Skeletal dysplasias US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Skeletal dysplasias. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Skeletal dysplasias US Medical PG Question 1: A 27-year-old G1P0 at 12 weeks gestation presents to her obstetrician for her first prenatal visit. She and her husband both have achondroplasia, and she is curious what are the chances that they will have a child of average height. What percent of pregnancies between two individuals with achondroplasia that result in a live birth will be expected to be offspring that are unaffected by this condition?
- A. 0%
- B. 50%
- C. 75%
- D. 33% (Correct Answer)
- E. 25%
Skeletal dysplasias Explanation: ***33%***
- Achondroplasia is an **autosomal dominant** condition, meaning only one copy of the mutated gene is needed to express the trait. However, individuals with achondroplasia are typically **heterozygous (Aa)** because the homozygous dominant state (AA) is **lethal in utero** or shortly after birth.
- When two heterozygous (Aa) parents mate, a Punnett square shows 25% AA, 50% Aa, and 25% aa. Since AA is a lethal genotype that is not viable for live birth, the surviving offspring will be 1/3 aa (unaffected) and 2/3 Aa (affected), meaning 33% will be of average height.
*0%*
- This would be true if all offspring were affected or if the condition was recessive and both parents were homozygous dominant, which is not the case for achondroplasia.
- The possibility of having an unaffected child exists because affected individuals are generally heterozygous.
*50%*
- This would be the percentage of affected offspring if one parent was homozygous dominant and the other was homozygous recessive, or if one parent was homozygous dominant and the other heterozygous.
- However, autosomal dominant traits typically result in a 2:1 ratio of affected to unaffected live births when both parents are heterozygous.
*75%*
- This would be the percentage of affected offspring if the homozygous dominant state were not lethal, resulting in 25% aa, 50% Aa, and 25% AA.
- Achondroplasia, however, has a **lethal homozygous dominant genotype**, which alters the observed phenotypic ratios in live births.
*25%*
- This percentage represents the chance of having an unaffected offspring (aa) before considering the lethality of the homozygous dominant genotype (AA).
- When accounting for the non-viability of AA genotypes, the proportion of unaffected offspring among live births increases.
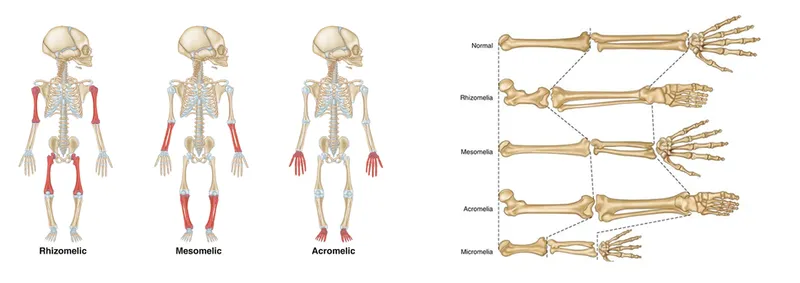
Skeletal dysplasias US Medical PG Question 2: A 4-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician by his mother for a routine medical examination. His medical history is relevant for delayed gross motor milestones. The mother is concerned about a growth delay because both of his brothers were twice his size at this age. Physical examination reveals a well-groomed and healthy boy with a prominent forehead and short stature, in addition to shortened upper and lower extremities with a normal vertebral column. The patient’s vitals reveal: temperature 36.5°C (97.6°F); pulse 60/min; and respiratory rate 17/min and a normal intelligence quotient (IQ). A mutation in which of the following genes is the most likely cause underlying the patient’s condition?
- A. Runt-related transcription factor 2
- B. Alpha-1 type I collagen
- C. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (Correct Answer)
- D. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- E. Fibrillin-1
Skeletal dysplasias Explanation: ***Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3***
- The constellation of **short stature**, prominent forehead, and **shortened upper and lower extremities** with a normal vertebral column in a child with normal intelligence is characteristic of **achondroplasia**.
- Achondroplasia is caused by a gain-of-function mutation in the **fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3)** gene, which inhibits chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation, leading to impaired endochondral ossification.
*Runt-related transcription factor 2*
- Mutations in **Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2)** are associated with **cleidocranial dysplasia**, a condition characterized by absent or hypoplastic clavicles, delayed closure of fontanelles, and dental abnormalities, which are not described in this patient.
- While it affects bone development, the specific features of achondroplasia, such as rhizomelic dwarfism and a prominent forehead, are not typical of RUNX2 mutations.
*Alpha-1 type I collagen*
- Mutations in **collagen genes**, particularly type I collagen (COL1A1, COL1A2), are linked to **osteogenesis imperfecta**, characterized by **fragile bones**, blue sclera, and hearing loss.
- The patient's presentation does not include these features, and the primary issue is disproportionate short stature due to impaired cartilage growth, not bone fragility.
*Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor*
- Mutations in the **insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R)** can lead to **pre- and postnatal growth retardation** and microcephaly, often associated with developmental delay and feeding difficulties.
- While IGF1R mutations cause short stature, the specific skeletal dysmorphology (e.g., prominent forehead, shortened limbs) and normal intelligence are much more suggestive of achondroplasia.
*Fibrillin-1*
- Mutations in **fibrillin-1** are responsible for **Marfan syndrome**, which typically presents with **tall stature**, long limbs (dolichostenomelia), joint hypermobility, and cardiovascular abnormalities such as aortic root dilation.
- The patient's short stature and shortened limbs directly contradict the clinical picture of Marfan syndrome.
Skeletal dysplasias US Medical PG Question 3: An 11-year-old girl presents to her primary care physician because she has been having difficulty hearing her teachers at school. She says that the difficulty hearing started about a year ago, and it has slowly been getting worse. Her past medical history is significant for multiple fractures in both her upper and lower extremities. She also recently had a growth spurt and says that her friends say she is tall and lanky. A mutation in which of the following genes is most likely associated with this patient's condition?
- A. Type 4 collagen
- B. Type 3 collagen
- C. Fibrillin
- D. Type 1 collagen (Correct Answer)
- E. Fibroblast growth factor receptor
Skeletal dysplasias Explanation: ***Type 1 collagen***
- This patient's symptoms—hearing difficulty, multiple fractures, and tall/lanky stature—are classic signs of **osteogenesis imperfecta (OI)**, a genetic disorder caused by mutations in genes encoding **Type I collagen**.
- **Type I collagen** is a major component of bone, so defects lead to fragile bones and susceptibility to fractures, and it also plays a role in the structure of the ear, affecting hearing.
*Type 4 collagen*
- Mutations in **Type 4 collagen** are primarily associated with **Alport syndrome**, which classically presents with **hematuria**, progressive renal failure, and hearing loss.
- While hearing loss is present, the patient's other key symptoms of **multiple fractures** and **tall, lanky stature** are not characteristic of Alport syndrome.
*Type 3 collagen*
- Defects in **Type 3 collagen** are linked to **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, vascular type**, which is characterized by fragile blood vessels, organs, and skin, leading to easy bruising, arterial rupture, and bowel perforation.
- While Type 3 collagen is found in connective tissues, its primary clinical manifestations do not align with the patient's presentation of recurrent fractures and hearing loss.
*Fibrillin*
- Mutations in **fibrillin-1** are responsible for **Marfan syndrome**, which presents with tall stature, long limbs (**arachnodactyly**), and cardiovascular issues like aortic dilation.
- While tall stature is observed, the patient's primary complaints of **recurrent fractures** and hearing loss are not typical features of Marfan syndrome.
*Fibroblast growth factor receptor*
- Mutations in **fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3)** are most commonly associated with **achondroplasia**, a form of dwarfism characterized by short stature, short limbs, and a large head.
- This is inconsistent with the patient's **tall and lanky stature** and does not account for the recurrent fractures or hearing difficulties.
Skeletal dysplasias US Medical PG Question 4: A 15-year-old boy comes to the physician for the evaluation of progressive difficulty climbing stairs for the last 2 years. During this period, he has also had problems running and standing up from a seated position. He is at the 50th percentile for height and weight. Examination shows enlarged calf muscles bilaterally and a waddling gait. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Large deletions (Correct Answer)
- B. Frameshift mutation
- C. Splice site mutation
- D. Missense mutation
- E. Nonsense mutation
Skeletal dysplasias Explanation: ***Large deletions***
- The presented symptoms (progressive difficulty climbing stairs, running, standing, enlarged calf muscles, waddling gait) are classic for **Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)**.
- **Large deletions** (involving one or more exons) are the **most common cause of DMD**, accounting for approximately **60-70%** of cases.
- These deletions typically cause a **frameshift** that leads to a premature stop codon, resulting in absent or severely truncated **dystrophin protein**.
- The **dystrophin gene** is one of the largest human genes, making it particularly susceptible to deletion mutations.
*Frameshift mutation*
- A **frameshift mutation** (insertion or deletion of nucleotides not in multiples of three) leads to an altered reading frame, resulting in a **premature stop codon** downstream.
- While frameshifts do cause **DMD**, they are typically the **consequence** of deletions or small insertions/duplications, not a primary mutation category.
- The question asks for the underlying genetic cause, which is most commonly a large deletion.
*Splice site mutation*
- **Splice site mutations** affect the splicing of introns and exons, potentially leading to exon skipping or inclusion of intronic sequences.
- These account for a small percentage of **DMD** cases but are much less common than large deletions.
- While they can disrupt the reading frame, they represent a minority of causative mutations.
*Missense mutation*
- A **missense mutation** results in a single amino acid change, producing an altered but full-length protein.
- This type of mutation is more characteristic of **Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD)**, a milder form with later onset and slower progression.
- The severe, early-onset phenotype described here is typical of **DMD**, which requires near-complete absence of functional dystrophin.
*Nonsense mutation*
- A **nonsense mutation** introduces a premature stop codon, leading to a truncated protein.
- While nonsense mutations do cause **DMD**, they account for only about **10-15%** of cases as part of the broader category of point mutations.
- Large deletions remain significantly more common as the causative mutation type.
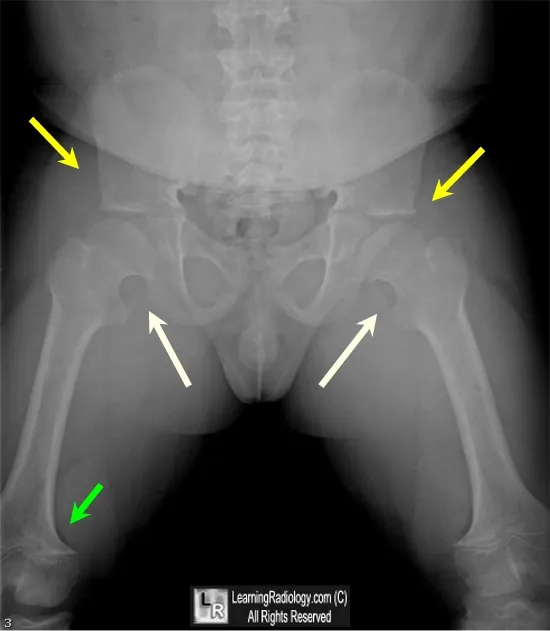
Skeletal dysplasias US Medical PG Question 5: A 2860-g (6-lb 3-oz) male newborn is born at term to a primigravid woman via spontaneous vaginal delivery. The mother has had no routine prenatal care. She reports that there is no family history of serious illness. The initial examination of the newborn shows bowing of the legs and respiratory distress upon palpation of the chest. The skin and joints are hyperextensible. X-rays of the chest and skull show multiple rib fractures and small, irregular bones along the cranial sutures. The patient is at increased risk of which of the following complications?
- A. Hearing loss (Correct Answer)
- B. Spinal canal stenosis
- C. Costochondral junction enlargement
- D. Intestinal rupture
- E. Intellectual disability
Skeletal dysplasias Explanation: ***Hearing loss***
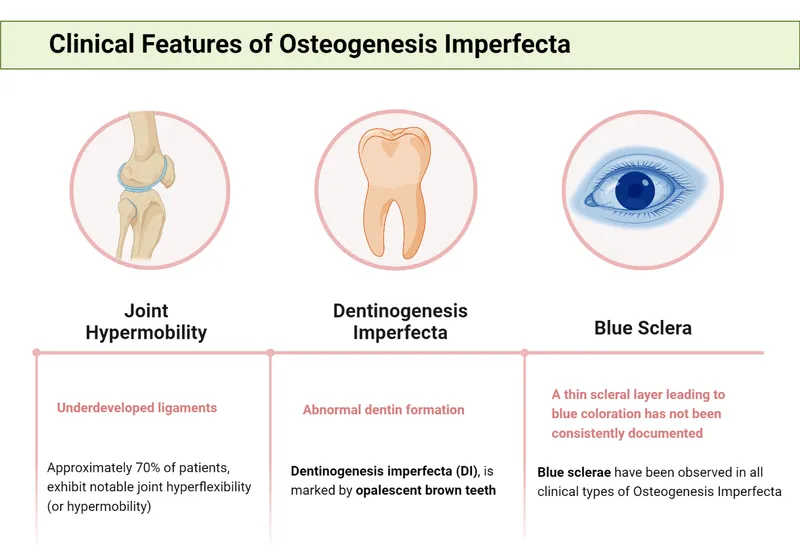
- The described clinical picture of **bone fragility (multiple rib fractures, bowing of legs)**, **hyperextensible skin and joints**, and **wormian bones** (small, irregular bones along cranial sutures) is classic for **osteogenesis imperfecta (OI)**.
- Individuals with OI are at increased risk for **conductive or sensorineural hearing loss**, which can manifest in childhood or adolescence.
*Spinal canal stenosis*
- While patients with OI can develop **scoliosis** and **vertebral compression fractures**, resulting in spinal cord compression, **spinal canal stenosis** itself is not a primary or direct complication of the underlying collagen defect in the same way hearing loss is.
- The primary spinal complications are related to **vertebral fractures** and **deformities**.
*Costochondral junction enlargement*
- **Costochondral junction enlargement** (rachitic rosary) is a hallmark of **rickets**, a disorder of **vitamin D or phosphate metabolism**, not osteogenesis imperfecta.
- The described features point to a **collagen synthesis defect**, not mineralization issues.
*Intestinal rupture*
- While there can be some smooth muscle abnormalities, **intestinal rupture** is not a commonly described or significant complication of osteogenesis imperfecta.
- The primary systemic manifestations relate to **collagen defects** in bone, skin, tendons, and blood vessels, but not typically leading to spontaneous gastrointestinal rupture.
*Intellectual disability*
- **Intellectual function** is typically **unaffected** in osteogenesis imperfecta.
- The disease primarily affects **connective tissue**, particularly bone development, and does not directly cause cognitive impairment.
Skeletal dysplasias US Medical PG Question 6: A 13-year-old boy presents with jaundice, fatigue, muscle stiffness, tremors, and behavioral changes. Examination reveals an enlarged liver and spleen. A Kayser-Fleischer ring was noted. What is the definitive diagnostic test?
- A. Urinary copper
- B. Serum ceruloplasmin
- C. Hepatic parenchymal copper concentration (Correct Answer)
- D. Slit lamp examination
- E. Genetic testing for ATP7B mutation
Skeletal dysplasias Explanation: ***Hepatic parenchymal copper concentration***
- This is considered the **gold standard** for diagnosing **Wilson's disease**, as it directly measures the accumulation of copper in the liver, which is the hallmark of the condition.
- A concentration of **>250 mcg/g of dry liver weight** is diagnostic of Wilson's disease, irrespective of other laboratory findings.
*Urinary copper*
- While **elevated 24-hour urinary copper excretion** is a common finding in Wilson's disease, it can also be influenced by other conditions and may not always be definitively diagnostic on its own.
- It is a **screening tool** and part of the diagnostic workup, but not the definitive diagnostic test as it's an indirect measure of copper overload.
*Serum ceruloplasmin*
- **Low serum ceruloplasmin levels** are characteristic of Wilson's disease because ceruloplasmin is the primary copper-carrying protein in the blood.
- However, ceruloplasmin levels can be **normal in some Wilson's patients**, especially those presenting with hepatic manifestations, and can be low in other conditions like severe liver failure or malabsorption.
*Slit lamp examination*
- A **slit lamp examination** is used to identify **Kayser-Fleischer rings**, which are corneal copper deposits.
- While their presence is highly suggestive of Wilson's disease, especially with neurological symptoms, they **may be absent in up to 30-50% of patients** with hepatic-only presentations, and their absence does not rule out the disease.
*Genetic testing for ATP7B mutation*
- **Molecular genetic testing** can identify mutations in the ATP7B gene, which encodes the copper-transporting ATPase.
- While highly specific for confirming Wilson's disease and useful for family screening, it is a **confirmatory test** rather than the definitive diagnostic test, as over 500 different mutations exist and not all are identified in routine testing.
- Hepatic copper measurement remains the diagnostic standard as it directly demonstrates the pathophysiologic defect.
Skeletal dysplasias US Medical PG Question 7: A child presents with a webbed neck, short stature, and a low posterior hairline. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Edwards syndrome
- B. Turner syndrome (Correct Answer)
- C. Patau syndrome
- D. Down syndrome
- E. Noonan syndrome
Skeletal dysplasias Explanation: ***Turner syndrome***
- **Turner syndrome** is characterized by the presence of a **single X chromosome (45,XO)** and is associated with a **webbed neck**, **short stature**, and a **low posterior hairline**.
- Other classic features include **gonadal dysgenesis**, **cardiac anomalies** (e.g., coarctation of the aorta), and **renal anomalies**.
- **Occurs only in females** due to the chromosomal abnormality.
*Edwards syndrome*
- **Edwards syndrome** (Trisomy 18) is characterized by severe developmental delays, a **rocker-bottom feet deformity**, **micrognathia**, and **clenched hands with overlapping fingers**.
- **Webbed neck** and **short stature** are not primary distinguishing features of Edwards syndrome.
*Patau syndrome*
- **Patau syndrome** (Trisomy 13) is associated with severe midline defects, including **cleft lip and palate**, **polydactyly**, **microphthalmia**, and **holoprosencephaly**.
- It does not typically present with a **webbed neck** or a **low posterior hairline**.
*Down syndrome*
- **Down syndrome** (Trisomy 21) is typically characterized by **upslanting palpebral fissures**, a **single palmar crease**, **intellectual disability**, and **cardiac defects**.
- While **short stature** can be present, the classic combination of a **webbed neck** and **low posterior hairline** is not characteristic of Down syndrome.
*Noonan syndrome*
- **Noonan syndrome** shares phenotypic similarities with Turner syndrome, including **webbed neck**, **short stature**, and **cardiac defects** (especially pulmonary stenosis).
- However, it occurs in **both males and females** with a **normal karyotype** and is caused by mutations in genes of the RAS-MAPK pathway.
- Key differentiating features include **pectus excavatum**, **cryptorchidism in males**, and the absence of gonadal dysgenesis.
Skeletal dysplasias US Medical PG Question 8: What is the characteristic metabolic finding in a baby with Congenital Hypertrophic Pyloric Stenosis (CHPS)?
- A. Mixed acid-base disorder with hyperkalemia
- B. Hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis (Correct Answer)
- C. Metabolic acidosis with hyperchloremia
- D. Respiratory alkalosis with hyponatremia
- E. Hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis with hypokalemia
Skeletal dysplasias Explanation: ***Hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis***
- The persistent **vomiting** in CHPS leads to a significant loss of gastric acid (HCl), causing profound **hypochloremia** and an increase in serum bicarbonate.
- This loss of stomach acid results in a shift towards alkalinity, manifesting as a **metabolic alkalosis**.
- **Hypokalemia** also develops due to renal compensation mechanisms and urinary potassium losses.
*Mixed acid-base disorder with hyperkalemia*
- While electrolyte imbalances can be complex, **hyperkalemia** is not a characteristic finding; rather, **hypokalemia** is common due to renal compensation for metabolic alkalosis.
- A **mixed acid-base disorder** is less specific than the classic hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis seen in CHPS.
*Metabolic acidosis with hyperchloremia*
- **Metabolic acidosis** would imply a gain of acid or loss of alkali, which is contrary to the loss of acid from vomiting in CHPS.
- **Hyperchloremia** is also incorrect; the characteristic finding is **hypochloremia** due to the loss of gastric HCl.
*Respiratory alkalosis with hyponatremia*
- **Respiratory alkalosis** is caused by hyperventilation and is not directly related to the pathophysiology of CHPS.
- While **hyponatremia** can occur in severe dehydration, it is not the primary or most characteristic electrolyte derangement in CHPS, which is marked by hypochloremia and hypokalemia.
*Hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis with hypokalemia*
- This combines incorrect elements: **hyperchloremia** and **metabolic acidosis** are opposite to what occurs in CHPS.
- While **hypokalemia** is correct, the acid-base and chloride abnormalities are wrong.
- CHPS causes **hypochloremia** and **metabolic alkalosis**, not hyperchloremia and acidosis.
Skeletal dysplasias US Medical PG Question 9: A 1-year-old Caucasian male is on pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT) to maintain a healthy body mass index. Sweat chloride test is 68 mmol/L (< 29 mmol/L = normal). The patient has a relative who was also on PERT but passed away in his mid-20s due to respiratory failure, and was unable to have children. Which of the following would be most improved by PERT?
- A. Hypoglycemia
- B. A lack of respiratory infections
- C. Bone mineral density (Correct Answer)
- D. Expression of the autosomal recessive mutations of CFTR gene
- E. Nasal polyps
Skeletal dysplasias Explanation: ***Bone mineral density***
- **Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT)** improves digestion and absorption of nutrients, including fat-soluble vitamins like **vitamin D** and calcium.
- Improved nutrient absorption directly leads to better **bone mineralization** and increased **bone mineral density**, addressing the malabsorption-related bone issues common in **cystic fibrosis (CF)**.
*Hypoglycemia*
- **PERT** primarily addresses **exocrine pancreatic insufficiency**, improving the digestion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins.
- While CF can eventually lead to **CF-related diabetes mellitus (CFRD)** with **hyperglycemia**, PERT does not directly treat endocrine dysfunction or regulate blood glucose levels.
- **Hypoglycemia** is not a typical manifestation of CF; PERT's role is in nutrient absorption, not blood glucose regulation.
*A lack of respiratory infections*
- **PERT** is specifically designed to alleviate symptoms related to **pancreatic insufficiency**, such as malabsorption and nutritional deficiencies.
- It does not directly affect the underlying **CFTR gene defect** in the lungs, which is responsible for the thick mucus and susceptibility to **respiratory infections**.
*Expression of the autosomal recessive mutations of CFTR gene*
- **PERT** provides exogenous digestive enzymes to compensate for the lack of endogenous enzymes in individuals with **cystic fibrosis**.
- It treats the symptoms of **pancreatic insufficiency** but does not alter the underlying **genetic mutation** or its expression.
*Nasal polyps*
- **Nasal polyps** are a common manifestation of **cystic fibrosis**, resulting from chronic inflammation and mucus accumulation in the nasal passages.
- **PERT** targets digestive issues and has no direct impact on the development or resolution of **nasal polyps**.
Skeletal dysplasias US Medical PG Question 10: A 12-year-old boy presents to the pediatrician for a routine checkup. He and his family immigrated from Pakistan to the United States when he was 9 years of age. Per his mother, he had measles when he was 4 years of age and a high fever following a sore throat at the age 7. He received all appropriate vaccinations when he arrived in the United States. He takes no medications. He does well academically and plays soccer in a recreational league. He was born at 38 weeks gestation. His temperature is 98.4°F (36.9°C), blood pressure is 115/65 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, and respirations are 18/min. On exam, he is a healthy boy in no apparent distress. Breath sounds are equal bilaterally with good aeration. Fixed splitting of the second heart sound is noted on auscultation. Without adequate treatment, this patient will be at increased risk for developing which of the following?
- A. Extra-cardiac left-to-right shunting
- B. Reversal of left-to-right shunting (Correct Answer)
- C. Acute endocarditis
- D. Mitral stenosis
- E. Mitral regurgitation
Skeletal dysplasias Explanation: ***Reversal of left-to-right shunting***
- The presence of **fixed splitting of the second heart sound** is a classic sign of an **atrial septal defect (ASD)**, a left-to-right shunt.
- Without adequate treatment, a long-standing left-to-right shunt can lead to **pulmonary hypertension** and eventual **Eisenmenger syndrome**, characterized by reversal of the shunt (right-to-left shunting) and cyanosis.
*Extra-cardiac left-to-right shunting*
- An ASD is an **intra-cardiac** shunt, not an extra-cardiac shunt.
- **Extra-cardiac shunts** typically involve vessels outside the heart, such as a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) which connects the aorta and pulmonary artery.
*Acute endocarditis*
- Patients with **secundum ASDs** (the type causing fixed splitting of S2) have a **low risk for infective endocarditis** and do not require prophylaxis according to current guidelines.
- While the patient's history of **streptococcal pharyngitis** (sore throat at age 7) could suggest **rheumatic fever**, the key finding of fixed S2 splitting points to a congenital heart defect (ASD), not acquired valvular disease.
*Mitral stenosis*
- **Mitral stenosis** is a narrowing of the mitral valve, often caused by **rheumatic fever**. While the patient's history of a high fever following a sore throat at age 7 might suggest rheumatic fever, fixed splitting of S2 is not a characteristic finding of mitral stenosis.
- Instead, mitral stenosis typically presents with a **diastolic murmur** and signs of left atrial enlargement.
*Mitral regurgitation*
- **Mitral regurgitation** is the leakage of blood backward through the mitral valve. Like mitral stenosis, it can be a complication of **rheumatic heart disease**.
- However, fixed splitting of S2 is not a typical finding for isolated mitral regurgitation, which presents with a **holosystolic murmur** best heard at the apex with radiation to the axilla.
More Skeletal dysplasias US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.