Inborn errors of metabolism US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Inborn errors of metabolism. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Inborn errors of metabolism US Medical PG Question 1: A 27-year-old woman gives birth to a boy at 36 weeks gestational age. The infant weighs 4022 grams at birth, is noted to have a malformed sacrum, and appears to be in respiratory distress. Apgar scores are 5 and 7 at 1 minute and 5 minutes respectively. Hours after birth, the infant is found to be irritable, bradycardic, cyanotic, and hypotonic, and the infant's serum is sent to the laboratory for evaluation. Which of the following abnormalities would you expect to observe in this infant?
- A. Hypoinsulinemia
- B. Hypoglycemia (Correct Answer)
- C. Hyperglycemia
- D. Hypermagnesemia
- E. Hypercalcemia
Inborn errors of metabolism Explanation: ***Hypoglycemia***
- The infant is macrosomic (4022g at 36 weeks), indicating potential **maternal diabetes**, which often leads to fetal **hyperinsulinemia** and subsequent rapid glucose consumption after birth.
- Symptoms like irritability, bradycardia, cyanosis, and hypotonia are classic signs of neonatal hypoglycemia due to inadequate glucose supply for metabolic demands.
*Hypoinsulinemia*
- Maternal diabetes typically causes **fetal hyperglycemia**, leading to reactive fetal **hyperinsulinemia** as the fetal pancreas attempts to regulate glucose.
- After birth, the sudden cessation of maternal glucose supply to a hyperinsulinemic infant rapidly leads to hypoglycemia, not hypoinsulinemia.
*Hyperglycemia*
- While the infant experienced hyperglycemia *in utero* due to maternal diabetes, after birth and the separation from the maternal glucose supply, the infant's own hyperinsulinemia would rapidly consume endogenous glucose, leading to **hypoglycemia**.
- Neonatal hyperglycemia is more common in stressed or very low birth weight infants receiving excessive intravenous glucose, which is not described.
*Hypermagnesemia*
- **Hypermagnesemia** in newborns is typically associated with maternal treatment with magnesium sulfate for preeclampsia, which is not mentioned in the clinical scenario.
- Common symptoms include respiratory depression, hypotonia, and decreased reflexes, but **hypoglycemia** is a more direct and expected complication given the infant's macrosomia and maternal diabetes association.
*Hypercalcemia*
- Neonatal **hypercalcemia** is rare and is often associated with genetic conditions like Williams syndrome or idiopathic infantile hypercalcemia.
- Hypoglycemia is a much more common finding in infants of diabetic mothers, and there is no indication for hypercalcemia in this presentation.
Inborn errors of metabolism US Medical PG Question 2: A 10-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department due to vomiting and weakness. He is attending a summer camp and was on a hike with the other kids and a camp counselor. His friends say that the boy skipped breakfast, and the counselor says he forgot to pack snacks for the kids during the hike. The child’s parents are contacted and report that the child has been completely healthy since birth. They also say there is an uncle who would have to eat regularly or he would have similar symptoms. At the hospital, his heart rate is 90/min, respiratory rate is 17/min, blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, and temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F). Physical examination reveals a visibly lethargic child with slight disorientation to time and place. Mild hepatosplenomegaly is observed but no signs of dehydration are noted. A blood sample is drawn, and fluids are started via an intravenous line.
Lab report
Serum glucose 44 mg/dL
Serum ketones absent
Serum creatinine 1.0 mg/dL
Blood urea nitrogen 32 mg/dL
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) 425 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 372 U/L
Hemoglobin (Hb%) 12.5 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) 80 fl
Reticulocyte count 1%
Erythrocyte count 5.1 million/mm3
Which of the following is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (Correct Answer)
- B. α-glucosidase
- C. Glucose-6-phosphatase
- D. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase
- E. Nicotinic acid
Inborn errors of metabolism Explanation: ***Acyl-CoA dehydrogenase***
- This patient presents with **hypoglycemia** (44 mg/dL) and **absent ketone bodies** after prolonged fasting, along with elevated **liver transaminases** and **hepatosplenomegaly**, which are classic signs of a **fatty acid oxidation disorder**.
- A deficiency in **acyl-CoA dehydrogenase**, particularly **medium-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase (MCAD)**, prevents adequate fatty acid breakdown for energy and ketone production, leading to **hypoketotic hypoglycemia** during periods of fasting.
*α-glucosidase*
- A deficiency in **α-glucosidase** (Pompe disease) leads to the accumulation of **glycogen** in lysosomes, primarily affecting muscles, heart, and liver.
- While it can cause hepatomegaly and muscle weakness, it typically presents with **cardiomyopathy** and does not directly cause hypoketotic hypoglycemia.
*Glucose-6-phosphatase*
- A deficiency in **glucose-6-phosphatase** (Von Gierke disease) is a type of **glycogen storage disease** characterized by severe **fasting hypoglycemia with lactic acidosis**, **massive hepatomegaly**, and **hyperlipidemia**.
- Unlike fatty acid oxidation disorders, Von Gierke disease typically presents with **lactic acidosis** as the predominant metabolic derangement, and patients often have a **doll-like face** and **growth retardation** from chronic presentation.
*Acetyl-CoA carboxylase*
- **Acetyl-CoA carboxylase** is a key enzyme in **fatty acid synthesis**, not fatty acid oxidation.
- A deficiency would primarily impair the body's ability to synthesize fatty acids, which is not consistent with the hypoketotic hypoglycemia observed here.
*Nicotinic acid*
- **Nicotinic acid** (niacin or vitamin B3) is a precursor to **NAD+** and **NADP+**, coenzymes involved in various metabolic reactions, including fatty acid synthesis and breakdown.
- While a deficiency (pellagra) can cause dermatitis, diarrhea, and dementia, it does not directly lead to **hypoketotic hypoglycemia** or fatty liver disease.
Inborn errors of metabolism US Medical PG Question 3: A 3-week-old newborn is brought to the pediatrician by his mother. His mother is concerned about her son’s irritability and vomiting, particularly after breastfeeding him. The infant was born at 39 weeks via spontaneous vaginal delivery. His initial physical was benign. Today the newborn appears mildly jaundiced with palpable hepatomegaly, and his eyes appear cloudy, consistent with the development of cataracts. The newborn is also in the lower weight-age percentile. The physician considers a hereditary enzyme deficiency and orders blood work and a urinalysis to confirm his diagnosis. He recommends that milk and foods high in galactose and/or lactose be eliminated from the diet. Which of the following is the most likely deficient enzyme in this metabolic disorder?
- A. Aldose reductase
- B. Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase (Correct Answer)
- C. UDP-galactose-4-epimerase
- D. Galactokinase
- E. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
Inborn errors of metabolism Explanation: ***Galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase***
- The constellation of symptoms including **vomiting**, **irritability**, **jaundice**, **hepatomegaly**, **cataracts**, and **failure to thrive** in a neonate, with improvement upon eliminating galactose/lactose from the diet, is highly characteristic of **classic galactosemia**.
- **Classic galactosemia** is caused by a deficiency in **galactose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase (GALT)**, leading to the accumulation of galactose-1-phosphate, which is toxic to various tissues.
*Aldose reductase*
- This enzyme converts galactose to **galactitol**, which can accumulate in the lens and cause **cataracts** in all forms of galactosemia if left untreated.
- However, isolated aldose reductase deficiency does not explain the full spectrum of severe systemic symptoms like hepatomegaly, jaundice, and failure to thrive observed in this neonate, which are indicative of classic galactosemia.
*UDP-galactose-4-epimerase*
- Deficiency in **UDP-galactose-4-epimerase (GALE)**, also known as epimerase deficiency galactosemia, has a wide range of severity.
- While it can present with similar symptoms to GALT deficiency, its severe form is rarer, and the classic, pronounced presentation described here is more commonly associated with GALT deficiency.
*Galactokinase*
- Deficiency in **galactokinase (GALK)** causes **Type II galactosemia**, which primarily manifests as **cataracts** due to galactitol accumulation.
- It typically does not present with the severe hepatic (jaundice, hepatomegaly) or systemic symptoms (vomiting, failure to thrive) seen in classic galactosemia.
*Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase*
- **Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency** primarily causes **hemolytic anemia** triggered by certain drugs, infections, or fava beans.
- It does not present with the specific constellation of symptoms related to galactose metabolism, such as cataracts, hepatomegaly, and vomiting upon milk ingestion, as described in this case.
Inborn errors of metabolism US Medical PG Question 4: A 2-day-old male is seen in the newborn nursery for repeated emesis and lethargy. He was born at 39 weeks to a 24-year-old mother following an uncomplicated pregnancy and birth. He has been breastfeeding every 2 hours and has 10 wet diapers per day. His father has a history of beta-thalassemia minor. Laboratory results are as follows:
Hemoglobin: 12 g/dL
Platelet count: 200,000/mm³
Mean corpuscular volume: 95 µm³
Reticulocyte count: 0.5%
Leukocyte count: 5,000/mm³ with normal differential
Serum:
Na+: 134 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
K+: 3.3 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen: 1 mg/dL
Creatinine: 0.6 mg/dL
Ammonia: 150 µmol/L (normal: 50-80 µmol/L)
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Phenylketonuria
- B. Orotic aciduria
- C. Alkaptonuria
- D. Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (Correct Answer)
- E. Beta-thalassemia minor
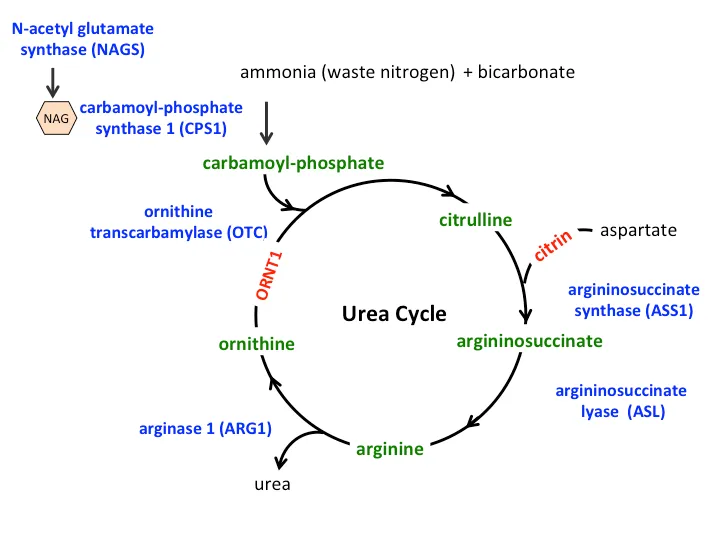
Inborn errors of metabolism Explanation: ***Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency***
- The combination of **lethargy**, vomiting (emesis), and **significantly elevated ammonia levels** in a neonate strongly points to a **urea cycle disorder**, with ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency being the most common.
- This X-linked disorder leads to a buildup of ammonia due to the inability to convert carbamoyl phosphate and ornithine into citrulline, a crucial step in the urea cycle.
*Phenylketonuria*
- Characterized by the inability to metabolize **phenylalanine**, leading to its accumulation and neurological damage if untreated.
- Typically presents with developmental delay, seizures, and a musty odor, not acute hyperammonemia and vomiting in the neonatal period.
*Orotic aciduria*
- A rare metabolic disorder caused by a defect in **pyrimidine synthesis**, leading to accumulation of **orotic acid**.
- Presents with megaloblastic anemia, developmental delay, and failure to thrive, but not typically with severe neonatal hyperammonemia.
*Alkaptonuria*
- An autosomal recessive disorder of **tyrosine metabolism** where homogentisic acid oxidase is deficient, leading to a buildup of **homogentisic acid**.
- Characterized by dark urine when exposed to air, ochronosis (bluish-black pigmentation of cartilage), and early-onset osteoarthritis; it does not cause acute neonatal illness with hyperammonemia.
*Beta-thalassemia minor*
- This is an **inherited blood disorder** causing mild anemia, often asymptomatic, due to reduced or absent beta-globin chain production.
- While the father has this condition, the infant's symptoms of lethargy, vomiting, and hyperammonemia are **not consistent** with beta-thalassemia minor.
Inborn errors of metabolism US Medical PG Question 5: An 8-month-old female infant from a first-degree consanguineous couple was brought to the physician because the mother noticed abnormalities in the growth of her child as well as the different lengths of her child's legs. The infant had gingival hyperplasia, restricted movement in both shoulders, a prominent, pointed forehead, and enophthalmos with a slight opacity in both corneas. A blood test revealed 10 fold higher than normal levels of the following enzymes: N-acetyl-ß-glucosaminidase, ß-glucuronidase, ß-hexosaminidase A, and alkaline phosphatase. Which of the following is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Lysosomal alpha-1,4-glucosidase
- B. Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- C. N-acetyl-glucosamine-1-phosphotransferase (Correct Answer)
- D. Glucocerebrosidase
- E. Alpha-galactosidase A
Inborn errors of metabolism Explanation: ***N-acetyl-glucosamine-1-phosphotransferase***
- The clinical presentation with **gingival hyperplasia**, **restricted joint movement**, **skeletal abnormalities** (growth abnormalities, leg length discrepancy, prominent forehead), and **corneal opacity** with elevated lysosomal enzymes (N-acetyl-ß-glucosaminidase, ß-glucuronidase, ß-hexosaminidase A) is highly characteristic of **I-cell disease** (mucolipidosis II).
- I-cell disease is caused by a deficiency in **N-acetyl-glucosamine-1-phosphotransferase**, an enzyme crucial for phosphorylating mannose residues on lysosomal enzymes, tagging them for delivery to lysosomes. Without this tag, lysosomal enzymes are secreted extracellularly, leading to their accumulation in the blood and their deficiency within lysosomes, causing the clinical features.
*Lysosomal alpha-1,4-glucosidase*
- Deficiency of **lysosomal alpha-1,4-glucosidase** causes **Pompe disease (glycogen storage disease type II)**, which is characterized by **cardiomegaly**, hypotonia, and liver involvement, but typically does not present with the skeletal dysplasias, gingival hyperplasia, or corneal clouding seen in this patient.
- While it is a lysosomal storage disorder, the specific clinical features and panel of elevated enzymes differ significantly from this case.
*Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase*
- Deficiency of **glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)** causes **G6PD deficiency**, an X-linked disorder leading to **hemolytic anemia** in response to oxidative stress (e.g., fava beans, certain drugs, infections).
- It does not present with the systemic skeletal, connective tissue, and corneal abnormalities described, nor does it involve elevated lysosomal enzyme levels.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- Deficiency of **glucocerebrosidase** causes **Gaucher disease**, which presents with **hepatosplenomegaly**, bone crises, pancytopenia, and sometimes neurological involvement.
- While it is a lysosomal storage disorder, the clinical features (e.g., absence of gingival hyperplasia, corneal opacity, or specific skeletal dysplasias like restricted joint movement) and the pattern of elevated enzymes do not match the patient's presentation.
*Alpha-galactosidase A*
- Deficiency of **alpha-galactosidase A** causes **Fabry disease**, an X-linked lysosomal storage disorder characterized by **neuropathic pain**, **angiokeratomas**, renal failure, and cardiac involvement.
- The clinical picture of Fabry disease does not include gingival hyperplasia, prominent skeletal abnormalities, or the specific pattern of elevated lysosomal enzymes observed in this patient.
Inborn errors of metabolism US Medical PG Question 6: You are counseling a mother whose newborn has just screened positive for a deficit of phenylalanine hydroxylase enzyme. You inform her that her child will require dietary supplementation of which of the following?
- A. Aspartame
- B. Niacin
- C. Homogentisic Acid
- D. Tyrosine (Correct Answer)
- E. Leucine
Inborn errors of metabolism Explanation: ***Tyrosine***
- A deficit of **phenylalanine hydroxylase** prevents the conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine, making **tyrosine** an essential amino acid that must be supplemented.
- Dietary restriction of **phenylalanine** is also crucial to prevent the accumulation of toxic byproducts that can cause severe neurological damage.
*Aspartame*
- **Aspartame** is an artificial sweetener that contains **phenylalanine**, which would be harmful for a child with phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency.
- Consumption of aspartame would increase the body's phenylalanine load, exacerbating the metabolic disorder.
*Niacin*
- **Niacin** (vitamin B3) is a vitamin and its supplementation is not related to the phenylalanine hydroxylase pathway or its deficiency.
- Deficiency of niacin is associated with **pellagra**, characterized by dermatitis, diarrhea, and dementia.
*Homogentisic Acid*
- **Homogentisic acid** is an intermediate in the metabolism of tyrosine, and its accumulation is characteristic of **alkaptonuria**, a different metabolic disorder.
- It is not a therapeutic supplement for phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency.
*Leucine*
- **Leucine** is a branched-chain amino acid, and its metabolism is unrelated to phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency.
- Supplemental leucine is not required in this condition and would not address the metabolic defect.
Inborn errors of metabolism US Medical PG Question 7: A 2-week-old boy presents to the emergency department because of unusual irritability and lethargy. The patient is admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit and minutes later develops metabolic encephalopathy. This progressed to a coma, followed by death before any laboratory tests are completed. The infant was born at home via vaginal delivery at 39 weeks' of gestation. His mother says that the symptoms started since the infant was 4-days-old, but since he only seemed ‘tired’, she decided not to seek medical attention. Further testing during autopsy shows hyperammonemia, low citrulline, and increased orotic acid. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase
- B. Propionyl-CoA carboxylase
- C. Homogentisic acid dioxygenase
- D. Ornithine transcarbamylase (Correct Answer)
- E. Cystathionine beta-synthase
Inborn errors of metabolism Explanation: **Ornithine transcarbamylase**
- **Hyperammonemia**, **low citrulline**, and **increased orotic acid** are classic findings in **Ornithine Transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency**. OTC is an X-linked urea cycle disorder.
- The rapid progression to **metabolic encephalopathy** and death in a neonate with these laboratory findings is highly characteristic of severe OTC deficiency, often presenting in the first few days of life.
*Branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **Maple Syrup Urine Disease**, characterized by elevated **branched-chain amino acids** and their corresponding ketoacids in blood and urine.
- While it can cause neurological symptoms, it does not typically present with the specific constellation of **hyperammonemia**, low citrulline, and high orotic acid.
*Propionyl-CoA carboxylase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme leads to **Propionic acidemia**, a type of organic acidemia, characterized by **propionic acid accumulation** and often **metabolic acidosis**, ketosis, and hyperammonemia.
- However, it would not typically cause **low citrulline** or isolated **elevated orotic acid** as seen in urea cycle disorders.
*Homogentisic acid dioxygenase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **Alkaptonuria**, an inborn error of metabolism characterized by the accumulation of **homogentisic acid**.
- This condition is usually benign in infancy, with symptoms appearing later in life such as **dark urine** on standing and **ochronosis** (darkening of cartilage). It does not present with acute hyperammonemia or metabolic encephalopathy.
*Cystathionine beta-synthase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **homocystinuria**, an inborn error of methionine metabolism, leading to elevated **homocysteine** and methionine.
- Clinical features include **ectopia lentis**, skeletal abnormalities, and intellectual disability, but not usually acute neonatal hyperammonemia or the specific findings of low citrulline and high orotic acid.
Inborn errors of metabolism US Medical PG Question 8: On a medical trip to Nicaragua, you observe a sweet odor in the cerumen of a 12-hour-old female newborn. Within 48 hours, the newborn develops ketonuria, poor feeding, and a sweet odor is also noticed in the urine. By 96 hours, the newborn is extremely lethargic and opisthotonus is observed. In order to prevent a coma and subsequent death, which of the following amino acids is one of those that should be withheld from this newborn's diet?
- A. Methionine
- B. Valine (Correct Answer)
- C. Phenylalanine
- D. Threonine
- E. Tyrosine
Inborn errors of metabolism Explanation: ***Valine***
- The clinical presentation with a **sweet odor in cerumen** and urine, followed by **ketonuria**, poor feeding, lethargy, and opisthotonus, is highly characteristic of **Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)**.
- MSUD is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by a deficiency in the **branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex (BCKDC)**, which is responsible for the metabolism of the branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs): **leucine, isoleucine, and valine**. Therefore, restricting these amino acids from the diet is crucial.
*Methionine*
- **Methionine** is an essential amino acid, but its dietary restriction is primarily associated with conditions like **homocystinuria**, not MSUD.
- The deficiency in MSUD specifically impacts the branched-chain amino acid pathway, not the methionine metabolism pathway.
*Phenylalanine*
- **Phenylalanine** is restricted in the diet of individuals with **phenylketonuria (PKU)**, a different inborn error of metabolism.
- PKU is characterized by the inability to metabolize phenylalanine to tyrosine, leading to its accumulation and neurotoxicity, with different clinical features than described.
*Threonine*
- **Threonine** is a different essential amino acid and is not one of the branched-chain amino acids whose catabolism is impaired in MSUD.
- Restricting threonine would not directly address the metabolic defect seen in MSUD.
*Tyrosine*
- **Tyrosine** is a non-essential amino acid that becomes essential in conditions like **phenylketonuria (PKU)**, where it cannot be synthesized from phenylalanine.
- It is not directly implicated in the pathogenesis or dietary management of MSUD.
Inborn errors of metabolism US Medical PG Question 9: A 9-month-old girl is brought to the physician because of a 1-month history of poor feeding and irritability. She is at the 15th percentile for height and 5th percentile for weight. Examination shows hypotonia and wasting of skeletal muscles. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. There is hepatomegaly. Her serum glucose is 61 mg/dL, creatinine kinase is 100 U/L, and lactic acid is within the reference range. Urine ketone bodies are elevated. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Glucose-6-phosphatase
- B. Muscle phosphorylase
- C. Acid alpha-glucosidase
- D. Glycogen debrancher (Correct Answer)
- E. Glucocerebrosidase
Inborn errors of metabolism Explanation: ***Glycogen debrancher***
- The patient's symptoms of **hepatomegaly**, **hypoglycemia**, **poor feeding**, **growth failure**, and **elevated urine ketones** in the presence of normal lactic acid suggest Type III glycogen storage disease (Cori disease), caused by a deficiency in **glycogen debrancher enzyme**.
- **Muscle wasting** and **hypotonia** are also consistent with Type III GSD, as the debranching enzyme is present in both liver and muscle.
*Glucose-6-phosphatase*
- Deficiency in **glucose-6-phosphatase** (Type I GSD, Von Gierke disease) also presents with **hepatomegaly** and **hypoglycemia**.
- However, Type I GSD is characterized by **lactic acidosis**, which is explicitly stated as normal in this patient, and **hyperlipidemia**, which is not mentioned.
*Muscle phosphorylase*
- Deficiency in **muscle phosphorylase** (Type V GSD, McArdle disease) primarily affects skeletal muscle, causing **exercise intolerance** and **muscle pain**.
- It does not typically present with **hypoglycemia**, **hepatomegaly**, or **growth failure** in infancy.
*Acid alpha-glucosidase*
- Deficiency in **acid alpha-glucosidase** (Type II GSD, Pompe disease) causes accumulation of glycogen in lysosomes, leading to severe **cardiomyopathy**, **hypotonia**, and **muscle weakness**.
- While hypotonia is present, the absence of **cardiomegaly** and significant **liver involvement** makes this diagnosis less likely.
*Glucocerebrosidase*
- Deficiency in **glucocerebrosidase** causes Gaucher disease, a lysosomal storage disorder, not a glycogen storage disorder.
- Symptoms include **hepatosplenomegaly**, **bone crises**, and neurological symptoms, but not **hypoglycemia** or isolated muscle wasting directly related to glycogen metabolism.
Inborn errors of metabolism US Medical PG Question 10: A 3-year-old male presents with his parents to a pediatrician for a new patient visit. The child was recently adopted and little is known about his prior medical or family history. The parents report that the child seems to be doing well, but they are concerned because the patient is much larger than any of the other 3-year-olds in his preschool class. They report that he eats a varied diet at home, and that they limit juice and snack foods. On physical exam, the patient is in the 73rd percentile for weight, 99th percentile for height, and 86th percentile for head circumference. He appears mildly developmentally delayed. He has a fair complexion and tall stature with a prominent sternum. The patient also has joint hypermobility and hyperelastic skin. He appears to have poor visual acuity and is referred to an ophthalmologist, who diagnoses upward lens subluxation of the right eye.
This child is most likely to develop which of the following complications?
- A. Osteoarthritis
- B. Wilms tumor
- C. Medullary thyroid cancer
- D. Aortic dissection (Correct Answer)
- E. Thromboembolic stroke
Inborn errors of metabolism Explanation: ***Aortic dissection***
- The constellation of **tall stature**, **prominent sternum**, **joint hypermobility**, **hyperelastic skin**, and **upward lens subluxation (ectopia lentis)** in a young child strongly suggests **Marfan syndrome**.
- **Aortic root dilation** and subsequent **aortic dissection** are the most serious cardiovascular complications in Marfan syndrome due to weakened connective tissue in the aortic wall caused by **fibrillin-1 deficiency**.
- This is the **leading cause of mortality** in untreated Marfan syndrome.
*Osteoarthritis*
- While joint hypermobility can contribute to **joint instability** and accelerate degenerative changes, typical **osteoarthritis** is less common as a primary, severe complication in childhood Marfan syndrome.
- Early-onset, severe osteoarthritis is not the major life-threatening complication associated with Marfan syndrome at this age.
*Wilms tumor*
- **Wilms tumor** is a type of kidney cancer typically associated with syndromes like **WAGR (Wilms tumor, Aniridia, Genitourinary anomalies, intellectual disability)** or **Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome**, none of which fit the patient's presentation.
- There is no known direct association between Wilms tumor and Marfan syndrome.
*Medullary thyroid cancer*
- **Medullary thyroid cancer** is a feature of **Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2 (MEN 2) syndromes**, which also present with pheochromocytomas and parathyroid hyperplasia.
- The clinical features described in the patient are not consistent with MEN 2.
*Thromboembolic stroke*
- While Marfan syndrome can lead to cardiovascular issues, a **thromboembolic stroke** is not a primary or characteristic complication, especially in comparison to the high risk of aortic dissection.
- The main vascular pathology in Marfan is related to connective tissue weakness, not primarily hypercoagulability or mural thrombi leading to stroke.
- Thromboembolic complications are more characteristic of **homocystinuria**, which presents with **downward** lens subluxation.
More Inborn errors of metabolism US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.