Osteosarcoma US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Osteosarcoma. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Osteosarcoma US Medical PG Question 1: A 62-year-old retired professor comes to the clinic with the complaints of back pain and increasing fatigue over the last 4 months. For the past week, his back pain seems to have worsened. It radiates to his legs and is burning in nature, 6/10 in intensity. There is no associated tingling sensation. He has lost 4.0 kg (8.8 lb) in the past 2 months. There is no history of trauma. He has hypertension which is well controlled with medications. Physical examination is normal. Laboratory studies show normocytic normochromic anemia. Serum calcium is 12.2 mg/dL and Serum total proteins is 8.8 gm/dL. A serum protein electrophoresis shows a monoclonal spike. X-ray of the spine shows osteolytic lesions over L2–L5 and right femur. A bone marrow biopsy reveals plasmacytosis. Which of the following is the most preferred treatment option?
- A. Renal dialysis
- B. Palliative care
- C. Chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplant (Correct Answer)
- D. Bisphosphonates
- E. Chemotherapy alone
Osteosarcoma Explanation: ***Chemotherapy and autologous stem cell transplant***
- This patient presents with classic features of **multiple myeloma**, including bone pain with osteolytic lesions, hypercalcemia, normocytic anemia, elevated total protein with a monoclonal spike, and plasmacytosis in the bone marrow.
- In a relatively healthy patient with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who is fit for intensive therapy (as suggested by the absence of significant comorbidities beyond controlled hypertension), **chemotherapy followed by autologous stem cell transplant (ASCT)** is the preferred treatment to achieve deeper and more durable remission.
*Renal dialysis*
- While **renal impairment** can occur in multiple myeloma due to myeloma kidney, it is not described in this patient, and **dialysis** is a supportive measure for end-stage kidney disease, not the primary treatment for the underlying malignancy.
- The patient's symptoms are primarily related to bone involvement and systemic effects of myeloma, not severe renal failure.
*Palliative care*
- **Palliative care** focuses on symptom relief and quality of life, which is essential at any stage of a serious illness, but it is not the initial primary therapeutic intervention for a newly diagnosed, symptomatic, and treatable cancer like multiple myeloma in a patient who could benefit from curative or remission-inducing therapy.
- The goal at this stage is disease control and prolonging survival.
*Bisphosphonates*
- **Bisphosphonates** (e.g., zoledronic acid) are an important adjunctive therapy in multiple myeloma to manage and prevent **skeletal-related events** by inhibiting osteoclast activity, but they do not treat the underlying plasma cell malignancy itself.
- They would be used in conjunction with chemotherapy, not as a standalone primary treatment.
*Chemotherapy alone*
- While **chemotherapy** (often a combination of proteasome inhibitors, immunomodulatory drugs, and dexamethasone) is central to treating multiple myeloma, **chemotherapy alone** without subsequent ASCT is typically reserved for patients who are not candidates for transplantation due to age, comorbidities, or frailty.
- For transplant-eligible patients, ASCT after induction chemotherapy significantly improves progression-free survival and overall survival compared to chemotherapy alone.
Osteosarcoma US Medical PG Question 2: An investigator studying targeted therapy in patients with gastrointestinal stromal tumors requires a reliable test to determine the spatial distribution of CD117-positive cells in biopsy specimens. Which of the following is the most appropriate test?
- A. Northern blot
- B. Immunohistochemistry (Correct Answer)
- C. Flow cytometry
- D. Fluorescence in-situ hybridization
- E. Western blot
Osteosarcoma Explanation: ***Immunohistochemistry***
- **Immunohistochemistry (IHC)** uses **antibodies** to target specific antigens (like **CD117**) within tissue sections, allowing for **visualization of their spatial distribution** under a microscope.
- This technique is ideal for identifying the precise location and quantity of **CD117-positive cells** within a biopsy, which is crucial for assessing targeted therapy in gastrointestinal stromal tumors.
*Northern blot*
- **Northern blot** is used to detect and quantify specific **RNA** sequences in a sample.
- It does not provide information about **protein expression** or the **spatial distribution of cells** within tissue.
*Flow cytometry*
- **Flow cytometry** is used for analyzing and sorting cells based on their **surface or intracellular markers** by passing them in a fluid stream through laser light.
- While it can quantify **CD117-positive cells**, it requires cells to be in suspension and thus **destroys the tissue architecture**, preventing analysis of spatial distribution.
*Fluorescence in-situ hybridization*
- **Fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH)** uses **fluorescent probes** to detect and locate specific **DNA or RNA sequences** on chromosomes or in cells.
- FISH is primarily used for genetic analysis and **does not directly assess protein expression** or cellular distribution in the context of targeted therapy.
*Western blot*
- **Western blot** is used to detect and quantify specific **proteins** from a sample by separating them by size, but it is performed on **tissue homogenates**.
- This technique provides information on the **total protein content** but **does not preserve the spatial arrangement** of cells within the original tissue.
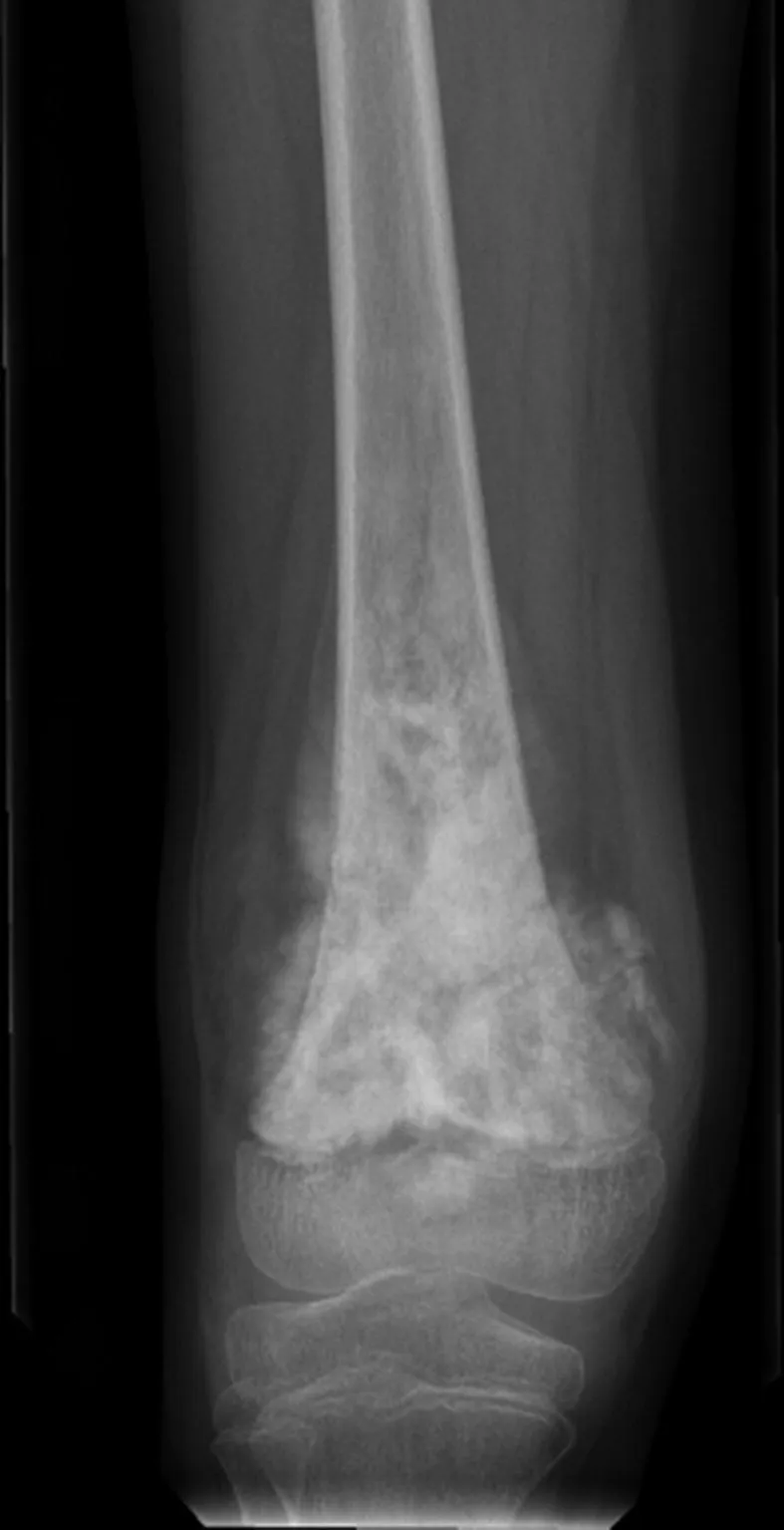
Osteosarcoma US Medical PG Question 3: A 12-year-old Caucasian male presents with his mother to the pediatrician’s office complaining of right thigh pain. He reports that he has noticed slowly progressive pain and swelling over the distal aspect of his right thigh over the past two months. He denies any recent trauma to the area and his temperature is 100.9°F (38.3°C). On exam, there is swelling and tenderness overlying the distal right femoral diaphysis. Laboratory evaluation is notable for an elevated white blood cell (WBC) count and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR). A radiograph of the patient’s right leg is shown. Biopsy of the lesion demonstrates sheets of monotonous small round blue cells with minimal cytoplasm. Which of the following genetic mutations is most likely associated with this patient’s condition?
- A. t(11;22) (Correct Answer)
- B. RB1 inactivation
- C. TP53 inactivation
- D. t(8;14)
- E. t(X;18)
Osteosarcoma Explanation: ***t(11;22)***
- The clinical presentation of a **12-year-old male** with progressive **thigh pain and swelling**, fever, elevated WBC and ESR, a radiograph showing a bone lesion [1], and a biopsy revealing **small round blue cells with minimal cytoplasm**, is highly suggestive of **Ewing sarcoma** [2].
- **Ewing sarcoma** is characterized by the **t(11;22)(q24;q12) chromosomal translocation**, which fuses the *EWSR1* gene with the *FLI1* gene, leading to the formation of a chimeric transcription factor.
*t(X;18)*
- The **t(X;18) translocation** is the characteristic genetic abnormality of **synovial sarcoma**, another soft tissue malignancy.
- While synovial sarcoma can also present in young patients, it typically affects older adolescents and young adults, and the histology differs from the small round blue cell pattern seen in Ewing sarcoma [2].
*RB1 inactivation*
- **RB1 gene inactivation** is centrally involved in the pathogenesis of **retinoblastoma**, a childhood eye cancer.
- It also plays a role in various other cancers, such as **osteosarcoma** [3] and small cell lung cancer, but its primary association is not with Ewing sarcoma.
*TP53 inactivation*
- **TP53 gene inactivation** is a common event in a wide range of human cancers, as *TP53* is a critical **tumor suppressor gene**.
- While *TP53* mutations can be found in some sarcomas, it is not the defining or most likely specific genetic mutation for **Ewing sarcoma**.
*t(8;14)*
- The **t(8;14)(q24;q32) chromosomal translocation** is the characteristic genetic abnormality found in **Burkitt lymphoma**.
- This translocation leads to the **c-MYC proto-oncogene** being placed near the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus, promoting its overexpression, which is unrelated to Ewing sarcoma.
**References:**
[1] Cross SS. Underwood's Pathology: A Clinical Approach. 6th ed. Common Clinical Problems From Osteoarticular And Connective Tissue Disease, pp. 671-672.
[2] Kumar V, Abbas AK, et al.. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 9th ed. Bones, Joints, and Soft Tissue Tumors, pp. 1204-1205.
[3] Kumar V, Abbas AK, et al.. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 9th ed. Bones, Joints, and Soft Tissue Tumors, pp. 1200-1202.
Osteosarcoma US Medical PG Question 4: A 38-year-old woman seeks evaluation at the emergency room for sudden onset of pain and swelling of her left leg since last night. Her family history is significant for maternal breast cancer (diagnosed at 52 years of age) and a grandfather with bronchioloalveolar carcinoma of the lungs at 45 years of age. When the patient was 13 years old, she was diagnosed with osteosarcoma of the right distal femur that was successfully treated with surgery. The physical examination shows unilateral left leg edema and erythema that was tender to touch and warm. Homan's sign is positive. During the abdominal examination, you also notice a large mass in the left lower quadrant that is firm and fixed with irregular borders. Proximal leg ultrasonography reveals a non-compressible femoral vein and the presence of a thrombus after color flow Doppler evaluation. Concerned about the association between the palpable mass and a thrombotic event in this patient, you order an abdominal CT scan with contrast that reports a large left abdominopelvic cystic mass with thick septae consistent with ovarian cancer, multiple lymph node involvement, and ascites. Which of the following genes is most likely mutated in this patient?
- A. MLH1
- B. STK11
- C. BRCA2
- D. BRCA1
- E. TP53 (Correct Answer)
Osteosarcoma Explanation: ***TP53***
- This patient's presentation with **early-onset ovarian cancer**, a history of childhood **osteosarcoma**, and a family history of early-onset cancers (maternal breast cancer, grandfather with bronchioloalveolar carcinoma) is highly suggestive of **Li-Fraumeni syndrome**, which is caused by a germline mutation in the **TP53 tumor suppressor gene**.
- The combination of a **sarcoma** (osteosarcoma), **breast cancer**, and other early-onset malignancies points strongly to a **TP53 mutation**.
*MLH1*
- **MLH1** mutations are associated with **Lynch syndrome** (Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer), which primarily predisposes to **colorectal** and **endometrial cancers**, not typically osteosarcoma or ovarian cancer in this pattern.
- While Lynch syndrome can increase the risk of ovarian cancer, the presence of childhood osteosarcoma and the specific family cancer spectrum are not characteristic of MLH1 mutations.
*STK11*
- **STK11** mutations cause **Peutz-Jeghers syndrome**, characterized by **gastrointestinal hamartomatous polyps** and mucocutaneous pigmentation.
- While it increases the risk of various cancers, including breast and ovarian, it does not typically present with osteosarcoma or the specific constellation of cancers seen in this patient.
*BRCA2*
- **BRCA2** mutations are primarily associated with an increased risk of **breast cancer** (in both males and females), **ovarian cancer**, and some other cancers like prostate and pancreatic cancer.
- While ovarian and breast cancer are present in this case, a history of childhood osteosarcoma is not typically linked to BRCA2 mutations.
*BRCA1*
- **BRCA1** mutations are strongly associated with **hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndrome**, leading to a significantly increased risk of developing these cancers at an earlier age.
- Similar to BRCA2, the presence of an **osteosarcoma** in childhood is not a typical feature of BRCA1-associated conditions.
Osteosarcoma US Medical PG Question 5: A 5-year-old boy is brought to the pediatric clinic for evaluation of fever, pain, swelling in the left leg, and limping. Review of systems and history is otherwise unremarkable. The vital signs include: pulse 110/min, temperature 38.1°C (100.6°F), and blood pressure 100/70 mm Hg. On examination, there is a tender swelling over the lower part of his left leg. Which 1 of the following X-ray findings is most suggestive of Ewing’s sarcoma?
- A. Mixed lytic and blastic appearance in the X-ray
- B. X-ray showing broad-based projections from the surface of the bone
- C. X-ray showing lytic bone lesion with periosteal reaction (Correct Answer)
- D. X-ray showing a sharply marginated radiolucent area within the apophysis
- E. X-ray showing deep muscle plane displacement from the metaphysis
Osteosarcoma Explanation: ***X-ray showing lytic bone lesion with periosteal reaction***
- **Ewing's sarcoma** typically presents as a **lytic bone lesion** with an **aggressive periosteal reaction**, often described as an **"onion-skin" appearance** due to layers of new bone formation.
- The combination of fever, localized pain, swelling, and limping in a child, along with a lytic lesion and periosteal reaction on X-ray, is highly suggestive of this diagnosis.
*Mixed lytic and blastic appearance in the X-ray*
- A mixed lytic and blastic appearance is more characteristic of metastatic disease or certain other bone tumors like osteosarcoma in later stages, but less specific for primary Ewing's sarcoma.
- While some blastic components can occur, the primary hallmark of Ewing's is its lytic and destructive nature with typical periosteal reactions.
*X-ray showing broad-based projections from the surface of the bone*
- Broad-based projections from the bone surface are characteristic of **osteochondromas**, which are benign bone tumors.
- These are typically painless unless they impinge on nerves or blood vessels, and do not usually present with systemic symptoms like fever.
*X-ray showing a sharply marginated radiolucent area within the apophysis*
- A sharply marginated radiolucent area within the apophysis could suggest a benign lesion like a **fibrous cortical defect** or a **non-ossifying fibroma**, particularly if it is well-defined and non-aggressive.
- It does not indicate the aggressive, destructive nature seen with Ewing's sarcoma.
*X-ray showing deep muscle plane displacement from the metaphysis*
- Deep muscle plane displacement can indicate a significant soft tissue mass, but it is a **non-specific finding** and does not point directly to the bony destruction or characteristic periosteal reaction of Ewing's sarcoma.
- This finding could be associated with various soft tissue tumors, hematomas, or infections.
Osteosarcoma US Medical PG Question 6: A 13-month-old boy with sickle cell anemia is brought to the emergency department because of continuous crying and severe left-hand swelling. His condition started 2 hours earlier without any preceding trauma. The child was given diclofenac syrup at home with no relief. The temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), blood pressure is 100/60 mm Hg, and pulse is 100/min. The physical examination reveals swelling and tenderness to palpation of the left hand. The hemoglobin level is 10.4 g/dL. Which of the following is the best initial step in management of this patient condition?
- A. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the affected joint
- B. Incentive spirometry
- C. Joint aspiration
- D. Intravenous meperidine
- E. Intravenous morphine (Correct Answer)
Osteosarcoma Explanation: ***Intravenous morphine***
- The patient presents with classic signs of **dactylitis**, a painful vaso-occlusive crisis in sickle cell anemia, characterized by acute onset of **painful swelling of hands and feet**.
- **Opioids** like intravenous morphine are the cornerstone for managing severe pain in sickle cell pain crises, and a **multimodal approach** to pain control is recommended.
*Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the affected joint*
- While MRI can visualize soft tissue and bone, it is **not the initial step** in managing a sickle cell pain crisis due to its cost, time, and potential need for sedation in a child.
- The diagnosis of **dactylitis is primarily clinical**, based on the patient's history and physical examination.
*Incentive spirometry*
- **Incentive spirometry** is primarily used to prevent or treat **pulmonary complications** like atelectasis, often in postoperative patients or those with acute chest syndrome.
- It is not indicated for the management of **acute pain due to dactylitis** and would not address the patient's immediate problem.
*Joint aspiration*
- **Joint aspiration** is performed to diagnose infectious arthritis or to relieve pressure from effusions, which presents with signs of inflammation.
- The patient's symptoms are consistent with **vaso-occlusive crisis** in sickle cell disease, not an infection, making aspiration unnecessary and potentially harmful.
*Intravenous meperidine*
- **Meperidine (Demerol)** is generally **avoided in sickle cell patients** due to the accumulation of its metabolite, **normeperidine**, which can cause **neurotoxicity**, including seizures.
- Other opioids like morphine or hydromorphone are preferred for severe pain in this population.
Osteosarcoma US Medical PG Question 7: A 1-month-old boy is brought to the physician because of a 5-day history of generalized fatigue and multiple episodes of vomiting which is most pronounced after formula feeding. His vomiting progressed from 2–3 episodes on the first day to 6–8 episodes at present. The vomitus is whitish in color. The mother reports that he has been very hungry after each episode of vomiting. The patient was born at 38 weeks' gestation and weighed 3100 g (6 lb 13 oz); he currently weighs 3500 g (7 lb 11 oz). He appears irritable. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.8°F), pulse is 130/min, respirations are 43/min, and blood pressure is 74/36 mm Hg. Examination shows dry mucous membranes. The abdomen is soft and not distended. There is a round mass palpable in the epigastric region. The liver is palpated 1 cm below the right costal margin. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 15.3 g/dL
Leukocyte count 6300/mm3
Platelet count 230,000/mm3
Serum
Na+ 133 mEq/L
K+ 3.4 mEq/L
Cl- 92 mEq/L
Glucose 77 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.0 mg/dL
A urinalysis shows a decreased pH. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Measure serum cortisol levels
- B. Perform upper GI endoscopy
- C. Administer IV 0.9% NaCl and replace electrolytes (Correct Answer)
- D. Perform emergency pyloromyotomy
- E. Obtain CT scan of the abdomen with contrast
Osteosarcoma Explanation: ***Administer IV 0.9% NaCl and replace electrolytes***
- The patient exhibits signs of **dehydration** (dry mucous membranes, irritability) and **hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis** (low Na+ 133, K+ 3.4, Cl- 92) secondary to persistent vomiting.
- The clinical presentation strongly suggests **pyloric stenosis** (progressive non-bilious vomiting, palpable epigastric mass, hungry after vomiting), but the patient's **electrolyte imbalances and dehydration must be corrected before any surgical intervention** to minimize operative risks.
- The paradoxical aciduria (decreased urine pH) occurs because severe volume depletion triggers aldosterone secretion, leading to preferential H+ excretion over HCO3- despite metabolic alkalosis.
*Measure serum cortisol levels*
- While adrenal insufficiency can cause vomiting and electrolyte abnormalities, the specific presentation of **non-bilious vomiting** with an **epigastric mass** and **hunger after vomiting** strongly points to **pyloric stenosis**.
- There are no other clear signs of adrenal insufficiency such as **hyperpigmentation**, **significant hypoglycemia**, or **hyperkalemia** that would make this the immediate priority over correcting dehydration and electrolytes.
*Perform upper GI endoscopy*
- Upper GI endoscopy is primarily used to visualize the upper digestive tract for conditions like **esophagitis**, **gastritis**, or **ulcers**.
- It is not the initial diagnostic test for **pyloric stenosis**; an **abdominal ultrasound** is preferred for confirming the diagnosis (showing pyloric wall thickness >3mm and channel length >15mm).
- Correcting the patient's severe dehydration and electrolyte imbalances takes precedence over diagnostic procedures.
*Perform emergency pyloromyotomy*
- Although pyloric stenosis is strongly suspected and **pyloromyotomy** is the definitive treatment, it is an elective surgical procedure.
- The patient is currently **dehydrated** with **electrolyte abnormalities** (hypochloremic, hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis), which must be corrected *before* surgery to minimize anesthetic and surgical risks and improve outcomes.
- Pyloric stenosis is **not a surgical emergency**; stabilization always precedes surgery.
*Obtain CT scan of the abdomen with contrast*
- A CT scan uses **ionizing radiation** and **contrast agents**, which are generally avoided in infants unless absolutely necessary.
- An **abdominal ultrasound** is the diagnostic study of choice for **pyloric stenosis** due to its non-invasiveness, lack of radiation exposure, and effectiveness in identifying the characteristic hypertrophied pylorus ("olive" or "target sign").
Osteosarcoma US Medical PG Question 8: A 4-year-old boy with Down syndrome presents with fatigue and recurrent infections. CBC shows WBC 150,000/μL with 90% myeloblasts, hemoglobin 6.5 g/dL, platelets 15,000/μL. Flow cytometry confirms acute myeloid leukemia with megakaryoblastic features (AMKL). The parents are concerned about treatment intensity given their child's baseline developmental delays and increased treatment-related toxicity risk in Down syndrome. Evaluate the treatment approach considering the unique biology and competing risks.
- A. Modified chemotherapy protocol with dose reductions of cytarabine but standard anthracyclines, given Down syndrome-associated AML excellent prognosis (Correct Answer)
- B. Bone marrow transplantation as first-line therapy
- C. Palliative care approach given poor baseline function and high treatment toxicity
- D. Reduced-intensity chemotherapy due to Down syndrome and baseline developmental concerns
- E. Standard AML chemotherapy protocol without modification
Osteosarcoma Explanation: ***Modified chemotherapy protocol with dose reductions of cytarabine but standard anthracyclines, given Down syndrome-associated AML excellent prognosis***
- Children with **Down syndrome-associated AML (DS-AML)**, specifically the **megakaryoblastic (AMKL)** subtype, exhibit hyper-sensitivity to **cytarabine** due to lower levels of the enzyme cytidine deaminase.
- While they have an **excellent prognosis** (cure rates >80%), they face a high risk of **treatment-related toxicity**, necessitating dose modifications to improve safety without sacrificing efficacy.
*Bone marrow transplantation as first-line therapy*
- **Hematopoietic stem cell transplant** is not indicated as first-line therapy because DS-AML responds exceptionally well to **chemotherapy** alone.
- Transplant carries a high risk of **morbidity and mortality**, which is unnecessary given the high survival rates with modified chemo regimens.
*Palliative care approach given poor baseline function and high treatment toxicity*
- Palliative care is inappropriate as the primary strategy because DS-AML is a **highly curable** malignancy in pediatric patients.
- Developmental delays and baseline status do not preclude aggressive **curative intent** therapy, as long as protocols are adjusted for toxicity.
*Reduced-intensity chemotherapy due to Down syndrome and baseline developmental concerns*
- While toxicity is a concern, broad "reduced-intensity" therapy may lead to **under-treatment** and increased risk of **relapse**.
- Specific modifications, rather than blanket reductions, are required to maintain the **high cure rate** associated with the **GATA1 mutation** characteristic of this disease.
*Standard AML chemotherapy protocol without modification*
- Using standard AML protocols in children with Down syndrome leads to **excessive toxicity**, particularly severe **mucositis** and life-threatening infections.
- The unique **pharmacogenomics** of Down syndrome patients requires dedicated protocols like the **Children's Oncology Group (COG) AAML0431** to manage treatment risks.
Osteosarcoma US Medical PG Question 9: A 15-year-old boy presents with right distal femur pain and a palpable mass. X-ray shows a mixed lytic-sclerotic lesion with periosteal elevation creating a Codman triangle and sunburst pattern. Biopsy confirms osteosarcoma. Staging shows pulmonary micrometastases. Alkaline phosphatase is markedly elevated. The family requests consideration of alternative therapies and limb salvage options. Synthesize the treatment plan addressing oncologic outcomes and functional preservation.
- A. Limb salvage surgery without chemotherapy followed by observation
- B. Radiation therapy alone as primary treatment
- C. Palliative care focus given metastatic disease at presentation
- D. Immediate amputation without chemotherapy due to metastatic disease
- E. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy, tumor necrosis assessment, limb salvage with endoprosthesis, and adjuvant chemotherapy with potential pulmonary metastasectomy (Correct Answer)
Osteosarcoma Explanation: ***Neoadjuvant chemotherapy, tumor necrosis assessment, limb salvage with endoprosthesis, and adjuvant chemotherapy with potential pulmonary metastasectomy***
- This comprehensive approach is the standard of care; **neoadjuvant chemotherapy** treats micrometastases and allows for **tumor necrosis assessment**, a critical prognostic factor (>90% necrosis).
- **Limb salvage** is oncologically equivalent to amputation when **wide margins** are achievable, and aggressive resection of **pulmonary metastases** can still lead to long-term survival in up to 40% of patients.
*Limb salvage surgery without chemotherapy followed by observation*
- Surgery alone is insufficient because **osteosarcoma** is considered a systemic disease at diagnosis, with **pulmonary micrometastases** present in nearly all patients.
- Omitting **adjuvant chemotherapy** results in high recurrence rates and significantly lower survival outcomes.
*Radiation therapy alone as primary treatment*
- Osteosarcoma is traditionally considered a **radioresistant** tumor, making radiation therapy ineffective as a primary or sole curative modality.
- Surgical resection with **clear margins** is mandatory for local control and achieving a cure.
*Palliative care focus given metastatic disease at presentation*
- Unlike many other adult cancers, **pediatric osteosarcoma** with limited metastatic disease (especially to the lungs) is potentially curable with aggressive therapy.
- A shift to purely **palliative care** would be premature and denies the patient a significant chance at long-term survival.
*Immediate amputation without chemotherapy due to metastatic disease*
- **Immediate amputation** does not address systemic micrometastases and provides no clinical benefit over **limb salvage** if negative margins can be obtained.
- Bypassing **neoadjuvant chemotherapy** loses the opportunity to assess **chemosensitivity**, which is vital for tailoring postoperative treatment.
Osteosarcoma US Medical PG Question 10: A 2-year-old girl presents with a large abdominal mass, aniridia, and developmental delay. Family history reveals a sibling who died of Wilms tumor at age 3. Genetic testing shows a germline WT1 mutation. Ultrasound reveals bilateral renal masses. The parents are concerned about treatment options that preserve renal function. Evaluate the optimal management strategy considering long-term outcomes.
- A. Chemotherapy followed by bilateral nephrectomy and immediate transplantation
- B. Bilateral renal biopsy followed by neoadjuvant chemotherapy and bilateral nephron-sparing surgery (Correct Answer)
- C. Close surveillance with delayed intervention until symptoms develop
- D. Immediate bilateral nephrectomy with dialysis and future transplantation
- E. Unilateral nephrectomy of the larger tumor followed by observation of contralateral kidney
Osteosarcoma Explanation: ***Bilateral renal biopsy followed by neoadjuvant chemotherapy and bilateral nephron-sparing surgery***
- The patient presents with **WAGR syndrome** (Wilms tumor, Aniridia, Genitourinary anomalies, and Range of developmental delays), which is associated with a high risk of **bilateral Wilms tumors** and subsequent chronic renal failure.
- **Neoadjuvant chemotherapy** is used to reduce tumor volume, facilitating **nephron-sparing surgery** (partial nephrectomy) to preserve as much renal parenchyma as possible and avoid the need for dialysis.
*Chemotherapy followed by bilateral nephrectomy and immediate transplantation*
- Complete **bilateral nephrectomy** results in permanent renal failure, requiring lifelong dialysis which is associated with high morbidity in very young children.
- **Kidney transplantation** is typically deferred for 1–2 years after completion of chemotherapy to ensure there is no tumor recurrence.
*Close surveillance with delayed intervention until symptoms develop*
- **Wilms tumors** are aggressive malignancies that require timely intervention to prevent local progression and **distant metastasis** (commonly to the lungs).
- Delaying treatment in a patient with a known **germline WT1 mutation** and visible masses is unethical and significantly worsens the oncologic prognosis.
*Immediate bilateral nephrectomy with dialysis and future transplantation*
- Proceeding directly to surgery without **neoadjuvant chemotherapy** misses the opportunity to shrink the tumors and increase the success rate of **nephron preservation**.
- Managing a 2-year-old on **long-term dialysis** is technically challenging and carries a significant risk of developmental delay and cardiovascular complications.
*Unilateral nephrectomy of the larger tumor followed by observation of contralateral kidney*
- Leaving a confirmed malignant tumor in the contralateral kidney without treatment allows for **metastatic spread** and continued tumor growth.
- The standard of care for bilateral disease involves treating both sides simultaneously or in a planned sequence to achieve **complete oncologic clearance**.
More Osteosarcoma US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.