Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects US Medical PG Question 1: A 40-year-old woman in her 18th week of pregnancy based on the last menstrual period (LMP) presents to her obstetrician for an antenatal check-up.
The antenatal testing is normal, except the quadruple screen results which are given below:
Maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MS-AFP) low
Unconjugated estriol low
Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) high
Inhibin-A high
Which of the following conditions is the most likely the cause of the abnormal quadruple screen?
- A. Fetal alcohol syndrome
- B. Spina bifida
- C. Gastroschisis
- D. Trisomy 21 (Correct Answer)
- E. Omphalocele
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects Explanation: ***Trisomy 21***
- The classic quadruple screen pattern for **Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)** includes **low MS-AFP**, **low unconjugated estriol**, **high hCG**, and **high inhibin-A**.
- This pattern reflects specific placental and fetal biochemical changes associated with the chromosomal abnormality.
*Fetal alcohol syndrome*
- **Fetal alcohol syndrome** is caused by maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy and is not detectable by a quadruple screen.
- It is characterized by specific facial features, growth restriction, and central nervous system abnormalities.
*Spina bifida*
- **Spina bifida**, an **open neural tube defect**, would typically present with a **high MS-AFP** due to leakage of fetal AFP from the open defect into the amniotic fluid and then into maternal circulation.
- This contradicts the **low MS-AFP** finding in the current case.
*Gastroschisis*
- **Gastroschisis**, an abdominal wall defect where intestines are outside the body, also results in a significantly **elevated MS-AFP** due to direct exposure of fetal blood vessels to the amniotic fluid.
- This condition is not associated with the pattern of unconjugated estriol, hCG, and inhibin-A seen in this quadruple screen.
*Omphalocele*
- **Omphalocele**, another abdominal wall defect where abdominal contents are covered by a membrane, usually presents with a **high MS-AFP**, though often less elevated than in gastroschisis or spina bifida.
- It is not associated with the specific pattern of low estriol, high hCG, and high inhibin-A seen in Trisomy 21.
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects US Medical PG Question 2: A 37-year-old woman presents for prenatal counseling at 18 weeks gestation. The patient tells you that her sister recently had a child with Down's syndrome, and the patient would like prenatal screening for Down's in her current pregnancy.
Which of the following prenatal screening tests and results would raise concern for Down's syndrome?
- A. Increased AFP, normal HCG, normal unconjugated estriol
- B. Decreased AFP, decreased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol
- C. Normal AFP, increased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol
- D. Normal AFP, decreased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol
- E. Decreased AFP, increased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol (Correct Answer)
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects Explanation: ***Decreased AFP, increased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol***
- A classic finding in **Down's syndrome (trisomy 21)** during the second-trimester screen is a **decreased alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)**, **increased human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG)**, and **decreased unconjugated estriol**.
- This combination, sometimes referred to as the "**triple screen**" (or "quad screen" with inhibin A), indicates a higher risk of chromosomal abnormalities like trisomy 21.
*Increased AFP, normal HCG, normal unconjugated estriol*
- **Increased AFP** is typically associated with **neural tube defects** (e.g., spina bifida, anencephaly) or **ventral wall defects**, not Down's syndrome.
- Normal HCG and unconjugated estriol would argue against trisomy 21.
*Decreased AFP, decreased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol*
- When all three markers (AFP, HCG, and unconjugated estriol) are **decreased**, it is highly suggestive of **trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)**, not Down's syndrome.
- Trisomy 18 is associated with severe developmental abnormalities and a poor prognosis.
*Normal AFP, increased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol*
- While **increased HCG** and **decreased unconjugated estriol** are consistent with Down's syndrome, a **normal AFP** alone would make this less classic for trisomy 21 compared to the option with decreased AFP.
- The combination of **decreased AFP** alongside the other two findings is more characteristic.
*Normal AFP, decreased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol*
- This pattern (normal AFP, decreased HCG, decreased unconjugated estriol) is not typically associated with Down's syndrome.
- **Decreased HCG** is more commonly seen in trisomy 18 in combination with decreased AFP and estriol.
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects US Medical PG Question 3: A 36-year-old G3P2002 presents to her obstetrician’s office for her first prenatal visit at ten weeks and two days gestation. She notes that she has felt nauseous the last several mornings and has been especially tired for a few weeks. Otherwise, she feels well. The patient has had two uncomplicated spontaneous vaginal deliveries at full term with her last child born six years ago. She is concerned about the risk of Down syndrome in this fetus, as her sister gave birth to an affected child at age 43. The patient has a history of generalized anxiety disorder, atopic dermatitis, and she is currently on escitalopram. At this visit, this patient’s temperature is 98.6°F (37.0°C), pulse is 70/min, blood pressure is 121/67 mmHg, and respirations are 13/min. The patient appears anxious, but overall comfortable, and cardiopulmonary and abdominal exams are unremarkable. Pelvic exam reveals normal female external genitalia, a closed and slightly soft cervix, a ten-week-sized uterus, and no adnexal masses. Which of the following is the best next step for definitively determining whether this patient’s fetus has Down syndrome?
- A. Anatomy ultrasound
- B. Genetic testing of patient’s sister
- C. Chorionic villus sampling (Correct Answer)
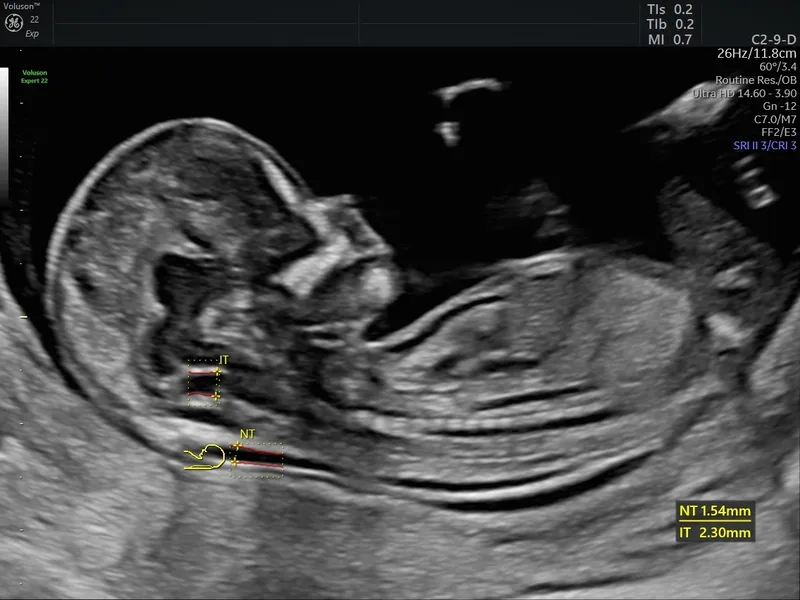
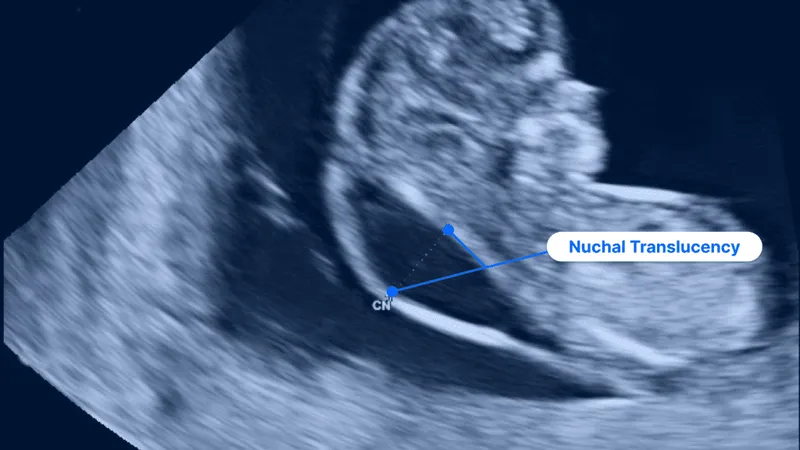
- D. Nuchal translucency test
- E. Amniocentesis
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects Explanation: ***Chorionic villus sampling***
- **Chorionic villus sampling (CVS)** is a diagnostic procedure performed between 10 and 13 weeks of gestation that involves taking a sample of placental tissue for genetic analysis. It provides a definitive diagnosis for chromosomal abnormalities like **Down syndrome** earlier in pregnancy than amniocentesis.
- Given the patient's anxiety and desire for definitive diagnosis due to family history, CVS is the most appropriate next step for an early and conclusive result.
*Anatomy ultrasound*
- An **anatomy ultrasound** (typically performed at 18-20 weeks) is a screening, not diagnostic, tool for fetal anomalies. While it can detect **structural abnormalities** associated with Down syndrome, it cannot definitively diagnose the condition.
- It would be too late to provide the early definitive diagnosis the patient is seeking regarding **Down syndrome**.
*Genetic testing of patient’s sister*
- The sister's genetic testing would confirm her child's diagnosis or carrier status for **chromosomal translocations**, but it does not provide information about the current patient's fetus.
- A definitive diagnosis for the current pregnancy must come from **fetal genetic material**.
*Nuchal translucency test*
- The **nuchal translucency test** is a **screening test** performed between 11 and 14 weeks that measures the fluid at the back of the fetal neck and is used in conjunction with biochemical markers (first-trimester screening) to assess the risk of Down syndrome. It is not diagnostic.
- An abnormal result would indicate an increased risk but would still require a **diagnostic test** like CVS or amniocentesis for confirmation.
*Amniocentesis*
- **Amniocentesis** is a diagnostic procedure that samples amniotic fluid for genetic analysis, typically performed between 15 and 20 weeks of gestation.
- While it provides a definitive diagnosis for **chromosomal abnormalities**, it is usually performed later in pregnancy than CVS. The patient is at 10 weeks and two days, making CVS a timelier option for early diagnosis.
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects US Medical PG Question 4: A 37-year-old woman comes for a follow-up prenatal visit at 18 weeks' gestation. At 12 weeks' gestation, ultrasonography showed increased nuchal translucency and pregnancy-associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A) was decreased by 2 standard deviations. Chorionic villus sampling showed a 47, XX, +21 karyotype. During this visit, ultrasonography shows a hypoplastic nasal bone, shortened femur length, shortened middle phalanges of the fifth digits with clinodactyly. A quadruple marker test would most likely show which of the following sets of findings?
$$$ α-Fetoprotein (AFP) %%% Estriol %%% β-Human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) %%% Inhibin A $$$
- A. ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
- B. ↑ normal normal normal
- C. ↓ ↓ ↑ ↑ (Correct Answer)
- D. Normal normal normal normal
- E. ↓ ↓ ↓ normal
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects Explanation: ***↓ ↓ ↑ ↑***
- This pattern (low **AFP**, low **estriol**, high **hCG**, high **inhibin A**) is characteristic of **Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)** in a quadruple marker screen.
- The patient's history, including **increased nuchal translucency**, low **PAPP-A**, and a **47, XX, +21 karyotype**, strongly confirms the diagnosis of Down syndrome, making this a consistent finding.
*↓ ↓ ↓ ↓*
- This pattern of uniformly low markers is not typical for **Down syndrome** and would more commonly suggest other chromosomal abnormalities or a different fetal condition altogether.
- While some markers are low in Down syndrome, the elevation of **hCG** and **inhibin A** is a key differentiator.
*↑ normal normal normal*
- An isolated elevated **AFP** is commonly associated with neural tube defects or ventral wall defects, which are not suggested by the patient's presentation.
- Down syndrome invariably affects multiple markers in a specific pattern, not just one.
*Normal normal normal normal*
- Normal quadruple markers would indicate a low risk for **chromosomal aneuploidies**, which contradicts the patient's confirmed diagnosis of **Down syndrome (47, XX, +21)**.
- This option is inconsistent with the presented clinical and previous genetic findings.
*↓ ↓ ↓ normal*
- This pattern does not align with the typical profile for **Down syndrome**, which characteristically shows elevated **hCG** and **inhibin A**.
- While **AFP** and **estriol** are decreased in Down syndrome, the normal inhibin A makes this option incorrect.
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects US Medical PG Question 5: A male neonate is being examined by a pediatrician. His mother informs the doctor that she had a mild fever with rash, muscle pain, and swollen and tender lymph nodes during the second month of gestation. The boy was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery with no prenatal care. On physical examination, the neonate has normal vital signs. Retinal examination reveals the findings shown in the image. Which of the following congenital heart defects is most likely to be present in this neonate?
- A. Double outlet right ventricle
- B. Atrial septal defect
- C. Patent ductus arteriosus (Correct Answer)
- D. Ventricular septal defect
- E. Tetralogy of Fallot
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects Explanation: ***Patent ductus arteriosus***
- This neonate has **congenital rubella syndrome (CRS)** based on maternal symptoms during the first trimester (fever, rash, lymphadenopathy) and the characteristic **"salt and pepper" retinopathy** shown on retinal examination
- **PDA is the most common cardiac defect** associated with CRS, occurring in approximately 50-85% of affected infants
- Other cardiac manifestations of CRS include peripheral pulmonary artery stenosis, but PDA predominates
- The classic triad of CRS includes cardiac defects, ocular abnormalities (cataracts, glaucoma, retinopathy), and sensorineural deafness
*Double outlet right ventricle*
- This is a **conotruncal anomaly** typically presenting with cyanosis in the neonatal period
- Not associated with maternal rubella infection or congenital rubella syndrome
- Would present with abnormal ventricular anatomy and significant hemodynamic compromise
*Atrial septal defect*
- While ASD is a common congenital heart defect, it is **not characteristically associated with CRS**
- Much less frequently linked to maternal viral infections compared to PDA
- Often asymptomatic in the neonatal period and detected later in childhood
*Ventricular septal defect*
- VSD is less commonly associated with **congenital rubella syndrome** compared to PDA
- When present, typically manifests with a holosystolic murmur at the left lower sternal border
- Can occur with maternal infections but is not the predominant cardiac finding in CRS
*Tetralogy of Fallot*
- Consists of four anatomic abnormalities: VSD, pulmonary stenosis, overriding aorta, and right ventricular hypertrophy
- Presents with **cyanosis** ("tet spells") and is not specifically linked to maternal rubella infection
- Not part of the congenital rubella syndrome spectrum
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects US Medical PG Question 6: A 26-year-old G1P0 mother is in the delivery room in labor. Her unborn fetus is known to have a patent urachus. Which of the following abnormalities would you expect to observe in the infant?
- A. Myelomeningocele
- B. Gastroschisis
- C. Urine discharge from umbilicus (Correct Answer)
- D. Omphalocele
- E. Meconium discharge from umbilicus
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects Explanation: ***Urine discharge from umbilicus***
- A **patent urachus** is a congenital anomaly where the **urachus**, a remnant of the **allantois**, fails to close completely, allowing a direct connection between the bladder and the umbilicus.
- This patent tract results in the **continuous discharge of urine from the umbilicus**, especially upon crying or straining, as the bladder pressure increases.
*Myelomeningocele*
- **Myelomeningocele** is a severe form of **spina bifida** where the spinal cord and nerves protrude through an opening in the back.
- It results from incomplete closure of the neural tube and is not directly related to the urachus or umbilical discharge.
*Gastroschisis*
- **Gastroschisis** is a birth defect where the intestines protrude through an opening in the abdominal wall, typically to the right of the umbilicus.
- Unlike a patent urachus, it involves the protrusion of abdominal contents and is not associated with umbilical urine discharge.
*Omphalocele*
- An **omphalocele** is a birth defect in which parts of the abdominal organs, such as the intestines, liver, or stomach, protrude through the umbilical opening, covered by a sac.
- This condition is also an abdominal wall defect but distinct from a patent urachus, which specifically involves the connection between the bladder and the umbilicus.
*Meconium discharge from umbilicus*
- **Meconium discharge from the umbilicus** would suggest a persistent communication between the bowel and the umbilicus, rather than the bladder.
- This condition, known as a **patent vitelline duct** or omphalomesenteric duct, is anatomically distinct from a patent urachus.
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects US Medical PG Question 7: A 6-year-old boy is brought in for evaluation by his adopted mother due to trouble starting 1st grade. His teacher has reported that he has been having trouble focusing on tasks and has been acting out while in class. His family history is unknown as he was adopted 2 years ago. His temperature is 36.2°C (97.2°F), pulse is 80/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure 110/70 mm Hg. Visual inspection of the boy's face shows a low set nasal bridge, a smooth philtrum, and small lower jaw. Which of the following findings would also likely be found on physical exam?
- A. Cataracts
- B. Congenital deafness
- C. Holosystolic murmur (Correct Answer)
- D. Limb hypoplasia
- E. Wide notched teeth
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects Explanation: **Holosystolic murmur**
- The child exhibits classic features of **fetal alcohol syndrome** (FAS), including the distinctive facial anomalies (low set nasal bridge, smooth philtrum, small lower jaw) and developmental/behavioral issues (trouble focusing, acting out).
- Up to 50% of children with FAS develop **congenital heart defects**, with **ventricular septal defects (VSDs)** being the most common, which are characterized by a **holosystolic murmur** at the lower left sternal border.
*Cataracts*
- **Cataracts** are not a typical feature of fetal alcohol syndrome but are often associated with congenital infections such as **rubella** or **cytomegalovirus**.
- While some genetic syndromes can include cataracts, they are not a primary finding for the constellation of symptoms observed here.
*Congenital deafness*
- **Congenital deafness** is not a hallmark of fetal alcohol syndrome; rather, it is commonly associated with congenital infections like **rubella**, **CMV**, or genetic syndromes such as **CHARGE syndrome**.
- Children with FAS may have hearing problems due to recurrent ear infections, but not typically congenital deafness.
*Limb hypoplasia*
- **Limb hypoplasia** is typically seen in conditions like **thalidomide embryopathy** or certain genetic syndromes, such as **Roberts syndrome**.
- While growth restriction is common in FAS, significant limb hypoplasia as described is not a characteristic feature.
*Wide notched teeth*
- **Wide notched teeth**, also known as **Hutchinson teeth**, are pathognomonic for **congenital syphilis**.
- This finding is unrelated to fetal alcohol syndrome, and the patient's other symptoms do not suggest congenital syphilis.
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects US Medical PG Question 8: A 45-day-old male infant is brought to a pediatrician by his parents with concerns of poor feeding and excessive perspiration for one week. On physical examination, his temperature is 37.7°C (99.8°F), pulse rate is 190/min, and respiratory rate is 70/min. Mild cyanosis is present over the lips, and over the nail beds. Oxygen is provided and his oxygen saturation is carefully monitored. The pediatrician orders a bedside echocardiogram of the infant. It reveals a single arterial trunk arising from 2 normally formed ventricles. The arterial trunk is separated from the ventricles by a single semilunar valve. There is a defect in the interventricular septum, and the arterial trunk overrides the defect. Which of the following congenital heart diseases can also present with similar clinical features?
- A. Infracardiac total anomalous pulmonary venous return
- B. Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum
- C. Severe Ebstein anomaly
- D. Double-inlet ventricle with unobstructed pulmonary flow
- E. Transposition of the great arteries with ventricular septal defect and pulmonary stenosis (Correct Answer)
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects Explanation: ***Transposition of the great arteries with ventricular septal defect and pulmonary stenosis***
- The described echocardiogram findings point to **Truncus Arteriosus**, characterized by a single great artery overriding a **ventricular septal defect (VSD)** and severe **cyanosis**.
- **Transposition of the great arteries (TGA)** with a VSD and pulmonary stenosis also presents with profound cyanosis, heart failure symptoms (poor feeding, tachypnea, tachycardia), and can lead to similar **hemodynamic instability** due to mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood and outflow tract obstruction.
*Infracardiac total anomalous pulmonary venous return*
- This condition involves all pulmonary veins draining into the systemic venous circulation below the diaphragm, often into the **portal vein** or **ductus venosus**.
- While it causes severe cyanosis and cardiopulmonary distress in infancy, the **echocardiogram findings** (single arterial trunk, VSD) are distinct from the typical features of infracardiac TAPVR, which would show abnormal pulmonary venous connection at the systemic level rather than a single great artery.
*Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum*
- This involves a **complete obstruction of the pulmonary valve**, preventing blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery, leading to severe cyanosis.
- However, the echocardiogram description of a **single arterial trunk overriding a VSD** is not consistent with pulmonary atresia with an intact ventricular septum.
*Severe Ebstein anomaly*
- This anomaly is characterized by apical displacement of the **tricuspid valve leaflets**, leading to severe tricuspid regurgitation and functional hypoplasia of the right ventricle.
- While it can cause cyanosis and heart failure, the echocardiogram findings of a single arterial trunk and overriding VSD are not typical of **Ebstein anomaly**.
*Double-inlet ventricle with unobstructed pulmonary flow*
- A double-inlet ventricle means both atria connect to a single functional ventricle, but with **unobstructed pulmonary flow**, there would likely be less severe cyanosis (or none) and more symptoms of **congestive heart failure** due to pulmonary overcirculation.
- This condition's echocardiogram findings are also distinct from the described single arterial trunk and overriding VSD, which are characteristic of **Truncus Arteriosus**.
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects US Medical PG Question 9: A 25-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, comes to the physician for her initial prenatal visit at 18 weeks’ gestation. She is a recent immigrant from Thailand. Her history is significant for anemia since childhood that has not required any treatment. Her mother and husband have anemia, as well. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Fundal height measures at 22 weeks. Ultrasound shows polyhydramnios and pleural and peritoneal effusion in the fetus with fetal subcutaneous edema. Which of the following is the most likely clinical course for this fetus?
- A. Neonatal death
- B. Normal development with regular blood transfusion
- C. Asymptomatic anemia
- D. Intrauterine fetal demise (Correct Answer)
- E. Carrier state
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects Explanation: ***Intrauterine fetal demise***
- The ultrasound findings of **polyhydramnios**, **pleural and peritoneal effusion**, and **fetal subcutaneous edema** are classic signs of **hydrops fetalis**.
- In a patient from Thailand with a history of lifelong anemia and a family history of anemia, these findings are highly suggestive of **alpha-thalassemia major (Hb Barts disease)**, which is almost always lethal in utero or shortly after birth.
*Neonatal death*
- While many cases of **hydrops fetalis** due to **alpha-thalassemia major** result in neonatal death, the severe findings often lead to **intrauterine fetal demise** before viability or at term.
- The combination of severe fetal compromise (multiple effusions, edema) and polyhydramnios often indicates a very poor prognosis and high likelihood of demise prior to full term delivery.
*Normal development with regular blood transfusion*
- This is typical for less severe forms of **thalassemia**, such as **beta-thalassemia major**, but not for **alpha-thalassemia major (Hb Barts disease)**, which is characterized by the complete absence of alpha-globin chains.
- **Hb Barts disease** is incompatible with life due to severe tissue hypoxia, as this hemoglobin has an extremely high affinity for oxygen and cannot release it to tissues effectively.
*Asymptomatic anemia*
- **Asymptomatic anemia** is generally associated with milder forms of anemia, such as alpha-thalassemia trait (two gene deletion) or beta-thalassemia minor.
- The severe manifestations of **hydrops fetalis** clearly indicate a profound, life-threatening condition for the fetus, not asymptomatic anemia.
*Carrier state*
- A **carrier state** (e.g., alpha-thalassemia trait) would typically involve mild or no anemia and would not cause **hydrops fetalis** in the fetus.
- The significant fetal pathology rules out a simple carrier state for the fetus; this fetus is severely affected by a major genetic disorder.
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects US Medical PG Question 10: An 8-year-old boy presents to your office for a routine well-child visit. Upon physical examination, he is found to have a harsh-sounding, holosystolic murmur that is best appreciated at the left sternal border. The murmur becomes louder when you ask him to make fists with his hands. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for these findings?
- A. Aortic stenosis
- B. Ventricular septal defect (Correct Answer)
- C. Left ventricular hypertrophy
- D. Pulmonary hypertension
- E. Tricuspid atresia
Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects Explanation: ***Ventricular septal defect***
- A **holosystolic murmur** heard best at the **left sternal border** is characteristic of a VSD, caused by blood shunting from the left to the right ventricle during systole.
- The murmur becoming louder with a maneuver that increases **afterload** (like making fists, which increases systemic vascular resistance) is consistent with a VSD, as it enhances the pressure gradient and shunting.
*Aortic stenosis*
- An aortic stenosis murmur is typically a **systolic ejection murmur**, not holosystolic, and is often heard best at the right upper sternal border with radiation to the carotids.
- While it can be affected by maneuvers that change cardiac output, the description of a harsh, holosystolic murmur at the left sternal border is not typical for aortic stenosis.
*Left ventricular hypertrophy*
- **Left ventricular hypertrophy** (LVH) is an anatomical change in the heart muscle and is not a direct cause of a primary murmur itself. It is usually a consequence of other conditions like aortic stenosis or hypertension.
- While significant LVH can alter heart sounds or be associated with murmurs from underlying conditions, it does not directly produce a harsh, holosystolic murmur with these specific characteristics.
*Pulmonary hypertension*
- Pulmonary hypertension can cause murmurs related to pulmonary regurgitation (a diastolic murmur) or tricuspid regurgitation (a holosystolic murmur), but these are usually associated with symptoms like dyspnea and fatigue, and a holosystolic murmur from **tricuspid regurgitation** is typically louder at the xiphoid process rather than the left sternal border and is often associated with venous distension.
- An increase in systemic afterload (making fists) would generally decrease the intensity of a murmur due to tricuspid regurgitation, not increase it.
*Tricuspid atresia*
- **Tricuspid atresia** is a severe congenital heart defect where the tricuspid valve fails to form, resulting in no direct communication between the right atrium and right ventricle. It typically presents with cyanosis and severe symptoms early in life.
- While it often coexists with a VSD (which would produce a murmur), the primary defect itself is not directly associated with the specific holosystolic murmur description that becomes louder with increased afterload in an otherwise apparently well 8-year-old.
More Prenatal diagnosis of congenital defects US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.