Down syndrome US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Down syndrome. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Down syndrome US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 14-weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. Routine first trimester screening shows increased nuchal translucency, decreased β-hCG concentration, and decreased levels of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A. Amniocentesis shows trisomy of chromosome 13. This fetus is at increased risk for which of the following?
- A. Duodenal atresia
- B. Cutis aplasia (Correct Answer)
- C. Cystic hygroma
- D. Optic glioma
- E. Prominent occiput
Down syndrome Explanation: ***Cutis aplasia***
- **Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)** is characterized by **cutis aplasia**, which is a congenital absence of skin, typically on the scalp.
- Other common features of Trisomy 13 include **midline defects**, microphthalmia, cleft lip/palate, polydactyly, and severe intellectual disability.
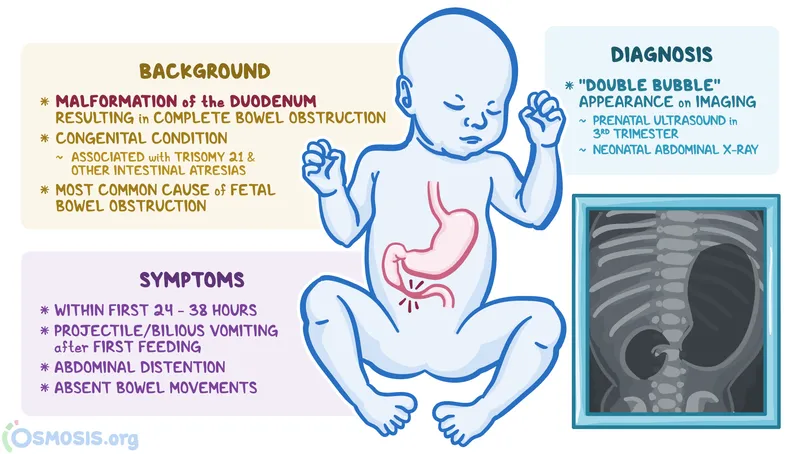
*Duodenal atresia*
- **Duodenal atresia** is strongly associated with **Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)**, not Trisomy 13.
- It presents with a "double bubble" sign on imaging due to dilation of the stomach and proximal duodenum.
*Cystic hygroma*
- **Cystic hygromas**, which are lymphatic malformations, are a common finding in **Turner syndrome (XO)** and **Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)**.
- While increased nuchal translucency is noted, a cystic hygroma itself is not a specific finding for Trisomy 13.
*Optic glioma*
- **Optic gliomas** are tumors of the optic nerve most frequently associated with **neurofibromatosis type 1**, an autosomal dominant disorder.
- They are not a characteristic finding of Trisomy 13.
*Prominent occiput*
- A **prominent occiput** is a classic feature of **Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)**.
- This condition is also associated with rocker-bottom feet, micrognathia, and clenched hands with overlapping fingers.
Down syndrome US Medical PG Question 2: A 37-year-old woman presents for prenatal counseling at 18 weeks gestation. The patient tells you that her sister recently had a child with Down's syndrome, and the patient would like prenatal screening for Down's in her current pregnancy.
Which of the following prenatal screening tests and results would raise concern for Down's syndrome?
- A. Increased AFP, normal HCG, normal unconjugated estriol
- B. Decreased AFP, decreased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol
- C. Normal AFP, increased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol
- D. Normal AFP, decreased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol
- E. Decreased AFP, increased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol (Correct Answer)
Down syndrome Explanation: ***Decreased AFP, increased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol***
- A classic finding in **Down's syndrome (trisomy 21)** during the second-trimester screen is a **decreased alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)**, **increased human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)**, and **decreased unconjugated estriol**.
- This combination, sometimes referred to as the "**triple screen**" (or "quad screen" with inhibin A), indicates a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities like trisomy 21.
*Increased AFP, normal HCG, normal unconjugated estriol*
- **Increased AFP** is typically associated with **neural tube defects** (e.g., spina bifida, anencephaly) or **ventral wall defects**, not Down's syndrome.
- Normal HCG and unconjugated estriol would argue against trisomy 21.
*Decreased AFP, decreased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol*
- When all three markers (AFP, HCG, and unconjugated estriol) are **decreased**, it is highly suggestive of **trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)**, not Down's syndrome.
- Trisomy 18 is associated with severe developmental abnormalities and a poor prognosis.
*Normal AFP, increased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol*
- While **increased HCG** and **decreased unconjugated estriol** are consistent with Down's syndrome, a **normal AFP** alone would make this less classic for trisomy 21 compared to the option with decreased AFP.
- The combination of **decreased AFP** alongside the other two findings is more characteristic.
*Normal AFP, decreased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol*
- This pattern (normal AFP, decreased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol) is not typically associated with Down's syndrome.
- **Decreased HCG** is more commonly seen in trisomy 18 in combination with decreased AFP and estriol.
Down syndrome US Medical PG Question 3: A 23-year-old pregnant woman (gravida 1, para 0) presents during her 16th week of pregnancy for a check-up. The course of her current pregnancy is unremarkable. She had normal results on the previous ultrasound examination. Her human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) level measured at week 12 of pregnancy was 0.9 multiples of the normal median (MoM). She is human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), and hepatitis C virus (HCV)-negative. She undergoes a quadruple test which shows the following results:
Serum alpha-fetoprotein Low
Unconjugated estriol Low
Beta-hCG High
Inhibin A High
The risk of which condition indicates these results?
- A. Trisomy 21 (Correct Answer)
- B. Trisomy 18
- C. Neural tube defect
- D. Congenital toxoplasmosis
- E. Trophoblastic disease
Down syndrome Explanation: ***Trisomy 21***
- The quadruple test results of **low alpha-fetoprotein**, **low unconjugated estriol**, **high beta-hCG**, and **high inhibin A** are highly characteristic of **Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)**.
- These specific maternal serum analyte patterns are used in **second-trimester screening** to assess the risk of chromosomal abnormalities.
*Trisomy 18*
- Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome) would typically show **low alpha-fetoprotein**, **low unconjugated estriol**, and **low beta-hCG**, often with **normal or low inhibin A**.
- The elevated beta-hCG and inhibin A in the patient's results make Trisomy 18 less likely.
*Neural tube defect*
- Neural tube defects (NTDs) are associated with **elevated alpha-fetoprotein** levels in maternal serum.
- The patient's results show **low alpha-fetoprotein**, which argues against an NTD.
*Congenital toxoplasmosis*
- Congenital toxoplasmosis is an infection and does not typically present with a specific pattern of abnormal maternal serum markers like those seen in the quadruple test.
- Diagnosis would involve specific **serological testing for Toxoplasma antibodies** or ultrasound findings.
*Trophoblastic disease*
- Trophoblastic disease, such as a **hydatidiform mole**, is associated with **extremely high levels of beta-hCG**, often much higher than what would be seen in Trisomy 21.
- It would also typically be detected earlier in pregnancy and present with distinct ultrasound findings, which were normal in this case.
Down syndrome US Medical PG Question 4: A 19-year-old male from rural West Virginia presents to his family medicine doctor to discuss why he is having trouble getting his wife pregnant. On exam, he is 6 feet 2 inches with a frail frame and broad hips for a male his size. He is noted to have mild gynecomastia, no facial hair, and small, underdeveloped testes. He claims that although he has a lower libido than most of his friends, he does have unprotected sex with his wife. His past medical history is notable for developmental delay and difficulties in school. What is the most likely chromosomal abnormality in this patient?
- A. Trisomy 13
- B. 45: XO
- C. Trisomy 21
- D. 47: XYY
- E. 47: XXY (Correct Answer)
Down syndrome Explanation: ***47: XXY***
- The patient's presentation with **infertility**, small testes, **gynecomastia**, eunuchoid body habitus (tall, frail frame, broad hips), lack of facial hair, and **developmental delay** are classic features of **Klinefelter syndrome (47, XXY)**.
- This chromosomal abnormality leads to primary **hypogonadism** due to the presence of an extra X chromosome in males.
*Trisomy 13*
- Trisomy 13, or **Patau syndrome**, is characterized by severe developmental anomalies, including **cleft lip and palate**, polydactyly, and severe neurological defects.
- Infants with Trisomy 13 rarely survive beyond the first year and do not present with the described signs of hypogonadism or gynecomastia in adolescence.
*45: XO*
- **45, XO** or **Turner syndrome** affects females and is characterized by **short stature**, primary amenorrhea, webbed neck, and **gonadal dysgenesis (streak gonads)**.
- This karyotype is incompatible with a male phenotype and the symptoms described.
*Trisomy 21*
- Trisomy 21, or **Down syndrome**, is associated with distinct facial features, intellectual disability, and congenital heart defects.
- While individuals with Down syndrome may have fertility issues, they do not typically present with the specific combination of **gynecomastia**, eunuchoid habitus, and **small testes** seen in this patient.
*47: XYY*
- **47, XYY syndrome** is associated with increased height and potentially some learning difficulties, but typically does not cause the significant **hypogonadism**, **gynecomastia**, or **small testes** seen in this patient.
- Men with 47, XYY usually have normal sexual development and fertility, though some may experience learning disabilities or behavioral problems.
Down syndrome US Medical PG Question 5: A 38-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 12 weeks' gestation comes to her obstetrician for a prenatal visit. Screening tests in the first trimester showed a decreased level of pregnancy-associated plasma protein and an increased level of β-hCG. A genetic disorder is suspected. Which of the following results from an additional diagnostic test is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
- A. Decreased estriol in maternal serum
- B. Increased inhibin A in maternal serum
- C. Triploidy in amniotic fluid
- D. Increased nuchal translucency on ultrasound
- E. Trisomy 21 on chorionic villus sampling (Correct Answer)
Down syndrome Explanation: ***Trisomy 21 on chorionic villus sampling***
- The combination of **decreased PAPP-A** and **increased β-hCG** in the first trimester is highly suggestive of **Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)**.
- **Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)** is a diagnostic test performed in the first trimester that can directly analyze fetal chromosomes to confirm the presence of Trisomy 21.
*Decreased estriol in maternal serum*
- This finding is typically seen in the **second-trimester quad screen** (along with α-fetoprotein, β-hCG, and inhibin A), not the first-trimester screening.
- While low estriol is associated with aneuploidies, it's not the most direct or earliest confirmatory diagnostic test in this specific scenario.
*Increased inhibin A in maternal serum*
- Similar to estriol, **increased inhibin A** is a marker used in the **second-trimester quad screen** and is associated with Trisomy 21.
- It is not a component of the standard first-trimester screening blood tests mentioned (PAPP-A and β-hCG).
*Triploidy in amniotic fluid*
- **Triploidy** is a rare and severe chromosomal abnormality (three sets of chromosomes) with a distinct pattern on first-trimester screening (often very low β-hCG and PAPP-A, along with severe growth restriction and structural anomalies).
- The observed screening results (decreased PAPP-A, increased β-hCG) are much more characteristic of Trisomy 21 than triploidy.
*Increased nuchal translucency on ultrasound*
- **Increased nuchal translucency (NT)** is a significant **screening marker** for aneuploidies, including Trisomy 21, and is part of the first-trimester combined screening.
- While a strong indicator, it is a screening result, not a definitive diagnostic confirmation like chromosomal analysis from CVS.
Down syndrome US Medical PG Question 6: A 28-year-old G2P1 female is concerned that she may give birth to another child with Down syndrome. She states that she may not be able to take care of another child with this disorder. Which of the following tests can confirm the diagnosis of Down syndrome in utero?
- A. Ultrasound
- B. Triple marker test
- C. Integrated test
- D. Quadruple marker test
- E. Amniocentesis (Correct Answer)
Down syndrome Explanation: ***Amniocentesis***
- **Amniocentesis** is a **diagnostic procedure** that involves collecting amniotic fluid to obtain fetal cells for **karyotyping**, which can definitively confirm the presence of an extra chromosome 21, the cause of Down syndrome.
- This test is typically performed between **15 and 20 weeks of gestation** and carries a small risk of complication but offers conclusive results.
*Ultrasound*
- **Ultrasound** is a **screening tool** that can detect anatomical features suggestive of Down syndrome, such as **nuchal translucency** or heart defects, but it cannot definitively diagnose the condition.
- It identifies **markers** that increase the suspicion of Down syndrome, prompting further diagnostic testing, but does not provide genetic confirmation.
*Triple marker test*
- The **triple marker test** is a **screening test** that measures levels of **alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)**, **unconjugated estriol (uE3)**, and **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)** in maternal blood.
- While it can estimate the risk of Down syndrome, it is not a diagnostic test and only provides a **risk assessment**, not a definitive diagnosis.
*Integrated test*
- The **integrated test** combines results from first-trimester screening (nuchal translucency and PAPP-A) and second-trimester screening (quadruple marker test) to provide a **single risk assessment**.
- Like other screening tests, it calculates a **risk probability** for Down syndrome but does not offer a definitive diagnosis.
*Quadruple marker test*
- The **quadruple marker test** measures AFP, uE3, hCG, and **inhibin A** in maternal blood during the second trimester.
- It is a **screening test** used to assess the risk of Down syndrome and open neural tube defects, but it is not a diagnostic tool.
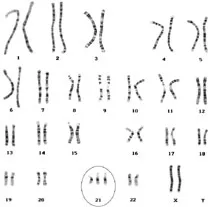
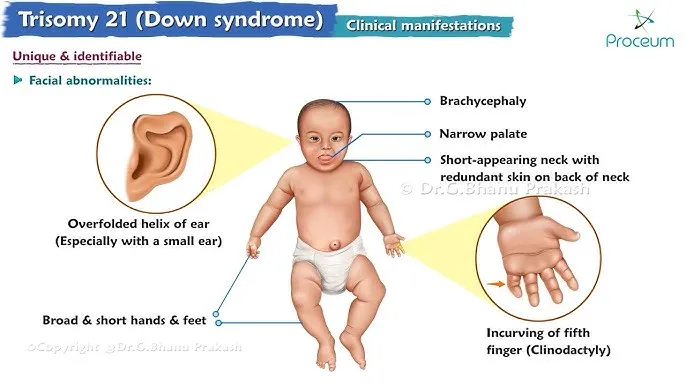
Down syndrome US Medical PG Question 7: A 2300-g (5.07-lb) male newborn is delivered at term to a 39-year-old woman. Examination shows a sloping forehead, a flat nasal bridge, increased interocular distance, low-set ears, a protruding tongue, a single palmar crease and an increased gap between the first and second toe. There are small white and brown spots in the periphery of both irises. The abdomen is distended. An x-ray of the abdomen shows two large air-filled spaces in the upper quadrant. This patient's condition is most likely associated with which of the following cardiac anomalies?
- A. Atrioventricular septal defect (Correct Answer)
- B. Tetralogy of Fallot
- C. Atrial septal defect
- D. Patent ductus arteriosus
- E. Ventricular septal defect
Down syndrome Explanation: ***Atrioventricular septal defect***
- The constellation of dysmorphic features (sloping forehead, flat nasal bridge, low-set ears, protruding tongue, single palmar crease, increased gap between first and second toe, Brushfield spots) and **duodenal atresia** (double bubble sign on X-ray) are highly suggestive of **Down syndrome** (Trisomy 21).
- **Atrioventricular septal defects (AVSDs)**, also known as endocardial cushion defects, are the most common and classic cardiac anomaly associated with **Down syndrome**, occurring in about 40-50% of affected children.
*Tetralogy of Fallot*
- While **Tetralogy of Fallot** is a cyanotic heart defect, it is not the most common cardiac anomaly associated with Down syndrome.
- It involves four specific defects: **ventricular septal defect**, **pulmonary stenosis**, **overriding aorta**, and **right ventricular hypertrophy**.
*Atrial septal defects*
- **Atrial septal defects (ASDs)** are a type of congenital heart defect where there is a hole in the septum between the two atria of the heart.
- While ASDs can occur in Down syndrome, they are less common than AVSDs and are often part of a more complex AVSD rather than isolated.
*Patent ductus arteriosus*
- **Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)** is the persistence of the fetal ductus arteriosus in a newborn after birth.
- While PDAs can occur in infants with Down syndrome, they are also very common in **premature infants** and are not the most characteristic cardiac lesion.
*Ventricular septal defect*
- **Ventricular septal defect (VSD)** is a hole in the septum separating the two ventricles of the heart.
- VSDs are common congenital heart defects and can be found in Down syndrome, but **AVSDs** are more specific and prevalent in this condition, often involving a component of a VSD.
Down syndrome US Medical PG Question 8: A 2-year-old boy is brought to a pediatrician because his parents have noticed that he seems to be getting tired very easily at home. Specifically, they have noticed that he is often panting for breath after walking around the house for a few minutes and that he needs to take naps fairly often throughout the day. He has otherwise been well, and his parents do not recall any recent infections. He was born at home, and his mom did not receive any prenatal care prior to birth. Physical exam reveals a high-pitched, harsh, holosystolic murmur that is best heard at the lower left sternal border. No cyanosis is observed. Which of the following oxygen tension profiles would most likely be seen in this patient? (LV = left ventricle, RV = right ventricle, and SC = systemic circulation).
- A. LV: normal, RV: normal, SC: normal
- B. LV: normal, RV: increased, SC: normal (Correct Answer)
- C. LV: decreased, RV: increased, SC: decreased
- D. LV: decreased, RV: normal, SC: decreased
- E. LV: normal, RV: normal, SC: decreased
Down syndrome Explanation: ***LV: normal, RV: increased, SC: normal***
- The patient's presentation with easy fatigability, dyspnea on exertion, and a **holosystolic murmur** at the **lower left sternal border** strongly suggests a **ventricular septal defect (VSD)**. These symptoms result from a **left-to-right shunt**, leading to increased blood flow and pressure in the **right ventricle (RV)** and pulmonary circulation.
- In a VSD, highly oxygenated blood from the **left ventricle (LV)** shunts into the RV. This increases the **oxygen tension** in the RV, while the LV and systemic circulation (SC) typically maintain normal oxygen tension if the shunt is not so large that it causes **pulmonary hypertension** with **Eisenmenger syndrome**.
*LV: normal, RV: normal, SC: normal*
- This profile would indicate a **normal cardiovascular system** without any significant shunting or cardiac anomaly.
- It does not align with the patient's symptoms of easy fatigability, dyspnea, and the presence of a pathological murmur.
*LV: decreased, RV: increased, SC: decreased*
- A **decreased oxygen tension in the left ventricle** and **systemic circulation** typically indicates a **right-to-left shunt** or severe **pulmonary disease**, often associated with **cyanosis**, which is noted as absent in this patient.
- While RV oxygen tension *could* be increased in some complex congenital heart diseases with right-to-left shunting (e.g., mixing lesions), the overall profile does not fit the characteristic presentation of a VSD without cyanosis.
*LV: decreased, RV: normal, SC: decreased*
- This profile with **decreased oxygen tension in the left ventricle** and **systemic circulation** suggests a condition where oxygenated blood supply to the systemic circulation is compromised, such as severe **left ventricular dysfunction** or a **right-to-left shunt**.
- A **normal RV oxygen tension** without **cyanosis** makes this unlikely in the context of the patient's symptoms.
*LV: normal, RV: normal, SC: decreased*
- A **decreased oxygen tension in the systemic circulation** with **normal LV and RV oxygen tension** is inconsistent with a **VSD**.
- This profile might be observed in conditions like severe **anemia** or **hypoxia** without a primary cardiac shunt.
Down syndrome US Medical PG Question 9: A 1-day-old infant in the general care nursery, born at full term by uncomplicated cesarean section delivery, is noted to have a murmur, but otherwise appears well. On examination, respiratory rate is 40/min and pulse oximetry is 96%. Precordium is normoactive. With auscultation, S1 is normal, S2 is single, and a 2/6 systolic ejection murmur is heard at the left upper sternal border. Echocardiography shows infundibular pulmonary stenosis, overriding aorta, ventricular septal defect and concentric right ventricular hypertrophy. Which of the following correlate with the presence or absence of cyanosis in this baby?
- A. The degree of right ventricular outflow tract obstruction (Correct Answer)
- B. The ratio of reduced hemoglobin to oxyhemoglobin
- C. The concentration of hemoglobin
- D. The size of ventricular septal defect
- E. The concentration of pulmonary surfactant
Down syndrome Explanation: ***The degree of right ventricular outflow tract obstruction***
- The severity of **pulmonary stenosis** in **tetralogy of Fallot** dictates the amount of blood shunted from the right ventricle to the aorta via the **ventricular septal defect (VSD)**.
- A **less severe obstruction** allows more blood to flow to the lungs, leading to less right-to-left shunting and consequently **less cyanosis**.
*The ratio of reduced hemoglobin to oxyhemoglobin*
- While this ratio directly reflects the presence of cyanosis, it does not explain its *cause* in the context of the given congenital heart defect.
- The question asks what *correlates* with the presence or absence of cyanosis, implying a causal or pathophysiological link rather than a descriptive measure.
*The concentration of hemoglobin*
- **Hemoglobin concentration** affects the *visibility* of cyanosis (e.g., polycythemia can make mild desaturation appear more cyanotic), but it doesn't primarily determine the *presence* or *absence* of shunt-related cyanosis itself.
- A patient can be significantly desaturated with a normal hemoglobin concentration, and the degree of desaturation is largely driven by the shunt.
*The size of ventricular septal defect*
- In tetralogy of Fallot, the **VSD is typically large and non-restrictive**, meaning its size itself doesn't limit blood flow between the ventricles.
- The **pulmonary stenosis** is the primary determinant of the shunt direction and magnitude, not the size of the VSD.
*The concentration of pulmonary surfactant*
- **Pulmonary surfactant** is crucial for maintaining alveolar stability and preventing atelectasis, thereby ensuring efficient gas exchange in the lungs.
- While important for overall respiratory function, it does not directly correlate with the degree of shunting and cyanosis in **tetralogy of Fallot**.
Down syndrome US Medical PG Question 10: A 1-month-old infant is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. His mother reports that she had previously breastfed her son every 2 hours for 15 minutes but is now feeding him every 4 hours for 40 minutes. She says that the infant sweats a lot and is uncomfortable during feeds. He has 6 wet diapers and 2 stools daily. He was born at 36 weeks' gestation. He currently weighs 3500 g (7.7 lb) and is 52 cm (20.4 in) in length. He is awake and alert. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), pulse is 170/min, respirations are 55/min, and blood pressure is 80/60 mm Hg. Pulse oximetry on room air shows an oxygen saturation of 99%. Cardiopulmonary examination shows a 4/6 continuous murmur along the upper left sternal border. After confirming the diagnosis via echocardiography, which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Digoxin and furosemide (Correct Answer)
- B. Percutaneous surgery
- C. X-ray of the chest
- D. Prostaglandin E1 infusion
- E. Indomethacin infusion
Down syndrome Explanation: ***Digoxin and furosemide***
- This 1-month-old infant presents with classic signs of **heart failure** from a symptomatic **patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)**: tachycardia (170/min), tachypnea (55/min), poor feeding with prolonged feeding times, diaphoresis during feeds, and a continuous murmur at the left upper sternal border.
- At **1 month of age**, the initial management focuses on **medical treatment of heart failure** with **furosemide** (loop diuretic to reduce volume overload) and **digoxin** (inotropic support to improve cardiac contractility).
- This stabilizes the infant before definitive closure is considered if medical management fails.
*Indomethacin infusion*
- **Indomethacin** (NSAID/prostaglandin inhibitor) is effective for **PDA closure only in premature infants within the first 7-14 days of life**.
- At **1 month of age** (approximately 40 weeks corrected gestational age), the ductus arteriosus is no longer responsive to prostaglandin inhibition, making indomethacin ineffective.
- This would have been appropriate if the infant was still in the early neonatal period.
*Percutaneous surgery*
- **Percutaneous transcatheter closure** or surgical ligation may be required if medical management of heart failure fails or the PDA remains hemodynamically significant.
- However, this is **not the initial step**—medical stabilization with heart failure management should be attempted first.
- Procedural closure is typically considered after 6 months of age if spontaneous closure has not occurred.
*X-ray of the chest*
- A chest X-ray would show **cardiomegaly** and **increased pulmonary vascular markings** consistent with the left-to-right shunt from PDA.
- However, the diagnosis has already been **confirmed by echocardiography**, and imaging does not constitute therapeutic management for this symptomatic infant.
*Prostaglandin E1 infusion*
- **Prostaglandin E1** is used to **maintain** ductal patency in **ductal-dependent congenital heart lesions** (e.g., critical coarctation, hypoplastic left heart syndrome, pulmonary atresia).
- In this case with symptomatic PDA, the goal is to manage heart failure and potentially achieve ductal closure, making PGE1 **contraindicated**.
More Down syndrome US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.