that maintains vaccine confidence while ensuring patient safety through systematic evaluation.
🔬 Differential Diagnosis Framework: Vaccine Reactions vs. Disease
⚖️ Evidence-Based Management: Treatment Algorithms and Outcomes
Immediate Management Protocols
-
Anaphylaxis Management (<5 minutes response time)
- Epinephrine 0.01 mg/kg IM (max 0.5 mg) immediately
- IV access and normal saline 20 ml/kg bolus
- Oxygen supplementation and airway assessment
- H1 antihistamine: diphenhydramine 1-2 mg/kg IV
- H2 antihistamine: ranitidine 1 mg/kg IV
- Corticosteroids: methylprednisolone 1-2 mg/kg IV
- Bronchodilators if wheezing: albuterol nebulizer
- Hospital observation minimum 4-6 hours
-
Extensive Limb Swelling (24-72 hour duration)
- Cold compresses for first 24 hours
- NSAIDs: ibuprofen 10 mg/kg every 6-8 hours
- Elevation of affected limb
- No antibiotics required (non-infectious)
- Complete vaccine series - not a contraindication
- Resolution typically within 72 hours
Evidence-Based Treatment Outcomes
| Adverse Event | Treatment | Success Rate | Time to Resolution | Recurrence Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Local reactions | Symptomatic care | 95-98% | 24-48 hours | <5% |
| Fever <39°C | Antipyretics | 90-95% | 6-12 hours | 10-15% |
| Extensive swelling | NSAIDs + elevation | 98-99% | 48-72 hours | 2-3% |
| Febrile seizure | Supportive care | 99% | Immediate | <1% |
| Anaphylaxis | Epinephrine protocol | 95-98% | 1-4 hours | <0.1% |
- Severe allergic reaction: Contraindication to same vaccine
- Extensive limb swelling: NOT a contraindication to future doses
- Febrile seizure: NOT a contraindication - continue series
- Encephalopathy within 7 days: Contraindication to pertussis vaccines
- Thrombocytopenia: Relative contraindication to MMR
- Shoulder injury (SIRVA): NOT a contraindication with proper technique
📌 Remember: CARE for vaccine reactions - Cold compress, Analgesics, Reassurance, Evaluate severity
⭐ Clinical Pearl: True contraindications to future vaccination are rare (<1% of adverse events). Most reactions are precautions requiring careful assessment but not permanent vaccine avoidance.
Long-term Monitoring and Follow-up
-
Adverse Event Reporting
- VAERS reporting for all serious adverse events
- Brighton Collaboration criteria for standardized assessment
- Follow-up documentation at 24-48 hours and 7 days
- Serious events: hospitalization, disability, death
- Unexpected events: not listed in package insert
- Cluster events: multiple cases in same location/time
-
Future Vaccination Decisions
- Risk-benefit assessment for subsequent doses
- Modified schedules for high-risk patients
- Alternative vaccines when available
- Premedication with antihistamines for mild allergic reactions
- Graded dosing for patients with egg allergy
- Specialist consultation for complex cases
💡 Master This: Effective adverse event management requires immediate recognition, systematic treatment, and appropriate follow-up. Most reactions are self-limited and resolve with symptomatic care, while maintaining vaccine series completion.
Evidence-based management protocols ensure optimal patient outcomes, maintain vaccine confidence, and contribute to robust safety surveillance systems that protect both individual patients and population health through systematic adverse event assessment and response.
⚖️ Evidence-Based Management: Treatment Algorithms and Outcomes
🌐 Systems Integration: Population Health and Vaccine Ecosystems
Multi-System Integration Framework
-
Clinical-Epidemiological Interface
- Individual vaccine decisions impact herd immunity thresholds
- Coverage rates >85-95% required for population protection
- Surveillance systems detect outbreaks and vaccine failures
- Real-time monitoring through electronic health records
- Seroprevalence studies assess population immunity
- Outbreak investigations identify transmission patterns
- Vaccine effectiveness studies measure real-world protection
-
Supply Chain-Clinical Practice Integration
- Cold chain maintenance from manufacturer to patient
- Inventory management prevents stockouts and waste
- Distribution networks ensure equitable access
- Temperature monitoring at every storage point
- Expiration date tracking minimizes waste (<2% target)
- Emergency stockpiles for outbreak response
- Global supply coordination for pandemic preparedness
Advanced Integration Concepts
-
Pharmacovigilance-Clinical Practice Loop
- Adverse event reporting informs safety profiles
- Signal detection identifies new safety concerns
- Risk communication updates clinical practice
- Post-marketing surveillance monitors millions of doses
- Rapid response systems for safety signals
- Benefit-risk assessments guide policy updates
- Healthcare provider education ensures informed decisions
-
Digital Health Integration
- Electronic immunization registries track coverage
- Clinical decision support optimizes timing
- Mobile health platforms improve access
- Interoperability standards enable data sharing
- Artificial intelligence predicts outbreak risks
- Blockchain technology ensures supply chain integrity
- Telemedicine platforms expand rural access
| Integration Level | Components | Success Metrics | Technology Requirements | Outcome Measures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Individual | Patient-Provider | >95% completion rates | EHR integration | Seroconversion rates |
| Facility | Clinic-Registry | <2% missed opportunities | Registry connectivity | Coverage rates |
| Regional | Multi-facility | >90% coverage | Data interoperability | Disease incidence |
| National | Policy-Practice | Herd immunity | Surveillance systems | Elimination goals |
| Global | International | Pandemic response | Real-time monitoring | Eradication targets |
Cutting-Edge Integration Innovations
-
Precision Vaccination Approaches
- Genetic markers predict vaccine response
- Immunosenescence assessment guides elderly vaccination
- Personalized schedules optimize individual protection
- HLA typing predicts adverse event risk
- Immune profiling identifies optimal timing
- Microbiome analysis influences vaccine efficacy
- Epigenetic factors affect immune memory
-
One Health Integration
- Zoonotic disease surveillance prevents spillover
- Veterinary-human health coordination controls reservoirs
- Environmental monitoring tracks pathogen circulation
- Wildlife vaccination programs reduce transmission
- Livestock immunization protects food security
- Vector control integration enhances protection
- Climate adaptation addresses changing disease patterns
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Systems-level vaccine failures often result from integration gaps rather than individual vaccine failures. Successful programs require coordination across multiple levels from molecular to global.
💡 Master This: Modern vaccine programs function as complex adaptive systems where individual clinical decisions aggregate to population-level outcomes. Understanding these interactions enables optimization strategies that maximize both individual and collective protection.
Advanced integration concepts reveal how vaccine programs transcend individual patient care to become sophisticated public health systems that require coordination across clinical practice, surveillance networks, supply chains, and policy frameworks to achieve optimal population health outcomes.
🌐 Systems Integration: Population Health and Vaccine Ecosystems
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid Assessment and Decision Tools
Essential Clinical Arsenal
📌 Remember: VACCINE assessment - Verify contraindications, Assess timing, Check interactions, Confirm storage, Inform patient, Note documentation, Evaluate response
-
Rapid Contraindication Screen (<2 minutes)
- Severe illness with fever >38.5°C: Defer vaccination
- Previous severe allergic reaction to vaccine component
- Immunocompromised state for live vaccines only
- Pregnancy contraindication for live vaccines
- Recent blood products delay live vaccines 3-11 months
- Moderate illness is NOT a contraindication
-
Timing Optimization Matrix
- Minimum intervals between doses must be respected
- Live vaccines given simultaneously or ≥4 weeks apart
- Inactivated vaccines can be given at any interval
- Catch-up schedules use minimum intervals
- Travel requirements may accelerate timing
- Pregnancy timing optimizes maternal antibody transfer
| Clinical Scenario | Decision Rule | Action Required | Evidence Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mild URI symptoms | Proceed with vaccination | Standard schedule | Grade A |
| Fever >38.5°C | Defer vaccination | Reschedule when well | Grade A |
| Antibiotic use | Proceed with vaccination | No interaction | Grade B |
| Recent live vaccine | Wait 4 weeks OR give same day | Prevent interference | Grade A |
| Immunocompromised | Avoid live vaccines | Inactivated only | Grade A |
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Missed opportunities account for >50% of under-vaccination. Every healthcare encounter should include vaccination status assessment, regardless of visit purpose.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Simultaneous administration of multiple vaccines is safe and effective. Separate injection sites by ≥1 inch and use different limbs when possible.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Valid doses given ≥4 days before minimum interval still count. Grace period prevents unnecessary revaccination while maintaining protection.
Rapid Reference Thresholds
-
Critical Numbers for Clinical Practice
- Anaphylaxis risk: 1 per million doses
- Observation period: 15 minutes minimum post-vaccination
- Fever threshold: >38.5°C for deferral consideration
- Minimum intervals: 4 weeks between live vaccines
- Maximum age: 6 years for DTaP (use Tdap after)
- Pregnancy timing: 27-36 weeks optimal for Tdap
- Travel timing: ≥2 weeks before departure for protection
-
Storage and Handling Essentials
- Refrigerator temperature: 2-8°C (35-46°F)
- Freezer temperature: -50 to -15°C for varicella/zoster
- Room temperature stability: <30 minutes for most vaccines
- Temperature excursions require immediate assessment
- Expired vaccines must never be administered
- Multi-dose vials expire 28 days after first use
💡 Master This: Clinical vaccine mastery requires systematic assessment, evidence-based decisions, and meticulous documentation. Every vaccination encounter contributes to both individual protection and population immunity through precise clinical practice.
These clinical mastery tools enable confident, efficient, and evidence-based vaccination practices that optimize patient outcomes while maintaining the highest standards of vaccine safety and effectiveness in routine clinical practice.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid Assessment and Decision Tools
Practice Questions: Vaccines
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 34-year-old female medical professional who works for a non-governmental organization visits her primary care provider for a routine health check-up. She made a recent trip to Sub-Saharan Africa where she participated in a humanitarian medical project. Her medical history and physical examination are unremarkable. A chest radiograph and a tuberculin skin test (PPD) are ordered. The chest radiograph is performed at the side and the PPD reaction measures 12 mm after 72 hours. Which of the following mechanisms is involved in the skin test reaction?













