Preventive strategies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Preventive strategies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
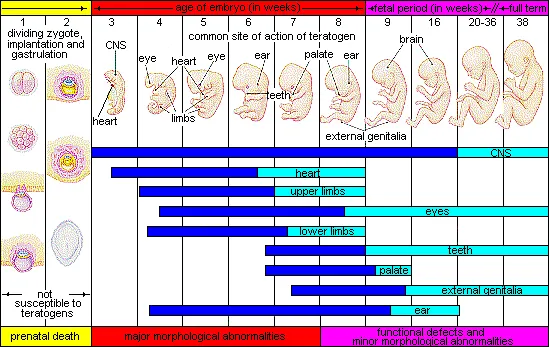
Preventive strategies US Medical PG Question 1: A 21-year-old G3P2 woman presents to her obstetrician at 6 weeks gestation for routine prenatal care. Her past medical history includes obesity and gestational diabetes. She has had two spontaneous vaginal deliveries at term. One infant was macrosomic with hypoglycemia, but otherwise, she has had no complications. Her physician informs her that she must start taking a multivitamin with folic acid daily. The defect that folic acid supplementation protects against arises in tissue that is derived from which germ cell layer?
- A. Mesoderm
- B. Notochord
- C. Endoderm
- D. Mesenchyme
- E. Ectoderm (Correct Answer)
Preventive strategies Explanation: ***Ectoderm***
- Folic acid supplementation primarily prevents **neural tube defects**, such as **spina bifida** and **anencephaly**.
- The **neural tube**, which forms the brain and spinal cord, is derived from the **ectoderm**.
*Mesoderm*
- The **mesoderm** gives rise to structures like muscle, bone, connective tissue, and the cardiovascular system.
- Defects in mesodermal development are not primarily prevented by folic acid supplementation.
*Notochord*
- The **notochord** is a transient embryonic structure that induces the formation of the neural plate from the ectoderm.
- While critical for nervous system development, it is not a germ cell layer itself, and defects in its development are not directly prevented by folic acid.
*Endoderm*
- The **endoderm** forms the lining of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts, as well as glands like the thyroid and pancreas.
- Anomalies of these internal organs are not the primary target of folic acid supplementation.
*Mesenchyme*
- **Mesenchyme** is embryonic connective tissue, largely derived from the mesoderm, but can also come from neural crest (ectoderm).
- It differentiates into connective tissues, blood, and lymphatic vessels; neural tube defects are not considered mesenchymal in origin.
Preventive strategies US Medical PG Question 2: A 24-year-old woman visits her physician to seek preconception advice. She is recently married and plans to have a child soon. Menses occur at regular 28-day intervals and last 5 days. She has sexual intercourse only with her husband and, at this time, they consistently use condoms for birth control. The patient consumes a well-balanced diet with moderate intake of meat and dairy products. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications currently. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. The patient’s history reveals no birth defects or severe genetic abnormalities in the family. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Pelvic examination indicates a normal vagina, cervix, uterus, and adnexa. To decrease the likelihood of fetal neural-tube defects in her future pregnancy, which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation for initiation of folic acid supplementation?
- A. As soon as her pregnancy is confirmed
- B. No folic acid supplement is required as nutritional sources are adequate
- C. As soon as possible (Correct Answer)
- D. When off contraception
- E. In the second half of pregnancy
Preventive strategies Explanation: ***As soon as possible***
- Folic acid supplementation is crucial for preventing **neural tube defects (NTDs)**, which occur very early in pregnancy, often before a woman even knows she is pregnant.
- To be effective, supplementation should begin at least **one month prior to conception** and continue through the first trimester.
*As soon as her pregnancy is confirmed*
- This timing is too late because **neurulation** (the formation of the neural tube) is completed by the **28th day post-conception**, often before a pregnancy is confirmed.
- Delaying supplementation until confirmation significantly reduces its preventative effect against neural tube defects.
*No folic acid supplement is required as nutritional sources are adequate*
- While a balanced diet contains some folic acid, it is generally **insufficient** to reach the protective levels needed to prevent NTDs.
- The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and other health organizations recommend universal folic acid supplementation for all women of childbearing age, regardless of diet.
*When off contraception*
- Although discontinuing contraception indicates an intent to conceive, starting folic acid *only* at this point might still be too late.
- It's recommended to start supplementation at least **1 month before attempting conception** to ensure adequate folate levels at the critical time of neural tube closure.
*In the second half of pregnancy*
- Supplementing in the second half of pregnancy is **too late** to prevent neural tube defects.
- By this stage, the neural tube has already fully developed or failed to close, and supplementation will not reverse any existing defects.
Preventive strategies US Medical PG Question 3: A 26-year-old gravida 3 para 1 is admitted to labor and delivery with uterine contractions. She is at 37 weeks gestation with no primary care provider or prenatal care. She gives birth to a boy after an uncomplicated vaginal delivery with APGAR scores of 7 at 1 minute and 8 at 5 minutes. His weight is 2.2 kg (4.4 lb) and the length is 48 cm (1.6 ft). The infant has weak extremities and poor reflexes. The physical examination reveals microcephaly, palpebral fissures, thin lips, and a smooth philtrum. A systolic murmur is heard on auscultation. Identification of which of the following factors early in the pregnancy could prevent this condition?
- A. Phenytoin usage
- B. Maternal hypothyroidism
- C. Alcohol consumption (Correct Answer)
- D. Physical abuse
- E. Maternal toxoplasmosis
Preventive strategies Explanation: ***Alcohol consumption***
- The constellation of **microcephaly**, **palpebral fissures**, **thin lips**, **smooth philtrum**, and **cardiac defects** (systolic murmur) in an infant points to **Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS)**.
- **FAS** is entirely preventable if alcohol is avoided during pregnancy, especially early in gestation, as there is no safe amount or time to drink alcohol during pregnancy.
*Phenytoin usage*
- **Phenytoin** is associated with **fetal hydantoin syndrome**, which can present with microcephaly, distinct facial features (e.g., broad nasal bridge, epicanthal folds), and hypoplastic nails, but typically not the specific facial features of FAS.
- While it is a teratogen, preventing its use would not specifically address the described clinical picture, which strongly aligns with alcohol exposure.
*Maternal hypothyroidism*
- **Untreated maternal hypothyroidism** can lead to **neurodevelopmental delays** and **cognitive impairment** in the child.
- It does not, however, cause the characteristic facial dysmorphology or cardiac defects seen in FAS.
*Physical abuse*
- **Physical abuse** does not cause congenital malformations or a specific syndrome evident at birth like FAS.
- While it is a serious concern for maternal and fetal well-being, it is not a direct teratogenic cause of the described neonatal findings.
*Maternal toxoplasmosis*
- **Congenital toxoplasmosis** can cause hydrocephalus, chorioretinitis, and intracranial calcifications.
- It does not cause the specific facial dysmorphology, cardiac defects, or microcephaly seen in this infant.
Preventive strategies US Medical PG Question 4: A 37-year-old woman comes for a follow-up prenatal visit at 18 weeks' gestation. At 12 weeks' gestation, ultrasonography showed increased nuchal translucency and pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A) was decreased by 2 standard deviations. Chorionic villus sampling showed a 47, XX, +21 karyotype. During this visit, ultrasonography shows a hypoplastic nasal bone, shortened femur length, shortened middle phalanges of the fifth digits with clinodactyly. A quadruple marker test would most likely show which of the following sets of findings?
$$$ α-Fetoprotein (AFP) %%% Estriol %%% β-Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) %%% Inhibin A $$$
- A. ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
- B. ↑ normal normal normal
- C. ↓ ↓ ↑ ↑ (Correct Answer)
- D. Normal normal normal normal
- E. ↓ ↓ ↓ normal
Preventive strategies Explanation: ***↓ ↓ ↑ ↑***
- This pattern (low **AFP**, low **estriol**, high **hCG**, high **inhibin A**) is characteristic of **Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)** in a quadruple marker screen.
- The patient's history, including **increased nuchal translucency**, low **PAPP-A**, and a **47, XX, +21 karyotype**, strongly confirms the diagnosis of Down syndrome, making this a consistent finding.
*↓ ↓ ↓ ↓*
- This pattern of uniformly low markers is not typical for **Down syndrome** and would more commonly suggest other chromosomal abnormalities or a different fetal condition altogether.
- While some markers are low in Down syndrome, the elevation of **hCG** and **inhibin A** is a key differentiator.
*↑ normal normal normal*
- An isolated elevated **AFP** is commonly associated with neural tube defects or ventral wall defects, which are not suggested by the patient's presentation.
- Down syndrome invariably affects multiple markers in a specific pattern, not just one.
*Normal normal normal normal*
- Normal quadruple markers would indicate a low risk for **chromosomal aneuploidies**, which contradicts the patient's confirmed diagnosis of **Down syndrome (47, XX, +21)**.
- This option is inconsistent with the presented clinical and previous genetic findings.
*↓ ↓ ↓ normal*
- This pattern does not align with the typical profile for **Down syndrome**, which characteristically shows elevated **hCG** and **inhibin A**.
- While **AFP** and **estriol** are decreased in Down syndrome, the normal inhibin A makes this option incorrect.
Preventive strategies US Medical PG Question 5: A 27-year-old G0P0 female presents to her OB/GYN for a preconception visit to seek advice before becoming pregnant. A detailed history reveals no prior medical or surgical history, and she appears to be in good health currently. Her vaccination history is up-to-date. She denies tobacco or recreational drug use and admits to drinking 2 glasses of wine per week. She states that she is looking to start trying to become pregnant within the next month, hopefully by the end of January. Which of the following is NOT recommended as a next step for this patient's preconception care?
- A. Begin 400 mcg folic acid supplementation
- B. Administer measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccination (Correct Answer)
- C. Obtain rubella titer
- D. Obtain varicella zoster titer
- E. Recommend inactivated influenza vaccination
Preventive strategies Explanation: ***Administer measles, mumps, rubella (MMR) vaccination***
- Live-attenuated vaccines like **MMR** are contraindicated during pregnancy and should ideally be given **at least one month prior to conception**.
- If her vaccination history is up-to-date and she plans to conceive within the month, administering MMR is not recommended at this time without confirming immunity first.
*Begin 400 mcg folic acid supplementation*
- **Folic acid supplementation** at 400 mcg daily is recommended for all women of childbearing age to prevent **neural tube defects**, ideally starting at least one month before conception and continuing through the first trimester.
- This is a crucial step in preconception care to ensure adequate levels when the neural tube is forming.
*Obtain rubella titer*
- Checking a **rubella titer** is standard preconception care to determine immunity, as rubella infection during pregnancy can lead to serious congenital anomalies.
- If she is not immune, the MMR vaccine can be offered, but with a **one-month contraception period** before attempting conception.
*Obtain varicella zoster titer*
- Determining **varicella immunity** is important because congenital varicella syndrome can occur if a non-immune mother contracts chickenpox during pregnancy.
- If she is not immune, the **varicella vaccine** can be administered, followed by a **one-month waiting period** before conception.
*Recommend inactivated influenza vaccination*
- **Inactivated influenza vaccination** is safe and recommended during any stage of pregnancy, including the preconception period, to protect both the mother and newborn from severe influenza outcomes.
- It can be given even if she plans to conceive within the month, as it is not a live vaccine.
Preventive strategies US Medical PG Question 6: A 30-year-old female with a history of epilepsy becomes pregnant. Her epilepsy has been well controlled by taking a medication that inhibits GABA transaminase and blocks voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels. Her obstetrician informs her that her epilepsy medication has been shown to have teratogenic effects. Of the following, which teratogenic effect is this woman's medication most likely to cause?
- A. Limb defects
- B. Neural tube defect (Correct Answer)
- C. Renal damage
- D. Ebstein's anomaly
- E. Discolored teeth
Preventive strategies Explanation: ***Neural tube defect***
- The medication described, which **inhibits GABA transaminase** and has multiple mechanisms including effects on voltage-gated channels, is **valproic acid** (valproate).
- **Valproic acid** is the antiepileptic drug with the **highest risk of neural tube defects** (e.g., spina bifida), with an incidence of approximately 1-2% when taken during pregnancy.
- This teratogenic effect occurs primarily during the first trimester and is believed to be due to interference with **folate metabolism** and **histone deacetylase inhibition**, which are crucial for proper neural tube closure.
- Folic acid supplementation is recommended for women of childbearing age taking valproate.
*Limb defects*
- **Limb defects** (e.g., phocomelia, limb reduction defects) are classically associated with **thalidomide** exposure during early pregnancy.
- While **phenytoin** (fetal hydantoin syndrome) can cause limb abnormalities including hypoplastic nails and distal phalanges, this is not the primary teratogenic concern with valproic acid.
*Renal damage*
- **Fetal renal damage** can be caused by medications such as **ACE inhibitors**, **ARBs**, and **NSAIDs** when taken during pregnancy.
- This is not a characteristic teratogenic effect of valproic acid or other antiepileptic medications.
*Ebstein's anomaly*
- **Ebstein's anomaly**, a congenital heart defect characterized by apical displacement of the tricuspid valve, is most notably associated with **lithium exposure** during the first trimester of pregnancy.
- This cardiac anomaly is not typically linked to valproic acid or other anticonvulsant medications.
*Discolored teeth*
- **Discolored teeth** (yellow-brown staining) and enamel hypoplasia are classic adverse effects of **tetracycline antibiotics** when administered during pregnancy (second and third trimesters) or early childhood.
- This effect is not associated with antiepileptic medications.
Preventive strategies US Medical PG Question 7: A 12-month-old boy presents for a routine checkup. The patient immigrated from the Philippines with his parents a few months ago. No prior immunization records are available. The patient’s mother claims that he had a series of shots at 6 months of age which gave him a severe allergic reaction with swelling of the tongue and the face. She also remembers that he had the same reaction when she introduced solid foods to his diet, including carrots, eggs, and bananas. Which of the following vaccinations are not recommended for this patient?
- A. Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine
- B. Hepatitis B vaccine
- C. Varicella vaccine
- D. Intranasal influenza vaccine
- E. Intramuscular influenza vaccine (Correct Answer)
Preventive strategies Explanation: ***Important Note on Current Guidelines***
Based on **current CDC/ACIP guidelines (2023-2024)**, egg allergy alone is **no longer a contraindication** to influenza vaccines. However, this question tests knowledge of vaccine safety in the context of **severe anaphylaxis to a prior vaccination**.
***Intramuscular influenza vaccine***
- **Historically**, this was considered the most concerning option for patients with severe egg allergy, as many influenza vaccines were produced using egg-based culture methods
- **Current practice**: Per CDC guidelines, persons with egg allergy of any severity can receive any age-appropriate influenza vaccine, as egg protein content is minimal or absent in modern formulations
- However, if this patient had a **documented anaphylactic reaction to the influenza vaccine itself** (not just eggs), then it would be contraindicated
- Given the timing (6 months) and symptoms described, this represents the **historically correct answer**, though modern practice has evolved
*Measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine*
- MMR vaccine is grown in **chick embryo fibroblast cells**, NOT in eggs, and contains **no egg protein**
- **Safe for patients with egg allergy** - no contraindication based on egg allergy
- Should be administered on schedule for catch-up immunization
*Hepatitis B vaccine*
- Produced using **recombinant DNA technology in yeast cells**
- Contains **no egg protein** and no animal-derived proteins
- **No contraindication** for this patient - safe to administer
*Varicella vaccine*
- Grown in **human diploid cell cultures**, NOT in eggs
- Contains **no egg protein**
- **Safe for patients with egg allergy** - no contraindication
- Should be administered as part of catch-up immunization
*Intranasal influenza vaccine (LAIV)*
- Like the intramuscular formulation, **current guidelines allow administration** to patients with egg allergy of any severity
- Contains similar or less egg protein than inactivated vaccines in modern formulations
- **Not contraindicated** based solely on egg allergy per current CDC guidelines
Preventive strategies US Medical PG Question 8: A 26-year-old G1P0 mother is in the delivery room in labor. Her unborn fetus is known to have a patent urachus. Which of the following abnormalities would you expect to observe in the infant?
- A. Myelomeningocele
- B. Gastroschisis
- C. Urine discharge from umbilicus (Correct Answer)
- D. Omphalocele
- E. Meconium discharge from umbilicus
Preventive strategies Explanation: ***Urine discharge from umbilicus***
- A **patent urachus** is a congenital anomaly where the **urachus**, a remnant of the **allantois**, fails to close completely, allowing a direct connection between the bladder and the umbilicus.
- This patent tract results in the **continuous discharge of urine from the umbilicus**, especially upon crying or straining, as the bladder pressure increases.
*Myelomeningocele*
- **Myelomeningocele** is a severe form of **spina bifida** where the spinal cord and nerves protrude through an opening in the back.
- It results from incomplete closure of the neural tube and is not directly related to the urachus or umbilical discharge.
*Gastroschisis*
- **Gastroschisis** is a birth defect where the intestines protrude through an opening in the abdominal wall, typically to the right of the umbilicus.
- Unlike a patent urachus, it involves the protrusion of abdominal contents and is not associated with umbilical urine discharge.
*Omphalocele*
- An **omphalocele** is a birth defect in which parts of the abdominal organs, such as the intestines, liver, or stomach, protrude through the umbilical opening, covered by a sac.
- This condition is also an abdominal wall defect but distinct from a patent urachus, which specifically involves the connection between the bladder and the umbilicus.
*Meconium discharge from umbilicus*
- **Meconium discharge from the umbilicus** would suggest a persistent communication between the bowel and the umbilicus, rather than the bladder.
- This condition, known as a **patent vitelline duct** or omphalomesenteric duct, is anatomically distinct from a patent urachus.
Preventive strategies US Medical PG Question 9: A 13-month-old girl is brought to the physician because of a pruritic rash for 2 days. The girl's mother says she noticed a few isolated skin lesions on her trunk two days ago that appear to be itching. The girl received her routine immunizations 18 days ago. Her mother has been giving her ibuprofen for her symptoms. The patient has no known sick contacts. She is at the 71st percentile for height and the 64th percentile for weight. She is in no acute distress. Her temperature is 38.1°C (100.6°F), pulse is 120/min, and respirations are 26/min. Examination shows a few maculopapular and pustular lesions distributed over the face and trunk. There are some excoriation marks and crusted lesions as well. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for these findings?
- A. Antigen contact with presensitized T-lymphocytes
- B. Reactivation of virus dormant in dorsal root ganglion
- C. Immune complex formation and deposition
- D. Crosslinking of preformed IgE antibodies
- E. Replication of the attenuated vaccine strain (Correct Answer)
Preventive strategies Explanation: ***Replication of the attenuated vaccine strain***
- The presentation of a **pruritic rash with maculopapular and pustular lesions**, along with crusted lesions, describes the classic **polymorphic rash** of **varicella (chickenpox)**.
- The timing of the rash, appearing **18 days after routine immunizations** (which commonly include the attenuated **MMRV vaccine** at 12-15 months), strongly suggests a vaccine-induced varicella rash due to the replication of the live attenuated virus.
*Antigen contact with presensitized T-lymphocytes*
- This mechanism describes a **Type IV hypersensitivity reaction** (delayed-type hypersensitivity), such as **contact dermatitis** or a **tuberculin skin test**.
- While it can cause a rash, it typically presents differently (e.g., vesicles in contact dermatitis) and the timeline of 18 days post-vaccination is less consistent with a primary contact-mediated reaction causing widespread varicella-like lesions.
*Reactivation of virus dormant in dorsal root ganglion*
- This process describes the pathogenesis of **herpes zoster (shingles)**, which occurs due to the reactivation of the **latent varicella-zoster virus (VZV)** from the dorsal root ganglia.
- Shingles typically presents with a **dermatomal rash** in older individuals or immunocompromised patients, not a widespread polymorphic rash in an otherwise healthy toddler.
*Immune complex formation and deposition*
- This mechanism describes a **Type III hypersensitivity reaction**, where antigen-antibody complexes deposit in tissues, leading to inflammation.
- Conditions like **serum sickness**, **lupus**, or some forms of **vasculitis** are examples, which present with fever, arthralgia, and urticarial or purpuric rashes, differing from the described varicella-like lesions.
*Crosslinking of preformed IgE antibodies*
- This mechanism describes a **Type I hypersensitivity reaction**, commonly known as an **allergic reaction**.
- It typically results in **urticaria (hives)**, angioedema, or anaphylaxis, which are acute reactions characterized by wheals and pruritus, rather than the polymorphic rash with pustules and crusts seen here.
Preventive strategies US Medical PG Question 10: A 3-year-old child presents with respiratory distress and a history of recurrent respiratory infections. Based on the provided imaging, what is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. CPAM (Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformation) (Correct Answer)
- B. Lung abscess
- C. Pyopneumothorax
- D. CDH (Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia)
- E. Pulmonary sequestration
Preventive strategies Explanation: ***CPAM (Congenital Pulmonary Airway Malformation)***
- The imaging shows **cystic lesions** within the lung parenchyma, which are characteristic of CPAM. These lesions can cause **respiratory distress** and predispose to **recurrent infections**.
- The age of the child (3 years old) and the history of recurrent respiratory infections are consistent with CPAM, as these malformations often manifest with symptoms in early childhood.
*Lung abscess*
- A lung abscess typically presents as a **cavity with an air-fluid level** and surrounding consolidation, usually in a single, well-defined area.
- While recurrent infections can occur, the widespread cystic appearance on imaging makes an abscess less likely than CPAM.
*Pyopneumothorax*
- Pyopneumothorax is characterized by the presence of both **pus and air in the pleural space**, leading to a visible air-fluid level that occupies the pleural cavity.
- The imaging does not show evidence of gas and fluid within the pleural space, nor the typical chest wall separation seen in pneumothorax.
*CDH (Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia)*
- CDH involves the **herniation of abdominal contents** into the chest cavity, displacing lung tissue and often causing severe respiratory distress from birth due to pulmonary hypoplasia.
- The images show cystic changes within the lung parenchyma, not abdominal organs in the chest, and the age of presentation makes a new diagnosis of uncorrected CDH less likely, as it usually presents as a neonatal emergency.
*Pulmonary sequestration*
- Pulmonary sequestration is a congenital malformation characterized by **non-functioning lung tissue with aberrant systemic arterial supply**, typically from the aorta.
- While it can present with recurrent infections, the imaging typically shows a **solid or mixed solid-cystic mass**, often in the lower lobes with visible feeding vessels on contrast imaging, rather than the predominantly multicystic appearance seen in CPAM.
More Preventive strategies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.