Neonatal infections

On this page
🦠 The Neonatal Infection Battlefield: Tiny Warriors Under Siege
Newborns enter the world with immune systems still learning to fight, making infection one of the most dangerous threats in the first weeks of life. You'll discover how to distinguish early sepsis acquired during birth from later healthcare-associated infections, master the diagnostic clues that catch these stealthy invaders before they overwhelm fragile patients, and deploy targeted antimicrobial strategies that save lives. We'll also explore the congenital TORCH infections that strike before birth and the prevention measures that transform NICUs into fortresses against microbial threats.
The Immune Immaturity Arsenal
Neonatal susceptibility stems from five critical immune deficiencies that create perfect pathogen conditions:
-
Neutrophil Dysfunction
- Chemotaxis reduced by 60-70% compared to adults
- Bactericidal activity decreased 40-50%
- Storage pool contains only 3-5 days of reserves (adults: 7-10 days)
- Rapid depletion during infection
- Left shift appears within 6-12 hours
-
Complement System Deficits
- Classical pathway activity 50-75% of adult levels
- Alternative pathway 60-80% functional
- C3 levels 60-70% of maternal values
- Impaired opsonization capacity
- Reduced bacterial clearance
📌 Remember: CHIN for neonatal immune deficits - Complement low, Humoral immunity poor, Innate responses blunted, Neutrophils dysfunctional
| Immune Component | Term Neonate | Preterm <32w | Adult Level | Clinical Impact | Time to Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IgG Levels | 70-100% | 40-60% | 100% | ↓ Bacterial resistance | 6-12 months |
| IgM Production | 10-20% | 5-10% | 100% | ↓ Gram-negative defense | 12-24 months |
| Neutrophil Function | 40-60% | 20-40% | 100% | ↓ Bacterial killing | 2-6 months |
| T-Cell Response | 30-50% | 15-30% | 100% | ↓ Viral/fungal defense | 12-18 months |
| NK Cell Activity | 20-40% | 10-25% | 100% | ↓ Tumor surveillance | 6-12 months |
Understanding maternal antibody transfer reveals critical vulnerability windows. IgG transfer occurs primarily after 32 weeks gestation, leaving preterm infants with inadequate passive immunity for 6-12 months. This knowledge transforms infection prevention strategies.
🦠 The Neonatal Infection Battlefield: Tiny Warriors Under Siege
🎯 Early-Onset Sepsis: The Birth Canal Gauntlet
EOS represents vertical transmission during the perinatal period, with Group B Streptococcus (GBS) and E. coli accounting for 70-80% of cases. Master the risk stratification, and you predict which neonates require immediate intervention.
The Perinatal Risk Matrix
EOS risk factors create multiplicative, not additive, danger:
-
Maternal Intrapartum Factors
- Prolonged rupture of membranes >18 hours: 2-3x risk increase
- Maternal fever >38°C: 3-4x risk elevation
- Chorioamnionitis: 5-10x risk multiplication
- Clinical diagnosis: fever + uterine tenderness + foul discharge
- Histologic diagnosis: >5 neutrophils/hpf in chorion-decidua
-
Delivery Complications
- Meconium-stained amniotic fluid: 1.5-2x risk
- Instrumental delivery: 1.3-1.8x risk increase
- Emergency cesarean: 2-3x risk (vs. elective)
- Prolonged labor preceding cesarean
- Multiple vaginal examinations
📌 Remember: PROM-F for major EOS risks - Prolonged rupture >18h, Risk factors maternal, Obstetric complications, Maternal fever, Fetal distress
| Risk Category | Criteria | Incidence Rate | Management | Antibiotic Duration | Mortality Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High Risk | Chorioamnionitis + PROM >18h | 8-15/1000 | Immediate antibiotics | 48-72h minimum | 5-15% |
| Moderate Risk | Single major factor | 2-5/1000 | Enhanced monitoring | If started: 48h | 2-5% |
| Low Risk | No risk factors | 0.5-1/1000 | Routine care | None unless symptomatic | <1% |
| GBS Positive | Inadequate prophylaxis | 1-2/1000 | Case-by-case | 48h if asymptomatic | 2-8% |
| Preterm <35w | Any gestation <35w | 10-25/1000 | Lower threshold | 48-72h minimum | 10-25% |
💡 Master This: EOS mortality correlates directly with time to antibiotic initiation-every 6-hour delay doubles mortality risk, making rapid recognition and treatment the cornerstone of neonatal intensive care.
The transition from intrauterine sterility to extrauterine microbial exposure creates a critical 24-48 hour vulnerability window where maternal antibodies provide incomplete protection.
🎯 Early-Onset Sepsis: The Birth Canal Gauntlet
🕐 Late-Onset Sepsis: The Healthcare-Associated Invaders
The Healthcare-Associated Pathogen Hierarchy
LOS pathogens reflect NICU ecology and intervention intensity:
-
Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci (CONS)
- 50-60% of LOS cases in VLBW infants
- Biofilm formation on central lines within 24-48 hours
- Methicillin resistance in 70-80% of NICU isolates
- Vancomycin remains first-line therapy
- MIC creep: increasing vancomycin requirements
-
Gram-Negative Enteric Bacteria
- Klebsiella, Enterobacter, Serratia: 20-30% of LOS
- ESBL production in 30-50% of isolates
- Carbapenem resistance emerging: 5-15% in some NICUs
- Meropenem/imipenem as empiric therapy
- Colistin for resistant organisms
📌 Remember: SCANK organisms dominate LOS - Staph epidermidis, Candida, Acinetobacter, Necrotizing enterocolitis bugs, Klebsiella
Risk Stratification Matrix
LOS risk increases exponentially with intervention burden:
-
Central Venous Access
- PICC lines: 2-4 infections per 1000 catheter-days
- Umbilical catheters: 5-10 infections per 1000 catheter-days
- Surgical central lines: 3-8 infections per 1000 catheter-days
- Duration >7 days: 3x risk increase
- Multiple lumens: 1.5-2x risk elevation
-
Respiratory Support
- Mechanical ventilation >7 days: 4-6x LOS risk
- Endotracheal intubation: 2-3x risk vs. CPAP
- Ventilator-associated pneumonia: 1-3 cases per 1000 ventilator-days
- Gram-negative predominance
- Pseudomonas and Acinetobacter concerns
| Risk Factor | Relative Risk | Pathogen Pattern | Prevention Strategy | Surveillance Frequency | Mortality Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PICC Line | 3-5x baseline | CONS (60%), GNR (25%) | Bundle compliance | Daily line assessment | 10-20% |
| Mechanical Ventilation | 4-6x baseline | GNR (40%), CONS (35%) | VAP prevention | Q8h respiratory assessment | 15-30% |
| Prolonged Antibiotics | 2-4x baseline | Candida (30%), resistant bacteria | Stewardship protocols | Weekly review | 20-40% |
| Necrotizing Enterocolitis | 8-12x baseline | Enteric GNR, anaerobes | Feeding protocols | Continuous monitoring | 30-50% |
| Extreme Prematurity | 5-10x baseline | All categories | Developmental care | Continuous assessment | 25-45% |
💡 Master This: LOS prevention requires systems thinking-every intervention creates infection risk, making the decision to place or maintain devices as critical as choosing antibiotics.
Understanding device-associated infection rates transforms NICU care from reactive treatment to proactive prevention, where bundle compliance becomes as important as antibiotic selection.
🕐 Late-Onset Sepsis: The Healthcare-Associated Invaders
🔬 Diagnostic Precision: The Laboratory Detective Work
The Sepsis Laboratory Hierarchy
Diagnostic tests provide complementary, not redundant, information:
-
Blood Culture: The Gold Standard
- Sensitivity: 80-90% with adequate volume (≥1mL)
- Time to positivity: 12-24 hours for most bacteria
- False negative rate: 10-20% due to low-level bacteremia
- Prior antibiotic exposure increases false negatives
- Anaerobic cultures rarely positive in neonates
-
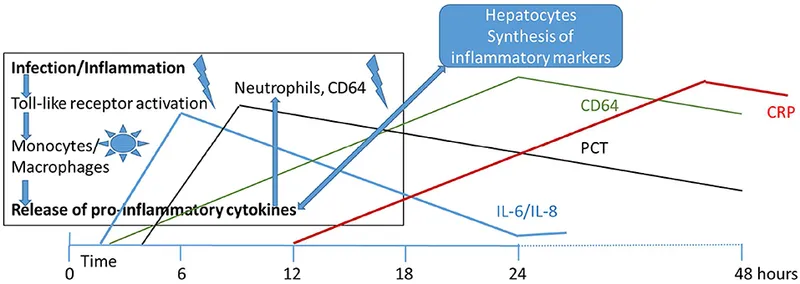
Inflammatory Markers: The Supporting Cast
- C-reactive protein (CRP): peaks 24-48 hours after infection onset
- Procalcitonin (PCT): rises 6-12 hours after bacterial invasion
- Interleukin-6 (IL-6): earliest marker (2-6 hours) but short half-life
- CRP >10mg/L: 70-80% sensitivity for bacterial infection
- PCT >0.5ng/mL: 75-85% sensitivity, 80-90% specificity
📌 Remember: CLIP for sepsis markers timing - CRP peaks late (24-48h), Lactate immediate, IL-6 early (2-6h), Procalcitonin intermediate (6-12h)
Complete Blood Count Interpretation
CBC changes reflect immune system activation and consumption:
-
White Blood Cell Dynamics
- Normal range: 5,000-30,000/μL (varies by age)
- Leukopenia <5,000/μL: more concerning than leukocytosis
- Left shift: >20% bands suggests bacterial infection
- I:T ratio >0.2 (immature:total neutrophils) abnormal
- Toxic granulation and Döhle bodies support infection
-
Platelet Count Significance
- Thrombocytopenia <100,000/μL: suggests consumption or sepsis
- Rapid decline: >50% drop in 24 hours highly concerning
- DIC development: platelets <50,000/μL with prolonged coagulation
- Fibrinogen <100mg/dL suggests consumption
- D-dimer elevation supports DIC diagnosis
| Laboratory Test | Normal Range | Sepsis Threshold | Sensitivity | Specificity | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blood Culture | Negative | Any growth | 80-90% | 95-99% | Gold standard diagnosis |
| CRP | <3mg/L | >10mg/L | 70-80% | 80-90% | Late marker, trending valuable |
| Procalcitonin | <0.1ng/mL | >0.5ng/mL | 75-85% | 80-90% | Earlier than CRP |
| WBC Count | 5-30K/μL | <5K or >30K | 60-70% | 70-80% | Age-dependent interpretation |
| I:T Ratio | <0.2 | >0.2 | 80-90% | 70-80% | Reflects left shift |
💡 Master This: Negative blood cultures don't exclude sepsis in neonates-clinical deterioration with rising inflammatory markers may justify continued antibiotic therapy, especially in culture-negative sepsis scenarios.
The diagnostic approach must balance sensitivity for life-threatening infections against specificity to avoid unnecessary antibiotic exposure in this vulnerable population.
🔬 Diagnostic Precision: The Laboratory Detective Work
⚔️ Antimicrobial Warfare: The Treatment Arsenal
The Empiric Antibiotic Algorithm
First-line therapy targets the most likely pathogens based on timing and risk factors:
-
Early-Onset Sepsis Protocol
- Ampicillin 100-150mg/kg/day divided Q8-12h
- Gentamicin 4-5mg/kg/day Q24-48h (based on levels)
- Duration: 48-72 hours if cultures negative
- GBS coverage: ampicillin MIC ≤0.25μg/mL
- E. coli resistance: 80-90% ampicillin-resistant
-
Late-Onset Sepsis Protocol
- Vancomycin 10-15mg/kg/dose Q8-24h (renal function-dependent)
- Gentamicin or cefepime for gram-negative coverage
- Target levels: vancomycin trough 10-15μg/mL
- CONS coverage: vancomycin remains effective
- Gram-negative resistance: increasing concern
📌 Remember: AGE determines dosing intervals - Ampicillin Q8-12h, Gentamicin Q24-48h, Extended intervals in preterm infants
Dosing Precision Matrix
Neonatal dosing requires gestational age and postnatal age adjustments:
| Antibiotic | <29 weeks | 30-36 weeks | >37 weeks | Monitoring | Toxicity Concerns |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ampicillin | 50mg/kg Q12h | 75mg/kg Q8h | 100mg/kg Q6h | Clinical response | Minimal toxicity |
| Gentamicin | 4mg/kg Q48h | 4mg/kg Q36h | 5mg/kg Q24h | Peak/trough levels | Nephro/ototoxicity |
| Vancomycin | 10mg/kg Q18h | 10mg/kg Q12h | 15mg/kg Q8h | Trough levels | Nephrotoxicity |
| Cefotaxime | 50mg/kg Q12h | 50mg/kg Q8h | 50mg/kg Q6h | Clinical response | Minimal toxicity |
| Meropenem | 20mg/kg Q12h | 20mg/kg Q8h | 20mg/kg Q8h | Clinical response | Seizure risk |
💡 Master This: Antibiotic stewardship in NICUs focuses on narrow-spectrum therapy when possible, shortest effective duration, and de-escalation based on culture results-48-72 hour empiric courses are standard for culture-negative sepsis.
Understanding developmental pharmacology transforms antibiotic therapy from guesswork to precision medicine, where therapeutic drug monitoring becomes essential for optimizing outcomes.
⚔️ Antimicrobial Warfare: The Treatment Arsenal
🧬 TORCH Infections: The Congenital Invaders
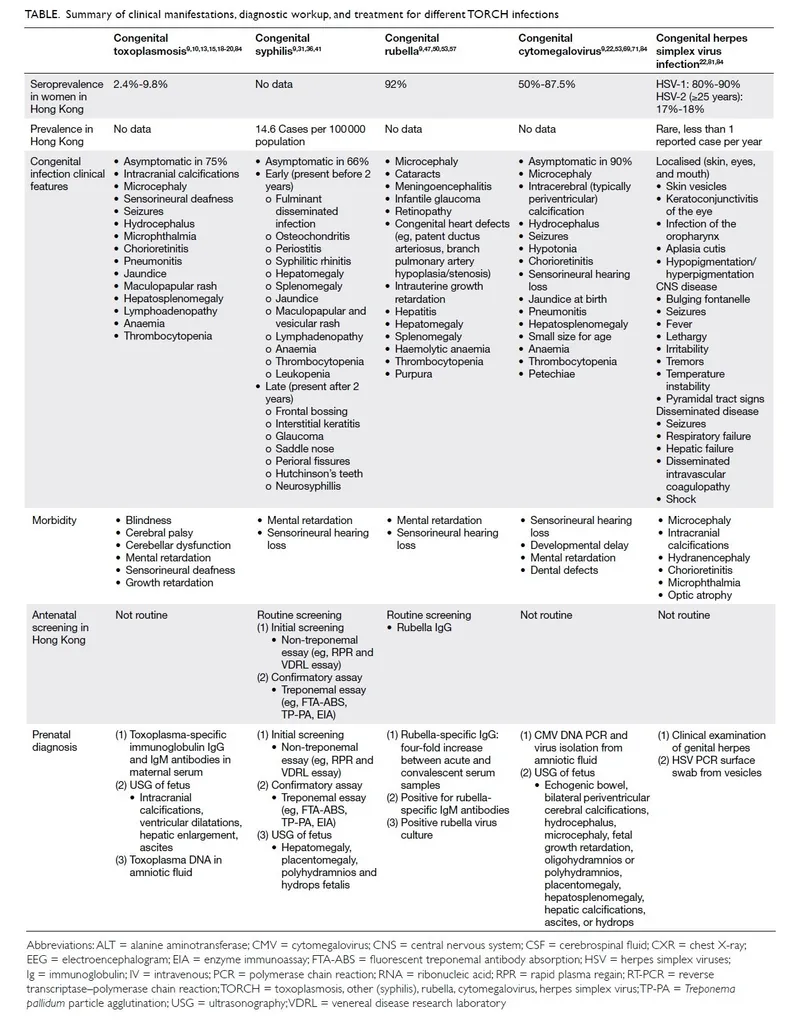
TORCH represents Toxoplasmosis, Other (syphilis, VZV, parvovirus), Rubella, CMV, and HSV-congenital infections that cross the placental barrier or infect during delivery. Each pathogen creates distinct clinical signatures requiring specific diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
The TORCH Clinical Constellation
Pattern recognition separates TORCH infections from other neonatal conditions:
-
Cytomegalovirus (CMV): The Silent Destroyer
- Most common congenital infection: 0.6% of all births
- Symptomatic at birth: only 10% of infected infants
- Classic triad: microcephaly, hepatosplenomegaly, thrombocytopenia
- Periventricular calcifications on neuroimaging
- Sensorineural hearing loss: 15-20% of infected infants
- Intellectual disability: 8-15% of symptomatic cases
-
Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV): The Rapid Destroyer
- Incidence: 1 in 3,000-5,000 deliveries
- Three clinical forms: skin/eye/mouth (45%), CNS (30%), disseminated (25%)
- Mortality without treatment: 85% disseminated, 50% CNS
- Vesicular lesions: present in only 60-70% of cases
- CSF pleocytosis: >20 cells/μL with lymphocytic predominance
📌 Remember: TORCH clinical clues - Thrombocytopenia, Ocular abnormalities, Rash/growth restriction, Calcifications, Hepatosplenomegaly
Diagnostic Strategy Matrix
TORCH diagnosis combines serology, PCR, and clinical correlation:
-
Maternal vs. Fetal Testing
- Maternal IgM: indicates recent infection but timing unclear
- Maternal IgG avidity: low avidity suggests recent primary infection
- Fetal IgM: definitive evidence of congenital infection
- IgM doesn't cross placenta: fetal production indicates infection
- False negatives: 20-30% in early infection
-
Molecular Diagnostics
- CMV PCR: urine or saliva within 21 days of birth
- HSV PCR: CSF, vesicle fluid, or surface swabs
- Toxoplasma PCR: amniotic fluid or fetal blood
- Quantitative PCR: viral load correlates with severity
- Resistance testing: for treatment failures
| TORCH Agent | Primary Diagnostic Test | Sensitivity | Specificity | Timing Considerations | Treatment Available |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CMV | Urine PCR <21 days | 95-99% | 99% | Must be within 3 weeks | Ganciclovir/valganciclovir |
| HSV | PCR (CSF/lesion) | 90-95% | 99% | Early collection critical | Acyclovir |
| Toxoplasma | IgM + PCR | 80-90% | 95-99% | Maternal screening important | Sulfadiazine + pyrimethamine |
| Rubella | IgM + RT-PCR | 85-95% | 99% | Rare due to vaccination | Supportive only |
| Syphilis | RPR/VDRL + FTA-ABS | 95-99% | 95-99% | Quantitative titers key | Penicillin |
💡 Master This: HSV infection can present without skin lesions in 30-40% of cases-maintain high suspicion in neonates with unexplained fever, seizures, or elevated liver enzymes, especially with maternal history of genital lesions.
TORCH infections demonstrate how maternal screening, delivery management, and neonatal surveillance integrate to prevent devastating congenital infections through evidence-based protocols.
🧬 TORCH Infections: The Congenital Invaders
🎯 Infection Control Mastery: The Prevention Fortress
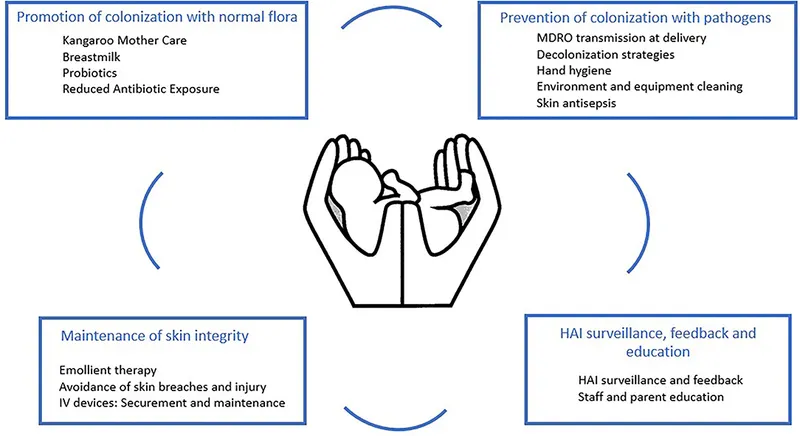
Infection prevention in NICUs demands systems-based approaches that address environmental factors, healthcare worker behaviors, and device-related risks. Master these prevention strategies, and you transform the NICU from an infection reservoir into a protective sanctuary.
The Infection Control Hierarchy
Prevention strategies follow the hierarchy of controls-elimination, substitution, engineering, administrative, and personal protective equipment:
-
Hand Hygiene: The Foundation
- WHO 5 Moments: before patient contact, before aseptic procedures, after body fluid exposure, after patient contact, after patient environment contact
- Compliance rates: 40-60% baseline, >90% achievable with interventions
- Alcohol-based hand rub: 15-30 second application time
- Soap and water: required for C. difficile and norovirus
- Hand hygiene duration: 20-30 seconds minimum effective time
-
Environmental Controls
- HEPA filtration: ≥12 air changes/hour in NICU
- Positive pressure: ≥2.5 Pa relative to corridors
- Surface disinfection: quaternary ammonium or bleach-based solutions
- High-touch surfaces: Q2-4h cleaning frequency
- Equipment disinfection: between patient use mandatory
📌 Remember: CLEAN hand hygiene moments - Coming to patient, Leaving patient, Exposure to fluids, Aseptic procedures, Near patient environment
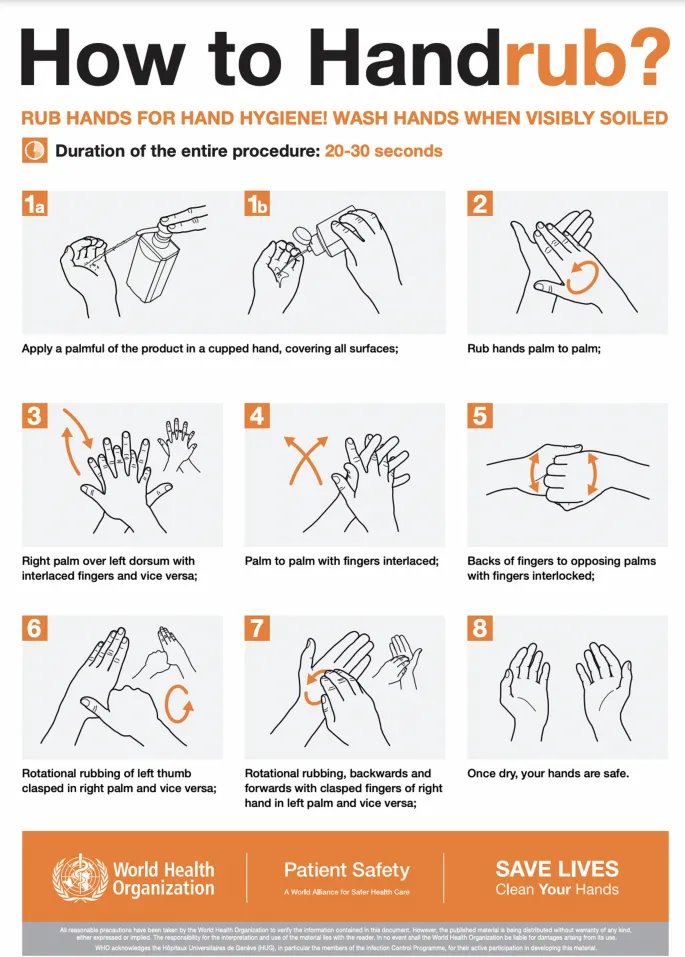
Outbreak Investigation Protocol
NICU outbreaks require rapid response and systematic investigation:
-
Case Definition Development
- Confirmed case: laboratory-confirmed infection with outbreak organism
- Probable case: clinical syndrome consistent with outbreak
- Time period: epidemic curve analysis for transmission patterns
- Attack rates: percentage of exposed individuals infected
- Secondary transmission: evidence of person-to-person spread
-
Control Measure Implementation
- Cohorting: infected patients and exposed contacts
- Contact precautions: gown and gloves for all patient contact
- Enhanced cleaning: increased frequency and broader spectrum disinfectants
- Staff restriction: symptomatic healthcare workers excluded
- Visitor limitations: essential personnel only during outbreaks
| Outbreak Organism | Transmission Mode | Control Measures | Investigation Priority | Typical Duration | Attack Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MRSA | Contact, healthcare worker hands | Contact precautions, cohorting | Staff colonization screening | 2-8 weeks | 10-30% |
| Klebsiella | Environmental, equipment | Enhanced cleaning, equipment review | Water sources, devices | 1-4 weeks | 15-40% |
| Candida | Cross-contamination, devices | Antifungal protocols, line review | Central line practices | 2-6 weeks | 5-20% |
| Rotavirus | Fecal-oral, environmental | Enteric precautions, hand hygiene | Visitor screening | 1-3 weeks | 20-60% |
| RSV | Respiratory droplets | Droplet precautions, cohorting | Staff illness, visitors | 2-8 weeks | 25-50% |
💡 Master This: Outbreak prevention requires proactive surveillance-weekly infection rates, organism trends, and resistance patterns enable early detection before widespread transmission occurs.
Understanding infection control transforms NICU care from reactive crisis management to proactive prevention, where evidence-based protocols create sustainable safety cultures that protect the most vulnerable patients.
🎯 Infection Control Mastery: The Prevention Fortress
Practice Questions: Neonatal infections
Test your understanding with these related questions
A neonate born at 33 weeks is transferred to the NICU after a complicated pregnancy and C-section. A week after being admitted, he developed a fever and became lethargic and minimally responsive to stimuli. A lumbar puncture is performed that reveals the following: Appearance Cloudy Protein 64 mg/dL Glucose 22 mg/dL Pressure 330 mm H20 Cells 295 cells/mm³ (> 90% PMN) A specimen is sent to microbiology and reveals gram-negative rods. Which of the following is the next appropriate step in management?










