Early-onset sepsis US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Early-onset sepsis. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Early-onset sepsis US Medical PG Question 1: A neonate born at 33 weeks is transferred to the NICU after a complicated pregnancy and C-section. A week after being admitted, he developed a fever and became lethargic and minimally responsive to stimuli. A lumbar puncture is performed that reveals the following:
Appearance Cloudy
Protein 64 mg/dL
Glucose 22 mg/dL
Pressure 330 mm H20
Cells 295 cells/mm³ (> 90% PMN)
A specimen is sent to microbiology and reveals gram-negative rods. Which of the following is the next appropriate step in management?
- A. MRI scan of the head
- B. Start the patient on IV ceftriaxone
- C. Provide supportive measures only
- D. Start the patient on IV cefotaxime (Correct Answer)
- E. Start the patient on oral rifampin
Early-onset sepsis Explanation: ***Start the patient on IV cefotaxime***
- The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis with **cloudy appearance, elevated protein, low glucose, high pressure, and predominant PMNs**, coupled with **gram-negative rods** on microscopy, is highly suggestive of **bacterial meningitis** in a neonate.
- **Cefotaxime** is a third-generation cephalosporin commonly used for neonatal meningitis caused by gram-negative organisms due to its excellent CSF penetration and broad-spectrum activity, particularly against common neonatal pathogens like *E. coli* which can present as gram-negative rods.
*MRI scan of the head*
- An MRI would be considered **after initiating appropriate antibiotic treatment** to assess for complications like abscess formation or ventriculitis, not as the immediate next step in an acute, life-threatening infection.
- Delaying antibiotic treatment for imaging in acute bacterial meningitis can lead to increased morbidity and mortality.
*Start the patient on IV ceftriaxone*
- While ceftriaxone is a third-generation cephalosporin, it is **generally avoided in neonates** due to the risk of **biliary sludging** and **kernicterus**.
- Ceftriaxone competes with bilirubin for albumin binding sites, which is particularly risky in neonates who are already prone to hyperbilirubinemia.
*Provide supportive measures only*
- Given the strong evidence of **bacterial meningitis**, providing only supportive measures without specific antibiotic treatment would be inadequate and would lead to rapid deterioration and potentially fatal outcomes.
- Bacterial meningitis requires prompt and aggressive antimicrobial therapy.
*Start the patient on oral rifampin*
- **Rifampin is never used as monotherapy for bacterial meningitis** due to rapid resistance development and its primary role is in specific infections like tuberculosis or as part of combination therapy for certain resistant bacteria.
- Oral administration is also not ideal for acutely ill neonates with meningitis needing rapid, high-concentration antibiotics in the CSF.
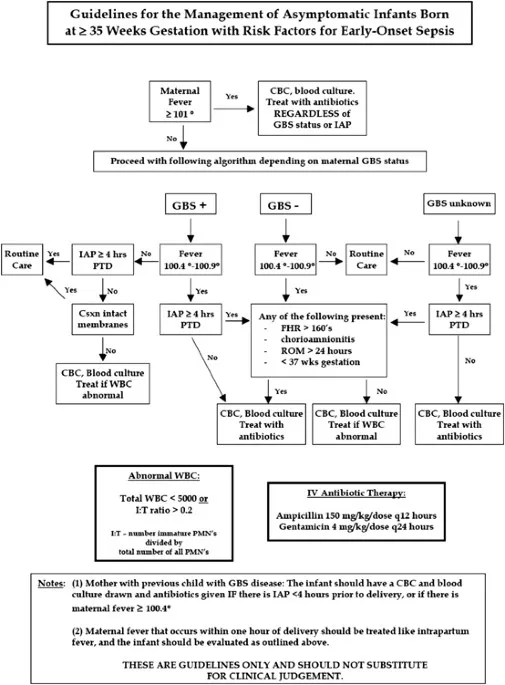
Early-onset sepsis US Medical PG Question 2: A 27-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 37 weeks' gestation is admitted to the hospital in active labor. She has received routine prenatal care, but she has not been tested for group B streptococcal (GBS) colonization. Pregnancy and delivery of her first child were complicated by an infection with GBS that resulted in sepsis in the newborn. Current medications include folic acid and a multivitamin. Vital signs are within normal limits. The abdomen is nontender and contractions are felt every 4 minutes. There is clear amniotic fluid pooling in the vagina. The fetus is in a cephalic presentation. The fetal heart rate is 140/min. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Obtain vaginal-rectal swab for nucleic acid amplification testing
- B. Obtain vaginal-rectal swab for GBS culture
- C. Administer intrapartum intravenous penicillin (Correct Answer)
- D. Reassurance
- E. Obtain vaginal-rectal swab for GBS culture and nucleic acid amplification testing
Early-onset sepsis Explanation: ***Administer intrapartum intravenous penicillin***
- This patient has a **previous infant with invasive GBS disease**, which is a strong indication for **intrapartum antibiotic prophylaxis (IAP)** regardless of current GBS colonization status.
- Penicillin is the **first-line agent** for GBS prophylaxis during labor to prevent vertical transmission to the newborn.
*Obtain vaginal-rectal swab for nucleic acid amplification testing*
- While **NAAT** can provide rapid results, the presence of a prior infant with invasive GBS disease is an **absolute indication** for IAP, making testing unnecessary.
- Waiting for NAAT results would **delay necessary antibiotic administration**, increasing the risk of GBS transmission.
*Obtain vaginal-rectal swab for GBS culture*
- A **GBS culture** typically takes 24-48 hours for results, which is too long given the patient is in active labor and requires immediate management.
- As with NAAT, a prior affected infant means that **IAP is indicated regardless of current culture results**.
*Reassurance*
- Reassurance alone is **insufficient** given the patient's history of a previous infant with GBS sepsis, which places her current fetus at high risk.
- **Active intervention** with antibiotics is crucial to prevent recurrence of GBS disease in the newborn.
*Obtain vaginal-rectal swab for GBS culture and nucleic acid amplification testing*
- Performing both tests is **unnecessary and delays treatment** in a patient with a clear indication for intrapartum antibiotics.
- The patient's history of a prior infant with GBS sepsis is classified as a **high-risk factor, necessitating immediate antibiotic prophylaxis** without waiting for test results.
Early-onset sepsis US Medical PG Question 3: A 70-year-old woman is on hospital day 2 in the medical intensive care unit. She was admitted from the emergency department for a 2-day history of shortness of breath and fever. In the emergency department, her temperature is 39.4°C (103.0°F), the pulse is 120/min, the blood pressure is 94/54 mm Hg, the respiratory rate is 36/min, and oxygen saturation was 82% while on 4L of oxygen via a non-rebreather mask. Chest X-ray shows a right lower lobe consolidation. She was intubated, sedated, and started on broad-spectrum antibiotics for sepsis of pulmonary origin and intravenous norepinephrine for blood pressure support. Since then, her clinical condition has been stable, though her vasopressor and oxygen requirements have not improved. Today, her physician is called to the bedside because her nurse noted some slow bleeding from her intravenous line sites and around her urinary catheter. Which of the following most likely represents the results of coagulation studies for this patient?
- A. D-dimer: negative, fibrinogen level: low, platelet count: low
- B. D-dimer: elevated, fibrinogen level: normal, platelet count: normal
- C. D-dimer: elevated, fibrinogen level: low, platelet count: low (Correct Answer)
- D. D-dimer: negative, fibrinogen level: elevated, platelet count: elevated
- E. D-dimer: negative, fibrinogen level: normal, platelet count: normal
Early-onset sepsis Explanation: ***D-dimer: elevated, fibrinogen level: low, platelet count: low***
- The patient's presentation with **sepsis** requiring intubation and vasopressors, along with diffuse **bleeding from IV sites and urinary catheter**, strongly suggests **disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)**.
- In DIC, widespread activation of the coagulation cascade leads to consumption of **platelets** and **clotting factors (including fibrinogen)**, resulting in thrombocytopenia and hypofibrinogenemia. The breakdown of clots produces **elevated D-dimer** levels.
*D-dimer: negative, fibrinogen level: low, platelet count: low*
- A **negative D-dimer** would contradict the diagnosis of DIC, as D-dimer is a product of fibrin degradation and is almost always elevated in DIC due to extensive clot formation and subsequent fibrinolysis.
- While low fibrinogen and platelet count are characteristic of DIC, the negative D-dimer makes this option unlikely in the context of active bleeding from multiple sites.
*D-dimer: elevated, fibrinogen level: normal, platelet count: normal*
- While an **elevated D-dimer** is consistent with fibrinolysis occurring in DIC, normal **fibrinogen** and **platelet counts** would argue against the consumptive coagulopathy that defines DIC.
- The presence of diffuse bleeding in a patient with sepsis usually indicates significant depletion of clotting factors and platelets.
*D-dimer: negative, fibrinogen level: elevated, platelet count: elevated*
- This profile suggests an **inflammatory state** or a hypercoagulable state without significant fibrinolysis or consumption of clotting factors.
- A **negative D-dimer** and **elevated fibrinogen/platelets** contradict the signs and symptoms of DIC with active bleeding.
*D-dimer: negative, fibrinogen level: normal, platelet count: normal*
- This result would be inconsistent with **DIC** and the patient's clinical picture of widespread bleeding.
- In DIC, there is active coagulation and fibrinolysis, leading to consumption of platelets and fibrinogen and production of D-dimers.
Early-onset sepsis US Medical PG Question 4: A baby is born after the 32nd gestational week by cesarean delivery. The mother suffered from gestational diabetes; however, she had no other pregnancy-related diseases and was otherwise healthy. The baby has a blood pressure of 100/58 mm Hg, heart rate of 104/min, and oxygen saturation of 88%. The child has tachypnea, subcostal and intercostal retractions, nasal flaring, and cyanosis. The cyanosis is responding well to initial administration of oxygen. The nasogastric tube was positioned without problems. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Tracheoesophageal fistula
- B. Pneumonia
- C. Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (NRDS) (Correct Answer)
- D. Sepsis
- E. Congenital heart anomaly with right-to-left shunt
Early-onset sepsis Explanation: ***Neonatal respiratory distress syndrome (NRDS)***
- The premature birth (32nd week), presence of **tachypnea**, **retractions**, **nasal flaring**, **cyanosis** responding to oxygen, and maternal **gestational diabetes** are all highly suggestive of NRDS.
- Maternal gestational diabetes can delay fetal lung maturity, increasing the risk of **surfactant deficiency**, which is the primary cause of NRDS.
*Tracheoesophageal fistula*
- This condition typically presents with **choking**, **coughing**, and **regurgitation** during feeding, often with inability to pass a nasogastric tube into the stomach.
- The successful positioning of the **nasogastric tube** makes this diagnosis less likely.
*Pneumonia*
- While pneumonia can cause respiratory distress, the **early onset** in a premature infant with maternal gestational diabetes points more strongly towards **NRDS**.
- Pneumonia would typically have signs of **infection** such as fever, though early neonatal pneumonia can be atypical.
*Sepsis*
- Sepsis can cause respiratory distress, but it's usually accompanied by other signs of systemic infection, such as **fever or hypothermia**, **lethargy**, and poor feeding and often signs of **circulatory compromise**.
- The clinical picture provided primarily points towards a respiratory rather than a systemic infectious cause primarily.
*Congenital heart anomaly with right-to-left shunt*
- While this can cause **cyanosis** and respiratory distress, the prompt response to oxygen management makes a significant right-to-left shunt less likely.
- A significant right-to-left shunt would typically cause **cyanosis** that is refractory to oxygen administration.
Early-onset sepsis US Medical PG Question 5: A 6-month old child is brought to the ER by parents for one day of fever, decreased feeding, and lethargy. They report that neither she nor her siblings are immunized due to their concerns about vaccinations. On exam, the infant is toxic-appearing. Antibiotics are started and lumbar puncture reveals bacterial meningitis caused by a gram-negative, encapsulated organism that requires chocolate agar and the two factors shown in Image A for growth. Which organism does this best describe?
- A. Group B Streptococcus
- B. Haemophilus influenzae (Correct Answer)
- C. Moraxella catarrhalis
- D. Streptococcus pneumoniae
- E. Listeria monocytogenes
Early-onset sepsis Explanation: **Haemophilus influenzae**
- This organism is a **gram-negative, encapsulated coccobacillus** that requires **chocolate agar** and **factors X (hemin) and V (NAD+)** for growth, which perfectly matches the description.
- In unvaccinated children, *H. influenzae* type b (Hib) is a significant cause of **bacterial meningitis**, epiglottitis, and other invasive infections, especially considering the family's anti-vaccination stance.
*Group B Streptococcus*
- **Group B Streptococcus (GBS)** is a **gram-positive coccus** and a common cause of early-onset neonatal sepsis and meningitis, typically in infants less than 3 months old.
- It does not require chocolate agar or specific growth factors X and V, and is **gram-positive**, not gram-negative.
*Moraxella catarrhalis*
- *Moraxella catarrhalis* is a **gram-negative diplococcus** and a common cause of otitis media, sinusitis, and bronchitis, but it is a rare cause of meningitis.
- While it is a gram-negative organism, it does not typically require chocolate agar or specific growth factors X and V for isolation, usually growing on standard blood agar.
*Streptococcus pneumoniae*
- *Streptococcus pneumoniae* is a **gram-positive coccus** that is a leading cause of bacterial meningitis in children and adults.
- It is **gram-positive**, not gram-negative, and grows on blood agar, not specifically requiring chocolate agar or factors X and V.
*Listeria monocytogenes*
- *Listeria monocytogenes* is a **gram-positive rod** and a cause of meningitis in neonates, immunocompromised individuals, and the elderly.
- It is a **gram-positive rod**, contrary to the gram-negative, encapsulated organism described, and does not require chocolate agar or factors X and V for growth.
Early-onset sepsis US Medical PG Question 6: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of a 3-day history of generalized fatigue, myalgia, and fever. He has sickle cell disease. His current medications include hydroxyurea and folic acid. He appears ill. His temperature is 39.2°C (102.6°F), pulse is 103/min, and respirations are 28/min. Examination shows pale conjunctivae. The lungs are clear to auscultation. The abdomen is soft and nontender. Neurologic examination shows no focal findings, His hemoglobin concentration is 10.3 g/dL and leukocyte count is 14,100/mm3. Intravenous fluid is administered and blood cultures are obtained. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in treatment?
- A. Clindamycin
- B. Prednisone
- C. Vancomycin
- D. Ceftriaxone (Correct Answer)
- E. Levofloxacin
Early-onset sepsis Explanation: ***Ceftriaxone***
- This patient presents with **fever** and **sickle cell disease**, placing him at high risk for bacterial infections, especially from **encapsulated organisms** like *Streptococcus pneumoniae* and *Haemophilus influenzae*. **Ceftriaxone** is a broad-spectrum third-generation cephalosporin that provides excellent coverage against these common pathogens.
- Due to the high risk of **sepsis** and rapid progression of infection in sickle cell patients, empiric, prompt administration of **intravenous antibiotics** is crucial, even before culture results are available.
*Clindamycin*
- **Clindamycin** is primarily effective against **anaerobic bacteria** and some gram-positive organisms, including methicillin-sensitive *Staphylococcus aureus* (MSSA).
- It does not provide adequate coverage against the most common and life-threatening pathogens in febrile sickle cell patients, such as encapsulated bacteria.
*Prednisone*
- **Prednisone** is a corticosteroid used for its **anti-inflammatory** and immunosuppressive effects. It is not indicated for the initial management of fever and suspected bacterial infection.
- Administering corticosteroids in a patient with suspected infection without appropriate antibiotic coverage could worsen the infection.
*Vancomycin*
- **Vancomycin** is a powerful antibiotic primarily used to cover **multi-drug resistant gram-positive bacteria**, especially **MRSA** and drug-resistant *S. pneumoniae*.
- While it covers gram-positive organisms well, it does **not cover gram-negative bacteria** such as *H. influenzae* or *Salmonella* species, which are important pathogens in sickle cell patients. **Ceftriaxone** provides broader coverage including both gram-positive and gram-negative encapsulated organisms, making it the preferred empiric choice.
*Levofloxacin*
- **Levofloxacin** is a fluoroquinolone that provides broad-spectrum coverage, including against atypical organisms and some gram-negatives and gram-positives.
- However, **fluoroquinolones** are generally avoided in children due to potential adverse effects on cartilage development, and it is not the first-line empiric choice for severe bacterial infections in this age group, especially when **cephalosporins** are highly effective and safer.
Early-onset sepsis US Medical PG Question 7: A worried mother brings her 12-day-old son to the emergency room concerned that his body is turning "yellow". The patient was born at 39 weeks via spontaneous vaginal delivery without complications. The mother received adequate prenatal care and has been breastfeeding her son. The patient has had adequate urine and stool output. Physical exam demonstrates a comfortable, well nourished neonate with a jaundiced face and chest. The patient's indirect bilirubin was 4 mg/dL at 48 hours of life. Today, indirect bilirubin is 10 mg/dL, and total bilirubin is 11 mg/dL. All other laboratory values are within normal limits. What is the next best treatment in this scenario?
- A. Exchange transfusion
- B. Stop breastfeeding and switch to formula
- C. Phototherapy (Correct Answer)
- D. Reassure mother that jaundice will remit, advise her to continue breastfeeding
- E. Phenobarbital
Early-onset sepsis Explanation: ***Phototherapy***
- The infant's bilirubin levels (total bilirubin 11 mg/dL, indirect bilirubin 10 mg/dL at 12 days old) are within the range that warrants **phototherapy** for a healthy term neonate to prevent **kernicterus**.
- Phototherapy helps convert unconjugated bilirubin into water-soluble isomers that can be excreted more easily.
*Exchange transfusion*
- **Exchange transfusion** is reserved for much higher bilirubin levels, typically above 20-25 mg/dL, or if there are signs of **acute bilirubin encephalopathy**.
- The current bilirubin levels do not meet the criteria for this invasive procedure.
*Phenobarbital*
- **Phenobarbital** induces hepatic enzymes, including UDP-glucuronosyltransferase, which aids bilirubin conjugation, but its effect is delayed and primarily used to prevent jaundice in specific high-risk situations (e.g., in infants of mothers with anti-Rh antibodies) or in treating **Crigler-Najjar syndrome**.
- It is not the immediate treatment for typical neonatal jaundice at these bilirubin levels.
*Stop breastfeeding and switch to formula*
- While **breast milk jaundice** can cause prolonged unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia, the infant's bilirubin levels are not dangerously high, and there is no indication to interrupt breastfeeding.
- Interruption is typically considered if bilirubin levels are very high and unresponsive to phototherapy, to differentiate from **breastfeeding jaundice** caused by inadequate intake.
*Reassure mother that jaundice will remit, advise her to continue breastfeeding*
- Although the infant is comfortable and well-nourished, a bilirubin level of 11 mg/dL at 12 days old in a term infant, especially with an indirect component of 10 mg/dL, is significant enough to warrant intervention like phototherapy to prevent potential complications.
- Simple reassurance without intervention would be inappropriate as it risks allowing bilirubin levels to rise further.
Early-onset sepsis US Medical PG Question 8: A 3-month-old male presents to the pediatrician with his mother for a well child visit. The patient drinks 4 ounces of conventional cow’s milk formula every three hours. He usually stools once per day, and urinates up to six times per day. His mother reports that he regurgitates a moderate amount of formula through his nose and mouth after most feeds. He does not seem interested in additional feeding after these episodes of regurgitation, and he has become progressively more irritable around meal times. The patient is starting to refuse some feeds. His mother denies ever seeing blood or streaks of red in his stool, and she denies any family history of food allergies or dermatological problems. The patient’s weight was in the 75th percentile for weight throughout the first month of life. Four weeks ago, he was in the 62nd percentile, and he is now in the 48th percentile. His height and head circumference have followed similar trends. On physical exam, the patient smiles reciprocally and can lift his head and chest when in the prone position. His abdomen is soft, non-tender, and non-distended.
Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. Switch to hydrolyzed formula
- B. Obtain abdominal ultrasound
- C. Initiate proton pump inhibitor
- D. Provide reassurance
- E. Counsel on positioning and thickening feeds (Correct Answer)
Early-onset sepsis Explanation: ***Counsel on positioning and thickening feeds***
- The infant's symptoms, including **regurgitation**, **irritability during feeds**, and **dropping weight percentiles**, are indicative of severe gastroesophageal reflux (GER). Initial management should focus on **conservative measures** like positioning modifications (keeping upright after feeds), thickening feeds, and smaller, more frequent feedings.
- Given the absence of **hematemesis**, **hematochezia**, or **projectile vomiting**, further invasive diagnostics or medication are not immediately warranted.
*Switch to hydrolyzed formula*
- This would be considered if there were signs suggestive of a **cow's milk protein allergy**, such as **bloody stools**, **diarrhea**, **eczema**, or a strong family history of allergies, which are all absent in this case.
- Allergy is less likely to be the primary cause of isolated severe regurgitation with failure to thrive without other allergic manifestations.
*Obtain abdominal ultrasound*
- An **abdominal ultrasound** is primarily used to evaluate for conditions like **pyloric stenosis** if there is **projectile vomiting**, an **olive-shaped mass**, or severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalances, none of which are present.
- While it can assess for **malrotation or intussusception**, these conditions typically present with more acute, severe symptoms like **bilious vomiting**, abdominal distension, or currant jelly stools, which are not described.
*Initiate proton pump inhibitor*
- **Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs)** are reserved for infants with confirmed **erosive esophagitis** or severe symptoms unresponsive to lifestyle modifications.
- Starting a PPI without first attempting conservative measures or confirming pathological acid reflux is generally not recommended, especially given potential side effects like increased risk of infections.
*Provide reassurance*
- While **reassurance** is important, it is not the sole appropriate next step. The infant's **dropping weight percentiles** and significant feeding difficulties suggest that this is beyond typical "spitting up" and requires intervention to prevent further impact on growth and comfort.
- Simply reassuring the mother would ignore the clinical signs of **failure to thrive** and significant discomfort during feeds.
Early-onset sepsis US Medical PG Question 9: Three days after delivery, a 1100-g (2-lb 7-oz) newborn has a tonic seizure that lasts for 25 seconds. She has become increasingly lethargic over the past 18 hours. She was born at 31 weeks' gestation. Antenatal period was complicated by chorioamnionitis. Apgar scores were 3 and 6 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. She appears ill. Her pulse is 123/min, respirations are 50/min and irregular, and blood pressure is 60/30 mm Hg. Examination shows a tense anterior fontanelle. The pupils are equal and react sluggishly to light. Examination shows slow, conjugate back and forth movements of the eyes. Muscle tone is decreased in all extremities. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Intraventricular hemorrhage (Correct Answer)
- B. Spinal muscular atrophy
- C. Galactosemia
- D. Congenital hydrocephalus
- E. Phenylketonuria
Early-onset sepsis Explanation: ***Intraventricular hemorrhage***
- The combination of **prematurity** (31 weeks' gestation, 1100g), **tonic seizures**, increasing **lethargy**, tense **anterior fontanelle**, **sluggishly reactive pupils**, and **slow conjugate back-and-forth eye movements** (suggesting brainstem involvement from increased intracranial pressure) are classical signs of intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) in a neonate.
- **IVH** is common in premature infants due to the fragility of germinal matrix vessels and can manifest acutely with neurological deterioration and increased intracranial pressure, typically within the first 72 hours of life.
- While maternal **chorioamnionitis** and low Apgar scores raise concern for neonatal sepsis/meningitis, the specific **ocular movement pattern** and acute neurological signs on day 3 are more characteristic of IVH in this extremely premature infant.
*Spinal muscular atrophy*
- This is a **neuromuscular genetic disorder** characterized by progressive muscle weakness and hypotonia due to anterior horn cell degeneration.
- It would typically present with **decreased muscle tone but without acute neurological signs** like seizures, tense fontanelle, or sluggish pupillary responses.
- Does not cause acute-onset seizures or rapidly progressing lethargy in the neonatal period.
*Galactosemia*
- This is a **metabolic disorder** that presents with symptoms such as **vomiting, jaundice, hepatomegaly**, and **sepsis-like symptoms** upon introduction of lactose-containing feeds (breast milk or regular formula), typically after several days of feeding.
- While it can cause lethargy and seizures, the acute neurological findings including **tense fontanelle** and **abnormal eye movements** in the immediate postnatal period of a premature infant more strongly suggest an anatomical/structural etiology like IVH.
*Congenital hydrocephalus*
- While **hydrocephalus** can cause a **tense fontanelle** and seizures, the **acute onset** of symptoms (day 3 of life with rapid deterioration over 18 hours following a specific tonic seizure) in an extremely premature infant strongly suggests an **acute hemorrhagic event** rather than congenital hydrocephalus.
- Congenital hydrocephalus typically presents with **progressively enlarging head circumference** over time, rather than such acute neurological deterioration in the first 72 hours of life.
- IVH can lead to secondary post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus, but the acute presentation favors primary IVH.
*Phenylketonuria*
- This is a **metabolic disorder** caused by phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency that, if untreated, leads to **intellectual disability** and seizures.
- Symptoms typically manifest **several months after birth** (usually 3-6 months) as phenylalanine accumulates, and are not associated with acute neonatal neurological distress like tense fontanelle, abnormal eye movements, or acute lethargy in the first few days of life.
- Would not explain the acute deterioration on day 3 of life in this clinical context.
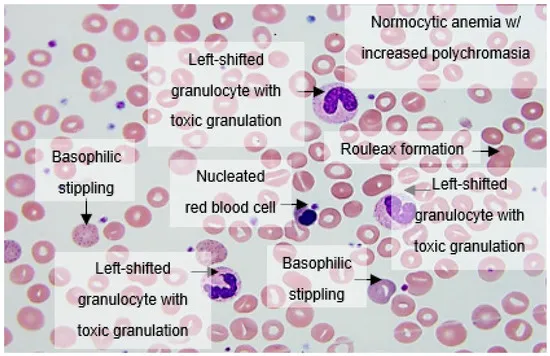
Early-onset sepsis US Medical PG Question 10: A 4-year-old girl is brought to the physician because of diarrhea and vomiting for 5 days. Vaccinations are up-to-date. She appears pale and irritable. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows petechiae on her trunk and extremities. Abdominal examination shows diffuse abdominal tenderness with hyperactive bowel sounds. The remainder of the exam shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 8 g/dL
Leukocyte count 17,000/mm3
Platelet count 49,000/mm3
Serum
Creatinine 1.6 mg/dL
Lactate dehydrogenase 300 U/L
Coagulation studies are normal. A peripheral blood smear is shown. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of these findings?
- A. Parvovirus B19 infection
- B. Disseminated intravascular coagulation
- C. Acute lymphocytic leukemia
- D. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura
- E. Escherichia coli infection (Correct Answer)
Early-onset sepsis Explanation: ***Escherichia coli infection***
- The constellation of **diarrhea, vomiting, hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, and acute kidney injury** (elevated creatinine) is characteristic of **hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS)**, which is most often caused by **Shiga toxin-producing *E. coli*** (STEC), particularly O157:H7.
- The peripheral blood smear showing **schistocytes** (fragmented red blood cells) further supports the diagnosis of microangiopathic hemolytic anemia seen in HUS.
*Parvovirus B19 infection*
- Parvovirus B19 primarily causes **transient aplastic crisis** in individuals with underlying hemolytic disorders or fifth disease (erythema infectiosum) with a "slapped cheek" rash, not typically **hemolytic uremic syndrome**.
- While it can cause anemia, it does not typically lead to the **combination of thrombocytopenia and acute kidney injury** seen in this patient.
*Disseminated intravascular coagulation*
- DIC would present with **abnormal coagulation studies** (prolonged PT/aPTT, decreased fibrinogen, elevated D-dimer), which are explicitly stated as normal in this case.
- Although it involves microangiopathic hemolysis and thrombocytopenia, the normal coagulation profile makes DIC unlikely.
*Acute lymphocytic leukemia*
- ALL typically presents with **pancytopenia** or various cytopenias, but the primary features are often **blast cells** on the peripheral smear and bone marrow biopsy, along with frequent **lymphadenopathy, hepatosplenomegaly**, and constitutional symptoms, which are not described.
- It does not primarily cause **acute kidney injury** or the specific combination of hemolytic anemia and thrombocytopenia seen in HUS.
*Immune thrombocytopenic purpura*
- ITP is characterized by **isolated thrombocytopenia** with otherwise normal blood counts and morphology. Hemolytic anemia and renal failure are not features of ITP.
- The presence of **schistocytes and hemolytic anemia** rules out ITP as the primary diagnosis.
More Early-onset sepsis US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.