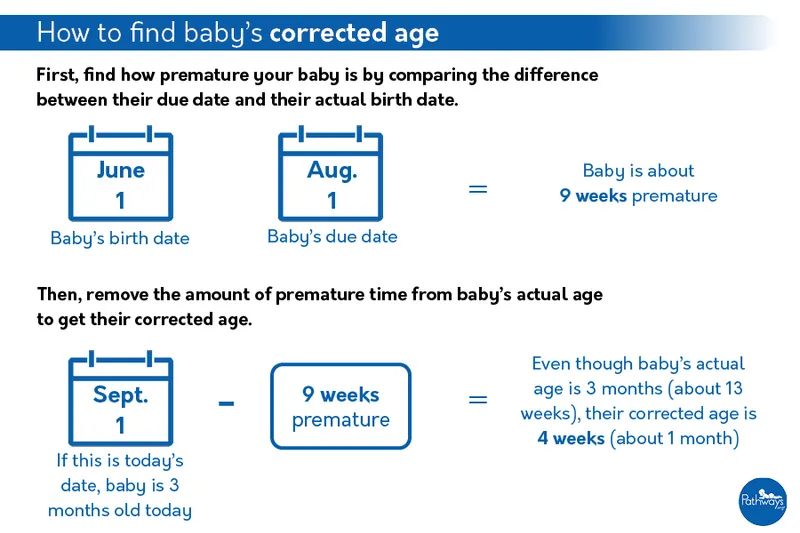
Milestone variations in preterm infants US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Milestone variations in preterm infants. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Milestone variations in preterm infants US Medical PG Question 1: An 11-year-old boy is brought to his pediatrician by his parents for the routine Tdap immunization booster dose that is given during adolescence. Upon reviewing the patient’s medical records, the pediatrician notes that he was immunized according to CDC recommendations, with the exception that he received a catch-up Tdap immunization at the age of 8 years. When the pediatrician asks the boy’s parents about this delay, they inform the doctor that they immigrated to this country 3 years ago from Southeast Asia, where the child had not been immunized against diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis. Therefore, he received a catch-up series at 8 years of age, which included the first dose of the Tdap vaccine. Which of the following options should the pediatrician choose to continue the boy’s immunization schedule?
- A. A single dose of Td vaccine at 18 years of age
- B. A single dose of Td vaccine now
- C. No further vaccination needed
- D. A single dose of Tdap vaccine now
- E. A single dose of Tdap vaccine at 13 years of age (Correct Answer)
Milestone variations in preterm infants Explanation: ***A single dose of Tdap vaccine at 13 years of age***
- The CDC recommends a **minimum interval of 5 years** between Tdap doses when Tdap is given as part of a catch-up series.
- Since this patient received his first Tdap at age 8, the earliest he should receive the adolescent booster is at **age 13** (5 years later).
- This timing ensures adequate spacing while still providing the recommended adolescent booster for **pertussis, tetanus, and diphtheria** protection.
- The 5-year interval prevents excessive antigen exposure and optimizes immune response.
*A single dose of Tdap vaccine now*
- Giving Tdap now would result in only a **3-year interval** from the previous Tdap dose at age 8.
- This violates the CDC recommendation of a **minimum 5-year interval** between Tdap doses.
- Shorter intervals may increase local reactogenicity without improving protection.
*A single dose of Td vaccine now*
- While this would provide tetanus and diphtheria protection, it would **not protect against pertussis**, which is a critical component of adolescent vaccination.
- The Tdap vaccine is specifically recommended for adolescents to boost waning pertussis immunity.
- Additionally, giving it now would still be earlier than the recommended 5-year interval from the previous pertussis-containing vaccine.
*A single dose of Td vaccine at 18 years of age*
- This option would result in a **10-year gap** from the last pertussis-containing vaccine, leaving the adolescent vulnerable during high-risk years.
- The adolescent Tdap booster is specifically timed for ages 11-13 to protect during peak transmission periods in middle and high school.
- Waiting until 18 would miss the critical window for pertussis protection.
*No further vaccination needed*
- While the patient completed a catch-up series, the CDC still recommends an **adolescent Tdap booster** even for those who received Tdap in a catch-up series.
- The adolescent booster is important to maintain immunity against pertussis, which wanes significantly over time.
- The booster should be given at age 13 to maintain the 5-year minimum interval.
Milestone variations in preterm infants US Medical PG Question 2: A 15-month-old boy is brought to the pediatrician’s office by his mother due to abnormal muscle tone and an inability to walk. He was able to control his head at 5 months of age, roll at 8 months of age, sit at 11 months of age, and develop hand preference at 13 months of age. On physical exam, he is observed to asymmetrically crawl. He has a velocity-dependent increase in tone and 3+ biceps and patellar reflexes. His startle, asymmetric tonic neck, and Babinski reflexes are present. Which of the following is the most common risk factor for developing this patient’s clinical presentation?
- A. Intrauterine growth restriction
- B. Prematurity (Correct Answer)
- C. Perinatal hypoxic injury
- D. Multiparity
- E. Stroke
Milestone variations in preterm infants Explanation: ***Prematurity***
- **Cerebral palsy (CP)** is characterized by **delayed motor milestones**, **abnormal muscle tone (spasticity)**, **hyperreflexia**, and **persistent primitive reflexes** beyond the expected age.
- **Prematurity** (especially birth before 32 weeks' gestation) is the **most common risk factor** for CP overall, accounting for approximately 40-50% of cases.
- The developing brain of premature infants is particularly vulnerable to periventricular leukomalacia (PVL) and intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH), which can lead to various CP subtypes.
- While this patient's **early hand preference** and **asymmetric crawling** suggest hemiplegic CP (often associated with stroke), the question asks for the most common risk factor **epidemiologically**, not the most likely cause in this specific case.
*Intrauterine growth restriction*
- While **IUGR** can be associated with developmental delays and is a risk factor for CP, it is less common than prematurity as the primary risk factor.
- IUGR alone without complications (like prematurity or hypoxia) accounts for a smaller proportion of CP cases.
*Perinatal hypoxic injury*
- **Perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)** can cause CP, especially severe cases resulting in basal ganglia or watershed area damage.
- However, with modern obstetric monitoring and intervention, severe perinatal hypoxia accounts for only ~10% of CP cases—less common than prematurity.
*Multiparity*
- **Multiparity** (having multiple previous births) is generally not considered a direct or common risk factor for cerebral palsy.
- Any slight associations are typically due to confounding factors like increased risk of preterm birth in subsequent pregnancies, rather than multiparity itself.
*Stroke*
- **Perinatal stroke** can cause CP, typically presenting as **hemiplegic CP** with early hand preference and asymmetric motor findings—features seen in this patient.
- While stroke is a significant cause of hemiplegic CP specifically, it accounts for a smaller proportion of overall CP cases compared to prematurity, which causes various CP subtypes and is more prevalent.
Milestone variations in preterm infants US Medical PG Question 3: A 12-month-old boy is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. He was born at 38 weeks' gestation and was 48 cm (19 in) in length and weighed 3061 g (6 lb 12 oz); he is currently 60 cm (24 in) in length and weighs 7,910 g (17 lb 7 oz). He can walk with one hand held and can throw a small ball. He can pick up an object between his thumb and index finger. He can wave 'bye-bye'. He can say 'mama', 'dada' and 'uh-oh'. He cries if left to play with a stranger alone. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is most likely delayed in this child?
- A. Fine motor skills
- B. Language skills
- C. Growth (Correct Answer)
- D. Gross motor skills
- E. Social skills
Milestone variations in preterm infants Explanation: ***Growth***
- At 1 year of age, a child's **birth weight should triple**, and their **birth length should increase by 50%**.
- This child's birth weight was 3061 g (6 lb 12 oz), meaning his expected weight at 1 year should be around **9183 g (20 lb 4 oz)**, but he only weighs **7910 g (17 lb 7 oz)**, indicating **inadequate weight gain** (~1273 g below expected).
- This child's birth length was 48 cm (19 in), meaning his expected length at 1 year should be around **72 cm (28 in)**, but he is only **60 cm (24 in)**, indicating **poor linear growth** (12 cm below expected).
- Both **weight-for-age and length-for-age are delayed**, making growth the most likely delayed parameter.
*Fine motor skills*
- The child can **pick up an object between his thumb and index finger**, demonstrating a **pincer grasp**, which is an appropriate fine motor skill for a 12-month-old.
- He can also **throw a small ball**, further indicating age-appropriate fine motor development.
*Language skills*
- The child can say **'mama', 'dada'**, and **'uh-oh'**, which are appropriate first words for a 12-month-old.
- He also **waves 'bye-bye'**, showing appropriate receptive and expressive communication.
*Gross motor skills*
- The child can **walk with one hand held**, which is an expected gross motor milestone for a 12-month-old.
- Many 12-month-olds are just beginning to cruise or take their first independent steps.
*Social skills*
- The child **waves 'bye-bye'** and **cries if left with a stranger alone**, which are age-appropriate demonstrations of **social interaction** and **stranger anxiety**, respectively, for a 12-month-old.
- These behaviors indicate typical social and emotional development.
Milestone variations in preterm infants US Medical PG Question 4: A 2-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother for a well-child examination. She is at the 55th percentile for height and the 40th percentile for weight. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. She is able to follow simple commands, such as “close your eyes, then stick out your tongue,” but she is unable to follow 3-step commands. She knows approximately 75 words, and half of her speech is understandable. She can say 2-word phrases, and she is able to name many parts of the body. Assuming normal development, which of the following milestones would be expected in a patient this age?
- A. Hops on one foot
- B. Engages in role-playing
- C. Separates easily from parents
- D. Pedals a tricycle
- E. Builds a tower of 6 cubes (Correct Answer)
Milestone variations in preterm infants Explanation: ***Builds a tower of 6 cubes***
- At 2 years old, children typically develop fine motor skills enabling them to stack **6 to 7 cubes** to build a tower, demonstrating good hand-eye coordination.
- This milestone aligns well with the described cognitive development, such as following multi-step commands and early language acquisition.
*Hops on one foot*
- **Hopping on one foot** is a gross motor skill usually achieved later, typically around **4 years of age**.
- A 2-year-old child is more likely to be developing skills like running, jumping with two feet, or walking up and down stairs.
*Engages in role-playing*
- While toddlers engage in **imitative play**, true imaginative **role-playing** with complex scenarios and multiple characters typically develops later, around **3 years of age or older**.
- At 2, play is often more focused on mimicking observed actions.
*Separates easily from parents*
- At 2 years old, many children are still experiencing **separation anxiety**, especially in unfamiliar situations.
- **Easy separation** from parents is a milestone typically achieved later as children develop more independence and social confidence, often closer to 3 or 4 years of age.
*Pedals a tricycle*
- **Pedaling a tricycle** requires coordinated gross motor skills, balance, and cognitive understanding that are typically developed around **3 years of age**.
- A 2-year-old may be able to sit on a tricycle and push with their feet, but not yet pedal efficiently.
Milestone variations in preterm infants US Medical PG Question 5: A 1-minute-old newborn is being examined by the pediatric nurse. The nurse auscultates the heart and determines that the heart rate is 89/min. The respirations are spontaneous and regular. The chest and abdomen are both pink while the tips of the fingers and toes are blue. When the newborn’s foot is slapped the face grimaces and he cries loud and strong. When the arms are extended by the nurse they flex back quickly. What is this patient’s Apgar score?
- A. 5
- B. 10
- C. 8 (Correct Answer)
- D. 6
- E. 9
Milestone variations in preterm infants Explanation: ***8***
- The Apgar score is calculated by assigning 0, 1, or 2 points to five criteria: **Appearance**, **Pulse**, **Grimace (reflex irritability)**, **Activity (muscle tone)**, and **Respiration**.
- This newborn scores 1 point for **Appearance** (pink body, blue extremities/acrocyanosis), 1 point for **Pulse** (89/min, which is below 100), 2 points for **Grimace** (cries loud and strong), 2 points for **Activity** (arms flex back quickly), and 2 points for **Respiration** (spontaneous and regular), totaling **8**.
*5*
- An Apgar score of 5 would indicate a more compromised state, with lower scores in multiple categories.
- This newborn demonstrates strong respiratory effort, vigorous cry, and active muscle tone, all inconsistent with a score of 5.
*10*
- A perfect score of 10 is rare and would require the newborn to have a **pink appearance throughout** (including extremities), a heart rate over 100 bpm, strong cry, active movement, and vigorous breathing.
- This newborn has two findings preventing a score of 10: **acrocyanosis** (blue extremities) and **heart rate of 89/min** (below 100).
*6*
- An Apgar score of 6 would imply more significant compromise, such as weak respiratory effort, minimal response to stimulation, or poor muscle tone.
- This newborn's strong cry, vigorous grimace response, and quick flexion indicate better performance than a score of 6.
*9*
- A score of 9 would mean only one parameter scores 1 point, with all others scoring 2 points.
- This newborn has **two parameters scoring 1 point**: **Appearance** (acrocyanosis) and **Pulse** (89/min, below 100), making the maximum possible score 8, not 9.
Milestone variations in preterm infants US Medical PG Question 6: A male child is presented at the pediatric clinic for a well-child visit by his mother who reports previously normal developmental milestones. The child was born at 40 weeks with no complications during pregnancy or birth. The mother notes that the infant is able to sit without support. He is able to feed himself crackers and pureed food. He is constantly shaking his toy teddy bear but is able to stop when the mother says 'no'. Which of the following indicate the most likely language milestone the child presents with?
- A. Two-word combinations
- B. Saying words such as apple and cat, though limited to around 4 different words
- C. Able to say his first and last name
- D. Cooing
- E. Babbling (Correct Answer)
Milestone variations in preterm infants Explanation: ***Babbling***
- The developmental milestones described (sitting without support, feeding himself, responding to "no") are consistent with an infant around **6-9 months of age**.
- **Babbling** (e.g., "bababa", "dadada") is the primary language milestone expected at this age, as infants begin to experiment with sounds.
*Two-word combinations*
- This milestone typically emerges around **18-24 months of age**, when infants start to combine words like "more milk" or "mama up."
- The child's overall developmental stage, especially his motor skills, suggests he is significantly younger than the age at which two-word combinations are expected.
*Saying words such as apple and cat, though limited to around 4 different words*
- Saying a few distinct words usually occurs around **12-18 months of age**, after a period of extensive babbling.
- The child's other milestones place him in an earlier developmental period.
*Able to say his first and last name*
- Knowing and saying one's first and last name is a more advanced language and cognitive skill, typically seen in children around **2-3 years of age**.
- This milestone is far beyond the developmental stage indicated by the child's motor and social skills.
*Cooing*
- **Cooing**, characterized by vowel sounds like "ooh" and "aah," is an early vocalization skill typically observed in infants aged **2-4 months**.
- The child's ability to sit unsupported, feed himself, and respond to commands indicates a more advanced developmental stage than cooing.
Milestone variations in preterm infants US Medical PG Question 7: A mother brings her infant for a regular well-child check-up with the pediatrician. During the routine developmental examination, the physician notes that the child is looking at him with his head lifted upwards when he is about to pick up the child from the table. At what age is it common to begin to observe this finding in a child, assuming that the child is developmentally normal?
- A. 2 months
- B. 6 months
- C. 12 months
- D. 9 months
- E. 4 months (Correct Answer)
Milestone variations in preterm infants Explanation: ***4 months***
- By **4 months of age**, infants typically develop good **head control** and can hold their head steady while looking around, including when being picked up.
- This signifies strengthening neck muscles and improved coordination, allowing them to **lift their head against gravity** to maintain eye contact with an approaching person.
*2 months*
- At **2 months**, infants can lift their head briefly while on their tummy but generally have limited and **unsteady head control** when pulled to a sitting position or lifted.
- They are unlikely to consistently hold their head up in anticipation of being picked up.
*6 months*
- By **6 months**, infants have excellent head control and can often **sit with support**, and even briefly without it.
- While they can certainly lift their head, this milestone is usually observed earlier, around 4 months.
*12 months*
- At **12 months**, infants are typically **pulling to stand** and cruising, with fully developed head control.
- Observing this specific behavior at 12 months would indicate a significant delay in gross motor development.
*9 months*
- By **9 months**, infants are often crawling, pulling themselves to stand, and have very strong head and neck muscles.
- This developmental stage is well past the initial acquisition of head control needed for the described action.
Milestone variations in preterm infants US Medical PG Question 8: Three days after delivery, a 1100-g (2-lb 7-oz) newborn has a tonic seizure that lasts for 25 seconds. She has become increasingly lethargic over the past 18 hours. She was born at 31 weeks' gestation. Antenatal period was complicated by chorioamnionitis. Apgar scores were 3 and 6 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. She appears ill. Her pulse is 123/min, respirations are 50/min and irregular, and blood pressure is 60/30 mm Hg. Examination shows a tense anterior fontanelle. The pupils are equal and react sluggishly to light. Examination shows slow, conjugate back and forth movements of the eyes. Muscle tone is decreased in all extremities. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Intraventricular hemorrhage (Correct Answer)
- B. Spinal muscular atrophy
- C. Galactosemia
- D. Congenital hydrocephalus
- E. Phenylketonuria
Milestone variations in preterm infants Explanation: ***Intraventricular hemorrhage***
- The combination of **prematurity** (31 weeks' gestation, 1100g), **tonic seizures**, increasing **lethargy**, tense **anterior fontanelle**, **sluggishly reactive pupils**, and **slow conjugate back-and-forth eye movements** (suggesting brainstem involvement from increased intracranial pressure) are classical signs of intraventricular hemorrhage (IVH) in a neonate.
- **IVH** is common in premature infants due to the fragility of germinal matrix vessels and can manifest acutely with neurological deterioration and increased intracranial pressure, typically within the first 72 hours of life.
- While maternal **chorioamnionitis** and low Apgar scores raise concern for neonatal sepsis/meningitis, the specific **ocular movement pattern** and acute neurological signs on day 3 are more characteristic of IVH in this extremely premature infant.
*Spinal muscular atrophy*
- This is a **neuromuscular genetic disorder** characterized by progressive muscle weakness and hypotonia due to anterior horn cell degeneration.
- It would typically present with **decreased muscle tone but without acute neurological signs** like seizures, tense fontanelle, or sluggish pupillary responses.
- Does not cause acute-onset seizures or rapidly progressing lethargy in the neonatal period.
*Galactosemia*
- This is a **metabolic disorder** that presents with symptoms such as **vomiting, jaundice, hepatomegaly**, and **sepsis-like symptoms** upon introduction of lactose-containing feeds (breast milk or regular formula), typically after several days of feeding.
- While it can cause lethargy and seizures, the acute neurological findings including **tense fontanelle** and **abnormal eye movements** in the immediate postnatal period of a premature infant more strongly suggest an anatomical/structural etiology like IVH.
*Congenital hydrocephalus*
- While **hydrocephalus** can cause a **tense fontanelle** and seizures, the **acute onset** of symptoms (day 3 of life with rapid deterioration over 18 hours following a specific tonic seizure) in an extremely premature infant strongly suggests an **acute hemorrhagic event** rather than congenital hydrocephalus.
- Congenital hydrocephalus typically presents with **progressively enlarging head circumference** over time, rather than such acute neurological deterioration in the first 72 hours of life.
- IVH can lead to secondary post-hemorrhagic hydrocephalus, but the acute presentation favors primary IVH.
*Phenylketonuria*
- This is a **metabolic disorder** caused by phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency that, if untreated, leads to **intellectual disability** and seizures.
- Symptoms typically manifest **several months after birth** (usually 3-6 months) as phenylalanine accumulates, and are not associated with acute neonatal neurological distress like tense fontanelle, abnormal eye movements, or acute lethargy in the first few days of life.
- Would not explain the acute deterioration on day 3 of life in this clinical context.
Milestone variations in preterm infants US Medical PG Question 9: Five weeks after delivery, a 1350-g (3-lb 0-oz) male newborn has respiratory distress. He was born at 26 weeks' gestation. He required intubation and mechanical ventilation for a month following delivery and has been on noninvasive pressure ventilation for 5 days. His temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F), pulse is 148/min, respirations are 63/min, and blood pressure is 60/32 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on 40% oxygen shows an oxygen saturation of 91%. Examination shows moderate intercostal and subcostal retractions. Scattered crackles are heard in the thorax. An x-ray of the chest shows diffuse granular densities and basal atelectasis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (Correct Answer)
- B. Tracheomalacia
- C. Bronchiolitis obliterans
- D. Interstitial emphysema
- E. Pneumonia
Milestone variations in preterm infants Explanation: ***Bronchopulmonary dysplasia***
- The presentation of a premature infant (26 weeks' gestation) with persistent respiratory distress requiring prolonged mechanical ventilation and oxygen, along with characteristic chest X-ray findings (diffuse granular densities and basal atelectasis), is highly indicative of **bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)**.
- BPD is a chronic lung disease of prematurity defined by the need for supplemental oxygen and/or positive pressure ventilation for at least 28 days after birth, with severity classified at 36 weeks postmenstrual age (or discharge if earlier).
- The pathophysiology involves ventilator-induced injury, oxygen toxicity, and inflammation in the developing lung, leading to impaired alveolarization and abnormal vascular development.
*Tracheomalacia*
- While **tracheomalacia** can cause respiratory symptoms, it typically presents with expiratory stridor, a characteristic "barking" cough, or wheezing that may improve with neck extension or prone positioning.
- It is a structural abnormality of the trachea involving weakness of the tracheal wall, and would not typically manifest with diffuse granular densities or basal atelectasis on chest X-ray in this context.
*Bronchiolitis obliterans*
- **Bronchiolitis obliterans** is irreversible obstruction of the small airways, often occurring after severe viral infections (especially adenovirus or RSV), lung transplantation, or toxic inhalational injury.
- While it can occur in neonates post-ventilation, it is less common in this specific context and would typically present with more severe obstructive findings, hyperinflation, and air trapping on imaging rather than chronic diffuse granular densities and atelectasis.
*Interstitial emphysema*
- **Pulmonary interstitial emphysema** usually occurs acutely in the first days to weeks of mechanical ventilation, characterized by air dissecting into the lung interstitium and perivascular spaces.
- While it can be a complication that contributes to the development of BPD, the persistent nature of respiratory distress five weeks post-delivery, along with diffuse granular densities and chronic radiographic changes, points toward the established chronic lung disease of BPD rather than acute interstitial emphysema.
*Pneumonia*
- Neonatal **pneumonia** would typically present with acute onset or worsening of respiratory distress, temperature instability, and signs of systemic infection.
- While a chest X-ray might show infiltrates or consolidations, the chronic progressive course over 5 weeks, history of extreme prematurity, and prolonged ventilation make BPD a more fitting diagnosis than acute pneumonia in this clinical scenario.
Milestone variations in preterm infants US Medical PG Question 10: An infant boy is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. He was born at term and has been healthy since. He is beginning to crawl but can not yet walk or run. He feeds himself small foods and can bang 2 cubes together. He is just beginning to successfully use a pincer grasp. He has stranger anxiety. He is at the 40th percentile for height and weight. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following additional skills or behaviors would be expected in a healthy patient of this developmental age?
- A. Follows one-step commands
- B. Says mama or dada (Correct Answer)
- C. Enjoys peek-a-boo
- D. Gives objects to others
- E. Knows 3–6 words
Milestone variations in preterm infants Explanation: ***Says mama or dada***
- The infant is at roughly **9–10 months** based on developmental milestones like crawling, banging cubes, developing pincer grasp, and stranger anxiety.
- At this age, saying **"mama" or "dada" specifically** (not just babbling) is a common and expected **emerging language milestone**.
- This represents a NEW skill being acquired at this developmental stage.
*Follows one-step commands*
- Following one-step commands, especially without gestures, is typically a milestone achieved later, around **12–15 months** of age.
- The infant's current stage of development, particularly concerning language acquisition, indicates they are not yet at this level of comprehension.
*Enjoys peek-a-boo*
- While infants at **9–10 months** do enjoy peek-a-boo, this is not a NEW or emerging skill at this age.
- Peek-a-boo is typically enjoyed starting around **6–9 months** and represents an **already established** skill by this developmental stage.
- The question asks for "additional skills expected" at this age, and "mama/dada" is the emerging milestone, whereas peek-a-boo enjoyment is already well-developed.
*Gives objects to others*
- **Giving objects to others** as a communicative gesture or to share is a more complex social milestone, typically emerging around **12–15 months** of age.
- This action requires a greater understanding of social interaction and reciprocity than what's expected for this infant's current stage.
*Knows 3–6 words*
- Knowing and using **multiple specific words** (3-6 words) is a language milestone typically reached closer to **12–15 months**.
- At 9–10 months, the infant is just beginning to say specific words like "mama" or "dada", indicating an earlier stage of vocabulary development.
More Milestone variations in preterm infants US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.