Teratogenic exposures US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Teratogenic exposures. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Teratogenic exposures US Medical PG Question 1: A 26-year-old woman (gravida 3 para 1) with no prenatal care delivers a boy at 37 weeks gestation. His Apgar score is 5 at 1 minute and 8 at 5 minutes. His weight is 2.1 kg (4.2 lb) and length is 47 cm (1 ft 7 in). The mother’s history is significant for chronic pyelonephritis, atrial fibrillation, and gastroesophageal reflux disease. She has a 5-pack-year smoking history and also reports alcohol consumption during pregnancy. Examination of the infant shows a short depressed nasal bridge, wide nose, brachydactyly, and a short neck. Ophthalmoscopy reveals bilateral cataracts. What is the most likely cause of the newborn’s symptoms?
- A. Omeprazole
- B. Warfarin (Correct Answer)
- C. Atenolol
- D. Alcohol
- E. Gentamicin
Teratogenic exposures Explanation: **Warfarin**
- The constellation of **nasal hypoplasia (short depressed nasal bridge, wide nose)**, **stippled epiphyses (brachydactyly)**, and **ophthalmologic abnormalities (bilateral cataracts)** are classic features of **warfarin embryopathy (fetal warfarin syndrome)**.
- Warfarin crosses the placenta and inhibits **vitamin K-dependent carboxylation**, affecting bone and cartilage development and leading to these characteristic fetal anomalies.
*Omeprazole*
- **Omeprazole** is a proton pump inhibitor generally considered **safe in pregnancy** and is not associated with teratogenic effects like those described.
- It is commonly used to treat **gastroesophageal reflux disease** during pregnancy.
*Atenolol*
- **Atenolol** is a beta-blocker that can cause **fetal growth restriction** and **neonatal bradycardia** or **hypoglycemia** if used in late pregnancy.
- However, it does not typically cause the specific craniofacial or skeletal malformations seen in this infant.
*Alcohol*
- **Fetal alcohol syndrome** is characterized by **growth restriction**, **facial dysmorphology (e.g., short palpebral fissures, smooth philtrum, thin upper lip)**, and **CNS abnormalities**.
- While the infant has growth restriction, the specific facial and skeletal features do not align with fetal alcohol syndrome.
*Gentamicin*
- **Gentamicin** is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that can cause **ototoxicity** (hearing loss) and **nephrotoxicity** in both the mother and fetus.
- It is not associated with the **craniofacial, skeletal, or ocular anomalies** described in this case.
Teratogenic exposures US Medical PG Question 2: A 26-year-old woman with poor prenatal care and minimal antenatal screening presents to the emergency department in labor. Shortly thereafter, she delivers a baby girl who subsequently demonstrates symptoms of chorioretinitis on examination. A series of postpartum screening questions is significant only for the presence of multiple cats in the mother’s household. The clinical team orders an enhanced MRI examination of the infant’s brain which reveals hydrocephalus, multiple punctate intracranial calcifications, and 2 sub-cortical ring-enhancing lesions. Which is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Rubella
- B. Syphilis
- C. CMV
- D. HSV
- E. Toxoplasmosis (Correct Answer)
Teratogenic exposures Explanation: ***Toxoplasmosis***
- The triad of **chorioretinitis**, **hydrocephalus**, and **intracranial calcifications** is classic for congenital toxoplasmosis.
- The mother's exposure to **cats** (definitive hosts) and poor prenatal care supports the diagnosis of an acute maternal infection with vertical transmission.
*Rubella*
- Congenital rubella presents with **sensorineural hearing loss**, **cardiac defects** (e.g., patent ductus arteriosus, pulmonary artery stenosis), and **cataracts**, not chorioretinitis and intracranial calcifications.
- While it can cause microcephaly, the specific **hydrocephalus** and diffuse calcifications seen here are not typical.
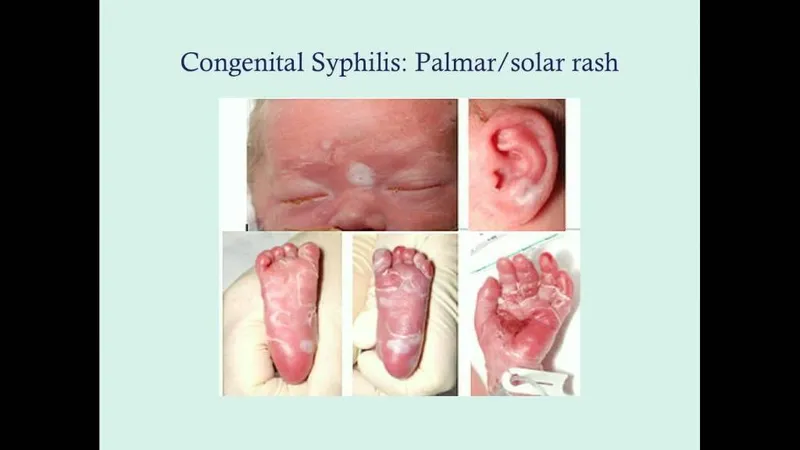
*Syphilis*
- Congenital syphilis manifests with early symptoms like **hepatosplenomegaly**, **rash**, and **rhinitis**, and later signs such as **Hutchinson's teeth** and **saddle nose**.
- **Chorioretinitis** and the specific pattern of **intracranial calcifications** observed are not characteristic features of congenital syphilis.
*CMV*
- Congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) often causes **periventricular calcifications**, **microcephaly**, and **sensorineural hearing loss**, but typically not the diffuse punctate calcifications and subcortical ring-enhancing lesions seen in this case.
- While chorioretinitis can occur, the overall clinical picture with **hydrocephalus** points away from CMV as the most likely diagnosis.
*HSV*
- Congenital herpes simplex virus (HSV) infection typically presents with **skin vesicles**, **keratoconjunctivitis**, and encephalitis, often with focal brain lesions.
- The lack of skin lesions and the specific pattern of diffuse **intracranial calcifications** and **chorioretinitis** make HSV less likely.
Teratogenic exposures US Medical PG Question 3: A 32-year-old primigravid woman with a history of seizures comes to the physician because she had a positive pregnancy test at home. Medications include valproic acid and a multivitamin. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. A urine pregnancy test is positive. Her baby is at increased risk for requiring which of the following interventions?
- A. Lower spinal surgery (Correct Answer)
- B. Kidney transplantation
- C. Arm surgery
- D. Cochlear implantation
- E. Respiratory support
Teratogenic exposures Explanation: ***Lower spinal surgery***
- Maternal use of **valproic acid** during pregnancy significantly increases the risk of neural tube defects, particularly **spina bifida**, which often requires surgical correction of the lower spine in affected infants.
- **Spina bifida** results from the incomplete closure of the neural tube, leading to exposed spinal cord or meninges, and frequently necessitates surgical intervention to prevent further neurological damage and infection.
*Kidney transplantation*
- While some fetal anomalies can involve the kidneys, **valproic acid** exposure is not primarily associated with renal agenesis or severe kidney malformations requiring transplantation.
- Birth defects affecting the kidneys are more commonly linked to genetic syndromes or other teratogens, not specifically valproic acid.
*Arm surgery*
- **Valproic acid** has been associated with limb defects, but these are typically minor and do not usually directly necessitate extensive arm surgery.
- **Phocomelia** (shortened or absent limbs) is more typically associated with **thalidomide** exposure, not valproic acid.
*Cochlear implantation*
- Although **valproic acid** exposure has been occasionally linked to some congenital anomalies, it is not a primary risk factor for **severe hearing loss** requiring cochlear implantation.
- Hearing loss requiring such intervention is more often due to genetic factors, congenital infections, or other specific teratogens.
*Respiratory support*
- While a variety of congenital conditions can lead to respiratory compromise, **valproic acid** exposure does not specifically cause severe pulmonary hypoplasia or other defects that commonly necessitate prolonged or intense neonatal respiratory support.
- Respiratory distress in neonates is often related to prematurity, meconium aspiration, or other direct pulmonary issues.
Teratogenic exposures US Medical PG Question 4: A 32-year-old G2P0A1 woman presents at 36 weeks of gestation for the first time during her pregnancy. The patient has no complaints, currently. However, her past medical history reveals seizure disorder, which is under control with valproic acid and lithium. She has not seen her neurologist during the past 2 years, in the absence of any complaints. She also reports a previous history of elective abortion. The physical examination is insignificant. Her blood pressure is 130/75 mm Hg and pulse is 80/min. The patient is scheduled to undergo regular laboratory tests and abdominal ultrasound. Given her past medical history, which of the following conditions is her fetus most likely going to develop?
- A. Neural tube defects (NTDs) (Correct Answer)
- B. Intrauterine growth restriction
- C. Iron deficiency anemia
- D. Trisomy 21
- E. Limb anomalies
Teratogenic exposures Explanation: **Neural tube defects (NTDs)**
* The use of **valproic acid** during pregnancy is significantly associated with an increased risk of **neural tube defects (NTDs)**, such as spina bifida and anencephaly, in the fetus.
* Valproic acid interferes with **folate metabolism**, which is crucial for proper neural tube closure during early fetal development.
*Intrauterine growth restriction*
* While some medications and maternal conditions can cause **intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR)**, valproic acid and lithium are **not primary causes** of IUGR.
* Other factors, such as **placental insufficiency**, severe maternal hypertension, or infections, are more commonly associated with IUGR.
*Iron deficiency anemia*
* **Iron deficiency anemia** is a common maternal condition in pregnancy, but it is **not a direct fetal outcome** of maternal valproic acid or lithium use.
* Fetal anemia might occur due to other causes like **Rh incompatibility** or parvovirus infection.
*Trisomy 21*
* **Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)** is a **chromosomal anomaly** caused by the presence of an extra copy of chromosome 21.
* It is not related to maternal medication use like valproic acid or lithium; its incidence is primarily correlated with **advanced maternal age**.
*Limb anomalies*
* Although several teratogenic medications can cause **limb anomalies**, **valproic acid** is more strongly linked to **neural tube defects** and certain **cardiac anomalies**.
* **Thalidomide**, for example, is notoriously associated with severe limb malformations.
Teratogenic exposures US Medical PG Question 5: A 30-year-old female with a history of epilepsy becomes pregnant. Her epilepsy has been well controlled by taking a medication that inhibits GABA transaminase and blocks voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels. Her obstetrician informs her that her epilepsy medication has been shown to have teratogenic effects. Of the following, which teratogenic effect is this woman's medication most likely to cause?
- A. Limb defects
- B. Neural tube defect (Correct Answer)
- C. Renal damage
- D. Ebstein's anomaly
- E. Discolored teeth
Teratogenic exposures Explanation: ***Neural tube defect***
- The medication described, which **inhibits GABA transaminase** and has multiple mechanisms including effects on voltage-gated channels, is **valproic acid** (valproate).
- **Valproic acid** is the antiepileptic drug with the **highest risk of neural tube defects** (e.g., spina bifida), with an incidence of approximately 1-2% when taken during pregnancy.
- This teratogenic effect occurs primarily during the first trimester and is believed to be due to interference with **folate metabolism** and **histone deacetylase inhibition**, which are crucial for proper neural tube closure.
- Folic acid supplementation is recommended for women of childbearing age taking valproate.
*Limb defects*
- **Limb defects** (e.g., phocomelia, limb reduction defects) are classically associated with **thalidomide** exposure during early pregnancy.
- While **phenytoin** (fetal hydantoin syndrome) can cause limb abnormalities including hypoplastic nails and distal phalanges, this is not the primary teratogenic concern with valproic acid.
*Renal damage*
- **Fetal renal damage** can be caused by medications such as **ACE inhibitors**, **ARBs**, and **NSAIDs** when taken during pregnancy.
- This is not a characteristic teratogenic effect of valproic acid or other antiepileptic medications.
*Ebstein's anomaly*
- **Ebstein's anomaly**, a congenital heart defect characterized by apical displacement of the tricuspid valve, is most notably associated with **lithium exposure** during the first trimester of pregnancy.
- This cardiac anomaly is not typically linked to valproic acid or other anticonvulsant medications.
*Discolored teeth*
- **Discolored teeth** (yellow-brown staining) and enamel hypoplasia are classic adverse effects of **tetracycline antibiotics** when administered during pregnancy (second and third trimesters) or early childhood.
- This effect is not associated with antiepileptic medications.
Teratogenic exposures US Medical PG Question 6: A 3-day-old female newborn delivered vaginally at 36 weeks to a 27-year-old woman has generalized convulsions lasting 3 minutes. Prior to the event, she was lethargic and had difficulty feeding. The infant has two healthy older siblings and the mother's immunizations are up-to-date. The infant appears icteric. The infant's weight and length are at the 5th percentile, and her head circumference is at the 99th percentile for gestational age. There are several purpura of the skin. Ocular examination shows posterior uveitis. Cranial ultrasonography shows ventricular dilatation, as well as hyperechoic foci within the cortex, basal ganglia, and periventricular region. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Congenital parvovirus infection
- B. Congenital Toxoplasma gondii infection (Correct Answer)
- C. Congenital Treponema pallidum infection
- D. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection
- E. Congenital rubella infection
Teratogenic exposures Explanation: ***Congenital Toxoplasma gondii infection***
- **Ventricular dilatation** with widespread **hyperechoic foci** (calcifications) in the brain, along with **posterior uveitis**, highly suggests congenital toxoplasmosis.
- Other features like **generalized convulsions**, **icterus**, **purpura**, and **microcephaly** (indicated by 5th percentile weight/length vs 99th percentile head circumference discrepancy suggesting hydrocephalus with macrocephaly) are also consistent with this diagnosis.
*Congenital parvovirus infection*
- Primarily causes severe **anemia**, **hydrops fetalis**, and **myocarditis**; it does not typically present with extensive cerebral calcifications or uveitis.
- While it can lead to neurological issues, the specific brain imaging findings and ocular involvement described are not characteristic.
*Congenital Treponema pallidum infection*
- Characterized by rhinitis (**snuffles**), **hepatosplenomegaly**, **bone abnormalities** (e.g., osteochondritis), and **rash**.
- While it can cause CNS involvement and developmental delays, the distinct pattern of brain calcifications and uveitis is not typical.
*Congenital cytomegalovirus infection*
- Can cause **periventricular calcifications**, but the widespread, diffuse calcifications (cortex, basal ganglia, periventricular) are less typical than with toxoplasmosis, which often shows more diffuse parenchymal calcifications.
- While it shares features like small for gestational age, icterus, and purpura, **posterior uveitis** is more strongly associated with toxoplasmosis.
*Congenital rubella infection*
- Classic triad includes **cataracts** (or glaucoma), **sensorineural hearing loss**, and **congenital heart defects** (e.g., PDA, pulmonary artery stenosis).
- While CNS involvement (e.g., intellectual disability, microcephaly) can occur, the widespread cerebral calcifications and posterior uveitis are not characteristic.
Teratogenic exposures US Medical PG Question 7: A 26-year-old woman comes to the physician for evaluation of nausea and fatigue. Her last menstrual period was 8 weeks ago. She has a history of bipolar disorder controlled by a drug known to sometimes cause hypothyroidism and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. She does not smoke cigarettes or drink alcohol. A urine pregnancy test is positive. An ultrasound of the pelvis shows a viable intrauterine pregnancy. The fetus is most likely at increased risk for which of the following anomalies?
- A. Neural tube defects
- B. Aplasia cutis
- C. Hypoplastic or absent limbs
- D. Abnormal placentation
- E. Atrialization of the right ventricle (Correct Answer)
Teratogenic exposures Explanation: ***Atrialization of the right ventricle***
- The patient's history of **bipolar disorder** controlled by a drug causing **hypothyroidism** and **nephrogenic diabetes insipidus** strongly points to **lithium**.
- **Lithium** exposure during the first trimester of pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of **Ebstein's anomaly**, which involves the **apical displacement of the tricuspid valve** leaflets leading to **atrialization of the right ventricle**.
*Neural tube defects*
- These anomalies are often associated with deficiencies in **folic acid** or exposure to certain **antiepileptic drugs** like valproate, not lithium.
- While concerning, there is no information in the vignette to suggest these specific risk factors exist for this patient besides lithium use.
*Aplasia cutis*
- This is a localized absence of skin at birth, most commonly on the scalp. It is associated with gestational exposure to **methimazole** or **carbimazole**, used to treat hyperthyroidism, which is not indicated here.
- There is no direct link between lithium exposure and aplasia cutis.
*Hypoplastic or absent limbs*
- This type of anomaly is historically associated with exposure to **thalidomide** during early pregnancy.
- Lithium is not known to cause limb reduction defects.
*Abnormal placentation*
- Conditions like **placenta previa** or **placenta accreta** can result from previous uterine surgery (e.g., C-section) or advanced maternal age.
- Lithium use is not a recognized risk factor for abnormal placentation.
Teratogenic exposures US Medical PG Question 8: A 6-year-old boy is brought in for evaluation by his adopted mother due to trouble starting 1st grade. His teacher has reported that he has been having trouble focusing on tasks and has been acting out while in class. His family history is unknown as he was adopted 2 years ago. His temperature is 36.2°C (97.2°F), pulse is 80/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure 110/70 mm Hg. Visual inspection of the boy's face shows a low set nasal bridge, a smooth philtrum, and small lower jaw. Which of the following findings would also likely be found on physical exam?
- A. Cataracts
- B. Congenital deafness
- C. Holosystolic murmur (Correct Answer)
- D. Limb hypoplasia
- E. Wide notched teeth
Teratogenic exposures Explanation: **Holosystolic murmur**
- The child exhibits classic features of **fetal alcohol syndrome** (FAS), including the distinctive facial anomalies (low set nasal bridge, smooth philtrum, small lower jaw) and developmental/behavioral issues (trouble focusing, acting out).
- Up to 50% of children with FAS develop **congenital heart defects**, with **ventricular septal defects (VSDs)** being the most common, which are characterized by a **holosystolic murmur** at the lower left sternal border.
*Cataracts*
- **Cataracts** are not a typical feature of fetal alcohol syndrome but are often associated with congenital infections such as **rubella** or **cytomegalovirus**.
- While some genetic syndromes can include cataracts, they are not a primary finding for the constellation of symptoms observed here.
*Congenital deafness*
- **Congenital deafness** is not a hallmark of fetal alcohol syndrome; rather, it is commonly associated with congenital infections like **rubella**, **CMV**, or genetic syndromes such as **CHARGE syndrome**.
- Children with FAS may have hearing problems due to recurrent ear infections, but not typically congenital deafness.
*Limb hypoplasia*
- **Limb hypoplasia** is typically seen in conditions like **thalidomide embryopathy** or certain genetic syndromes, such as **Roberts syndrome**.
- While growth restriction is common in FAS, significant limb hypoplasia as described is not a characteristic feature.
*Wide notched teeth*
- **Wide notched teeth**, also known as **Hutchinson teeth**, are pathognomonic for **congenital syphilis**.
- This finding is unrelated to fetal alcohol syndrome, and the patient's other symptoms do not suggest congenital syphilis.
Teratogenic exposures US Medical PG Question 9: A 26-year-old G1P0 mother is in the delivery room in labor. Her unborn fetus is known to have a patent urachus. Which of the following abnormalities would you expect to observe in the infant?
- A. Myelomeningocele
- B. Gastroschisis
- C. Urine discharge from umbilicus (Correct Answer)
- D. Omphalocele
- E. Meconium discharge from umbilicus
Teratogenic exposures Explanation: ***Urine discharge from umbilicus***
- A **patent urachus** is a congenital anomaly where the **urachus**, a remnant of the **allantois**, fails to close completely, allowing a direct connection between the bladder and the umbilicus.
- This patent tract results in the **continuous discharge of urine from the umbilicus**, especially upon crying or straining, as the bladder pressure increases.
*Myelomeningocele*
- **Myelomeningocele** is a severe form of **spina bifida** where the spinal cord and nerves protrude through an opening in the back.
- It results from incomplete closure of the neural tube and is not directly related to the urachus or umbilical discharge.
*Gastroschisis*
- **Gastroschisis** is a birth defect where the intestines protrude through an opening in the abdominal wall, typically to the right of the umbilicus.
- Unlike a patent urachus, it involves the protrusion of abdominal contents and is not associated with umbilical urine discharge.
*Omphalocele*
- An **omphalocele** is a birth defect in which parts of the abdominal organs, such as the intestines, liver, or stomach, protrude through the umbilical opening, covered by a sac.
- This condition is also an abdominal wall defect but distinct from a patent urachus, which specifically involves the connection between the bladder and the umbilicus.
*Meconium discharge from umbilicus*
- **Meconium discharge from the umbilicus** would suggest a persistent communication between the bowel and the umbilicus, rather than the bladder.
- This condition, known as a **patent vitelline duct** or omphalomesenteric duct, is anatomically distinct from a patent urachus.
Teratogenic exposures US Medical PG Question 10: A 24-year-old woman comes to the physician for preconceptional advice. She has been married for 2 years and would like to conceive within the next year. Menses occur at regular 30-day intervals and last 4 days with normal flow. She does not smoke or drink alcohol and follows a balanced diet. She takes no medications. She is 160 cm (5 ft 3 in) tall and weighs 55 kg (121 lb); BMI is 21.5 kg/m2. Physical examination, including pelvic examination, shows no abnormalities. She has adequate knowledge of the fertile days of her menstrual cycle. Which of the following is most appropriate recommendation for this patient at this time?
- A. Begin high-dose vitamin A supplementation
- B. Begin vitamin B12 supplementation
- C. Begin folate supplementation (Correct Answer)
- D. Begin iron supplementation
- E. Gain 2 kg prior to conception
Teratogenic exposures Explanation: ***Begin folate supplementation***
- **Folate supplementation** of 400 mcg daily is recommended for all women of childbearing age to reduce the risk of **neural tube defects** (NTDs) in the fetus. This should ideally begin at least one month before conception and continue through the first trimester.
- The patient is planning to conceive, making preemptive folate supplementation critical for preventing serious birth defects.
*Begin high-dose vitamin A supplementation*
- **High-dose vitamin A** (more than 10,000 IU/day) can be **teratogenic** and is therefore contraindicated during preconception and pregnancy.
- While vitamin A is essential for fetal development, excessive amounts can lead to fetal abnormalities.
*Begin vitamin B12 supplementation*
- **Vitamin B12 supplementation** is generally not necessary unless the patient has a diagnosed deficiency, such as in strict vegetarians or those with malabsorption issues.
- There is no indication of B12 deficiency in this patient's history or presentation.
*Begin iron supplementation*
- Routine **iron supplementation** is not recommended preconception unless the patient is diagnosed with **iron deficiency anemia**.
- Excessive iron intake without a clear indication can cause gastrointestinal upset and has not been shown to improve pregnancy outcomes in non-anemic women.
*Gain 2 kg prior to conception*
- The patient has a **healthy BMI of 21.5 kg/m2**, which is within the normal range (18.5-24.9 kg/m2).
- There is no medical indication for her to gain weight prior to conception.
More Teratogenic exposures US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.