Multiple malformation syndromes US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Multiple malformation syndromes. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Multiple malformation syndromes US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 14-weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. Routine first trimester screening shows increased nuchal translucency, decreased β-hCG concentration, and decreased levels of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A. Amniocentesis shows trisomy of chromosome 13. This fetus is at increased risk for which of the following?
- A. Duodenal atresia
- B. Cutis aplasia (Correct Answer)
- C. Cystic hygroma
- D. Optic glioma
- E. Prominent occiput
Multiple malformation syndromes Explanation: ***Cutis aplasia***
- **Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)** is characterized by **cutis aplasia**, which is a congenital absence of skin, typically on the scalp.
- Other common features of Trisomy 13 include **midline defects**, microphthalmia, cleft lip/palate, polydactyly, and severe intellectual disability.
*Duodenal atresia*
- **Duodenal atresia** is strongly associated with **Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)**, not Trisomy 13.
- It presents with a "double bubble" sign on imaging due to dilation of the stomach and proximal duodenum.
*Cystic hygroma*
- **Cystic hygromas**, which are lymphatic malformations, are a common finding in **Turner syndrome (XO)** and **Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)**.
- While increased nuchal translucency is noted, a cystic hygroma itself is not a specific finding for Trisomy 13.
*Optic glioma*
- **Optic gliomas** are tumors of the optic nerve most frequently associated with **neurofibromatosis type 1**, an autosomal dominant disorder.
- They are not a characteristic finding of Trisomy 13.
*Prominent occiput*
- A **prominent occiput** is a classic feature of **Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)**.
- This condition is also associated with rocker-bottom feet, micrognathia, and clenched hands with overlapping fingers.
Multiple malformation syndromes US Medical PG Question 2: A 1-year-old boy presents to pediatrics clinic for a well-child visit. He has no complaints. He has a cleft palate and an abnormal facial appearance. He has been riddled with recurrent infections and is followed by cardiology for a ventricular septal defect (VSD). Vital signs are stable, and the patient's physical exam is benign. If this patient's medical history is part of a larger syndrome, what might one also discover that is consistent with the manifestations of this syndrome?
- A. Kidney stones
- B. A positive Chvostek's sign (Correct Answer)
- C. B-cell deficiency
- D. Hypoactive deep tendon reflexes
- E. A shortened QT Interval
Multiple malformation syndromes Explanation: ***A positive Chvostek's sign***
- The constellation of **cleft palate**, **abnormal facial appearance**, **recurrent infections**, and a **ventricular septal defect (VSD)** strongly suggests **DiGeorge syndrome**.
- In DiGeorge syndrome, hypoparathyroidism leads to **hypocalcemia**, which can manifest as neuromuscular irritability, including a positive **Chvostek's sign** (facial muscle twitching upon tapping the facial nerve).
*Kidney stones*
- **Kidney stones** are typically associated with **hypercalcemia** or other metabolic disorders, not hypocalcemia seen in DiGeorge syndrome.
- While DiGeorge patients can have renal anomalies, **nephrolithiasis** is not a characteristic feature of the syndrome.
*B-cell deficiency*
- DiGeorge syndrome is characterized by **T-cell deficiency** due to thymic hypoplasia or aplasia, not primarily B-cell deficiency.
- While **B cells** may be secondarily affected due to lack of T-cell help, the primary immunodeficiency is related to T-lymphocytes.
*Hypoactive deep tendon reflexes*
- **Hypocalcemia** typically causes **hyperactive deep tendon reflexes** and increased neuromuscular excitability, not hypoactivity.
- **Hypoactive reflexes** might suggest conditions like hypothyroidism or certain neurological disorders.
*A shortened QT Interval*
- **Hypocalcemia** is associated with a **prolonged QT interval** on an electrocardiogram, not a shortened one.
- A **shortened QT interval** can occur in conditions like hypercalcemia or genetic channelopathies.
Multiple malformation syndromes US Medical PG Question 3: A 14-year-old boy presents as a new patient to your practice. While conducting your physical exam, you observe the findings depicted in Figures A and B. Which of the following additional findings would most likely be found in this patient?
- A. Multiple café-au-lait macules (Correct Answer)
- B. A white tuft of scalp hair since birth
- C. The presence of ash-leaf spots
- D. Facial angiofibromas
- E. A family history of seizures and intellectual disability
Multiple malformation syndromes Explanation: ***Multiple café-au-lait macules***
- The images show **Lisch nodules** (iris hamartomas), which are pathognomonic for **Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)**.
- **Café-au-lait macules** are the most common and often earliest manifestation of NF1, present in **>99% of patients**.
- Diagnostic criteria require **≥6 café-au-lait macules** (>5mm in diameter prepubertal, >15mm postpubertal).
- This is the **most likely additional finding** in a patient with Lisch nodules.
*A family history of seizures and intellectual disability*
- While **learning disabilities** occur in ~50% of NF1 patients and **seizures** can occur, this is not the most specific or common finding.
- **Café-au-lait macules** and **cutaneous neurofibromas** are far more consistent and diagnostically significant.
*A white tuft of scalp hair since birth*
- A **white tuft of scalp hair** (poliosis) is characteristic of **Waardenburg syndrome**, not NF1.
- Waardenburg syndrome presents with **hearing loss**, **heterochromia iridis**, and **dystopia canthorum**.
*The presence of ash-leaf spots*
- **Ash-leaf spots** (hypopigmented macules) are a hallmark of **Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)**.
- TSC has different ocular findings like **retinal hamartomas**, not Lisch nodules.
*Facial angiofibromas*
- **Facial angiofibromas** (adenoma sebaceum) are a classic manifestation of **Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)**, not NF1.
- NF1 typically presents with **cutaneous and plexiform neurofibromas**, not angiofibromas.
Multiple malformation syndromes US Medical PG Question 4: A 5-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of behavioral problems. His mother says that he has frequent angry outbursts and gets into fights with his classmates. He constantly complains of feeling hungry, even after eating a full meal. He has no siblings, and both of his parents are healthy. He is at the 25th percentile for height and is above the 95th percentile for weight. Physical examination shows central obesity, undescended testes, almond-shaped eyes, and a thin upper lip. Which of the following genetic changes is most likely associated with this patient's condition?
- A. Mitotic nondisjunction of chromosome 21
- B. Mutation of FBN-1 gene on chromosome 15
- C. Microdeletion of long arm of chromosome 7
- D. Loss of paternal gene expression on chromosome 15 (Correct Answer)
- E. Deletion of Phe508 on chromosome 7
Multiple malformation syndromes Explanation: ***Loss of paternal gene expression on chromosome 15***
- The patient's symptoms, including **hyperphagia**, **obesity**, behavioral issues, short stature, and **hypogonadism** (undescended testes), are characteristic of **Prader-Willi syndrome**.
- Prader-Willi syndrome is most commonly caused by the **loss of paternal gene expression** from the **q11-q13 region of chromosome 15**, either due to a paternal deletion, maternal uniparental disomy, or a defect in the imprinting center.
*Microdeletion of long arm of chromosome 7*
- A microdeletion on the long arm of chromosome 7 (7q11.23) is associated with **Williams syndrome**, characterized by an **elfin facial appearance**, supravalvular aortic stenosis, and intellectual disability.
- This does not match the patient's symptoms of obesity, hyperphagia, or hypogonadism.
*Deletion of Phe508 on chromosome 7*
- A deletion of phenylalanine at position 508 (**ΔF508**) on chromosome 7 is the most common mutation in the **cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR)** gene, causing **cystic fibrosis**.
- Cystic fibrosis is an **autosomal recessive disorder** requiring mutations in both alleles (inherited from both parents), and primarily affects the exocrine glands, leading to lung disease, pancreatic insufficiency, and infertility, which are unrelated to the patient's presentation.
*Mutation of FBN-1 gene on chromosome 15*
- A mutation in the **FBN1 gene** on chromosome 15 (15q21.1) causes **Marfan syndrome**, which is a connective tissue disorder.
- Marfan syndrome presents with tall stature, long limbs (**arachnodactyly**), lens dislocation, and aortic root dilation, none of which are described in this patient.
*Mitotic nondisjunction of chromosome 21*
- Mitotic nondisjunction of chromosome 21 can lead to **mosaic Down syndrome**, but **trisomy 21** (due to meiotic nondisjunction) is the most common cause of Down syndrome.
- Down syndrome is associated with characteristic facial features, intellectual disability, and congenital heart defects, which are distinct from the symptoms presented.
Multiple malformation syndromes US Medical PG Question 5: An infant boy of unknown age and medical history is dropped off in the emergency department. The infant appears lethargic and has a large protruding tongue. Although the infant exhibits signs of neglect, he is in no apparent distress. The heart rate is 70/min, the respiratory rate is 30/min, and the temperature is 35.7°C (96.2°F). Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient’s physical exam findings?
- A. Autosomal dominant mutation in the SERPING1 gene
- B. Genetic imprinting disorder affecting chromosome 11p15.5
- C. Type I hypersensitivity reaction
- D. Excess growth hormone secondary to pituitary gland tumor
- E. Congenital agenesis of an endocrine gland in the anterior neck (Correct Answer)
Multiple malformation syndromes Explanation: ***Congenital agenesis of an endocrine gland in the anterior neck***
- This description is highly suggestive of **congenital hypothyroidism**, caused by **thyroid dysgenesis** (agenesis or hypoplasia of the thyroid gland).
- Symptoms include **lethargy**, **macroglossia** (large protruding tongue), **hypotonia**, **feeding difficulties**, **umbilical hernia**, and **hypothermia**, all consistent with the clinical picture.
*Autosomal dominant mutation in the SERPING1 gene*
- A mutation in the **SERPING1 gene** causes **hereditary angioedema**, characterized by recurrent episodes of unpredictable swelling in various body parts.
- While swelling can affect the tongue, it is typically episodic, painful, and often triggered, which is not suggested by the chronic lethargy and physical signs described.
*Genetic imprinting disorder affecting chromosome 11p15.5*
- This describes **Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome**, an overgrowth disorder caused by imprinting defects involving genes like **IGF2**, **H19**, and **CDKN1C** on chromosome 11p15.5.
- Features include **macroglossia**, **macrosomia**, **umbilical hernia**, **hemihyperplasia**, and increased risk of embryonal tumors like **Wilms tumor**.
- However, Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome does not typically present with profound **lethargy** and **hypothermia** as seen in congenital hypothyroidism.
*Type I hypersensitivity reaction*
- A **Type I hypersensitivity reaction** (e.g., anaphylaxis) could cause acute **angioedema** of the tongue, but this would be an acute, rapidly progressing, and life-threatening event.
- The infant's description of being "in no apparent distress" and exhibiting chronic signs like lethargy and hypothermia makes an acute allergic reaction unlikely.
*Excess growth hormone secondary to pituitary gland tumor*
- **Excess growth hormone** (gigantism in children, acromegaly in adults) can cause **macroglossia** and coarse facial features in the long term.
- However, it does not explain the associated **lethargia**, **hypothermia**, and profound developmental delay seen in congenital hypothyroidism in an infant.
Multiple malformation syndromes US Medical PG Question 6: A 5-year-old boy presents for a regularly scheduled check-up. The child is wheelchair bound due to lower extremity paralysis and suffers from urinary incontinence. At birth, it was noted that the child had lower limbs of disproportionately small size in relation to the rest of his body. Radiograph imaging at birth also revealed several abnormalities in the spine, pelvis, and lower limbs. Complete history and physical performed on the child's birth mother during her pregnancy would likely have revealed which of the following?
- A. Maternal use of nicotine
- B. Maternal use of tetracyclines
- C. Maternal hyperthyroidism
- D. Maternal use of lithium
- E. Uncontrolled maternal diabetes mellitus (Correct Answer)
Multiple malformation syndromes Explanation: ***Uncontrolled maternal diabetes mellitus***
- **Maternal diabetes** is a significant risk factor for **caudal regression syndrome**, which presents with **lower limb paralysis**, **urinary incontinence**, and **spinal/pelvic abnormalities**.
- The combination of disproportionately small lower limbs and the associated neurological and skeletal issues strongly points to a congenital anomaly linked to **poor glycemic control** during pregnancy.
*Maternal use of nicotine*
- Maternal nicotine use is associated with a range of adverse pregnancy outcomes, including **low birth weight**, **premature birth**, and **respiratory problems**, but not typically caudal regression syndrome.
- While concerning, it does not directly explain the specific constellation of skeletal, neurological, and urological abnormalities described.
*Maternal use of tetracyclines*
- **Tetracycline exposure** during pregnancy can lead to **tooth discoloration** and **bone growth inhibition**, particularly in the developing fetus.
- It is not known to cause the severe spinal and lower limb malformations, paralysis, or urinary incontinence seen in this case.
*Maternal hyperthyroidism*
- Uncontrolled maternal hyperthyroidism can lead to complications such as **fetal tachycardia**, **goiter**, and **preterm birth**.
- It is not directly associated with congenital malformations like caudal regression syndrome that affect the lower spine and limbs.
*Maternal use of lithium*
- Maternal lithium use is most notably associated with an increased risk of **Ebstein's anomaly**, a congenital **heart defect**.
- It does not explain the specific musculoskeletal, neurological, and urological abnormalities presented in the case.
Multiple malformation syndromes US Medical PG Question 7: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his parents because of a 4.5-kg (10-lb) weight loss during the last 3 months. During this period, he has complained of abdominal pain and fullness, and his parents feel that he has been eating less. His parents also report that his urine has appeared pink for several weeks. He has been performing poorly in school lately, with reports from teachers that he has not been paying attention in class and has been distracting to other students. He was born at term and has been healthy except for a history of several infantile seizures. His vital signs are within normal limits. He is at the 60th percentile for height and 20th percentile for weight. Physical examination shows a palpable abdominal mass, abdominal tenderness in the left upper quadrant, and left costovertebral angle tenderness. There are several ellipsoid, hypopigmented macules on the back and legs and a 4-cm raised plaque of rough, dimpled skin on the right lower back that is the same color as the surrounding skin. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Von Hippel‑Lindau disease
- B. Sturge-Weber syndrome
- C. Neurofibromatosis type 1
- D. Tuberous sclerosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Neurofibromatosis type 2
Multiple malformation syndromes Explanation: ***Tuberous sclerosis***
- The combination of **abdominal mass/tenderness** (suggesting **renal angiomyolipoma**), **pink urine** (indicating **hematuria**), **seizures**, developmental/behavioral issues (poor school performance), **hypopigmented macules** (ash-leaf spots), and a **raised plaque of rough, dimpled skin** (shagreen patch) is highly characteristic of tuberous sclerosis.
- Tuberous sclerosis is a **neurocutaneous disorder** with highly variable manifestations, including **benign tumors** in many organs (e.g., brain, kidneys, heart, skin, lungs).
*Von Hippel–Lindau disease*
- This is an **autosomal dominant disorder** characterized by **hemangioblastomas** of the retina, cerebellum, and spinal cord; **renal cell carcinoma**; and **pheochromocytomas**.
- While it can cause renal masses and hematuria, the absence of cutaneous findings like ash-leaf spots and shagreen patches, and the specific history of seizures and developmental issues, make it less likely.
*Sturge-Weber syndrome*
- Characterized by a **port-wine stain** (facial cutaneous angioma), **leptomeningeal angioma** (leading to seizures, intellectual disability), and **ocular involvement** (glaucoma).
- The patient does not present with a port-wine stain or the specific neurologic findings associated with leptomeningeal angiomas.
*Neurofibromatosis type 1*
- Characterized by **café-au-lait spots**, **axillary/groin freckling**, **neurofibromas**, **Lisch nodules** (iris hamartomas), and optic pathway gliomas.
- While seizures can occur, the presence of ash-leaf spots and a shagreen patch, along with significant renal involvement (angiomyolipoma/hematuria), are not typical features of NF1.
*Neurofibromatosis type 2*
- Primarily involves **bilateral vestibular schwannomas**, leading to hearing loss, tinnitus, and balance problems.
- Cutaneous manifestations are typically limited to a few café-au-lait spots and subcutaneous neurofibromas, which do not match this patient's diverse skin lesions.
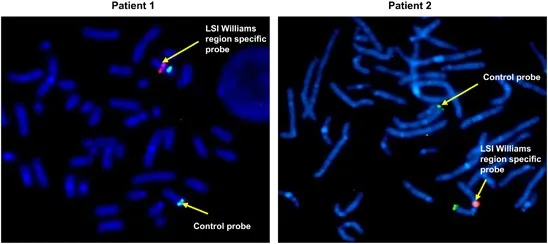
Multiple malformation syndromes US Medical PG Question 8: An 8-year-old child with “elfin” facial features is very friendly with strangers. He has a history of mild mental retardation, and a hemizygous deletion on chromosome 7q11.23, that includes a portion of the elastin gene. Which of the following is most likely true in this patient?
- A. Vitamin D supplementation is recommended
- B. Symptoms may develop secondary to left ventricular outflow tract obstruction (Correct Answer)
- C. This patient is less likely to experience angina
- D. Holosystolic murmur heard at the apex with radiation to the axilla
- E. Carpopedal spasm induced by sphygmomanometer inflation
Multiple malformation syndromes Explanation: ***Symptoms may develop secondary to left ventricular outflow tract obstruction***
* The clinical description of **elfin facies**, extreme friendliness, mild mental retardation, and a deletion on **chromosome 7q11.23** (involving the **elastin gene**) are classic features of **Williams syndrome**.
* **Supravalvular aortic stenosis (SVAS)**, a form of left ventricular outflow tract obstruction, is a common and serious cardiac anomaly in Williams syndrome due to the elastin gene deletion.
*Vitamin D supplementation is recommended*
* Patients with Williams syndrome often experience **hypercalcemia** in infancy, making vitamin D supplementation generally contraindicated rather than recommended.
* This hypercalcemia usually resolves spontaneously in later childhood.
*This patient is less likely to experience angina*
* Due to the high prevalence of **supravalvular aortic stenosis** and other vascular abnormalities in Williams syndrome, these patients are actually **more likely** to experience cardiovascular symptoms, including **angina**, especially with physical exertion.
* Stenosis can lead to increased myocardial oxygen demand, potentially causing angina.
*Holosystolic murmur heard at the apex with radiation to the axilla*
* A holosystolic murmur at the apex radiating to the axilla is characteristic of **mitral regurgitation**, which is not the primary or most common cardiac anomaly in Williams syndrome.
* The characteristic murmur in Williams syndrome due to supravalvular aortic stenosis is typically a **systolic ejection murmur** heard best in the right upper sternal border, often radiating to the neck.
*Carpopedal spasm induced by sphygmomanometer inflation*
* **Carpopedal spasm** induced by sphygmomanometer inflation (Trousseau's sign) is indicative of **hypocalcemia**.
* Patients with Williams syndrome typically experience **hypercalcemia**, not hypocalcemia, particularly during infancy.
Multiple malformation syndromes US Medical PG Question 9: A newborn girl is rushed to the neonatal ICU after an emergency cesarean section due to unstable vital signs after delivery. The pregnancy was complicated due to oligohydramnios and pulmonary hypoplasia. Gestation was at 38 weeks. APGAR scores were 6 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes respectively. The newborn’s temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), the blood pressure is 60/40 mm Hg, the respiratory rate is 45/min, and the pulse is 140/min. Physical examination reveals irregularly contoured bilateral abdominal masses. Abdominal ultrasound reveals markedly enlarged echogenic kidneys (5 cm in the vertical dimension) with multiple cysts in the cortex and medulla. This patient is at highest risk of which of the following complications?
- A. Portal hypertension (Correct Answer)
- B. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- C. Acute renal failure
- D. Recurrent UTI
- E. Emphysema
Multiple malformation syndromes Explanation: ***Portal hypertension***
* The presentation of **oligohydramnios**, **pulmonary hypoplasia**, and **enlarged, echogenic kidneys with multiple cysts** in a newborn is consistent with **autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD)**.
* ARPKD is invariably associated with **congenital hepatic fibrosis**, which leads to **portal hypertension** due to periportal fibrosis and obstruction of intrahepatic portal blood flow. This is the hallmark extra-renal complication of ARPKD.
*Subarachnoid hemorrhage*
* Subarachnoid hemorrhage from berry aneurysm rupture is associated with **autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)**, not ARPKD.
* There are no specific clinical features or imaging findings in this case that would suggest intracranial hemorrhage as the highest risk complication.
*Acute renal failure*
* While neonates with ARPKD can develop renal insufficiency and progressive chronic kidney disease, the question asks for the "highest risk **complication**" rather than the primary disease manifestation.
* **Portal hypertension from congenital hepatic fibrosis** is the most significant distinct complication that develops as a consequence of ARPKD, often manifesting in childhood with hepatosplenomegaly, esophageal varices, and hypersplenism.
*Recurrent UTI*
* Recurrent UTIs require structural abnormalities like vesicoureteral reflux or urinary stasis, which are not primary features of ARPKD.
* While children with kidney disease may have increased infection risk, recurrent UTIs are not a direct or characteristic complication of the cystic kidney disease in ARPKD.
*Emphysema*
* **Pulmonary hypoplasia** (underdeveloped lungs from oligohydramnios/Potter sequence) is present in this case, but this is not the same as emphysema.
* Emphysema involves destruction of alveolar walls and is typically seen in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency, not in neonates with pulmonary hypoplasia.
Multiple malformation syndromes US Medical PG Question 10: A 1-week-old baby is brought to the pediatrician’s office for a routine checkup. On examination, she is observed to have microcephaly with a prominent occiput. She also has clenched fists and rocker-bottom feet with prominent calcanei. A cardiac murmur is evident on auscultation. Based on the clinical findings, a diagnosis of nondisjunction of chromosome 18 is suspected. The pediatrician orders a karyotype for confirmation. He goes on to explain to the mother that her child will face severe growth difficulties. Even if her daughter progresses beyond a few months, she will not be able to reach developmental milestones at the appropriate age. In addition to the above, which of the following is most likely a consequence of this genetic disturbance?
- A. Supravalvular aortic stenosis
- B. Alzheimer’s disease
- C. Macroglossia
- D. Cutis aplasia
- E. Death within the first year of life (Correct Answer)
Multiple malformation syndromes Explanation: ***Death within the first year of life***
- This patient has Trisomy 18, also known as Edwards syndrome, which is characterized by a high mortality rate, with **90-95% of affected infants dying within the first year** due to severe congenital anomalies, especially cardiac defects.
- **Rocker-bottom feet**, **clenched fists with overlapping fingers**, **microcephaly with a prominent occiput**, and **congenital heart defects** (such as ventricular septal defects or patent ductus arteriosus) are classic features of Trisomy 18.
*Cutis aplasia*
- **Cutis aplasia** (a congenital absence of skin) is a characteristic symptom of **Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)**, not Trisomy 18.
- While both are chromosomal abnormalities, their specific phenotypic presentations differ, making cutis aplasia less likely in this case.
*Macroglossia*
- **Macroglossia** (an enlarged tongue) is a common feature of **Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)**.
- It is not typically associated with Trisomy 18, which presents with distinct facial and oral features.
*Alzheimer’s disease*
- Individuals with **Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)** have an increased risk of developing **early-onset Alzheimer's disease**, often by middle age.
- This is due to the triplication of the **APP gene**, located on chromosome 21, which is involved in amyloid-beta plaque formation.
*Supravalvular aortic stenosis*
- **Supravalvular aortic stenosis** (narrowing of the aorta above the aortic valve) is a characteristic cardiac finding in **Williams syndrome**, a microdeletion syndrome involving chromosome 7.
- Williams syndrome is also associated with elfin facies, intellectual disability, and a friendly personality, none of which align with this patient's presentation.
More Multiple malformation syndromes US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.