Red flags for developmental delay US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Red flags for developmental delay. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
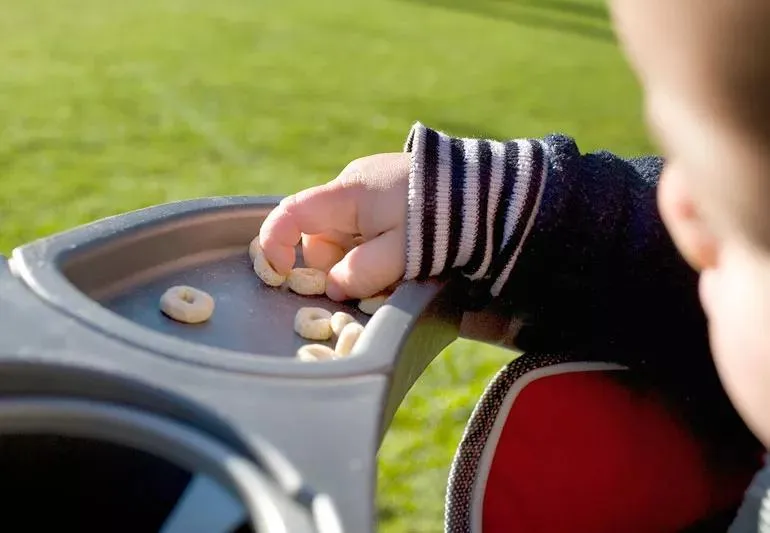
Red flags for developmental delay US Medical PG Question 1: A 1-year-old male presents to his pediatrician for a well-child visit. Through a history from the mother and physical examination, the pediatrician learns that the baby babbles non-specifically, takes several steps independently, and picks up his cereal using two fingers. His weight is currently 22 lbs (birth-weight 6 lbs, 9 oz), and his height is 30 inches (birth length 18 inches). Are there any aspects of this child's development that are delayed?
- A. Fine motor skill delay
- B. Language delay (Correct Answer)
- C. Inadequate growth
- D. Gross motor skill delay
- E. There are no developmental concerns
Red flags for developmental delay Explanation: ***Language delay***
- At 1 year of age, a child should typically be babbling with **specific sounds** and attempting to say their **first words**.
- The child's non-specific babbling suggests a delay in typical **expressive language development**.
*Fine motor skill delay*
- The child is able to pick up cereal using **two fingers**, indicating the development of a **pincer grasp**.
- This is an **age-appropriate fine motor skill** for a 1-year-old.
*Inadequate growth*
- The child has over **tripled his birth weight** (from 6 lbs, 9 oz to 22 lbs) and more than doubled his birth length (from 18 to 30 inches), which are **normal growth patterns** for the first year of life.
- While weight values can be plotted on growth charts, the provided information strongly suggests **adequate growth**.
*Gross motor skill delay*
- The child is taking **several steps independently**, which is an **age-appropriate gross motor milestone** for a 1-year-old.
- Many children take their first independent steps between 9 and 15 months.
*There are no developmental concerns*
- While many milestones are met, the **non-specific babbling** at 1 year strongly suggests a **language delay**.
- It is crucial to identify and address any potential delays early for intervention.
Red flags for developmental delay US Medical PG Question 2: A 4-month-old boy is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. He was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery and is exclusively breastfed. He weighed 3,400 g (7 lb 8 oz) at birth. At the physician's office, he appears well. His pulse is 146/min, the respirations are 39/min, and the blood pressure is 78/44 mm Hg. He weighs 7.5 kg (16 lb 9 oz) and measures 65 cm (25.6 in) in length. The remainder of the physical examination is normal. Which of the following developmental milestones has this patient most likely met?
- A. Sits with support of pelvis
- B. Grasps small objects between thumb and finger
- C. Transfers objects from hand to hand
- D. Intentionally rolls over (Correct Answer)
- E. Bounces actively when held in standing position
Red flags for developmental delay Explanation: ***Intentionally rolls over***
- Rolling over is a common developmental milestone achieved between **4 to 6 months** of age.
- At 4 months, an infant typically has sufficient **head control** and **trunk strength** to intentionally roll from tummy to back or back to tummy.
*Sits with support of pelvis*
- Sitting with **pelvic support** (tripod sitting) is generally achieved around **6 to 7 months** of age.
- A 4-month-old typically lacks the necessary **trunk stability** and strength for this milestone.
*Grasps small objects between thumb and finger*
- This describes a **pincer grasp**, which is a fine motor skill usually developed around **9-12 months** of age.
- At 4 months, infants primarily use a **palmar grasp** (raking motion) to pick up objects.
*Transfers objects from hand to hand*
- Transferring objects from hand to hand is a fine motor milestone typically achieved between **5 and 7 months** of age.
- A 4-month-old is beginning to reach for objects but usually has difficulty with **smooth transfers** between hands.
*Bounces actively when held in standing position*
- Active bouncing when held in a standing position is typically seen around **6 months** when infants start putting more weight on their legs.
- At 4 months, while an infant might bear some weight, **active bouncing** is usually more rudimentary or absent.
Red flags for developmental delay US Medical PG Question 3: A 13-month-old girl is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. She was born at 38 weeks' gestation. There is no family history of any serious illnesses. She cannot pull herself to stand from a sitting position. She can pick an object between her thumb and index finger but cannot drink from a cup or feed herself using a spoon. She comes when called by name and is willing to play with a ball. She cries if she does not see her parents in the same room as her. She coos “ma” and “ba.” She is at the 50th percentile for height and weight. Physical examination including neurologic examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate assessment of her development?
- A. Fine motor: normal | Gross motor: delayed | Language: normal | Social skills: delayed
- B. Fine motor: normal | Gross motor: delayed | Language: delayed | Social skills: normal (Correct Answer)
- C. Fine motor: delayed | Gross motor: normal | Language: delayed | Social skills: normal
- D. Fine motor: delayed | Gross motor: delayed | Language: normal | Social skills: normal
- E. Fine motor: delayed | Gross motor: normal | Language: normal | Social skills: delayed
Red flags for developmental delay Explanation: ***Fine motor: normal | Gross motor: delayed | Language: delayed | Social skills: normal***
- **Fine motor** is normal because she demonstrates **pincer grasp** (picking up objects between thumb and index finger), which is the key fine motor milestone expected by 9-12 months. The inability to drink from a cup or self-feed with a spoon represents more complex feeding skills that develop later (12-18 months) and are not primary fine motor milestones at 13 months.
- **Gross motor** is delayed because she cannot pull herself to stand, a milestone typically achieved by 9-12 months. At 13 months, she should be cruising along furniture or beginning to walk independently.
- **Language** is delayed because she only coos "ma" and "ba" without meaningful words. By 13 months, children should typically say 1-2 words with meaning (like "mama" or "dada" used specifically) and have varied babbling patterns.
- **Social skills** are normal as she responds to her name, engages in play (willing to play with a ball), and demonstrates appropriate **separation anxiety** when her parents are not in the room—all expected social-emotional milestones for this age.
*Fine motor: normal | Gross motor: delayed | Language: normal | Social skills: delayed*
- Language is delayed, not normal—cooing "ma" and "ba" without meaningful words does not meet the expected milestone of 1-2 words with meaning by 13 months.
- Social skills are normal, not delayed—responding to her name and showing separation anxiety are appropriate for her age.
*Fine motor: delayed | Gross motor: normal | Language: delayed | Social skills: normal*
- Fine motor is normal, not delayed—the presence of **pincer grasp** is the key indicator, and feeding difficulties reflect more complex coordination rather than delayed fine motor development.
- Gross motor is delayed, not normal—inability to pull to stand at 13 months represents a significant delay.
*Fine motor: delayed | Gross motor: delayed | Language: normal | Social skills: normal*
- Fine motor is normal—**pincer grasp** is present and appropriate for age.
- Language is delayed, not normal—she lacks meaningful words expected at 13 months.
*Fine motor: delayed | Gross motor: normal | Language: normal | Social skills: delayed*
- Fine motor is normal—**pincer grasp** is the key milestone and is present.
- Gross motor is delayed, not normal—cannot pull to stand, which should have been achieved months earlier.
- Social skills are normal, not delayed—separation anxiety and responding to name are age-appropriate behaviors.
Red flags for developmental delay US Medical PG Question 4: A 2-month-old is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. She was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery and is exclusively breastfed. She weighed 3,400 g (7 lb 8 oz) at birth. At the physician's office, she appears well. Her pulse is 136/min, the respirations are 41/min, and the blood pressure is 82/45 mm Hg. She weighs 5,200 g (11 lb 8 oz) and measures 57.5 cm (22.6 in) in length. The remainder of the physical examination is normal. Which of the following developmental milestones has this patient most likely met?
- A. Reaches for objects
- B. Stares at own hand
- C. Smiles in response to face (Correct Answer)
- D. Absence of asymmetric tonic neck reflex
- E. Monosyllabic babble
Red flags for developmental delay Explanation: ***Smiles in response to face***
- A 2-month-old infant typically achieves **social smiling**, often in response to a parent's face, indicating social engagement and developing emotional recognition.
- This milestone is an expected part of **normal social and emotional development** at this age.
*Reaches for objects*
- **Reaching for objects** is a more complex motor skill, generally expected around **4 to 6 months of age**, as fine motor control and hand-eye coordination develop.
- At 2 months, an infant may briefly swipe at objects but usually lacks the coordinated effort to intentionally reach and grasp.
*Stares at own hand*
- **Staring at one's own hand** is an early sign of self-discovery and visual exploration, typically emerging closer to **3 to 4 months of age** as vision matures.
- While a 2-month-old infant can focus on objects, sustained fascination with their own hands usually develops later.
*Absence of asymmetric tonic neck reflex*
- The **asymmetric tonic neck reflex (ATNR)**, or 'fencing reflex', is a primitive reflex normally present at 2 months of age and typically **disappears around 4 to 6 months**.
- Its presence is normal at 2 months, and its absence would be an abnormal finding, not a developmental milestone.
*Monosyllabic babble*
- **Monosyllabic babbling**, such as "ba" or "da", indicates developing language skills and typically begins around **6 to 9 months of age**.
- At 2 months, infants usually produce cooing sounds and simple vocalizations, but not structured babbling.
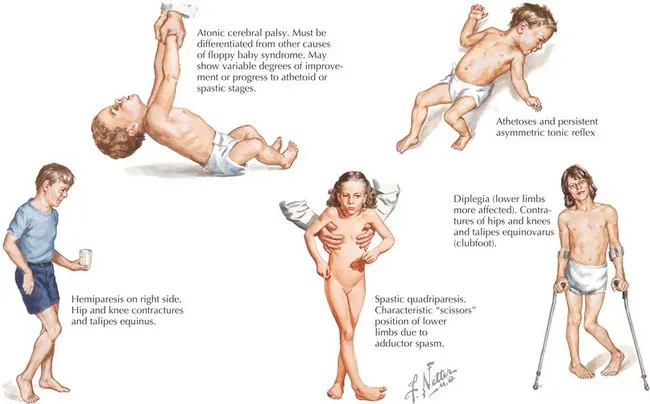
Red flags for developmental delay US Medical PG Question 5: A 15-month-old boy is brought to the pediatrician’s office by his mother due to abnormal muscle tone and an inability to walk. He was able to control his head at 5 months of age, roll at 8 months of age, sit at 11 months of age, and develop hand preference at 13 months of age. On physical exam, he is observed to asymmetrically crawl. He has a velocity-dependent increase in tone and 3+ biceps and patellar reflexes. His startle, asymmetric tonic neck, and Babinski reflexes are present. Which of the following is the most common risk factor for developing this patient’s clinical presentation?
- A. Intrauterine growth restriction
- B. Prematurity (Correct Answer)
- C. Perinatal hypoxic injury
- D. Multiparity
- E. Stroke
Red flags for developmental delay Explanation: ***Prematurity***
- **Cerebral palsy (CP)** is characterized by **delayed motor milestones**, **abnormal muscle tone (spasticity)**, **hyperreflexia**, and **persistent primitive reflexes** beyond the expected age.
- **Prematurity** (especially birth before 32 weeks' gestation) is the **most common risk factor** for CP overall, accounting for approximately 40-50% of cases.
- The developing brain of premature infants is particularly vulnerable to periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) and intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), which can lead to various CP subtypes.
- While this patient's **early hand preference** and **asymmetric crawling** suggest hemiplegic CP (often associated with stroke), the question asks for the most common risk factor **epidemiologically**, not the most likely cause in this specific case.
*Intrauterine growth restriction*
- While **IUGR** can be associated with developmental delays and is a risk factor for CP, it is less common than prematurity as the primary risk factor.
- IUGR alone without complications (like prematurity or hypoxia) accounts for a smaller proportion of CP cases.
*Perinatal hypoxic injury*
- **Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)** can cause CP, especially severe cases resulting in basal ganglia or watershed area damage.
- However, with modern obstetric monitoring and intervention, severe perinatal hypoxia accounts for only ~10% of CP cases—less common than prematurity.
*Multiparity*
- **Multiparity** (having multiple previous births) is generally not considered a direct or common risk factor for cerebral palsy.
- Any slight associations are typically due to confounding factors like increased risk of preterm birth in subsequent pregnancies, rather than multiparity itself.
*Stroke*
- **Perinatal stroke** can cause CP, typically presenting as **hemiplegic CP** with early hand preference and asymmetric motor findings—features seen in this patient.
- While stroke is a significant cause of hemiplegic CP specifically, it accounts for a smaller proportion of overall CP cases compared to prematurity, which causes various CP subtypes and is more prevalent.
Red flags for developmental delay US Medical PG Question 6: A 3-year-old boy is brought in by his mother because she is concerned that he has been “acting differently recently”. She says he no longer seems interested in playing with his friends from preschool, and she has noticed that he has stopped making eye contact with others. In addition, she says he flaps his hands when excited or angry and only seems to enjoy playing with objects that he can place in rows or rigid patterns. Despite these behaviors, he is meeting his language goals for his age (single word use). The patient has no significant past medical history. He is at the 90th percentile for height and weight for his age. He is afebrile and his vital signs are within normal limits. A physical examination is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Pervasive developmental disorder, not otherwise specified
- B. Autism spectrum disorder (Correct Answer)
- C. Rett’s disorder
- D. Childhood disintegrative disorder
- E. Asperger’s disorder
Red flags for developmental delay Explanation: ***Autism spectrum disorder***
- This patient exhibits **persistent deficits in social communication and social interaction** (e.g., lack of interest in friends, poor eye contact) and **restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests, or activities** (e.g., hand flapping, lining up objects). These are the core diagnostic criteria for **autism spectrum disorder (ASD)**.
- The symptoms are presenting in **early childhood** (age 3) and are causing **clinically significant impairment** in social, occupational, or other important areas of current functioning, consistent with an ASD diagnosis.
*Pervasive developmental disorder, not otherwise specified*
- This diagnosis was previously used when a child met some, but not all, criteria for autistic disorder or when there was atypical presentation. However, under **DSM-5**, these conditions are now unified under the single diagnosis of **Autism Spectrum Disorder**.
- Its usage has been largely superseded by the broader diagnosis of **Autism Spectrum Disorder** in the DSM-5.
*Rett’s disorder*
- **Rett's disorder** primarily affects **females** and is characterized by a period of normal development followed by a loss of acquired hand skills, severe intellectual disability, and characteristic hand-wringing movements. This patient is a male and does not exhibit these specific features.
- Patients typically experience **regression** in language and motor skills after normal early development, which is not described in this case, and they develop **microcephaly**.
*Childhood disintegrative disorder*
- This diagnosis involves a **marked regression** in multiple areas of functioning (social, communication, motor) after at least **2 years of normal development**.
- The patient's mother notes recent changes, but there is no indication of previous normal development followed by significant loss of skills across multiple domains after age 2, which differentiates it from the insidious onset of ASD symptoms.
*Asperger’s disorder*
- **Asperger’s disorder** was characterized by **significant difficulties in social interaction** and **restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior**, but with **no clinically significant delay in language or cognitive development**.
- In **DSM-5**, Asperger's disorder is no longer a distinct diagnosis and is now subsumed under the umbrella of **Autism Spectrum Disorder**, which better reflects the spectrum of symptom severity.
Red flags for developmental delay US Medical PG Question 7: A 12-month-old boy is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. He was born at 38 weeks' gestation and was 48 cm (19 in) in length and weighed 3061 g (6 lb 12 oz); he is currently 60 cm (24 in) in length and weighs 7,910 g (17 lb 7 oz). He can walk with one hand held and can throw a small ball. He can pick up an object between his thumb and index finger. He can wave 'bye-bye'. He can say 'mama', 'dada' and 'uh-oh'. He cries if left to play with a stranger alone. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is most likely delayed in this child?
- A. Fine motor skills
- B. Language skills
- C. Growth (Correct Answer)
- D. Gross motor skills
- E. Social skills
Red flags for developmental delay Explanation: ***Growth***
- At 1 year of age, a child's **birth weight should triple**, and their **birth length should increase by 50%**.
- This child's birth weight was 3061 g (6 lb 12 oz), meaning his expected weight at 1 year should be around **9183 g (20 lb 4 oz)**, but he only weighs **7910 g (17 lb 7 oz)**, indicating **inadequate weight gain** (~1273 g below expected).
- This child's birth length was 48 cm (19 in), meaning his expected length at 1 year should be around **72 cm (28 in)**, but he is only **60 cm (24 in)**, indicating **poor linear growth** (12 cm below expected).
- Both **weight-for-age and length-for-age are delayed**, making growth the most likely delayed parameter.
*Fine motor skills*
- The child can **pick up an object between his thumb and index finger**, demonstrating a **pincer grasp**, which is an appropriate fine motor skill for a 12-month-old.
- He can also **throw a small ball**, further indicating age-appropriate fine motor development.
*Language skills*
- The child can say **'mama', 'dada'**, and **'uh-oh'**, which are appropriate first words for a 12-month-old.
- He also **waves 'bye-bye'**, showing appropriate receptive and expressive communication.
*Gross motor skills*
- The child can **walk with one hand held**, which is an expected gross motor milestone for a 12-month-old.
- Many 12-month-olds are just beginning to cruise or take their first independent steps.
*Social skills*
- The child **waves 'bye-bye'** and **cries if left with a stranger alone**, which are age-appropriate demonstrations of **social interaction** and **stranger anxiety**, respectively, for a 12-month-old.
- These behaviors indicate typical social and emotional development.
Red flags for developmental delay US Medical PG Question 8: A male child is presented at the pediatric clinic for a well-child visit by his mother who reports previously normal developmental milestones. The child was born at 40 weeks with no complications during pregnancy or birth. The mother notes that the infant is able to sit without support. He is able to feed himself crackers and pureed food. He is constantly shaking his toy teddy bear but is able to stop when the mother says 'no'. Which of the following indicate the most likely language milestone the child presents with?
- A. Two-word combinations
- B. Saying words such as apple and cat, though limited to around 4 different words
- C. Able to say his first and last name
- D. Cooing
- E. Babbling (Correct Answer)
Red flags for developmental delay Explanation: ***Babbling***
- The developmental milestones described (sitting without support, feeding himself, responding to "no") are consistent with an infant around **6-9 months of age**.
- **Babbling** (e.g., "bababa", "dadada") is the primary language milestone expected at this age, as infants begin to experiment with sounds.
*Two-word combinations*
- This milestone typically emerges around **18-24 months of age**, when infants start to combine words like "more milk" or "mama up."
- The child's overall developmental stage, especially his motor skills, suggests he is significantly younger than the age at which two-word combinations are expected.
*Saying words such as apple and cat, though limited to around 4 different words*
- Saying a few distinct words usually occurs around **12-18 months of age**, after a period of extensive babbling.
- The child's other milestones place him in an earlier developmental period.
*Able to say his first and last name*
- Knowing and saying one's first and last name is a more advanced language and cognitive skill, typically seen in children around **2-3 years of age**.
- This milestone is far beyond the developmental stage indicated by the child's motor and social skills.
*Cooing*
- **Cooing**, characterized by vowel sounds like "ooh" and "aah," is an early vocalization skill typically observed in infants aged **2-4 months**.
- The child's ability to sit unsupported, feed himself, and respond to commands indicates a more advanced developmental stage than cooing.
Red flags for developmental delay US Medical PG Question 9: A 3-year-old boy is brought for general developmental evaluation. According to his parents he is playing alongside other children but not in a cooperative manner. He has also recently begun to ride a tricycle. Upon questioning you also find that he is toilet trained and can stack 9 blocks. Upon examination you find that he can copy a circle though he cannot yet copy a triangle or draw stick figures. In addition he is currently speaking in two word phrases but cannot yet use simple sentences. Based on these findings you tell the parents that their child's development is consistent with which of the following?
- A. Normal social, normal motor, delayed language (Correct Answer)
- B. Normal social, delayed motor, delayed language
- C. Delayed social, normal motor, delayed language
- D. Delayed social, normal motor, normal language
- E. Normal social, normal motor, normal language
Red flags for developmental delay Explanation: ***Normal social, normal motor, delayed language***
- The child's ability to play alongside other children without direct cooperation is typical for a 3-year-old, indicating **normal social development**.
- His motor skills (riding a tricycle, stacking 9 blocks, copying a circle) are largely age-appropriate, but his language (two-word phrases instead of simple sentences) is mildly **delayed for a 3-year-old**.
*Normal social, delayed motor, delayed language*
- This option is incorrect because the child's **motor skills** (riding a tricycle, stacking 9 blocks, copying a circle) are generally on track for a 3-year-old.
- While language is delayed, the motor development is not, making this option inconsistent with the overall clinical picture.
*Delayed social, normal motor, delayed language*
- This is incorrect because playing alongside peers (parallel play) is a **normal social behavior** for a 3-year-old, not a sign of delayed social development.
- The motor skills are normal, and language is indeed delayed, but the social assessment is inaccurate.
*Delayed social, normal motor, normal language*
- This option is incorrect due to an inaccurate assessment of both **social and language development**. Playing alongside peers is normal, not delayed social.
- The child's language use of only two-word phrases is considered delayed for a 3-year-old, not normal.
*Normal social, normal motor, normal language*
- This option is incorrect because the child's **language development** is not normal; 3-year-olds are typically using simple sentences, not just two-word phrases.
- While social and motor development appears normal, the language delay makes "normal language" an incorrect assessment.
Red flags for developmental delay US Medical PG Question 10: A six-year-old male presents to the pediatrician for a well child visit. The patient’s parents report that they are struggling to manage his temper tantrums, which happen as frequently as several times per day. They usually occur in the morning before school and during mealtimes, when his parents try to limit how much he eats. The patient often returns for second or third helpings at meals and snacks throughout the day. The patient’s parents have begun limiting the patient’s food intake because he has been gaining weight. They also report that the patient recently began first grade but still struggles with counting objects and naming letters consistently. The patient sat without support at 11 months of age and walked at 17 months of age. He is in the 99th percentile for weight and 5th percentile for height. On physical exam, he has almond-shaped eyes and a downturned mouth. He has poor muscle tone.
Which of the following additional findings would most likely be seen in this patient?
- A. Webbed neck
- B. Macroorchidism
- C. Ataxia
- D. Hemihyperplasia
- E. Hypogonadism (Correct Answer)
Red flags for developmental delay Explanation: ***Hypogonadism***
- The patient's presentation, including **hyperphagia**, **obesity**, developmental delay, and distinctive facial features (almond-shaped eyes, downturned mouth, poor muscle tone), is highly suggestive of **Prader-Willi Syndrome**.
- **Hypogonadism** (undescended testes in males, delayed puberty) is a classic feature of **Prader-Willi Syndrome** due to hypothalamic dysfunction, which also causes the voracious appetite.
*Webbed neck*
- A **webbed neck** is characteristic of **Turner Syndrome** (45, XO), which affects females and is associated with short stature, but not typically with the hyperphagia and obesity seen here.
- The patient is a male, making Turner Syndrome an unlikely diagnosis.
*Macroorchidism*
- **Macroorchidism** (enlarged testes) is a hallmark feature of **Fragile X Syndrome**, which is associated with intellectual disability and developmental delays.
- While fragile X syndrome involves developmental delay, it does not typically present with the extreme hyperphagia, obesity, and specific facial features described in the patient.
*Ataxia*
- **Ataxia** (lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements) in conjunction with developmental delays can be seen in various neurological disorders such as **Friedreich's ataxia** or **cerebral palsy**.
- This symptom is not a primary or characteristic finding in Prader-Willi Syndrome, and the other described features point away from ataxia as the most likely additional finding.
*Hemihyperplasia*
- **Hemihyperplasia** (overgrowth of one side of the body) is associated with conditions like **Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome**, which also involves macroglossia and an increased risk of tumors.
- This finding is not typically associated with the constellation of symptoms (hyperphagia, obesity, intellectual disability, hypotonia) seen in Prader-Willi Syndrome.
More Red flags for developmental delay US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.