Common childhood exanthems US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Common childhood exanthems. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
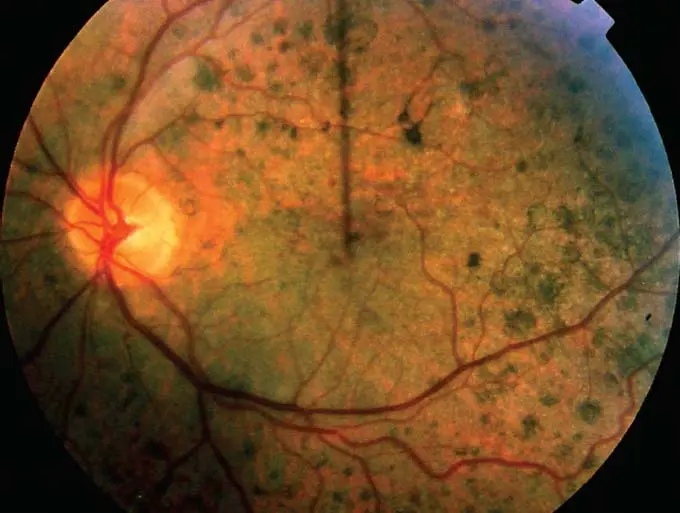
Common childhood exanthems US Medical PG Question 1: A male neonate is being examined by a pediatrician. His mother informs the doctor that she had a mild fever with rash, muscle pain, and swollen and tender lymph nodes during the second month of gestation. The boy was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery with no prenatal care. On physical examination, the neonate has normal vital signs. Retinal examination reveals the findings shown in the image. Which of the following congenital heart defects is most likely to be present in this neonate?
- A. Double outlet right ventricle
- B. Atrial septal defect
- C. Patent ductus arteriosus (Correct Answer)
- D. Ventricular septal defect
- E. Tetralogy of Fallot
Common childhood exanthems Explanation: ***Patent ductus arteriosus***
- This neonate has **congenital rubella syndrome (CRS)** based on maternal symptoms during the first trimester (fever, rash, lymphadenopathy) and the characteristic **"salt and pepper" retinopathy** shown on retinal examination
- **PDA is the most common cardiac defect** associated with CRS, occurring in approximately 50-85% of affected infants
- Other cardiac manifestations of CRS include peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis, but PDA predominates
- The classic triad of CRS includes cardiac defects, ocular abnormalities (cataracts, glaucoma, retinopathy), and sensorineural deafness
*Double outlet right ventricle*
- This is a **conotruncal anomaly** typically presenting with cyanosis in the neonatal period
- Not associated with maternal rubella infection or congenital rubella syndrome
- Would present with abnormal ventricular anatomy and significant hemodynamic compromise
*Atrial septal defect*
- While ASD is a common congenital heart defect, it is **not characteristically associated with CRS**
- Much less frequently linked to maternal viral infections compared to PDA
- Often asymptomatic in the neonatal period and detected later in childhood
*Ventricular septal defect*
- VSD is less commonly associated with **congenital rubella syndrome** compared to PDA
- When present, typically manifests with a holosystolic murmur at the left lower sternal border
- Can occur with maternal infections but is not the predominant cardiac finding in CRS
*Tetralogy of Fallot*
- Consists of four anatomic abnormalities: VSD, pulmonary stenosis, overriding aorta, and right ventricular hypertrophy
- Presents with **cyanosis** ("tet spells") and is not specifically linked to maternal rubella infection
- Not part of the congenital rubella syndrome spectrum
Common childhood exanthems US Medical PG Question 2: A 32-year-old G1P0 woman presents to her obstetrician for a prenatal visit. She is 30 weeks pregnant. She reports some fatigue and complains of urinary urgency. Prior to this pregnancy, she had no significant medical history. She takes a prenatal vitamin and folate supplements daily. Her mother has diabetes, and her brother has coronary artery disease. On physical examination, the fundal height is 25 centimeters. A fetal ultrasound shows a proportional reduction in head circumference, trunk size, and limb length. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient’s presentation?
- A. Gestational diabetes
- B. Antiphospholipid syndrome
- C. Rubella infection (Correct Answer)
- D. Pre-eclampsia
- E. Cigarette smoking
Common childhood exanthems Explanation: **Rubella infection**
- The **reduced fundal height** (25 cm at 30 weeks) and **symmetrically small fetus** (proportional reduction in head, trunk, and limbs) are characteristic findings of **intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)** due to a congenital infection like rubella.
- Maternal symptoms like **fatigue** and **urinary urgency** are non-specific but, in the context of fetal findings, point towards a systemic process affecting both mother and fetus.
*Gestational diabetes*
- Fetal growth in gestational diabetes is typically characterized by **macrosomia** (large for gestational age), not IUGR.
- Clinical findings would usually include a **fundal height larger than expected** for gestational age due to a larger fetus.
*Antiphospholipid syndrome*
- This condition is associated with **recurrent pregnancy loss**, **thrombosis**, and **placental insufficiency**, which can lead to IUGR.
- However, the IUGR associated with antiphospholipid syndrome is typically **asymmetric**, meaning the head circumference is spared while the abdomen and other body parts are disproportionately small.
*Pre-eclampsia*
- Pre-eclampsia can cause **IUGR** due to placental insufficiency, but it is primarily characterized by **new-onset hypertension** and **proteinuria** after 20 weeks of gestation, which are not mentioned in this case.
- While fatigue and urgency can be present, the absence of hypertension and proteinuria makes pre-eclampsia less likely as the primary cause.
*Cigarette smoking*
- Maternal cigarette smoking is a known risk factor for **IUGR**, particularly **symmetrical IUGR**.
- However, the patient's medical history states "no significant medical history" and does not mention smoking, making an infection a more likely explanation given the context.
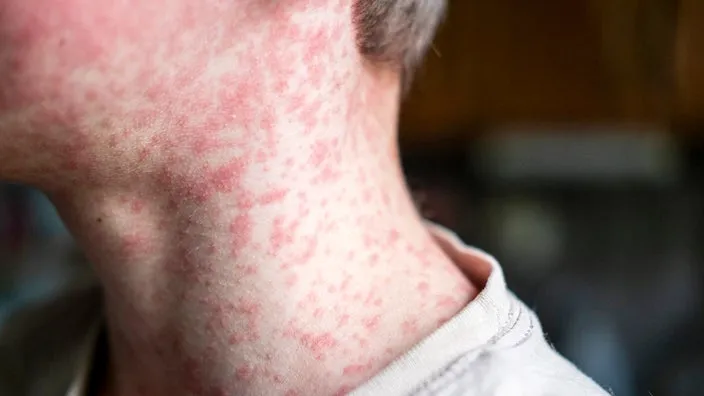
Common childhood exanthems US Medical PG Question 3: An 11-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents because of a mildly pruritic rash on her trunk and extremities for 2 days. One week ago, she developed a low-grade fever, rhinorrhea, and headache, followed by a facial rash 4 days later. The facial rash did not involve the perioral skin. Her temperature is 37.4°C (99.3°F). A photograph of the rash on her lower arms is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Exanthem subitum
- B. Hand, foot, and mouth disease
- C. Scarlet fever
- D. Erythema infectiosum (Correct Answer)
- E. Rubella
Common childhood exanthems Explanation: ***Erythema infectiosum***
- The combination of a prodromal illness (low-grade fever, rhinorrhea, headache) followed by a **facial rash that spares the perioral skin** (classically described as "slapped cheek" appearance) and a subsequent **body rash** (lacy, reticular pattern on the trunk and extremities) is pathognomonic for **erythema infectiosum**, caused by **Parvovirus B19**.
- The description of a **mildly pruritic rash on the trunk and extremities** appearing after the facial rash is consistent with the typical progression of the rash in erythema infectiosum.
*Exanthem subitum*
- Characterized by a **high fever** (often >39.5°C) for several days, followed by the sudden appearance of a **rose-pink maculopapular rash** once the fever breaks.
- The rash in exanthem subitum typically starts on the trunk and spreads outwards, and there is no characteristic "slapped cheek" facial rash.
*Hand, foot, and mouth disease*
- Presents with fever, malaise, sore throat, and a characteristic **vesicular rash on the hands, feet, and oral mucosa**.
- The rash described in the patient does not match the typical presentation or distribution of hand, foot, and mouth disease.
*Scarlet fever*
- Caused by **Group A Streptococcus** and typically presents with a **fine, sandpaper-like rash** that starts on the neck and chest and spreads to the trunk and extremities, often with circumoral pallor and a "strawberry tongue."
- The described rash pattern and facial involvement are not consistent with scarlet fever.
*Rubella*
- Features include a maculopapular rash that starts on the face and spreads rapidly downwards, and may be accompanied by **postauricular and occipital lymphadenopathy**.
- While it involves a facial rash, the characteristic "slapped cheek" appearance and the specific reticular body rash are not typical for rubella.
Common childhood exanthems US Medical PG Question 4: A 15-month-old girl is brought to the physician because of the sudden appearance of a rash on her trunk that started 6 hours ago and subsequently spread to her extremities. Four days ago, she was taken to the emergency department because of a high fever and vomiting. She was treated with acetaminophen and discharged the next day. The fever persisted for several days and abated just prior to appearance of the rash. Physical examination shows a rose-colored, blanching, maculopapular rash, and postauricular lymphadenopathy. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Roseola infantum (Correct Answer)
- B. Rubella
- C. Erythema infectiosum
- D. Drug allergy
- E. Nonbullous impetigo
Common childhood exanthems Explanation: ***Roseola infantum***
- The classic presentation includes several days of **high fever** that **abruptly resolves**, followed by the appearance of a **rose-colored, blanching maculopapular rash**, primarily on the trunk.
- This condition is most common in infants and young children, often accompanied by **postauricular lymphadenopathy**.
*Rubella*
- While rubella presents with a **maculopapular rash** and **postauricular lymphadenopathy**, the rash typically appears *with* or *shortly after* the fever, not after the fever has completely abated.
- The fever in rubella is usually milder than the high fever seen in roseola.
*Erythema infectiosum*
- This condition, also known as fifth disease, typically presents with a **"slapped cheek" rash** on the face, followed by a lacy rash on the extremities, often without the distinct pattern of high fever followed by rash offset.
- The fever is often low-grade or absent, unlike the high fever experienced by the patient.
*Drug allergy*
- A drug allergy could cause a rash, but it's less likely to selectively manifest several days after acetaminophen administration once the fever has disappeared, especially without other allergic symptoms like **pruritus** or **urticaria**.
- The precise sequence of high fever followed by rash resolution is not typical for most drug-induced rashes.
*Nonbullous impetigo*
- This is a **bacterial skin infection** characterized by **honey-crusted lesions**, most commonly around the nose and mouth, not a generalized maculopapular rash.
- It is typically not preceded by a systemic illness with high fever and vomiting in this manner.
Common childhood exanthems US Medical PG Question 5: A 9-month-old infant is brought to the physician because of a generalized nonpruritic rash for 2 days. The rash began on her trunk and spread to her extremities. Five days ago, she was taken to the emergency department for fever of 40.5°C (104.9°F) and a 1-minute generalized tonic-clonic seizure. She was born at term and has no history of serious illness. Her immunizations are up-to-date. Current medications include acetaminophen. Her temperature is 37.2°C (99.0°F) and pulse is 120/min. Examination shows a maculopapular rash that blanches on pressure. A photograph of the rash is shown. Posterior auricular lymphadenopathy is present. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Kawasaki disease
- B. Roseola infantum (Correct Answer)
- C. Drug allergy
- D. Impetigo
- E. Rubella
Common childhood exanthems Explanation: ***Roseola infantum***
- This diagnosis is supported by a classic presentation of **high fever** (often causing seizures) followed by the abrupt appearance of a **nonpruritic, maculopapular rash** on the trunk and spreading to the extremities, as the fever resolves. This pattern is characteristic of **human herpesvirus 6 (HHV-6)** infection.
- The presence of **posterior auricular lymphadenopathy** after fever resolution and rash onset further strengthens the diagnosis of roseola infantum, also known as exanthem subitum.
*Kawasaki disease*
- While Kawasaki disease can present with fever and rash, the rash is typically **polymorphous** and the fever is **persistent for at least 5 days** without other explanation.
- Other key features of Kawasaki disease, such as **cervical lymphadenopathy** (typically unilateral, >1.5 cm), **conjunctivitis**, **oral changes** (strawberry tongue, red cracked lips), and **extremity changes** (reddening, swelling, desquamation), are not described, and the fever here resolved before the rash.
*Drug allergy*
- A drug allergy rash would typically be **pruritic** and the timing of onset after a single dose of acetaminophen, a common and usually well-tolerated medication, makes a drug allergy less likely, especially given the preceding high fever episode.
- The distinct pattern of high fever followed by rash resolution as fever breaks is not typical for most drug allergies.
*Impetigo*
- Impetigo is a **bacterial skin infection** characterized by **honey-crusted lesions** or **blisters**, not a generalized maculopapular rash that blanches on pressure.
- It usually has a more localized presentation and is not preceded by a high fever followed by rash in this manner.
*Rubella*
- While rubella (German measles) can cause a **maculopapular rash** and **posterior auricular lymphadenopathy**, the rash typically spreads **cephalocaudally** (face to body) and the fever is usually **low-grade** or absent, not a high fever preceding the rash by several days.
- The severity of the initial fever, leading to a seizure, is more suggestive of roseola than rubella.
Common childhood exanthems US Medical PG Question 6: A 4-year-old boy is brought to the clinic by his mother with fever and a rash. The patient’s mother says his symptoms started 1 week ago with the acute onset of fever and a runny nose, which resolved over the next 3 days. Then, 4 days later, she noted a rash on his face, which, after a day, spread to his neck, torso, and extremities. The patient denies any pruritus or pain associated with the rash. No recent history of sore throat, chills, or upper respiratory infection. The patient has no significant past medical history and takes no medications. The vital signs include: temperature 37.2°C (99.9°F) and pulse 88/min. On physical examination, there is a maculopapular rash on his face, torso, and extremities, which spares the palms and soles. The appearance of the rash is shown in the exhibit (see image below). Which of the following would most likely confirm the diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Assay for IgM and IgG against measles virus
- B. Serology for human herpesvirus-6 IgM antibodies
- C. Throat culture
- D. ELISA for parvovirus B-19 IgM and IgG antibodies (Correct Answer)
- E. ELISA for IgM antibodies against Rubella virus
Common childhood exanthems Explanation: ***ELISA for parvovirus B-19 IgM and IgG antibodies***
- The presentation of a child with a prodrome of fever and runny nose followed a few days later by a **maculopapular rash** that started on the face and spread to the torso and extremities, sparing the palms and soles, is highly suggestive of **Erythema Infectiosum** (Fifth Disease) caused by **Parvovirus B19**.
- An **ELISA for parvovirus B-19 IgM antibodies**, indicating a recent infection, would confirm the diagnosis, with IgG antibodies suggesting past exposure and immunity.
*Assay for IgM and IgG against measles virus*
- Measles (Rubeola) typically presents with a prodrome of **cough, coryza, conjunctivitis, and Koplik spots** before the rash appears, which are not described in this patient.
- The rash of measles is usually **more confluent** and starts behind the ears, spreading downwards, and is often accompanied by a higher fever.
*Serology for human herpesvirus-6 IgM antibodies*
- Human herpesvirus-6 (HHV-6) causes **Roseola Infantum** (Sixth Disease), which is characterized by a **high fever** for 3-5 days that resolves abruptly, followed by the appearance of a **rose-colored maculopapular rash** on the trunk that spreads to the extremities.
- Though there is a rash after fever, the rash in this patient started on the face and the fever was mild, which is atypical for Roseola.
*ELISA for IgG antibodies against Rubella virus*
- A positive IgM antibody test would suggest an acute infection with Rubella (German Measles), which presents with a rash that often starts on the face and spreads downwards, similar to this case.
- However, Rubella is typically associated with **posterior auricular and suboccipital lymphadenopathy**, which is not mentioned in the patient's history or physical exam.
*Throat culture*
- A throat culture is primarily used to diagnose **bacterial infections** like Streptococcus pyogenes (strep throat), which can cause a rash such as scarlet fever.
- The rash of scarlet fever characteristically feels like sandpaper and is associated with a "strawberry tongue" and perioral pallor, which are not seen here.
Common childhood exanthems US Medical PG Question 7: An 8-year-old boy presents with recurrent infections including multiple episodes of pneumonia and diarrhea. He reports difficulty seeing in the dark. Physical examination reveals white patches on the sclera and conjunctival dryness. What is the most likely cause of these findings?
- A. Congenital rubella
- B. Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) type 1
- C. Deficiency of vitamin A (Correct Answer)
- D. Autoimmune neutropenia
- E. Vitamin B1 deficiency
Common childhood exanthems Explanation: ***Deficiency of vitamin A***
- The combination of **recurrent infections** (pneumonia, diarrhea), **night blindness**, and **ocular signs** like white patches on the sclera (Bitot's spots due to keratinized epithelium) and conjunctival dryness (xerophthalmia) are classic manifestations of **vitamin A deficiency**.
- Vitamin A is crucial for **immune function**, **vision** (a component of rhodopsin), and the **maintenance of epithelial tissues**.
*Congenital rubella*
- This typically presents with a **triad of cataracts**, **heart defects** (e.g., patent ductus arteriosus), and **sensorineural hearing loss**, often detected earlier in infancy.
- It does not explain the recurrent infections, night blindness, or specific ocular epithelial changes described.
*Spinocerebellar ataxia (SCA) type 1*
- This is a **neurodegenerative disorder** primarily affecting coordination and balance, leading to progressive **ataxia**.
- It does not cause recurrent infections, night blindness, or xerophthalmia; its symptoms are distinct and neurological in nature.
*Autoimmune neutropenia*
- Primarily causes **recurrent bacterial infections** due to low neutrophil counts.
- It does not explain the night blindness, diarrhea, or the specific ocular findings of keratinization.
*Vitamin B1 deficiency*
- Also known as **thiamine deficiency**, it leads to **beriberi**, characterized by cardiac (wet beriberi) or neurological (dry beriberi) symptoms.
- Common symptoms include **peripheral neuropathy**, **heart failure**, and **Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome**, none of which are descriptive of this patient's presentation.
Common childhood exanthems US Medical PG Question 8: A previously healthy 5-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of increasing weakness and a retroauricular rash that started 2 days ago. The rash spread rapidly and involves the trunk and extremities. Last week, he had a mild sore throat, pink eyes, and a headache. His family recently immigrated from Ethiopia. His immunization status is unknown. The patient appears severely ill. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F). Examination shows tender postauricular and suboccipital lymphadenopathy. There is a nonconfluent, maculopapular rash over the torso and extremities. Infection with which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Togavirus (Correct Answer)
- B. Human herpesvirus 6
- C. Parvovirus
- D. Varicella zoster virus
- E. Paramyxovirus
Common childhood exanthems Explanation: ***Togavirus***
- This patient's presentation is classic for **rubella** (German measles), caused by the **rubella virus**, a **togavirus**.
- The hallmark clinical finding is **tender postauricular and suboccipital lymphadenopathy**, which appears before the rash and is pathognomonic for rubella.
- The **maculopapular rash** begins on the face (retroauricular region) and spreads cephalocaudally to the trunk and extremities over 2-3 days.
- The prodrome includes **mild symptoms** (low-grade fever, sore throat, mild conjunctivitis, headache), which is characteristic of rubella.
- The patient's **unknown immunization status** and immigration from a region with lower vaccination coverage increases the likelihood of rubella infection.
*Paramyxovirus*
- **Measles virus** is a paramyxovirus that causes rubeola, but the clinical presentation differs significantly from this case.
- Measles typically presents with the **"3 Cs"**: severe **cough**, **coryza** (profuse nasal discharge), and **conjunctivitis** (more prominent than rubella).
- **Koplik spots** (white spots on buccal mucosa) are pathognomonic for measles and appear before the rash.
- Measles causes **higher fever** (often >40°C) and more severe systemic illness than described here.
- While measles can have lymphadenopathy, the **prominent postauricular and suboccipital nodes are characteristic of rubella, not measles**.
*Human herpesvirus 6*
- **HHV-6** causes **roseola infantum** (exanthem subitum), typically in infants 6-24 months old.
- The classic presentation is **high fever for 3-5 days** that suddenly resolves, followed immediately by a rash (**"fever then rash"**).
- This patient had prodromal symptoms followed by rash while still febrile, which does not fit roseola.
- Roseola does not cause significant lymphadenopathy or conjunctivitis.
*Parvovirus*
- **Parvovirus B19** causes **erythema infectiosum** (fifth disease), characterized by a **"slapped cheek"** facial erythema followed by a reticular (lacy) rash on the trunk and extremities.
- The rash pattern and prominent lymphadenopathy in this case are not consistent with fifth disease.
- Fifth disease typically causes mild or no fever and lacks the retroauricular distribution seen here.
*Varicella zoster virus*
- **VZV** causes **chickenpox**, which presents with a **pruritic, vesicular rash** that appears in successive crops and progresses through stages (macule → papule → vesicle → crust).
- This patient has a **maculopapular, nonconfluent rash** without vesicles, which is inconsistent with chickenpox.
- Chickenpox does not typically cause prominent postauricular lymphadenopathy.
Common childhood exanthems US Medical PG Question 9: A 10-year-old girl with a rash is brought to the clinic by her mother. The patient’s mother says that the onset of the rash occurred 2 days ago. The rash was itchy, red, and initially localized to the cheeks with circumoral pallor, and it gradually spread to the arms and trunk. The patient’s mother also says her daughter had been reporting a high fever of 39.4°C (102.9°F), headaches, myalgia, and flu-like symptoms about a week ago, which resolved in 2 days with acetaminophen. The patient has no significant past medical history. Her vital signs include: temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), pulse 90/min, blood pressure 125/85 mm Hg, respiratory rate 20/min. Physical examination shows a symmetric erythematous maculopapular rash on both cheeks with circumoral pallor, which extends to the patient’s trunk, arms, and buttocks. The remainder of the exam is unremarkable. Laboratory findings are significant for a leukocyte count of 7,100/mm3 and platelet count of 325,000/mm3. Which of the following is the next best step in the management of this patient?
- A. Administer intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)
- B. Discharge home, saying that the patient may return to school after the disappearance of the rash
- C. Transfuse with whole blood
- D. Discharge home with instructions for strict isolation from pregnant women until disappearance of the rash
- E. Discharge home, saying that the patient may immediately return to school (Correct Answer)
Common childhood exanthems Explanation: ***Discharge home, saying that the patient may immediately return to school***
- This patient likely has **Fifth Disease (Erythema Infectiosum)**, caused by **Parvovirus B19**, characterized by a **"slapped cheek" rash** and a **lacy, reticular rash** on the trunk and extremities.
- Patients with Fifth Disease are **contagious before the rash appears** and are generally **no longer contagious once the rash develops**, making immediate return to school safe.
*Administer intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)*
- **IVIG** is typically reserved for **severe cases of Parvovirus B19 infection** in immunocompromised individuals or those with chronic hemolytic anemias who develop **aplastic crisis**.
- The patient's symptoms are mild and self-limiting, without evidence of severe complications like aplastic anemia (normal leukocyte and platelet counts).
*Discharge home, saying that the patient may return to school after the disappearance of the rash*
- This advice is incorrect because the patient is **no longer contagious once the rash erupts**.
- Requiring isolation until the rash disappears would be unnecessarily disruptive and is not medically indicated for Fifth Disease.
*Transfuse with whole blood*
- **Whole blood transfusion** is not indicated for uncomplicated Fifth Disease, as it can cause significant complications.
- Transfusions are considered only in cases of **severe aplastic crisis** with significant anemia, which is not present in this patient (normal complete blood count).
*Discharge home with instructions for strict isolation from pregnant women until disappearance of the rash*
- While exposure to **Parvovirus B19 in pregnant women** can lead to significant fetal complications (e.g., hydrops fetalis), the patient is **no longer infectious once the rash appears**.
- Therefore, strict isolation from pregnant women **after rash onset** is not necessary, as the risk of transmission has passed.
Common childhood exanthems US Medical PG Question 10: A 9-year-old male presents to your office with an indurated rash on his face. You diagnose erythema infectiosum. Which of the following is characteristic of the virus causing this patient's disease?
- A. Enveloped virus with single-stranded RNA
- B. Non-enveloped virus with single-stranded DNA (Correct Answer)
- C. Non-enveloped virus with double-stranded DNA
- D. Enveloped virus with single-stranded DNA
- E. Enveloped virus with double-stranded DNA
Common childhood exanthems Explanation: ***Non-enveloped virus with single-stranded DNA***
- Erythema infectiosum (fifth disease) is caused by **Parvovirus B19**, which is a **non-enveloped virus** with a **single-stranded DNA** genome.
- Its unique genomic structure makes it distinct from many other common human viruses.
*Enveloped virus with single-stranded RNA*
- This description typically applies to viruses like **influenza virus** or **measles virus**, which are not the cause of erythema infectiosum.
- The presence of an **envelope** and an **RNA genome** differentiates them from parvoviruses.
*Non-enveloped virus with double-stranded DNA*
- Viruses such as **adenoviruses** and some **papillomaviruses** fit this description, but they cause different clinical syndromes.
- Parvovirus B19 specifically has a **single-stranded DNA** genome.
*Enveloped virus with single-stranded DNA*
- This is a rare combination for human viruses, as most DNA viruses are **double-stranded** and many enveloped viruses are **RNA viruses**.
- No major human pathogen causing erythema infectiosum fits this description.
*Enveloped virus with double-stranded DNA*
- This describes viruses like **herpesviruses** or **hepadnaviruses**, which cause diseases such as cold sores or hepatitis, respectively.
- These are distinct in both their **envelope** and **DNA structure** from Parvovirus B19.
More Common childhood exanthems US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.