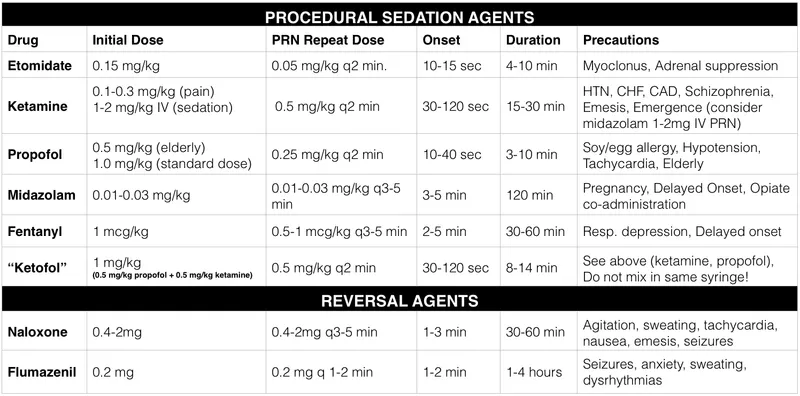
Procedural sedation in children US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Procedural sedation in children. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Procedural sedation in children US Medical PG Question 1: A previously healthy 35-year-old woman is brought into the emergency department after being found unresponsive by her husband. Her husband finds an empty bottle of diazepam tablets in her pocket. She is stuporous. At the hospital, her blood pressure is 90/40 mm Hg, the pulse is 58/min, and the respirations are 6/min. The examination of the pupils shows normal size and reactivity to light. Deep tendon reflexes are 1+ bilaterally. Babinski sign is absent. All 4 extremities are hypotonic. The patient is intubated and taken to the critical care unit for mechanical ventilation and treatment. Regarding the prevention of pneumonia in this patient, which of the following strategies is most likely to achieve this goal?
- A. Nasogastric tube insertion
- B. Daily evaluation for ventilator weaning
- C. Subglottic drainage of secretions (Correct Answer)
- D. Oropharynx and gut antibacterial decontamination
- E. Prone positioning during mechanical ventilation
Procedural sedation in children Explanation: ***Subglottic drainage of secretions***
- This is a highly effective strategy to prevent **ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP)** by continuously removing secretions that pool above the endotracheal tube cuff before they can be aspirated.
- Endotracheal tubes with a **subglottic secretion drainage port** reduce VAP incidence by preventing microaspiration of contaminated oropharyngeal secretions into the lower respiratory tract.
- This is a **specific mechanical intervention** that directly addresses one of the key pathogenic mechanisms of VAP.
*Nasogastric tube insertion*
- While an NG tube may be needed for feeding or gastric decompression, it does not directly prevent VAP and may **increase aspiration risk** by compromising the lower esophageal sphincter.
- NG tubes can promote gastroesophageal reflux and provide a conduit for bacterial migration.
*Daily evaluation for ventilator weaning*
- This is also a **critical component of VAP prevention** as part of the ventilator bundle, since reducing duration of mechanical ventilation is the most effective overall strategy to prevent VAP.
- However, in this question asking for a strategy to prevent pneumonia in an intubated patient, subglottic drainage is the more specific technical intervention, whereas daily weaning assessment is a broader protocol that reduces exposure time.
- Both strategies are important; subglottic drainage addresses the "how" of prevention during intubation, while weaning protocols address the "duration" of risk exposure.
*Oropharynx and gut antibacterial decontamination*
- Selective digestive decontamination (SDD) aims to reduce bacterial colonization, but evidence for routine use is mixed and raises concerns about **antimicrobial resistance**.
- Not universally recommended as a primary VAP prevention strategy in most guidelines.
*Prone positioning during mechanical ventilation*
- **Prone positioning** is primarily indicated for improving oxygenation in **Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)**, not for VAP prevention.
- While it may improve secretion drainage, it is not a standard VAP prevention measure and carries its own risks and logistical challenges.
Procedural sedation in children US Medical PG Question 2: A 15-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department one hour after sustaining an injury during football practice. He collided head-on into another player while wearing a mouthguard and helmet. Immediately after the collision he was confused but able to use appropriate words. He opened his eyes spontaneously and followed commands. There was no loss of consciousness. He also had a headache with dizziness and nausea. He is no longer confused upon arrival. He feels well. Vital signs are within normal limits. He is fully alert and oriented. His speech is organized and he is able to perform tasks demonstrating full attention, memory, and balance. Neurological examination shows no abnormalities. There is mild tenderness to palpation over the crown of his head but no signs of skin break or fracture. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step?
- A. Discharge without activity restrictions
- B. Discharge and refrain from all physical activity for one week
- C. Observe for 6 hours in the ED and refrain from contact sports for one week (Correct Answer)
- D. Administer prophylactic levetiracetam and observe for 24 hours
- E. Administer prophylactic phenytoin and observe for 24 hours
Procedural sedation in children Explanation: ***Observe for 6 hours in the ED and refrain from contact sports for one week***
- This patient experienced a brief period of **confusion, headache, dizziness**, and **nausea** immediately after a head injury, which are symptoms consistent with a **mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI)** or **concussion**.
- Although his symptoms have resolved at presentation, observation in the ED for a few hours is prudent to ensure no delayed onset of more severe symptoms, and he should **refrain from contact sports** for at least one week as part of concussion management.
*Discharge without activity restrictions*
- Discharging without activity restrictions is unsafe given the initial symptoms of **confusion** and the potential for delayed symptom presentation or complications from a concussion.
- Concussion management requires a period of **physical and cognitive rest** to allow the brain to heal and prevent **second impact syndrome**.
*Discharge and refrain from all physical activity for one week*
- While refraining from all physical activity for one week is part of concussion management, discharging immediately without any observation period after initial neurological symptoms could be risky.
- An observation period allows for monitoring of any **worsening neurological signs** or symptoms that might indicate a more serious injury.
*Administer prophylactic levetiracetam and observe for 24 hours*
- **Prophylactic anticonvulsants** like levetiracetam are typically not recommended for routine management of **mild traumatic brain injury** or concussion.
- Their use is generally reserved for patients with more severe injuries, evolving conditions, or those who have had **seizures post-trauma**.
*Administer prophylactic phenytoin and observe for 24 hours*
- Similar to levetiracetam, **phenytoin** is an anticonvulsant and its prophylactic use is not indicated for **mild head injuries** or concussions.
- Anticonvulsant prophylaxis is associated with potential side effects and is reserved for specific high-risk scenarios, such as **severe TBI** or **penetrating head trauma**.
Procedural sedation in children US Medical PG Question 3: A man is brought into the emergency department by police. The patient was found somnolent in the park and did not respond to questioning. The patient's past medical history is unknown, and he is poorly kempt. The patient's personal belongings include prescription medications and illicit substances such as alprazolam, diazepam, marijuana, cocaine, alcohol, acetaminophen, and a baggie containing an unknown powder. His temperature is 97.0°F (36.1°C), blood pressure is 117/58 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, respirations are 9/min, and oxygen saturation is 91% on room air. Physical exam reveals pupils that do not respond to light bilaterally, and a somnolent patient who only withdraws his limbs to pain. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. N-acetylcysteine
- B. Supportive therapy, thiamine, and dextrose
- C. Naloxone (Correct Answer)
- D. Intubation
- E. Flumazenil
Procedural sedation in children Explanation: ***Naloxone***
- The patient exhibits classic signs of **opioid overdose** including **respiratory depression** (bradypnea, SpO2 91%), **miosis** (though noted as non-reactive, pinpoint pupils are common in opioid overdose), and altered mental status (somnolence, withdrawal to pain).
- Naloxone is an **opioid antagonist** that can rapidly reverse these effects and is indicated in suspected opioid overdose to improve breathing and consciousness.
*N-acetylcysteine*
- This is the antidote for **acetaminophen overdose**, which is possible given the presence of acetaminophen among the patient's belongings.
- However, the patient's acute symptoms of **severe respiratory and CNS depression** are not typical of acute acetaminophen toxicity and require more immediate intervention.
*Supportive therapy, thiamine, and dextrose*
- **Supportive therapy** (e.g., airway management) is crucial, and **thiamine and dextrose** are often given empirically to patients with altered mental status to address potential **Wernicke's encephalopathy** or **hypoglycemia**.
- While important general measures, these do not specifically target the immediate life-threatening respiratory depression and CNS depression so highly suggestive of opioid overdose.
*Intubation*
- While the patient has respiratory depression, **intubation** is an invasive procedure and should be considered if naloxone fails to improve respiratory status or if persistent airway compromise exists.
- The first step in suspected opioid overdose is typically to administer naloxone, as it may avoid the need for intubation.
*Flumazenil*
- **Flumazenil** is an antagonist for **benzodiazepine overdose**, and alprazolam and diazepam were found in the patient's possession.
- However, flumazenil can precipitate **withdrawal seizures** in chronic benzodiazepine users and is generally avoided in undifferentiated comatose patients, especially when mixed ingestions are suspected.
Procedural sedation in children US Medical PG Question 4: A 42-year-old man is discovered unconscious by local police while patrolling in a park. He is unresponsive to stimulation. Syringes were found scattered around him. His heart rate is 70/min and respiratory rate is 6/min. Physical examination reveals a disheveled man with track marks on both arms. His glasgow coma scale is 8. Pupillary examination reveals miosis. An ambulance is called and a reversing agent is administered. Which of the following is most accurate regarding the reversal agent most likely administered to this patient?
- A. Works on dopamine receptors
- B. Has a short half-life
- C. Can be given per oral
- D. Results in acute withdrawal (Correct Answer)
- E. Is a non-competitive inhibitor
Procedural sedation in children Explanation: ***Results in acute withdrawal***
- The patient's presentation (unconscious, track marks, miosis, bradypnea) is characteristic of **opioid overdose**. The reversal agent, **naloxone**, rapidly displaces opioids from their receptors, leading to an abrupt onset of withdrawal symptoms.
- **Acute opioid withdrawal** can manifest with symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, muscle cramps, and agitation, as the body suddenly lacks the opioid-induced suppression.
- This is the **most clinically significant** characteristic of naloxone in the acute overdose setting, as it explains the immediate physiological response patients experience.
*Works on dopamine receptors*
- **Naloxone** primarily acts as an **opioid receptor antagonist**, particularly at the mu-opioid receptor.
- It does not significantly interact with or exert its primary effects through **dopamine receptors**.
*Has a short half-life*
- While this statement is **factually true** (naloxone has a half-life of 30-81 minutes), it describes a **pharmacokinetic property** rather than a characteristic of its reversal mechanism.
- The question asks about the reversal agent in the context of immediate administration, where the **acute precipitation of withdrawal** is the most defining and immediate clinical consequence.
- The short half-life is clinically relevant for monitoring (patients may re-sedate), but it is not the most accurate statement regarding what happens when the reversal agent is administered.
*Can be given per oral*
- Although **naloxone** can be administered orally, its **bioavailability via the oral route is very low** (less than 3%) due to extensive first-pass metabolism.
- For acute overdose reversal, it is typically administered via intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, or intranasal routes for rapid and effective absorption.
*Is a non-competitive inhibitor*
- **Naloxone** is a **competitive antagonist** of opioid receptors, meaning it competes with opioids for binding sites.
- It does not bind to an allosteric site to reduce the opioid's efficiency (non-competitive inhibition); rather, it directly blocks the receptor.
Procedural sedation in children US Medical PG Question 5: A 15-month-old girl is brought to the emergency department shortly after a 2-minute episode of rhythmic eye blinking and uncontrolled shaking of all limbs. She was unresponsive during the episode. For the past few days, the girl has had a fever and mild nasal congestion. Her immunizations are up-to-date. Her temperature is 39.2°C (102.6°F), pulse is 110/min, respirations are 28/min, and blood pressure is 88/45 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 100%. She is sleepy but opens her eyes when her name is called. Examination shows moist mucous membranes. Neurologic examination shows no abnormalities. The neck is supple with normal range of motion. An oral dose of acetaminophen is administered. On re-evaluation, the girl is alert and playing with toys in the examination room. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Observe the patient for 24 hours
- B. Perform a CT scan of the head
- C. Administer lorazepam
- D. Perform an EEG
- E. Discharge the patient (Correct Answer)
Procedural sedation in children Explanation: ***Discharge the patient***
- The girl presented with a classic **febrile seizure**, characterized by a brief, generalized seizure associated with fever in the absence of an intracranial infection or other metabolic cause.
- Given that she is now alert, afebrile (after acetaminophen), neurologically normal, and her vital signs are stable, the most appropriate next step is to discharge her with instructions for parental education regarding febrile seizures.
*Observe the patient for 24 hours*
- Prolonged observation for 24 hours is generally not required for a **simple febrile seizure** once the child has fully recovered and is neurologically intact, and serious causes have been ruled out.
- This would be more appropriate for a **complex febrile seizure** (e.g., prolonged duration >15 minutes, focal features, multiple seizures in 24 hours) or if the child had not returned to their baseline.
*Perform a CT scan of the head*
- A **head CT scan** is not indicated for a typical febrile seizure, as there is no suspicion of intracranial pathology, infection, or trauma.
- Neuroimaging is reserved for cases with **focal neurologic deficits**, signs of increased intracranial pressure, or a history of significant head trauma.
*Administer lorazepam*
- **Lorazepam** is a benzodiazepine used to terminate ongoing seizures.
- Since the seizure has already stopped and the patient has fully recovered and is alert and playing, administering lorazepam would be unnecessary and could cause excessive sedation.
*Perform an EEG*
- An **EEG** is generally not recommended after a simple febrile seizure because it rarely helps in predicting the recurrence of febrile seizures or the development of epilepsy.
- EEG may be considered in cases of **atypical febrile seizures** or if there is a strong suspicion of an underlying epileptic disorder.
Procedural sedation in children US Medical PG Question 6: A 3-month-old boy is brought to the emergency room by his mother for 2 days of difficulty breathing. He was born at 35 weeks gestation but has otherwise been healthy. She noticed a cough and some trouble breathing in the setting of a runny nose. His temperature is 100°F (37.8°C), blood pressure is 64/34 mmHg, pulse is 140/min, respirations are 39/min, and oxygen saturation is 93% on room air. Pulmonary exam is notable for expiratory wheezing and crackles throughout and intercostal retractions. Oral mucosa is noted to be dry. Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic test?
- A. Chest radiograph
- B. Sputum culture
- C. Viral culture
- D. Polymerase chain reaction
- E. No further testing needed (Correct Answer)
Procedural sedation in children Explanation: ***No further testing needed***
- This patient presents with classic signs and symptoms of **bronchiolitis**, including a **preterm infant** (risk factor), **URI symptoms** followed by **respiratory distress** (cough, difficulty breathing), **expiratory wheezing**, and **crackles**.
- Bronchiolitis is a clinical diagnosis, and **routine testing** like chest X-rays or viral studies is generally **not recommended** for uncomplicated cases as it rarely changes management unless there are atypical features or concerns for other diagnoses.
*Chest radiograph*
- A chest X-ray is generally **not indicated** for typical bronchiolitis presentations. It may show hyperinflation or peribronchial thickening but these findings often do not alter management.
- It should only be considered if there are atypical signs, such as a localized finding on exam or concern for **pneumonia** or **atelectasis**, which are not strongly suggested here.
*Sputum culture*
- **Infants** typically **do not produce sputum** for culture.
- Bronchiolitis is primarily a **viral infection**, making bacterial sputum cultures **irrelevant** for initial diagnosis and management unless secondary bacterial infection is strongly suspected, for which there is no evidence here.
*Viral culture*
- While bronchiolitis is caused by viruses, typically **RSV**, **routine viral culture** or rapid antigen testing for RSV is usually **not necessary** for diagnosis in typical cases.
- Identification of the specific virus does not change the clinical management, which is primarily **supportive care**.
*Polymerase chain reaction*
- **PCR testing** can identify viral pathogens but is generally **not recommended** for uncomplicated bronchiolitis cases as it does not change the management plan, which focuses on supportive care.
- It might be considered in severe cases, for **infection control** purposes in a hospital setting, or if there is a specific need for **epidemiological surveillance**, none of which are described as immediate priorities for this patient.
Procedural sedation in children US Medical PG Question 7: A group of researchers is studying various inhaled substances to determine their anesthetic properties. In particular, they are trying to identify an anesthetic with fast onset and quick recovery for use in emergencies. They determine the following data:
Inhalational anesthetic Blood-gas partition coefficient
A 0.15
B 0.92
C 5.42
Which of the following statements is accurate with regard to these inhaled anesthetic substances?
- A. Agent C has the fastest onset of action
- B. Agent A has the fastest onset of action (Correct Answer)
- C. Agent B is the most potent
- D. Agent B has the fastest onset of action
- E. Agent A is the most potent
Procedural sedation in children Explanation: ***Agent A has the fastest onset of action***
- **Agent A** has the lowest blood-gas partition coefficient (0.15), indicating very low solubility in blood.
- A **low blood-gas partition coefficient** means the anesthetic quickly equilibrates between the lungs and blood, leading to a rapid rise in partial pressure in the brain and thus **fast onset of action** and **quick recovery**.
*Agent C has the fastest onset of action*
- **Agent C** has the highest blood-gas partition coefficient (5.42), indicating high solubility in blood.
- High solubility means the anesthetic takes longer to saturate the blood and reach the brain, resulting in a **slow onset of action** and **slow recovery**.
*Agent B is the most potent*
- **Potency** of an inhaled anesthetic is inversely related to its **Minimum Alveolar Concentration (MAC)**, not directly to its blood-gas partition coefficient.
- While a higher blood-gas coefficient can sometimes correlate with other properties, it does not directly determine potency.
*Agent B has the fastest onset of action*
- **Agent B** has a blood-gas partition coefficient of 0.92, which is higher than Agent A (0.15).
- A higher blood-gas partition coefficient means the anesthetic is more soluble in blood, leading to a **slower onset of action** compared to Agent A.
*Agent A is the most potent*
- **Agent A** has the lowest blood-gas partition coefficient (0.15), which indicates **fast onset** and **rapid recovery**, but not necessarily high potency.
- **Potency** is determined by MAC (Minimum Alveolar Concentration), which is the concentration of anesthetic at 1 atmosphere that produces immobility in 50% of patients challenged with a surgical incision.
Procedural sedation in children US Medical PG Question 8: A 42-year-old man presents to his family physician for evaluation of oral pain. He states that he has increasing pain in a molar on the top left of his mouth. The pain started 1 week ago and has been progressively worsening since then. His medical history is significant for hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus, both of which are currently controlled with lifestyle modifications. His blood pressure is 124/86 mm Hg, heart rate is 86/min, and respiratory rate is 14/min. Physical examination is notable for a yellow-black discoloration of the second molar on his left upper mouth. The decision is made to refer him to a dentist for further management of this cavity. The patient has never had any dental procedures and is nervous about what type of sedation will be used. Which of the following forms of anesthesia utilizes solely an oral or intravenous anti-anxiety medication?
- A. Minimal Sedation (Correct Answer)
- B. Dissociation
- C. Regional anesthesia
- D. Epidural anesthesia
- E. Deep sedation
Procedural sedation in children Explanation: ***Minimal Sedation***
- This involves using **oral** or **intravenous anti-anxiety medications** to help a patient relax while remaining conscious and responsive.
- The patient can still respond to verbal commands but is in a state of decreased anxiety and awareness.
*Dissociation*
- This is a state induced by certain drugs, like **ketamine**, where the patient feels detached from their body and environment.
- While it can be achieved intravenously, it is not solely an anti-anxiety medication effect and involves a different neurological state.
*Regional anesthesia*
- This involves injecting a **local anesthetic** near nerves to numb a specific part of the body, such as a limb or a jaw section for dental procedures.
- It primarily provides pain relief by blocking nerve signals and does not typically involve anti-anxiety medication as its sole component for sedation.
*Epidural anesthesia*
- This form of regional anesthesia involves injecting a **local anesthetic** into the **epidural space** surrounding the spinal cord to block pain signals.
- It is used for pain control during surgery or childbirth and does not involve oral or intravenous anti-anxiety medication as the primary method of sedation.
*Deep sedation*
- This involves a more profound depression of consciousness than minimal sedation, where the patient may be difficult to arouse but still responds purposefully to repeated or painful stimulation.
- While it can use intravenous medications, it typically involves a combination of sedatives and analgesics to achieve a deeper state of unresponsiveness, beyond just anti-anxiety medication.
Procedural sedation in children US Medical PG Question 9: A mother brings her 6-month-old boy to the emergency department. She reports that her son has been breathing faster than usual for the past 2 days, and she has noted occasional wheezing. She states that prior to the difficulty breathing, she noticed some clear nasal discharge for several days. The infant was born full-term, with no complications, and no significant medical history. His temperature is 100°F (37.8°C), blood pressure is 60/30 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 40/min, and oxygen saturation is 95% on room air. Physical exam reveals expiratory wheezing, crackles diffusely, and intercostal retractions. The child is currently playing with toys. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Monitoring (Correct Answer)
- B. Intubation
- C. Albuterol
- D. Chest radiograph
- E. Azithromycin and ceftriaxone
Procedural sedation in children Explanation: ***Monitoring (Supportive Care)***
- This infant presents with classic **viral bronchiolitis** (tachypnea, wheezing, crackles, retractions following upper respiratory symptoms)
- The child is **clinically stable**: O2 saturation 95% on room air, alert and playing with toys
- **Current AAP guidelines** recommend **supportive care only** for bronchiolitis, which includes monitoring vital signs, assessing work of breathing, ensuring adequate hydration, and oxygen supplementation if saturation drops below 90%
- This patient requires close observation but no immediate intervention given stable vital signs and reassuring clinical appearance
*Albuterol*
- **Bronchodilators are NOT recommended** for routine use in bronchiolitis per current AAP clinical practice guidelines
- Multiple randomized controlled trials have shown **no significant benefit** from albuterol in bronchiolitis
- While a trial may be considered in select cases with strong family history of asthma, routine use is discouraged
- Bronchiolitis is caused by **small airway inflammation and mucus plugging**, not bronchospasm
*Intubation*
- **Intubation** is reserved for severe respiratory failure with impending respiratory arrest, persistent hypoxemia despite high-flow oxygen, apnea, or altered mental status
- This child has adequate oxygenation (95%), is alert, and playing—**no indication for intubation**
- Signs that would warrant intubation include lethargy, severe retractions with fatigue, O2 sat <90% despite supplementation
*Chest radiograph*
- **Not routinely indicated** in typical bronchiolitis
- Consider only if there's diagnostic uncertainty, concern for complications (pneumothorax, lobar consolidation suggesting bacterial pneumonia), or failure to improve with supportive care
- The clinical presentation is clearly consistent with bronchiolitis, and imaging would not change initial management
*Azithromycin and ceftriaxone*
- Bronchiolitis is a **viral infection** (most commonly RSV), and **antibiotics provide no benefit**
- Antibiotics should only be used if there is clear evidence of **bacterial superinfection** (high fever, focal consolidation, elevated inflammatory markers)
- Routine antibiotic use contributes to antimicrobial resistance and adverse effects
Procedural sedation in children US Medical PG Question 10: A 12-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her parents due to severe shortness of breath that started 20 minutes ago. She has a history of asthma and her current treatment regime includes a beta-agonist inhaler as well as a medium-dose corticosteroid inhaler. Her mother tells the physician that her daughter was playing outside with her friends when she suddenly started experiencing difficulty breathing and used her inhaler without improvement. On examination, she is struggling to breathe and with subcostal and intercostal retractions. She is leaning forward, and gasping for air and refuses to lie down on the examination table. Her blood pressure is 130/92 mm Hg, the respirations are 27/min, the pulse is 110/min and O2 saturation is 87%. There is prominent expiratory wheezes in all lung fields. The patient is put on a nonrebreather mask with 100% oxygen. An arterial blood gas is collected and sent for analysis. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Intramuscular epinephrine
- B. Intravenous corticosteroid
- C. Inhaled ipratropium bromide
- D. Inhaled albuterol (Correct Answer)
- E. Intravenous theophylline
Procedural sedation in children Explanation: ***Inhaled albuterol***
- Given the patient's acute and severe asthma exacerbation, **inhaled albuterol**, a short-acting beta-agonist (SABA), is the most crucial initial bronchodilator to relieve bronchospasm.
- Her symptoms (severe dyspnea, retractions, tachypnea, tachycardia, low oxygen saturation, and prominent wheezing despite prior SABA use) indicate a need for immediate and aggressive bronchodilation.
*Intramuscular epinephrine*
- **Epinephrine** is primarily used for **anaphylaxis** or severe allergic reactions, which is not suggested by this patient's history or presentation (no mention of allergen exposure, urticaria, angioedema, or circulatory collapse typical of anaphylaxis).
- While it has bronchodilatory effects, it is not the first-line treatment for acute asthma exacerbations.
*Intravenous corticosteroid*
- **Systemic corticosteroids** (e.g., prednisone, methylprednisolone) are essential for reducing airway inflammation in moderate to severe asthma exacerbations and preventing relapse.
- However, their onset of action is typically several hours, so they are not the immediate solution for acute bronchospasm but should be administered shortly after initial bronchodilators.
*Inhaled ipratropium bromide*
- **Ipratropium bromide**, an anticholinergic bronchodilator, is often used in conjunction with albuterol for severe asthma exacerbations.
- It provides additional bronchodilation by blocking muscarinic receptors, but albuterol (a SABA) remains the primary and most rapid-acting bronchodilator for acute relief.
*Intravenous theophylline*
- **Theophylline** is a methylxanthine bronchodilator administered intravenously or orally, not by inhalation.
- It is rarely used in acute asthma management due to its narrow therapeutic index, significant side effect profile, requirement for drug level monitoring, and availability of safer, more effective alternatives.
- It may be considered only in refractory cases that do not respond to standard therapy.
More Procedural sedation in children US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.