Group B streptococcal disease US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Group B streptococcal disease. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Group B streptococcal disease US Medical PG Question 1: An 18-month-old boy presents to the emergency department for malaise. The boy’s parents report worsening fatigue for 3 days with associated irritability and anorexia. The patient’s newborn screening revealed a point mutation in the beta-globin gene but the patient has otherwise been healthy since birth. On physical exam, his temperature is 102.4°F (39.1°C), blood pressure is 78/42 mmHg, pulse is 124/min, and respirations are 32/min. The child is tired-appearing and difficult to soothe. Laboratory testing is performed and reveals the following:
Serum:
Na+: 137 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
K+: 4.4 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen: 16 mg/dL
Creatinine: 0.9 mg/dL
Glucose: 96 mg/dL
Leukocyte count: 19,300/mm^3 with normal differential
Hemoglobin: 7.8 g/dL
Hematocrit: 21%
Mean corpuscular volume: 82 um^3
Platelet count: 324,000/mm^3
Reticulocyte index: 3.6%
Which of the following is the most likely causative organism for this patient's presentation?
- A. Streptococcus pneumoniae (Correct Answer)
- B. Listeria monocytogenes
- C. Haemophilus influenzae
- D. Neisseria meningitidis
- E. Salmonella
Group B streptococcal disease Explanation: ***Streptococcus pneumoniae***
- Patients with **sickle cell disease** (indicated by the beta-globin gene mutation) are functionally **asplenic** and highly susceptible to encapsulated bacteria, with *S. pneumoniae* being the most common cause of **sepsis** in this population.
- The patient's presentation with **fever**, **hypotension**, **tachycardia**, and **leukocytosis** is consistent with **sepsis**, and the elevated reticulocyte index suggests a hemolytic process or bone marrow response, common in sickle cell crises exacerbated by infection.
*Listeria monocytogenes*
- This pathogen primarily affects **neonates**, **immunocompromised individuals**, and **elderly** patients, often presenting as meningitis or sepsis.
- While it can cause sepsis, it is a less common cause of severe infection in a non-neonatal toddler with sickle cell disease compared to *S. pneumoniae*.
*Haemophilus influenzae*
- Although *H. influenzae* is an encapsulated bacterium that can cause severe infections in functionally asplenic patients, routine childhood vaccinations have significantly reduced its incidence.
- While possible, it is less likely than *S. pneumoniae* in an 18-month-old, especially if vaccinated, and *S. pneumoniae* remains the leading cause of sepsis in sickle cell patients.
*Neisseria meningitidis*
- *N. meningitidis* is another encapsulated bacterium that can cause serious infections, including **meningitis** and **sepsis**, particularly in immunocompromised individuals like those with sickle cell disease.
- However, the incidence of **meningococcal disease** is generally lower than **pneumococcal disease** in this age group, and the absence of classic meningeal signs or petechial rash makes it a less probable primary suspect compared to *S. pneumoniae*.
*Salmonella*
- *Salmonella* species can cause **osteomyelitis** and **sepsis** in patients with sickle cell disease, often presenting with gastrointestinal symptoms.
- While a known pathogen in this population, the clinical picture of **rapidly progressive sepsis** without clear GI focus makes *S. pneumoniae* a more immediate and common concern.
Group B streptococcal disease US Medical PG Question 2: A 3100-g (6.9-lb) male newborn is brought to the emergency department by his mother because of fever and irritability. The newborn was delivered at home 15 hours ago. He was born at 39 weeks' gestation. The mother's last prenatal visit was at the beginning of the first trimester. She received all standard immunizations upon immigrating from Mexico two years ago. Seven weeks ago, she experienced an episode of painful, itching genital vesicles, which resolved spontaneously. Four hours before going into labor she noticed a gush of blood-tinged fluid from her vagina. The newborn is ill-appearing and lethargic. His temperature is 39.9°C (103.8°F), pulse is 170/min, respirations are 60/min, and blood pressure is 70/45 mm Hg. His skin is mildly icteric. Expiratory grunting is heard on auscultation. Skin turgor and muscle tone are decreased. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 15 g/dL
Leukocyte count 33,800/mm3
Platelet count 100,000/mm3
Serum glucose 55 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely causal organism?
- A. Clostridium botulinum
- B. Staphylococcus epidermidis
- C. Streptococcus agalactiae (Correct Answer)
- D. Staphylococcus aureus
- E. Neisseria meningitidis
Group B streptococcal disease Explanation: ***Streptococcus agalactiae (Group B Streptococcus)***
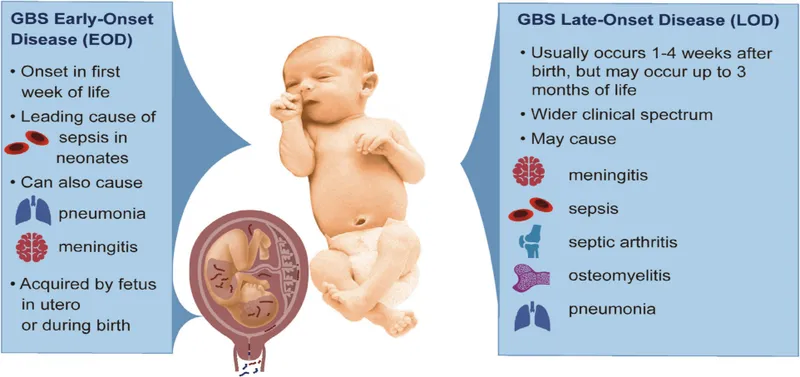
- **Most common cause of early-onset neonatal sepsis** (0-7 days of life), typically presenting within hours of birth
- Key risk factors present: **inadequate prenatal care** (no GBS screening at 35-37 weeks or intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis), **home delivery**, and possible **prolonged rupture of membranes**
- Classic presentation: **fever, lethargy, respiratory distress** (grunting), **hemodynamic instability**, leukocytosis with left shift, and thrombocytopenia
- The mother's history of genital vesicles 7 weeks ago is a **distractor** (resolved HSV would not cause this presentation; neonatal HSV presents with vesicular rash, seizures, or disseminated disease)
*Clostridium botulinum*
- Causes **infant botulism**, presenting with **descending flaccid paralysis** ("floppy baby syndrome"), constipation, poor feeding, and weak cry
- Does NOT cause fever or acute sepsis syndrome
- Acquired through ingestion of **spores** (e.g., honey), not vertical transmission during birth
*Staphylococcus epidermidis*
- Causes **late-onset sepsis** (>7 days) or **nosocomial infections** in hospitalized neonates, especially those with indwelling catheters or central lines
- **Not** a typical cause of early-onset sepsis in a full-term newborn delivered at home
- Associated with **coagulase-negative** staphylococci and biofilm formation on devices
*Staphylococcus aureus*
- Can cause neonatal infections but typically presents as **skin/soft tissue infections, omphalitis, or osteomyelitis** rather than early-onset sepsis
- When causing sepsis, usually occurs **later** in the neonatal period
- Less common than GBS for early-onset sepsis acquired during delivery
*Neisseria meningitidis*
- **Rare** cause of neonatal sepsis; more common in older infants and children
- Vertical transmission is uncommon
- When present, often associated with **petechial or purpuric rash** and fulminant sepsis with rapid progression
Group B streptococcal disease US Medical PG Question 3: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the physician for the evaluation of sore throat for the past 2 days. During this period, he has had intermittent nausea and has vomited once. The patient has no cough, hoarseness, or rhinorrhea. He had similar symptoms at the age of 5 years that resolved spontaneously. He is otherwise healthy. His temperature is 37.9°C (100.2°F), pulse is 85/min, and blood pressure is 108/70 mm Hg. Head and neck examination shows an erythematous pharynx with grayish exudates overlying the palatine tonsils. There is no lymphadenopathy. Rapid antigen detection test for group A streptococci is negative. Which of the following is most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Reassurance and follow-up in two weeks
- B. Obtain throat culture (Correct Answer)
- C. Measurement of antistreptolysin O titer
- D. Penicillin V therapy
- E. Measurement of antiviral capsid antigen IgM antibody
Group B streptococcal disease Explanation: ***Obtain throat culture***
- A negative **rapid antigen detection test (RADT)** for Group A Streptococcus (GAS) does not rule out GAS infection, especially with the presence of **exudative pharyngitis** and history of previous spontaneous resolution of similar symptoms. A throat culture is a more sensitive test to confirm or rule out GAS.
- Given the patient's age (7 years old) and the clinical presentation (sore throat, fever, tonsillar exudates, no cough), there's a risk of **rheumatic fever** if GAS is not adequately treated. A throat culture is crucial for definitive diagnosis and to guide antibiotic therapy.
*Reassurance and follow-up in two weeks*
- This approach is inappropriate as it carries the risk of missing a **GAS infection**, which could lead to serious complications like acute **rheumatic fever** or acute **post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis**.
- Although the RADT was negative, the clinical picture is still highly suspicious for bacterial pharyngitis, making immediate follow-up and definitive diagnosis necessary.
*Measurement of antistreptolysin O titer*
- **Antistreptolysin O (ASO) titer** measures past exposure to GAS and is not useful for diagnosing acute infection. It typically peaks 3-6 weeks after the infection.
- For guiding acute management and antibiotic therapy, a real-time diagnostic test like a **throat culture** or RADT is required.
*Penicillin V therapy*
- Initiating antibiotic therapy empirically based on a negative RADT is not recommended. It could lead to **antibiotic overuse** if the infection is viral, or delay appropriate treatment if the RADT is a false negative.
- **Penicillin V** is the drug of choice for GAS pharyngitis, but it should only be prescribed once a definitive diagnosis is made, typically by a positive culture after a negative RADT.
*Measurement of antiviral capsid antigen IgM antibody*
- This antibody test is used to diagnose **Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)** infection (infectious mononucleosis), which can cause pharyngitis with exudates.
- While EBV is a possibility, a throat culture is a more direct and immediate next step to rule out **GAS**, which carries a higher risk of serious complications if untreated in this age group and clinical context.
Group B streptococcal disease US Medical PG Question 4: You are treating a neonate with meningitis using ampicillin and a second antibiotic, X, that is known to cause ototoxicity. What is the mechanism of antibiotic X?
- A. It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex
- B. It binds the 30S ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex (Correct Answer)
- C. It binds the 30S ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation
- D. It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits peptidyltransferase
- E. It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation
Group B streptococcal disease Explanation: ***It binds the 30s ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex***
- The second antibiotic, X, is likely an **aminoglycoside**, such as **gentamicin** or **amikacin**, which are commonly used in combination with ampicillin for neonatal meningitis and are known to cause ototoxicity.
- Aminoglycosides exert their bactericidal effect by **irreversibly binding to the 30S ribosomal subunit**, thereby **inhibiting the formation of the initiation complex** and leading to misreading of mRNA.
*It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits formation of the initiation complex*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **linezolid**, which targets the 50S ribosomal subunit to prevent the formation of the initiation complex.
- While linezolid can cause side effects, **ototoxicity** is less commonly associated with it compared to aminoglycosides, and it is not a primary drug for neonatal meningitis alongside ampicillin.
*It binds the 50S ribosomal subunit and inhibits peptidyltransferase*
- This is the mechanism of action for **chloramphenicol**, which inhibits **peptidyltransferase** activity on the 50S ribosomal subunit, preventing peptide bond formation.
- Although chloramphenicol can cause **ototoxicity** and **aplastic anemia**, its use in neonates is limited due to the risk of **Gray Baby Syndrome**.
*It binds the 30s ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation*
- This describes the mechanism of action of **tetracyclines**, which reversibly bind to the 30S ribosomal subunit and prevent the attachment of aminoacyl-tRNA, thereby inhibiting protein synthesis.
- Tetracyclines are **contraindicated in neonates** due to their potential to cause **tooth discoloration** and **bone growth inhibition**, and ototoxicity is not their primary adverse effect.
*It binds the 50s ribosomal subunit and reversibly inhibits translocation*
- This mechanism of reversibly inhibiting translocation by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit is characteristic of **macrolides** (e.g., erythromycin, azithromycin) and **clindamycin**.
- While some macrolides can cause **transient ototoxicity**, they are not typically the second antibiotic of choice for neonatal meningitis in combination with ampicillin, and clindamycin's side effect profile is different.
Group B streptococcal disease US Medical PG Question 5: A 63-year-old man with aortic valve disease is admitted to the hospital for a 3-week history of progressively worsening fatigue, fever, and night sweats. He does not smoke, drink alcohol, or use illicit drugs. Temperature is 38.2°C (100.8°F). Physical examination shows a systolic murmur and tender, erythematous nodules on the finger pads. Blood cultures show alpha-hemolytic, gram-positive cocci that are catalase-negative and optochin-resistant. Which of the following is the most likely causal organism?
- A. Streptococcus pneumoniae
- B. Staphylococcus epidermidis
- C. Viridans streptococci (Correct Answer)
- D. Streptococcus pyogenes
- E. Streptococcus gallolyticus
Group B streptococcal disease Explanation: ***Viridans streptococci***
- The patient's presentation with **subacute onset** of fever, fatigue, cardiac murmur, and **Osler nodes** (tender finger nodules) points to **infective endocarditis**. The micro-organism is described as **alpha-hemolytic**, **catalase-negative**, and **optochin-resistant**, which are characteristic features of **Viridans streptococci**.
- **Viridans streptococci** are a common cause of **subacute bacterial endocarditis**, especially in patients with pre-existing valvular disease like the **aortic valve disease** mentioned.
*Streptococcus pneumoniae*
- While **Streptococcus pneumoniae** is also **alpha-hemolytic** and **catalase-negative**, it is typically **optochin-sensitive** and a common cause of **pneumonia** and **meningitis**, not usually subacute endocarditis from oral flora.
- Endocarditis caused by *S. pneumoniae* is rare and usually associated with a more fulminant course.
*Staphylococcus epidermidis*
- **Staphylococcus epidermidis** is a **coagulase-negative staphylococcus** that is a common cause of **prosthetic valve endocarditis** and is **catalase-positive**, unlike the organism described here.
- It is not typically alpha-hemolytic.
*Streptococcus pyogenes*
- **Streptococcus pyogenes** is **beta-hemolytic** and **catalase-negative**, and typically causes **pharyngitis** and **skin infections**, or sometimes **acute endocarditis**.
- It does not fit the description of an **alpha-hemolytic**, **optochin-resistant** organism.
*Streptococcus gallolyticus*
- **Streptococcus gallolyticus** (formerly *Streptococcus bovis*) is associated with **bacteremia** and **endocarditis**, particularly in patients with **gastrointestinal malignancies**.
- While it is **alpha-hemolytic** and **catalase-negative**, it is typically differentiated by its growth in **bile esculin** and is not primarily defined by optochin resistance characteristic of Viridans group.
Group B streptococcal disease US Medical PG Question 6: A 62-year-old woman presents to the emergency department for evaluation of a spreading skin infection that began from an ulcer on her foot. The patient has type 2 diabetes mellitus that is poorly controlled. On examination, there is redness and erythema to the lower limb with skin breakdown along an extensive portion of the leg. The patient’s tissues separate readily from the fascial plane, prompting a diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. What is the exotoxin most likely associated with this patient’s presentation?
- A. Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxin A
- B. TSST-1
- C. Diphtheria toxin
- D. Exfoliative toxin
- E. Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxin B (Correct Answer)
Group B streptococcal disease Explanation: ***Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxin B***
- **Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxin B** is a **cysteine protease** that directly degrades tissue, including collagen and fibronectin, leading to the rapid tissue destruction characteristic of **necrotizing fasciitis**.
- This exotoxin is frequently associated with **Group A Streptococcus (GAS)** infections, a common cause of severe soft tissue infections, especially in immunocompromised individuals like diabetics.
*Streptococcal pyogenic exotoxin A*
- This exotoxin acts as a **superantigen**, primarily causing symptoms of **streptococcal toxic shock syndrome** (STSS), characterized by fever, rash, and organ failure.
- While GAS can cause necrotizing fasciitis, Exotoxin A is more closely linked to toxic shock phenomena rather than direct tissue destruction.
*TSST-1*
- **Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 (TSST-1)** is produced by **Staphylococcus aureus** and is a classic cause of **staphylococcal toxic shock syndrome**.
- It acts as a **superantigen** but is not directly responsible for the extensive tissue necrosis seen in necrotizing fasciitis caused by streptococci.
*Diphtheria toxin*
- **Diphtheria toxin**, produced by *Corynebacterium diphtheriae*, inhibits **protein synthesis** by inactivating elongation factor-2 (EF-2), leading to cell death.
- It causes diphtheria, characterized by a **pseudomembrane** in the throat and myocarditis, not necrotizing fasciitis.
*Exfoliative toxin*
- **Exfoliative toxins A and B** are produced by **Staphylococcus aureus** and are responsible for **Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome (SSSS)**.
- These toxins cause cleavage of desmoglein-1 in the epidermis, leading to widespread blistering and desquamation, not deep tissue necrosis.
Group B streptococcal disease US Medical PG Question 7: An 82-year-old man presents with painless swelling of the neck for the past week. He reports no recent fever, night sweats, or weight loss. He has no significant medical history, and his only medication is daily aspirin. His temperature is 36.8℃ (98.2℉). On physical examination, there are several non-tender lymph nodes, each averaging 2 cm in diameter, which are palpable in the right anterior cervical triangle. No other palpable lymphadenopathy is noted. The remainder of the physical exam is unremarkable. Laboratory studies show the following:
Hemoglobin 10 g/dL
Leukocyte count 8000/mm3 with a normal differential
Platelet count 250,000/mm3
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
30 mm/h
An excisional biopsy of a cervical lymph node reveals the presence of Reed-Sternberg (RS) cells. Computed tomography (CT) scans and positron emission tomography (PET) scans reveal no mediastinal mass or signs of additional disease. Which of the following aspects most strongly indicates a good prognosis for this patient?
- A. Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- B. Leukocyte count and differential
- C. Absence of B symptoms
- D. Stage of the disease (Correct Answer)
- E. Hemoglobin level
Group B streptococcal disease Explanation: ***Stage of the disease***
- The **stage of Hodgkin lymphoma** is the most significant prognostic factor, with **earlier stages (I and II)** having a much better prognosis than advanced stages (III and IV). The prompt indicates **no mediastinal mass or additional disease**, suggesting an early stage.
- Absence of widespread disease in CT and PET scans is a critical indicator of **localized disease**, which is associated with higher cure rates.
*Absence of B symptoms*
- While the **absence of B symptoms** (fever, night sweats, weight loss) is a favorable prognostic indicator, it is secondary to the overall disease stage in predicting long-term outcomes in Hodgkin lymphoma.
- The patient's lack of B symptoms is positive, but the *extent of disease spread* (stage) remains the primary determinant of prognosis.
*Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)*
- An **elevated ESR** (30 mm/h in this case) is a known adverse prognostic factor in Hodgkin lymphoma, indicating systemic inflammation.
- While important, it is a **secondary indicator** and does not outweigh the significance of disease stage in determining prognosis.
*Hemoglobin level*
- A **hemoglobin level below 10.5 g/dL** is an adverse prognostic factor in Hodgkin lymphoma according to the International Prognostic Score, and this patient's hemoglobin is 10 g/dL.
- This factor suggests a potentially **worse prognosis**, making it an incorrect answer for "good prognosis."
*Leukocyte count and differential*
- An **elevated leukocyte count** (above 15,000/mm³) and a **lymphopenia** (absolute lymphocyte count less than 600/mm³ or less than 8% of the white cell count) are adverse prognostic factors in Hodgkin lymphoma.
- This patient has a normal leukocyte count and differential (8000/mm³ with normal differential), which is **neutral to good** but less impactful than the disease stage.
Group B streptococcal disease US Medical PG Question 8: A 5-year-old child is brought to a pediatric clinic by his mother for a rash that started a few days ago. The mother adds that her son has also had a fever and sore throat since last week. His immunizations are up to date. On examination, a rash is present over the trunk and upper extremities and feels like sandpaper to touch. An oropharyngeal examination is suggestive of exudative pharyngitis with a white coat over the tongue. The physician swabs the throat and uses the swab in a rapid antigen detection test kit. He also sends the sample for microbiological culture. The physician then recommends empiric antibiotic therapy and tells the mother that if the boy is left untreated, the likelihood of developing a complication later in life is very high. Which of the following best explains the mechanism underlying the development of the complication the physician is talking about?
- A. Antigenic shift
- B. Bacterial tissue invasion
- C. Toxin-mediated cellular damage
- D. Molecular mimicry (Correct Answer)
- E. Genetic drift
Group B streptococcal disease Explanation: ***Molecular mimicry***
- The clinical presentation suggests **streptococcal pharyngitis** (sore throat, fever, sandpaper rash, exudative pharyngitis), which, if untreated, can lead to **rheumatic fever**.
- **Molecular mimicry** occurs when antibodies produced against streptococcal M protein cross-react with self-antigens in the heart, joints, and brain, causing auto-immune damage characteristic of rheumatic fever.
*Antigenic shift*
- This mechanism involves **major genetic re-assortment** in viruses (e.g., influenza A) leading to new strains, which is not relevant to complications from bacterial infections like strep throat.
- It results in pandemics due to a lack of pre-existing immunity in the population, unlike the autoimmune sequelae of bacterial infections.
*Bacterial tissue invasion*
- While bacteria can invade tissues, the serious long-term complications of streptococcal pharyngitis (like rheumatic fever) are not primarily due to **direct tissue invasion** by the bacteria themselves.
- Instead, the tissue damage results from a **post-infectious autoimmune response**.
*Toxin-mediated cellular damage*
- **Streptococcal toxins** (e.g., erythrogenic toxins) are responsible for the rash (scarlatiniform rash or scarlet fever) but not for the specific long-term autoimmune complications like rheumatic fever.
- Toxin-mediated damage occurs acutely during the infection, whereas rheumatic fever is a delayed immune-mediated sequela.
*Genetic drift*
- This mechanism describes **minor genetic mutations** that accumulate over time in viruses (e.g., influenza), leading to seasonal epidemics.
- It does not explain the autoimmune complications associated with bacterial infections such as those caused by *Streptococcus pyogenes*.
Group B streptococcal disease US Medical PG Question 9: A 10-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents because of a dull persistent headache beginning that morning. He has nausea and has vomited twice. During the past four days, the patient has had left-sided ear pain and fever, but his parents did not seek medical attention. He is from Thailand and is visiting his relatives in the United States for the summer. There is no personal or family history of serious illness. He is at the 45th percentile for height and 40th percentile for weight. He appears irritable. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 110/min, and blood pressure is 98/58 mm Hg. The pupils are equal and reactive to light. Lateral gaze of the left eye is limited. The left tympanic membrane is erythematous with purulent discharge. There is no nuchal rigidity. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Intravenous ceftriaxone and clindamycin therapy
- B. Lumbar puncture
- C. MRI of the brain (Correct Answer)
- D. Intravenous cefazolin and metronidazole therapy
- E. Cranial burr hole evacuation
Group B streptococcal disease Explanation: ***MRI of the brain***
- The patient's presentation with **headache**, **nausea**, **vomiting**, recent **ear infection** (otitis media), **fever**, and **abducens nerve palsy** (limited lateral gaze of the left eye) is highly suggestive of an intracranial complication, such as a **brain abscess** or **epidural abscess**, secondary to the uncontrolled otitis media.
- An MRI of the brain is the **most sensitive and specific imaging modality** for detecting intracranial abscesses, which are critical to diagnose promptly due to their potential for surgical drainage and targeted antibiotic therapy.
*Intravenous ceftriaxone and clindamycin therapy*
- While broad-spectrum antibiotics are necessary, they should be initiated **after establishing a definitive diagnosis and ruling out conditions requiring immediate surgical intervention**.
- Without imaging, there's a risk of delaying crucial surgical management for a contained abscess or empyema.
*Lumbar puncture*
- A lumbar puncture is **contraindicated** in the presence of focal neurological deficits (like **abducens nerve palsy**) and symptoms of **increased intracranial pressure** (headache, nausea, vomiting), as it carries a significant risk of **herniation** if there's a mass lesion.
- Imaging should always precede LP in such cases.
*Intravenous cefazolin and metronidazole therapy*
- Cefazolin has **poor penetration into the CNS**, making it an inadequate choice for suspected intracranial infection.
- While metronidazole targets anaerobes common in brain abscesses, the overall regimen is not optimal, and imaging is still the priority.
*Cranial burr hole evacuation*
- This is a definitive surgical treatment for a brain abscess but should only be performed **after the abscess has been localized and characterized by imaging**.
- Performing a burr hole without prior imaging would be a blind procedure and is not the appropriate next step in diagnosis and management.
Group B streptococcal disease US Medical PG Question 10: A 10-year-old girl with a rash is brought to the clinic by her mother. The patient’s mother says that the onset of the rash occurred 2 days ago. The rash was itchy, red, and initially localized to the cheeks with circumoral pallor, and it gradually spread to the arms and trunk. The patient’s mother also says her daughter had been reporting a high fever of 39.4°C (102.9°F), headaches, myalgia, and flu-like symptoms about a week ago, which resolved in 2 days with acetaminophen. The patient has no significant past medical history. Her vital signs include: temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 90/min, blood pressure 125/85 mm Hg, respiratory rate 20/min. Physical examination shows a symmetric erythematous maculopapular rash on both cheeks with circumoral pallor, which extends to the patient’s trunk, arms, and buttocks. The remainder of the exam is unremarkable. Laboratory findings are significant for a leukocyte count of 7,100/mm3 and platelet count of 325,000/mm3. Which of the following is the next best step in the management of this patient?
- A. Administer intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)
- B. Discharge home, saying that the patient may return to school after the disappearance of the rash
- C. Transfuse with whole blood
- D. Discharge home with instructions for strict isolation from pregnant women until disappearance of the rash
- E. Discharge home, saying that the patient may immediately return to school (Correct Answer)
Group B streptococcal disease Explanation: ***Discharge home, saying that the patient may immediately return to school***
- This patient likely has **Fifth Disease (Erythema Infectiosum)**, caused by **Parvovirus B19**, characterized by a **"slapped cheek" rash** and a **lacy, reticular rash** on the trunk and extremities.
- Patients with Fifth Disease are **contagious before the rash appears** and are generally **no longer contagious once the rash develops**, making immediate return to school safe.
*Administer intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)*
- **IVIG** is typically reserved for **severe cases of Parvovirus B19 infection** in immunocompromised individuals or those with chronic hemolytic anemias who develop **aplastic crisis**.
- The patient's symptoms are mild and self-limiting, without evidence of severe complications like aplastic anemia (normal leukocyte and platelet counts).
*Discharge home, saying that the patient may return to school after the disappearance of the rash*
- This advice is incorrect because the patient is **no longer contagious once the rash erupts**.
- Requiring isolation until the rash disappears would be unnecessarily disruptive and is not medically indicated for Fifth Disease.
*Transfuse with whole blood*
- **Whole blood transfusion** is not indicated for uncomplicated Fifth Disease, as it can cause significant complications.
- Transfusions are considered only in cases of **severe aplastic crisis** with significant anemia, which is not present in this patient (normal complete blood count).
*Discharge home with instructions for strict isolation from pregnant women until disappearance of the rash*
- While exposure to **Parvovirus B19 in pregnant women** can lead to significant fetal complications (e.g., hydrops fetalis), the patient is **no longer infectious once the rash appears**.
- Therefore, strict isolation from pregnant women **after rash onset** is not necessary, as the risk of transmission has passed.
More Group B streptococcal disease US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.