Craniofacial anomalies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Craniofacial anomalies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Craniofacial anomalies US Medical PG Question 1: A 4-year-old boy presents to his pediatrician for severe developmental delay. On exam he is noted to have macroorchidism, hypertelorism, large protruding ears, a large jaw, and a long thin face. Suspicious of what the diagnosis may be, the pediatrician orders a PCR and DNA sequencing. The results reveal an expansion of 250 repeats of CGG. What is the diagnosis of the boy?
- A. Huntington's disease
- B. Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy
- C. Myotonic dystrophy type 1
- D. Fragile X syndrome (Correct Answer)
- E. Friedreich ataxia
Craniofacial anomalies Explanation: ***Fragile X syndrome***
- The combination of **developmental delay**, characteristic physical features (**macroorchidism, large protruding ears, long thin face, large jaw**), and a **CGG repeat expansion** (250 repeats) is pathognomonic for Fragile X syndrome.
- This is an **X-linked disorder** caused by an expansion of CGG trinucleotide repeats in the *FMR1* gene, leading to reduced or absent fragile X mental retardation protein (FMRP).
*Huntington's disease*
- Characterized by **chorea**, psychiatric symptoms, and cognitive decline, typically manifesting in adulthood, not early childhood developmental delay.
- Caused by a **CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion** in the *HTT* gene, not CGG.
*Spinal and bulbar muscular atrophy*
- This is an **X-linked recessive** neurodegenerative disorder leading to muscle weakness and atrophy, which usually presents in adulthood.
- It is caused by a **CAG repeat expansion** in the androgen receptor gene.
*Myotonic dystrophy type 1*
- Presents with progressive **muscle wasting and weakness**, myotonia, cataracts, and cardiac conduction defects, typically later in childhood or adulthood.
- Caused by a **CTG trinucleotide repeat expansion** in the *DMPK* gene.
*Friedreich ataxia*
- Characterized by progressive **ataxia**, dysarthria, and loss of vibration/proprioception, usually beginning in childhood or adolescence.
- Caused by a **GAA trinucleotide repeat expansion** in the *FXN* gene.
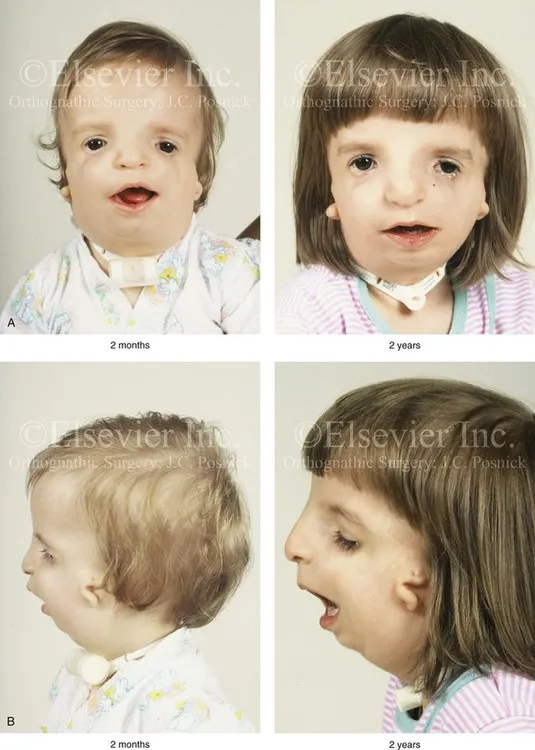
Craniofacial anomalies US Medical PG Question 2: A 10-year-old boy comes for a post-operative clinic visit with his ENT surgeon three months after airway reconstruction surgery and placement of a tracheostomy tube. Since the surgery, he says that he has been able to breathe better and is now getting used to tracheostomy care and tracheostomy tube changes. In addition to this surgery, he has had over twenty surgeries to implant hearing aids, reconstruct his cheekbones, and support his jaw to enable him to swallow. He was born with these abnormalities and had difficult breathing, hearing, and eating throughout his childhood. Fortunately, he is now beginning to feel better and is able to attend public school where he is one of the best students in the class. Abnormal development of which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient's malformations?
- A. Second branchial cleft
- B. First branchial pouch
- C. Third and fourth branchial pouches
- D. First branchial arch (Correct Answer)
- E. Second branchial arch
Craniofacial anomalies Explanation: ***First branchial arch***
- The clinical presentation describes features consistent with **Treacher Collins syndrome** (TCS), also known as mandibulofacial dysostosis, which results from maldevelopment of **both the first and second branchial arches**.
- However, the **predominant and most characteristic features** arise from **first branchial arch** abnormalities: **mandibular hypoplasia** (requiring jaw support for swallowing), **malar/zygomatic hypoplasia** (reconstructed cheekbones), and **maxillary hypoplasia**.
- These first arch skeletal abnormalities cause the **airway obstruction** (requiring tracheostomy) and feeding difficulties.
- The first branchial arch gives rise to: **mandible, maxilla, zygomatic bone, incus, malleus, muscles of mastication, and CN V** (trigeminal nerve).
- While hearing issues may involve second arch structures (stapes), the **overwhelming majority** of this patient's clinical problems stem from first arch malformations.
*Second branchial cleft*
- The second branchial cleft typically forms the **cervical sinus**, which normally obliterates. Persistence can lead to **cervical cysts or fistulas**, presenting as neck masses.
- Abnormalities of the second branchial cleft do not explain the extensive craniofacial malformations, hearing deficits, or airway compromise seen in this patient.
*First branchial pouch*
- The first branchial pouch gives rise to the **auditory (eustachian) tube** and the **tympanic cavity** (middle ear).
- While isolated first pouch defects could contribute to hearing problems, they would **not explain** the severe facial bone malformations (mandibular and malar hypoplasia), airway obstruction, or feeding difficulties.
- The pouch is distinct from the arch, which forms the skeletal and muscular structures.
*Third and fourth branchial pouches*
- The third branchial pouch contributes to the **inferior parathyroid glands** and the **thymus**. The fourth branchial pouch contributes to the **superior parathyroid glands** and the **ultimobranchial body** (parafollicular C cells of the thyroid).
- Abnormalities in these pouches, such as in **DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion)**, lead to **T-cell immunodeficiency, hypocalcemia, and cardiac defects** but do not account for the craniofacial and hearing abnormalities described.
*Second branchial arch*
- The second branchial arch gives rise to the **stapes**, **styloid process**, **lesser horn and upper body of hyoid bone**, **stapedius muscle**, and **CN VII** (facial nerve).
- While Treacher Collins syndrome involves both first and second arch abnormalities, the **second arch contributions** are less prominent clinically.
- Second arch defects could contribute to **conductive hearing loss** (via stapes abnormalities) and **facial nerve issues**, but these are not the predominant features in this case.
- The critical skeletal malformations causing airway compromise, feeding difficulties, and facial dysmorphism are primarily **first arch** derivatives.
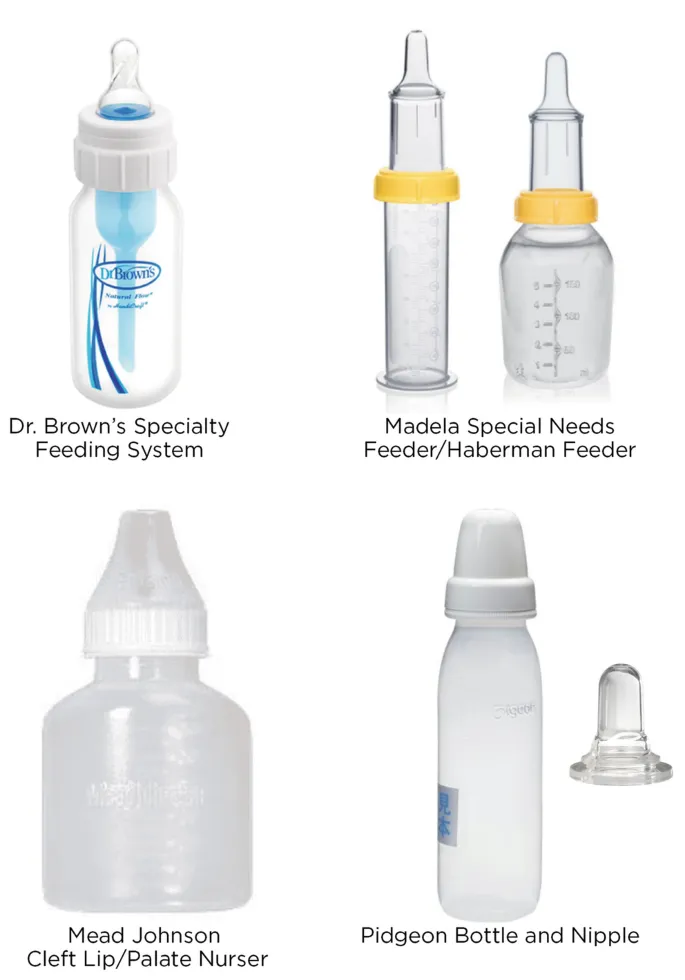
Craniofacial anomalies US Medical PG Question 3: A 29-year-old mother brings in her 2-week-old baby boy to a pediatrician because he has been having difficulty feeding. The mother reveals that she had no prenatal care during her pregnancy and gave birth at home without complications. She says that her son seems to be having difficulty sucking, and she occasionally sees breast milk coming out of the infant’s nose. Physical exam reveals that this patient has a gap between his oral and nasal cavities behind the incisive foramen. He is therefore prescribed specialized bottles and his mom is taught positional techniques to ensure better feeding. Failure to fuse which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient's disorder?
- A. Maxillary and medial nasal prominences
- B. Nasal septum with primary plates
- C. Maxillary and lateral nasal prominences
- D. Palatine shelves with primary plates
- E. Palatine shelves with nasal septum (Correct Answer)
Craniofacial anomalies Explanation: ***Palatine shelves with nasal septum***
- A **cleft palate** results from the **failure of fusion of the palatine shelves** with each other and/or with the **nasal septum**, creating an abnormal communication between the oral and nasal cavities.
- This anatomical defect explains the infant's **feeding difficulties** and the leakage of breast milk into the nose, as well as the observed **gap behind the incisive foramen**.
*Maxillary and medial nasal prominences*
- The failure of fusion between the maxillary and medial nasal prominences results in a **cleft lip**, which is an anterior defect and does not explain the posterior gap described.
- While cleft lip can coexist with cleft palate, the symptoms here specifically point to a palatal defect, not primarily a lip defect.
*Nasal septum with primary plates*
- The primary palate forms from the fusion of the medial nasal prominences, anterior to the incisive foramen.
- While crucial for normal development, the specific clinical presentation (gap *behind* the incisive foramen and feeding difficulties) is more characteristic of a secondary palate defect involving the palatine shelves.
*Maxillary and lateral nasal prominences*
- The fusion of these structures contributes to the formation of the **nasolacrimal groove** and parts of the cheek, not the palate.
- Deficiencies in this fusion would lead to defects in the lateral facial region, not an oro-nasal communication related to feeding.
*Palatine shelves with primary plates*
- The **primary palate** fuses with the anterior part of the secondary palate (formed by the palatine shelves) at the incisive foramen.
- However, the more common and clinically relevant defect leading to an open communication between the oral and nasal cavities, especially *behind* the incisive foramen, involves the failure of fusion of the **palatine shelves** with each other and the **nasal septum**.
Craniofacial anomalies US Medical PG Question 4: A group of investigators studying embryological defects in mice knock out a gene that is responsible for the development of the ventral wing of the third branchial pouch. A similar developmental anomaly in a human embryo is most likely to result in which of the following findings after birth?
- A. Cleft palate
- B. Discharging neck sinus (Correct Answer)
- C. Carpopedal spasm
- D. Conductive hearing loss
- E. White oral patches
Craniofacial anomalies Explanation: ***Discharging neck sinus***
- The **ventral wing of the third pharyngeal pouch** gives rise to the **thymus**
- During embryonic development, the thymus descends from the pharynx into the anterior mediastinum via the **thymopharyngeal duct**
- Normally, this duct obliterates completely, but **failure of obliteration** can result in a **cervical thymic cyst** or **persistent thymic tract**
- This presents as a **discharging neck sinus** along the lateral neck (anterior border of sternocleidomastoid), which may drain clear fluid or become infected
- This is a classic presentation of a **third pharyngeal pouch anomaly** affecting the thymic descent pathway
*Carpopedal spasm*
- **Carpopedal spasm** is a sign of **hypocalcemia** due to **hypoparathyroidism**
- The **dorsal wing** (not ventral wing) of the third pharyngeal pouch forms the **inferior parathyroid glands**
- Since the question specifically identifies a defect in the **ventral wing** (thymus), hypoparathyroidism would not result
- A dorsal wing defect would cause absent inferior parathyroid glands and hypocalcemia
*Cleft palate*
- Results from failure of **palatine shelf fusion** during weeks 8-12 of development
- Associated with **maxillary prominence** derivatives (first pharyngeal arch) and secondary palate formation
- Not related to third pharyngeal pouch development
*Conductive hearing loss*
- Associated with **first and second pharyngeal arch** derivatives affecting the middle ear structures
- First arch: malleus, incus (in part); Second arch: stapes (in part)
- The **third pharyngeal pouch** does not contribute to auditory structures
*White oral patches*
- Typically represent **mucosal lesions** (leukoplakia, candidiasis, lichen planus)
- Not associated with embryological defects of the pharyngeal apparatus
- Unrelated to third pharyngeal pouch derivatives
Craniofacial anomalies US Medical PG Question 5: A 31-year-old woman delivers a healthy boy at 38 weeks gestation. The delivery is vaginal and uncomplicated. The pregnancy was unremarkable. On examination of the newborn, it is noted that his head is tilted to the left and his chin is rotated to the right. Palpation reveals no masses or infiltration in the neck. The baby also shows signs of left hip dysplasia. Nevertheless, the baby is active and exhibits no signs of other pathology. What is the most probable cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Basal ganglia abnormalities
- B. Antenatal trauma
- C. Congenital infection
- D. Accessory nerve palsy
- E. Intrauterine malposition (Correct Answer)
Craniofacial anomalies Explanation: ***Intrauterine malposition***
- The combination of **congenital muscular torticollis** (head tilted left, chin rotated right) and **hip dysplasia** in a newborn strongly suggests **intrauterine confinement**.
- **Malposition** *in utero* can restrict fetal movement and lead to musculoskeletal abnormalities due to prolonged pressure on developing structures.
*Basal ganglia abnormalities*
- **Basal ganglia abnormalities** typically present with movement disorders such as dyskinesias, dystonia, or rigidity, often without the specific musculoskeletal findings described.
- While they can cause abnormal posturing, the concurrent **hip dysplasia** points away from a primary neurological cause.
*Antenatal trauma*
- **Antenatal trauma** (trauma occurring during pregnancy before labor) severe enough to cause these musculoskeletal findings would typically require significant force and would likely present with other signs of injury or complications during pregnancy.
- The **unremarkable pregnancy** and **uncomplicated delivery** make trauma an unlikely cause.
- These findings are better explained by chronic positional constraint rather than acute traumatic injury.
*Congenital infection*
- **Congenital infections** such as TORCH infections usually present with a broader range of symptoms including systemic illness, neurological impairments (e.g., microcephaly, seizures), or specific organ damage.
- The isolated musculoskeletal findings of torticollis and hip dysplasia, without other signs, are not characteristic of a congenital infection.
*Accessory nerve palsy*
- **Accessory nerve palsy** would primarily affect the **sternocleidomastoid** and **trapezius muscles**, leading to weakness and potentially torticollis.
- However, it would not explain the associated **hip dysplasia**, making it an incomplete diagnosis for the overall presentation.
Craniofacial anomalies US Medical PG Question 6: A 1-week-old baby is brought to the pediatrician’s office for a routine checkup. On examination, she is observed to have microcephaly with a prominent occiput. She also has clenched fists and rocker-bottom feet with prominent calcanei. A cardiac murmur is evident on auscultation. Based on the clinical findings, a diagnosis of nondisjunction of chromosome 18 is suspected. The pediatrician orders a karyotype for confirmation. He goes on to explain to the mother that her child will face severe growth difficulties. Even if her daughter progresses beyond a few months, she will not be able to reach developmental milestones at the appropriate age. In addition to the above, which of the following is most likely a consequence of this genetic disturbance?
- A. Supravalvular aortic stenosis
- B. Alzheimer’s disease
- C. Macroglossia
- D. Cutis aplasia
- E. Death within the first year of life (Correct Answer)
Craniofacial anomalies Explanation: ***Death within the first year of life***
- This patient has Trisomy 18, also known as Edwards syndrome, which is characterized by a high mortality rate, with **90-95% of affected infants dying within the first year** due to severe congenital anomalies, especially cardiac defects.
- **Rocker-bottom feet**, **clenched fists with overlapping fingers**, **microcephaly with a prominent occiput**, and **congenital heart defects** (such as ventricular septal defects or patent ductus arteriosus) are classic features of Trisomy 18.
*Cutis aplasia*
- **Cutis aplasia** (a congenital absence of skin) is a characteristic symptom of **Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)**, not Trisomy 18.
- While both are chromosomal abnormalities, their specific phenotypic presentations differ, making cutis aplasia less likely in this case.
*Macroglossia*
- **Macroglossia** (an enlarged tongue) is a common feature of **Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)**.
- It is not typically associated with Trisomy 18, which presents with distinct facial and oral features.
*Alzheimer’s disease*
- Individuals with **Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)** have an increased risk of developing **early-onset Alzheimer's disease**, often by middle age.
- This is due to the triplication of the **APP gene**, located on chromosome 21, which is involved in amyloid-beta plaque formation.
*Supravalvular aortic stenosis*
- **Supravalvular aortic stenosis** (narrowing of the aorta above the aortic valve) is a characteristic cardiac finding in **Williams syndrome**, a microdeletion syndrome involving chromosome 7.
- Williams syndrome is also associated with elfin facies, intellectual disability, and a friendly personality, none of which align with this patient's presentation.
Craniofacial anomalies US Medical PG Question 7: A 45-day-old male infant is brought to a pediatrician by his parents with concerns of poor feeding and excessive perspiration for one week. On physical examination, his temperature is 37.7°C (99.8°F), pulse rate is 190/min, and respiratory rate is 70/min. Mild cyanosis is present over the lips, and over the nail beds. Oxygen is provided and his oxygen saturation is carefully monitored. The pediatrician orders a bedside echocardiogram of the infant. It reveals a single arterial trunk arising from 2 normally formed ventricles. The arterial trunk is separated from the ventricles by a single semilunar valve. There is a defect in the interventricular septum, and the arterial trunk overrides the defect. Which of the following congenital heart diseases can also present with similar clinical features?
- A. Infracardiac total anomalous pulmonary venous return
- B. Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum
- C. Severe Ebstein anomaly
- D. Double-inlet ventricle with unobstructed pulmonary flow
- E. Transposition of the great arteries with ventricular septal defect and pulmonary stenosis (Correct Answer)
Craniofacial anomalies Explanation: ***Transposition of the great arteries with ventricular septal defect and pulmonary stenosis***
- The described echocardiogram findings point to **Truncus Arteriosus**, characterized by a single great artery overriding a **ventricular septal defect (VSD)** and severe **cyanosis**.
- **Transposition of the great arteries (TGA)** with a VSD and pulmonary stenosis also presents with profound cyanosis, heart failure symptoms (poor feeding, tachypnea, tachycardia), and can lead to similar **hemodynamic instability** due to mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood and outflow tract obstruction.
*Infracardiac total anomalous pulmonary venous return*
- This condition involves all pulmonary veins draining into the systemic venous circulation below the diaphragm, often into the **portal vein** or **ductus venosus**.
- While it causes severe cyanosis and cardiopulmonary distress in infancy, the **echocardiogram findings** (single arterial trunk, VSD) are distinct from the typical features of infracardiac TAPVR, which would show abnormal pulmonary venous connection at the systemic level rather than a single great artery.
*Pulmonary atresia with intact ventricular septum*
- This involves a **complete obstruction of the pulmonary valve**, preventing blood flow from the right ventricle to the pulmonary artery, leading to severe cyanosis.
- However, the echocardiogram description of a **single arterial trunk overriding a VSD** is not consistent with pulmonary atresia with an intact ventricular septum.
*Severe Ebstein anomaly*
- This anomaly is characterized by apical displacement of the **tricuspid valve leaflets**, leading to severe tricuspid regurgitation and functional hypoplasia of the right ventricle.
- While it can cause cyanosis and heart failure, the echocardiogram findings of a single arterial trunk and overriding VSD are not typical of **Ebstein anomaly**.
*Double-inlet ventricle with unobstructed pulmonary flow*
- A double-inlet ventricle means both atria connect to a single functional ventricle, but with **unobstructed pulmonary flow**, there would likely be less severe cyanosis (or none) and more symptoms of **congestive heart failure** due to pulmonary overcirculation.
- This condition's echocardiogram findings are also distinct from the described single arterial trunk and overriding VSD, which are characteristic of **Truncus Arteriosus**.
Craniofacial anomalies US Medical PG Question 8: A 15-year-old boy is brought to the physician for a well-child visit. His parents are concerned that he has not had his growth spurt yet. As a child, he was consistently in the 60th percentile for height; now he is in the 25th percentile. His classmates make fun of his height and high-pitched voice. His parents are also concerned that he does not maintain good hygiene. He frequently forgets to shower and does not seem aware of his body odor. As an infant, he had bilateral orchidopexy for cryptorchidism and a cleft palate repair. He is otherwise healthy. Vital signs are within normal limits. On physical exam, axillary and pubic hair is sparse. Genitals are Tanner stage 1 and the testicles are 2 mL bilaterally. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Constitutional delay of puberty
- B. Hyperprolactinemia
- C. Hypothyroidism
- D. Primary hypogonadism
- E. Kallmann syndrome (Correct Answer)
Craniofacial anomalies Explanation: ***Kallmann syndrome***
- This patient's presentation with **anosmia/hyposmia** (implied by poor hygiene and lack of awareness of body odor), **delayed puberty** (Tanner stage 1 at 15 years old, small testicular volume), and a history of **cryptorchidism** and **cleft palate** is highly suggestive of Kallmann syndrome.
- Kallmann syndrome is a form of **congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism** characterized by a deficiency in **GnRH** migration and function, leading to impaired sexual development and a lack of olfactory bulb development.
*Constitutional delay of puberty*
- While constitutional delay also presents with delayed puberty, it typically does **not include associated congenital anomalies** like cryptorchidism or cleft palate, nor does it present with features suggestive of anosmia.
- Children with constitutional delay often have a family history of delayed puberty, and their **growth deceleration** is usually less pronounced and still follows a growth curve.
*Hyperprolactinemia*
- **Hyperprolactinemia** causes hypogonadism by inhibiting GnRH, leading to delayed puberty, but it is not associated with **anosmia**, **cryptorchidism**, or **cleft palate**.
- It would typically be investigated if central nervous system symptoms like **headaches** or **visual field defects** were present, or in the context of certain medications.
*Hypothyroidism*
- **Hypothyroidism** can cause delayed puberty and growth deceleration, but it is not associated with **anosmia**, **cryptorchidism**, or **cleft palate**.
- Other classic symptoms of hypothyroidism, such as **fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, and constipation**, are not mentioned.
*Primary hypogonadism*
- **Primary hypogonadism** (e.g., Klinefelter syndrome) would present with elevated gonadotropins (LH and FSH) due to testicular failure, unlike the hypogonadotropic hypogonadism seen in Kallmann syndrome.
- While cryptorchidism can lead to primary hypogonadism, the additional features of **anosmia/hyposmia** and **cleft palate** point specifically to Kallmann syndrome.
Craniofacial anomalies US Medical PG Question 9: Thirty minutes after delivery, a 3400-g (7.5-lb) female newborn develops cyanosis of her lips and oral mucosa. She was born at 36 weeks of gestation to a 30-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 0. Apgar scores are 7 and 8 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Pregnancy was complicated by polyhydramnios. The patient's temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 144/min, respirations are 52/min, and blood pressure is 70/40 mm Hg. Examination shows foaming and drooling at the mouth. Bilateral crackles are heard at the lung bases. There is a harsh 3/6 systolic murmur along the left sternal border. The abdomen is soft and mildly distended. There is an anterior ectopic anus. Insertion of a nasogastric tube is attempted. An x-ray of the chest and abdomen is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. H‑type tracheoesophageal fistula without esophageal atresia
- B. Esophageal atresia with tracheoesophageal fistula to the distal esophageal segment (Correct Answer)
- C. Esophageal atresia with tracheoesophageal fistula to the proximal and distal esophageal segments
- D. Esophageal atresia without tracheoesophageal fistula
- E. Esophageal atresia with tracheoesophageal fistula to the proximal esophageal segment
Craniofacial anomalies Explanation: ***Esophageal atresia with tracheoesophageal fistula to the distal esophageal segment***
- This is **Type C EA/TEF**, the most common variant (85-90% of cases)
- **Inability to pass NG tube** (coils in proximal blind pouch on X-ray) confirms esophageal atresia
- **Foaming and drooling** occur because saliva cannot be swallowed past the atretic segment
- **Mild abdominal distension** results from air entering the stomach via the **distal TEF** during breathing
- **Cyanosis and crackles** indicate aspiration pneumonitis from gastric contents refluxing through the distal fistula into the trachea
- Associated with **VACTERL anomalies** (cardiac murmur, anorectal malformation seen here)
*H-type tracheoesophageal fistula without esophageal atresia*
- In H-type TEF, there is **no esophageal atresia**, so the NG tube would pass normally into the stomach
- Patients typically present later with **recurrent aspiration during feeds**, not immediate drooling at birth
- Would not cause the **immediate foaming and drooling** seen in this newborn
*Esophageal atresia with tracheoesophageal fistula to the proximal and distal esophageal segments*
- This is **Type D EA/TEF** (very rare, 1-2% of cases)
- Would cause **more severe abdominal distension** because air enters via both proximal and distal fistulas
- The clinical presentation here is most consistent with the more common Type C
*Esophageal atresia without tracheoesophageal fistula*
- This is **Type A** (pure EA, 5-8% of cases)
- Key differentiating feature: **scaphoid (flat) abdomen** because no air can enter the GI tract
- The **mild abdominal distension** in this case indicates a distal fistula is present
*Esophageal atresia with tracheoesophageal fistula to the proximal esophageal segment*
- This is **Type B EA/TEF** (very rare, <1% of cases)
- Would cause **severe aspiration** with feeding attempts as oral contents enter trachea via proximal fistula
- Would have **scaphoid abdomen** (no air pathway to stomach), not the mild distension seen here
Craniofacial anomalies US Medical PG Question 10: A 4-year-old boy is brought to a pediatrician with a history of repeated episodes of right-ear symptoms, including irritability, fever, ear pain, and pulling at the ear, for the last 2 years. Each episode has been treated with an appropriate antibiotic for the recommended duration of time as prescribed by the pediatrician. The boy had experienced 3 episodes during his 3rd year of life and 5 episodes during the last year; the last episode occurred 2 months ago. There is no history of recurrent rhinosinusitis or nasal obstruction. On physical examination, vital signs are stable. Otoscopic examination of the right ear reveals a white tympanic membrane with decreased mobility. There is no erythema or bulging of the tympanic membrane. Which of the following interventions is most likely to be considered for further management of this child?
- A. Antibiotic prophylaxis with subtherapeutic dose of sulfonamide
- B. Myringotomy without insertion of a tympanostomy tube
- C. Myringotomy with insertion of a tympanostomy tube (Correct Answer)
- D. Oral corticosteroids for 2 weeks
- E. Adenoidectomy
Craniofacial anomalies Explanation: ***Myringotomy with insertion of a tympanostomy tube***
- This child has recurrent **acute otitis media (AOM)**, defined as three or more episodes in 6 months or four or more episodes in 12 months, with the last episode having occurred within the past 2 months. The physical exam finding of a **white tympanic membrane with decreased mobility** suggests **otitis media with effusion (OME)**, a common sequela of recurrent AOM. Insertion of tympanostomy tubes is indicated for recurrent AOM, especially when associated with OME, as it ventilates the middle ear and reduces recurrence.
- **Tympanostomy tube insertion** helps in draining middle ear fluid, equalizing pressure, and preventing further episodes of AOM and OME, thereby preserving **hearing** and preventing developmental delays.
*Antibiotic prophylaxis with subtherapeutic dose of sulfonamide*
- While antibiotic prophylaxis can be considered for recurrent AOM, it is less favored now due to concerns about **antibiotic resistance** and is generally reserved for situations where surgical intervention is not an option or as a bridge to surgery.
- The efficacy of prophylactic antibiotics is modest, and the current recommendation for this frequency of AOM tends towards **tympanostomy tube insertion**.
*Myringotomy without insertion of a tympanostomy tube*
- **Myringotomy** alone provides temporary relief by draining fluid, but the incision typically heals within days, leading to a recurrence of fluid accumulation and pressure issues.
- Without a tube, the benefits are short-lived, failing to address the underlying issue of ** Eustachian tube dysfunction** in the long term, which contributes to recurrent OME and AOM.
*Oral corticosteroids for 2 weeks*
- **Corticosteroids** are sometimes considered for OME to reduce inflammation, but their long-term efficacy in recurrent AOM with OME is limited and not a primary treatment option.
- Their use is generally reserved for specific cases and not recommended as a standalone treatment for recurrent AOM, especially given the established benefits of **tympanostomy tubes**.
*Adenoidectomy*
- **Adenoidectomy** is primarily considered for children with recurrent AOM only if they also have **nasal obstruction**, chronic rhinosinusitis, or evidence of adenoid hypertrophy contributing to Eustachian tube dysfunction, none of which are mentioned in this case.
- While adenoidectomy can be beneficial, it's typically an adjunct to or considered after **tympanostomy tube placement** in specific situations, and not the initial primary intervention for this presentation.
More Craniofacial anomalies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.