Precocious puberty US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Precocious puberty. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Precocious puberty US Medical PG Question 1: A 6-year-old girl is brought to the pediatrician by her father for an annual physical examination. The father reports that the patient is a happy and healthy child, but he sometimes worries about her weight. He says that she is a “picky” eater and only wants chicken nuggets and French fries. He also notes some mild acne on her cheeks and forehead but thinks it’s because she “doesn’t like baths.” The father says she has met all her pediatric milestones. She has recently started kindergarten, can tell time, and is beginning to read. Her teacher says she gets along with her classmates well. The patient was born at 38 weeks gestation. She has no chronic medical conditions and takes only a multivitamin. Height and weight are above the 95th percentile. Physical examination reveals scattered comedones on the patient’s forehead and bilateral cheeks. There is palpable breast tissue bilaterally with raised and enlarged areolae. Scant axillary hair and coarse pubic hair are also noted. A radiograph of the left hand shows a bone age of 9 years. Serum follicular stimulating hormone (FSH) level is 9.6 mU/mL (normal range 0.7-5.3 mU/mL) and luteinizing hormone (LH) level is 6.4 mU/mL (normal range < 0.26 mU/mL). Which of the following is the most appropriate diagnostic test?
- A. Pelvic ultrasound
- B. Estrogen levels
- C. 17-hydroxyprogesterone levels
- D. Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate levels
- E. Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) (Correct Answer)
Precocious puberty Explanation: ***Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)***
- The constellation of **precocious puberty** (breast development, pubic and axillary hair, advanced bone age) and **elevated FSH and LH levels** in a 6-year-old girl indicates central precocious puberty, which is often caused by a CNS lesion.
- **Brain MRI is the gold standard imaging** to rule out **hypothalamic hamartomas**, **gliomas**, **craniopharyngiomas**, or other structural abnormalities of the **hypothalamic-pituitary axis**.
- MRI provides superior soft tissue resolution without radiation exposure, making it the preferred modality in children.
*Pelvic ultrasound*
- A pelvic ultrasound is primarily used to evaluate **gonadal tumors** or cysts in cases of **peripheral precocious puberty**, where FSH and LH levels would be suppressed.
- Given the elevated FSH and LH, the puberty is central (gonadotropin-dependent), making CNS imaging more appropriate than ovarian imaging.
*Estrogen levels*
- While estrogen levels would certainly be elevated in this patient, measuring them would confirm sexual precocity but would not differentiate between **central** and **peripheral precocious puberty**.
- The **elevated FSH and LH levels** already indicate active gonadal stimulation, making direct estrogen measurement less informative for pinpointing the etiology.
*17-hydroxyprogesterone levels*
- Elevated 17-hydroxyprogesterone levels are indicative of **congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)**, particularly the 21-hydroxylase deficiency.
- CAH typically causes signs of **virilization** (e.g., clitoromegaly) but not breast development, and would not cause elevated FSH and LH levels.
*Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate levels*
- Elevated DHEAS levels suggest an **adrenal source of androgens**, which could contribute to **pubic and axillary hair growth** (adrenarche).
- However, DHEAS elevation alone would not explain the **breast development** and **elevated gonadotropins**, which point towards central precocious puberty.
Precocious puberty US Medical PG Question 2: A 6-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother who is concerned about his early sexual development. He has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. He is at the 99th percentile for height and 70th percentile for weight. His blood pressure is 115/78 mm Hg. Examination shows greasy facial skin and cystic acne on his forehead and back. There is coarse axillary and pubic hair. Serum studies show:
Cortisol (0800 h) 4 μg/dL
Deoxycorticosterone 2.5 ng/dL (N = 3.5–11.5)
Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate 468 mcg/dL (N = 29–412)
Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Deficiency of 21β-hydroxylase (Correct Answer)
- B. Idiopathic overproduction of GnRH
- C. Constitutive activation of adenylyl cyclase
- D. Deficiency of 11β-hydroxylase
- E. Deficiency of 17α-hydroxylase
Precocious puberty Explanation: ***Deficiency of 21β-hydroxylase***
- The combination of **precocious puberty** (early sexual development, acne, coarse hair), elevated **DHEA-S**, and low **cortisol** with **low-normal DOC** confirms 21β-hydroxylase deficiency, causing **congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)**.
- This enzyme deficiency blocks cortisol and aldosterone synthesis, shunting precursors towards **androgen production**, causing **adrenal androgen excess** and virilization.
- The **low DOC level (2.5 ng/dL, below normal 3.5-11.5)** is the key finding that distinguishes this from 11β-hydroxylase deficiency.
- The mild hypertension may be due to increased androgen-mediated effects or represents an atypical presentation.
*Idiopathic overproduction of GnRH*
- This would cause **central precocious puberty**, characterized by activation of the **hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis** (HPGA).
- While it causes precocious puberty, it would not typically lead to isolated elevation of **adrenal androgens** like DHEA-S with concurrent low cortisol, which points to an adrenal rather than central cause.
- Laboratory findings would show elevated LH, FSH, and gonadal sex steroids rather than adrenal androgens.
*Constitutive activation of adenylyl cyclase*
- This is linked to conditions like **McCune-Albright syndrome**, which can cause peripheral precocious puberty but typically presents with the classic triad: **café-au-lait spots**, **fibrous dysplasia of bone**, and **autonomous endocrine hyperfunction**.
- The hormonal profile reflects the specific endocrine gland involved (often gonadal), not the pattern of **adrenal androgen excess** with low cortisol and low DOC seen here.
*Deficiency of 11β-hydroxylase*
- This is the second most common cause of CAH and also causes adrenal androgen excess leading to virilization and precocious puberty.
- However, 11β-hydroxylase deficiency results in **accumulation of deoxycorticosterone (DOC)**, which causes **hypertension** and **hypokalemia**.
- This patient's **DOC is LOW (2.5 ng/dL, below normal range 3.5-11.5)**, which definitively rules out this diagnosis despite the presence of hypertension.
*Deficiency of 17α-hydroxylase*
- This deficiency impairs synthesis of **cortisol** and **sex steroids**, but increases production of mineralocorticoids (DOC and corticosterone).
- Patients present with **hypertension**, **hypokalemia**, sexual infantilism, and in XY individuals, **female external genitalia** due to lack of androgens.
- This is the opposite of the **virilization and elevated DHEA-S** seen in this patient.
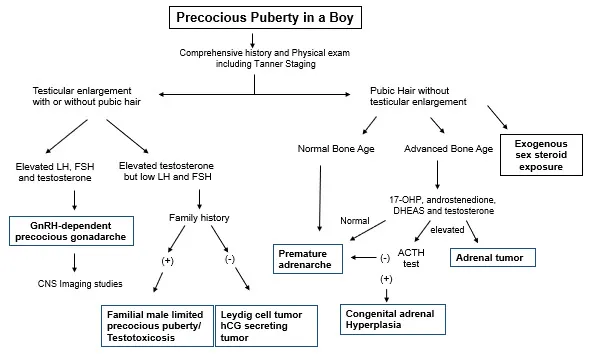
Precocious puberty US Medical PG Question 3: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the physician because his parents are concerned about his early sexual development. He has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. His brother was diagnosed with testicular cancer 5 years ago and underwent a radical orchiectomy. The patient is at the 85th percentile for height and 70th percentile for weight. Examination shows greasy facial skin. There is coarse axillary hair. Pubic hair development is at Tanner stage 3 and testicular development is at Tanner stage 2. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. An x-ray of the wrist shows a bone age of 10 years. Basal serum luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone are elevated. An MRI of the brain shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Leuprolide therapy (Correct Answer)
- B. Testicular ultrasound
- C. Cortisol supplementation
- D. Radiation therapy
- E. Observation
Precocious puberty Explanation: ***Leuprolide therapy***
- This patient presents with **central precocious puberty** (CPP), indicated by elevated **basal LH and FSH levels** in the context of advanced bone age, Tanner stage 3 pubic hair, and Tanner stage 2 testicular development at a young age.
- **Leuprolide** is a GnRH analog that, when given continuously, downregulates the pituitary's GnRH receptors, suppressing gonadotropin release and halting pubertal progression. This is the appropriate treatment for CPP.
*Testicular ultrasound*
- While useful for evaluating testicular size and consistency, it is typically performed when there is suspicion of **peripheral precocious puberty** (e.g., Leydig cell tumor) with low LH/FSH or significant testicular asymmetry, which is not the primary presentation here.
- The elevated basal LH and FSH values indicate a **central origin** of puberty, making a testicular ultrasound less immediately relevant as a *next step* compared to directly addressing the central hormonal drive.
*Cortisol supplementation*
- This would be indicated for conditions causing **adrenal insufficiency**, such as **congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)** with salt-wasting or Addison's disease.
- CAH typically presents with virilization and advanced bone age but would show **low LH/FSH** (due to peripheral androgen excess) and elevated adrenal androgens (e.g., DHEA-S, 17-hydroxyprogesterone), which are not described.
*Radiation therapy*
- This is a treatment for **malignant tumors**, often used in cases of brain tumors.
- The MRI of the brain showed **no abnormalities**, ruling out a pituitary or hypothalamic tumor as the cause of CPP in this case, thus making radiation therapy inappropriate.
*Observation*
- **Observation** alone is inappropriate given the significant **advancement of bone age** (10 years in a 7-year-old) and clear signs of central precocious puberty.
- Untreated CPP can lead to **compromised adult height potential** due to premature epiphyseal fusion and psychosocial issues, necessitating intervention.
Precocious puberty US Medical PG Question 4: A 7-year-old girl is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. She is at 95th percentile for height and 70th percentile for weight. Examination shows elevated breast buds that extend beyond the areola. Coarse pubic and axillary hair is present. The external genitalia appear normal. An x-ray of the left wrist shows a bone age of 10 years. Serum luteinizing hormone levels do not increase following GnRH agonist stimulation. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
- A. Ovarian fibroma
- B. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- C. Hypothalamic glioma
- D. Granulosa cell tumor
- E. McCune-Albright syndrome (Correct Answer)
Precocious puberty Explanation: ***McCune-Albright syndrome***
- This syndrome is characterized by the classic triad of **peripheral precocious puberty**, **café-au-lait spots**, and **polyostotic fibrous dysplasia**.
- The key diagnostic finding is **lack of LH response to GnRH agonist stimulation**, indicating **peripheral (GnRH-independent) precocious puberty** caused by activating mutations in the GNAS1 gene, leading to autonomous ovarian estrogen production.
- The presentation of **isolated peripheral precocious puberty** with breast development, pubic/axillary hair, and advanced bone age (10 years in a 7-year-old) in the absence of a palpable ovarian mass is most consistent with McCune-Albright syndrome.
- While café-au-lait spots and fibrous dysplasia are not mentioned in the stem, **not all features of the triad need to be present simultaneously**, and precocious puberty may be the presenting feature.
*Ovarian fibroma*
- Ovarian fibromas are **non-functional benign tumors** that do not produce hormones and therefore do not cause precocious puberty or estrogenic effects.
- They typically occur in older women and present with pelvic symptoms or as incidental findings, not with endocrine abnormalities.
*Congenital adrenal hyperplasia*
- CAH causes excessive **androgen production**, leading to **virilization** (clitoromegaly, hirsutism, acne) rather than estrogenic effects.
- While CAH can cause pubic/axillary hair and advanced bone age, it would **not cause breast development** and would typically present with **ambiguous genitalia or clitoromegaly**, which are absent in this patient.
*Hypothalamic glioma*
- Hypothalamic lesions cause **central (GnRH-dependent) precocious puberty** by premature activation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis.
- In central precocious puberty, there would be a **robust increase in LH levels** following GnRH agonist administration, which is **not seen in this patient**.
- The lack of LH response rules out any central cause of precocious puberty.
*Granulosa cell tumor*
- Granulosa cell tumors are **estrogen-secreting ovarian tumors** that can cause peripheral precocious puberty with breast development and advanced bone age.
- However, these tumors typically present as a **palpable pelvic or abdominal mass** on examination, which is not described in this case.
- They are also extremely rare in prepubertal girls and would more commonly be detected on imaging or physical exam before causing advanced pubertal changes.
Precocious puberty US Medical PG Question 5: A 16-year-old female presents to her pediatrician’s office because she has not yet started menstruating. On review of systems, she states that she has been increasingly tired, constipated, and cold over the last 6 months. She also endorses a long history of migraines with aura that have increased in frequency over the last year. She complains that these symptoms have affected her performance on the track team. She states that she is not sexually active. Her mother and sister both underwent menarche at age 15. The patient is 5 feet, 4 inches tall and weighs 100 pounds (BMI 17.2 kg/m^2). Temperature is 98.4°F (36.9°C), blood pressure is 98/59 mmHg, pulse is 98/min, and respirations are 14/min. On exam, the patient appears pale and has thinning hair. She has Tanner stage IV breasts and Tanner stage III pubic hair. Which of the following would be most useful in determining this patient’s diagnosis?
- A. TSH level (Correct Answer)
- B. GnRH level
- C. FSH and estrogen levels
- D. Prolactin level
- E. Pelvic exam
Precocious puberty Explanation: ***TSH level***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of **hypothyroidism**, including fatigue, constipation, cold intolerance, and potentially **menstrual irregularities** (primary amenorrhea).
- An elevated **TSH** would confirm primary hypothyroidism, which can cause delayed puberty and amenorrhea by affecting the **hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis**.
*GnRH level*
- **GnRH levels** are pulsatile and difficult to measure accurately; they are not a standard diagnostic test for primary amenorrhea.
- Evaluation of the **hypothalamic-pituitary axis** typically involves assessing downstream hormones like LH and FSH.
*FSH and estrogen levels*
- While important for evaluating primary amenorrhea, **FSH and estrogen levels** would primarily help differentiate between ovarian (**hypergonadotropic hypogonadism**) and central (**hypogonadotropic hypogonadism**) causes.
- However, given the systemic symptoms suggestive of hypothyroidism, evaluating TSH is a more immediate and likely diagnostic step.
*Prolactin level*
- An elevated **prolactin level** could cause amenorrhea by suppressing GnRH, but the patient's other symptoms (fatigue, constipation, cold intolerance) are not typical of hyperprolactinemia.
- While useful in some cases of amenorrhea, it's less likely to be the primary cause of this patient's constellation of symptoms.
*Pelvic exam*
- A **pelvic exam** would assess for anatomical abnormalities of the reproductive tract, such as imperforate hymen or vaginal agenesis, which can cause primary amenorrhea.
- However, the patient's systemic symptoms strongly suggest an endocrine disorder rather than an anatomical issue.
Precocious puberty US Medical PG Question 6: A 7-year-old girl is brought to the physician because of vaginal bleeding for 2 days. There is no personal or family history of serious illness. She is at the 95th percentile for height and at the 90th percentile for weight. Examination shows enlarged breasts, and the areola and papilla have formed a secondary mound. There is coarse pubic hair that does not extend to the inner thigh. The remainder of the examination show no abnormalities. An x-ray of the left hand and wrist shows a bone age of 11 years. Her serum luteinizing hormone concentration is 0.1 mIU/mL (N < 0.2 mIU/mL). Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Serum dehydroepiandrosterone level
- B. Reassurance and follow-up
- C. Ultrasound of the pelvis
- D. GnRH stimulation test (Correct Answer)
- E. MRI of the brain
Precocious puberty Explanation: ***GnRH stimulation test***
- This patient presents with signs of **precocious puberty** (vaginal bleeding, enlarged breasts, pubic hair, advanced bone age) but a **low basal LH level**. A **GnRH stimulation test** is crucial to differentiate between **central (gonadotropin-dependent)** and **peripheral (gonadotropin-independent)** precocious puberty.
- A significant rise in LH after GnRH administration indicates **central precocious puberty**, while a lack of significant response suggests **peripheral precocious puberty**.
*Serum dehydroepiandrosterone level*
- **DHEA** is a precursor to androgens and its elevation might indicate **adrenal causes** of precocious puberty (e.g., congenital adrenal hyperplasia, adrenal tumor).
- However, the prominent signs of **breast development** and **vaginal bleeding** point more towards estrogen production, making a GnRH stimulation test a more direct and comprehensive initial step to evaluate the source of puberty.
*Reassurance and follow-up*
- Reassurance is inappropriate given the presence of **vaginal bleeding** and signs of **accelerated skeletal maturation** (bone age of 11 years at chronological age 7).
- These findings warrant further investigation to determine the underlying cause and initiate appropriate management to prevent complications like **compromised adult height**.
*Ultrasound of the pelvis*
- A **pelvic ultrasound** would be useful to evaluate for ovarian cysts or tumors, which can cause **peripheral precocious puberty**.
- However, the GnRH stimulation test is a **more critical first step** to determine whether the puberty is central or peripheral before focusing on specific peripheral etiologies.
*MRI of the brain*
- An **MRI of the brain** is indicated if **central precocious puberty** is confirmed by the GnRH stimulation test, especially in a young child, to rule out **hypothalamic or pituitary tumors** or other CNS lesions.
- Doing an MRI of the brain before establishing the type of precocious puberty (central vs. peripheral) is **premature** as it is only indicated for central causes.
Precocious puberty US Medical PG Question 7: A 3-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents for complaints of breast development and pubic hair growth for the past 6 months. She has no significant birth or medical history. The temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), the pulse is 88/min, and the respirations are 20/min. Physical examination shows enlarged breasts at Tanner stage 3 and pubic hair at stage 2. Height and weight are in the normal range. On GnRH stimulation testing, a luteinizing hormone (LH) response of < 5 IU/L is detected. What is the most appropriate next step in diagnosis?
- A. Perform leuprolide stimulation test to measure testosterone
- B. Measure baseline estradiol levels and perform pelvic ultrasound (Correct Answer)
- C. Measure FSH levels to evaluate pituitary function
- D. Calculate LH:FSH ratio from previous GnRH test
- E. Repeat GnRH stimulation test to confirm LH response
Precocious puberty Explanation: ***Measure baseline estradiol levels and perform pelvic ultrasound***
- This patient presents with **precocious puberty** (breast development and pubic hair at age 3). The **low LH response** (<5 IU/L) to GnRH stimulation confirms **peripheral (gonadotropin-independent) precocious puberty**.
- In peripheral precocious puberty, sex hormones are produced **autonomously** (independent of pituitary control), which **suppresses** the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis through negative feedback.
- The next step is to **identify the source** of autonomous sex hormone production. **Measuring estradiol levels** confirms elevated estrogen, and **pelvic ultrasound** evaluates for ovarian causes such as **ovarian cysts** or **tumors** (e.g., granulosa cell tumor), which are common causes of peripheral precocious puberty in girls.
- Other causes to consider include **McCune-Albright syndrome** (café-au-lait spots, polyostotic fibrous dysplasia) or exogenous estrogen exposure.
*Measure FSH levels to evaluate pituitary function*
- Measuring FSH is **not helpful** in this clinical context because the low LH response to GnRH stimulation **already indicates** that the pituitary is suppressed.
- In peripheral precocious puberty, both LH and FSH are **suppressed** due to negative feedback from peripherally produced sex hormones. Measuring FSH would simply confirm what we already know - that the pituitary axis is not activated.
- The priority is to find the **source** of the sex hormones, not to further characterize pituitary suppression.
*Perform leuprolide stimulation test to measure testosterone*
- Leuprolide is a **GnRH agonist** used to evaluate **central precocious puberty**, where the HPG axis is prematurely activated.
- This test is **not indicated** for peripheral precocious puberty, which has already been confirmed by the low LH response.
- Additionally, measuring testosterone would not be useful in a female patient presenting with estrogenic signs (breast development).
*Calculate LH:FSH ratio from previous GnRH test*
- The **LH:FSH ratio** is useful in diagnosing **central precocious puberty**, where an LH-predominant response (LH:FSH ratio >0.6-1.0) is characteristic.
- Since the LH response is already **low** (<5 IU/L), confirming peripheral precocious puberty, this ratio would not provide diagnostic value.
- The focus should be on investigating the **peripheral source** of sex hormones.
*Repeat GnRH stimulation test to confirm LH response*
- Repeating the GnRH stimulation test is **unnecessary** when the initial test provides clear results.
- The low LH response (<5 IU/L) definitively indicates peripheral precocious puberty, and repeating the test would only delay appropriate diagnostic workup for the underlying cause.
Precocious puberty US Medical PG Question 8: An 8-year-old boy is brought to the hospital because of blurred vision and headache for 3 months. During this period, the father has noticed that the child has been tilting his head back to look straight ahead. The patient has also had difficulty falling asleep for 2 months. He has had a 3.5 kg (7.7 lb) weight loss over the past 6 months. His temperature is 37.7°C (99.8°F), pulse is 105/min, and blood pressure is 104/62 mm Hg. Examination shows equal pupils that are not reactive to light. The pupils constrict when an object is brought near the eye. His upward gaze is impaired; there is nystagmus and eyelid retraction while attempting to look upwards. Neurologic examination shows no other focal findings. Which of the following is the most likely sequela of this patient's condition?
- A. Diabetes insipidus
- B. Blindness
- C. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- D. Diabetic ketoacidosis
- E. Precocious puberty (Correct Answer)
Precocious puberty Explanation: ***Precocious puberty***
- The constellation of **Parinaud syndrome** (impaired upward gaze, nystagmus, eyelid retraction, and pupillary abnormalities) combined with symptoms of **increased intracranial pressure** (headache, blurred vision, weight loss, difficulty sleeping) in a child points to a **pineal tumor**, specifically a **germinoma**.
- Pineal germinomas are known to secrete **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)**, which can cross-react with LH receptors, leading to stimulation of **testosterone production** and subsequent **precocious puberty** in boys.
*Diabetes insipidus*
- While diabetes insipidus can be associated with suprasellar tumors, it's less commonly a direct sequela of a **pineal germinoma** itself compared to precocious puberty, although mass effect on the hypothalamus could potentially lead to it.
- The primary symptoms described are classic for **Parinaud syndrome** and increased intracranial pressure, not specific signs of diabetes insipidus (e.g., polyuria, polydipsia).
*Blindness*
- **Vision loss or blindness** can occur due to long-standing **papilledema** from increased intracranial pressure, or direct compression of the **optic chiasm** or **optic nerves** by a large tumor.
- While a possible serious complication, **precocious puberty** is a more specific and direct endocrinological sequela linked to the hormonal activity of a pineal germinoma in boys.
*Subarachnoid hemorrhage*
- Although any intracranial tumor can potentially bleed, a **subarachnoid hemorrhage** typically presents with a sudden onset of **"thunderclap" headache**, stiff neck, and altered consciousness.
- The patient's symptoms have been evolving over 3 months, which is inconsistent with the acute presentation of a subarachnoid hemorrhage.
*Diabetic ketoacidosis*
- **Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA)** is a severe complication of **type 1 diabetes mellitus**, characterized by hyperglycemia, metabolic acidosis, and ketonemia.
- There are no clinical signs or symptoms in this presentation (e.g., polyuria, polydipsia, Kussmaul respirations, fruity breath) to suggest uncontrolled diabetes or DKA, and it is not a direct sequela of a pineal tumor.
Precocious puberty US Medical PG Question 9: An 11-year-old girl presents to the pediatrician with her mother, who is concerned about her sexual development. She mentions that she herself experienced the onset of menses at the age of 10.5 years, while her daughter has still not had a menstrual period. However, she is otherwise a healthy girl with no significant medical problems since birth. On physical examination, her vital signs are stable. Evaluation of breast and pubic hair are Tanner stage 2. The pediatrician reassures the mother that her daughter's sexual development is within the normal range for girls and there is nothing to worry about at present. Which is a sign of Tanner stage 2?
- A. Pubarche
- B. Adrenarche
- C. Menarche
- D. Thelarche (Correct Answer)
- E. Coarse pubic hair
Precocious puberty Explanation: ***Thelarche***
- **Thelarche** refers to the initial development of breast buds, which is the defining characteristic of **Tanner stage 2** breast development.
- This stage indicates the beginning of puberty, marked by a slight elevation of the breast and papilla, forming a small mound.
*Pubarche*
- **Pubarche** refers to the appearance of **pubic hair**, which is typically seen in **Tanner stage 2** for pubic hair development, but not breast development.
- While girls often experience pubarche around the same time as thelarche, the term specifically describes pubic hair growth, not breast development.
*Adrenarche*
- **Adrenarche** is the maturation of the adrenal cortex, leading to increased production of adrenal androgens and typically precedes the physical changes of puberty.
- It refers to the biochemical process of adrenal androgen secretion, not a specific physical sign of **Tanner stage 2** development.
*Menarche*
- **Menarche** is the first menstrual period, which occurs much later in puberty, typically after a significant progression through **Tanner stages 2-4**.
- This event signifies reproductive maturity and is not present at the initial stage of breast budding.
*Coarse pubic hair*
- The presence of **coarse pubic hair** indicates a more advanced stage of pubic hair development, typically **Tanner stage 3 or 4**, as hair becomes darker and coarser.
- **Tanner stage 2** pubic hair is usually sparse, long, straight, and lightly pigmented.
Precocious puberty US Medical PG Question 10: A laborer's younger child is brought to the OPD with a swollen belly and dull face. He has been fed rice water (rice milk) in his diet mostly. On investigations, the child is found to have low serum protein and low albumin. What is the probable diagnosis?
- A. Kwashiorkor (Correct Answer)
- B. Kawasaki disease
- C. Marasmus
- D. Indian childhood cirrhosis
- E. Nephrotic syndrome
Precocious puberty Explanation: ***Kwashiorkor***
- The symptoms of a **swollen belly** (due to **edema** from low albumin), **dull face**, and a diet primarily of **rice water** (low in protein) are classic signs of Kwashiorkor.
- Kwashiorkor is a form of severe protein-energy malnutrition characterized by **protein deficiency** that is greater than the calorie deficit, leading to **hypoalbuminemia** and fluid retention.
- The **dietary history** of rice water (carbohydrate-rich but protein-poor) is the key distinguishing feature.
*Kawasaki disease*
- This is an **acute vasculitis** primarily affecting young children, presenting with fever, rash, conjunctivitis, mouth changes, and lymphadenopathy.
- It does not involve a swollen belly or dull face as primary symptoms, nor is it linked to dietary protein deficiency.
*Marasmus*
- Marasmus is a form of severe malnutrition characterized by an **overall deficiency of calories** and nutrients, resulting in severe **wasting** of muscle and fat.
- While it involves low weight and energy deficit, the prominent **edema** (swollen belly) seen in this case points away from marasmus.
*Indian childhood cirrhosis*
- This is a rare, **fatal liver disease** in young children, often characterized by jaundice, hepatosplenomegaly, and liver failure.
- It is not primarily caused by protein deficiency and its symptoms are distinct from the presentation described.
*Nephrotic syndrome*
- While nephrotic syndrome also presents with **hypoalbuminemia and edema**, it would show **proteinuria** (>3.5 g/day), hyperlipidemia, and lipiduria on urinalysis.
- The **dietary history** and absence of urinary findings distinguish kwashiorkor from nephrotic syndrome.
More Precocious puberty US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.