Cancer predisposition syndromes US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Cancer predisposition syndromes. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
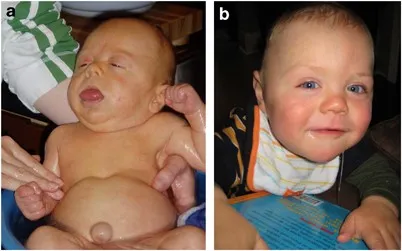
Cancer predisposition syndromes US Medical PG Question 1: A 4-year-old boy is brought to his pediatrician by his mother for a physical exam before summer camp. They have no complaints or concerns at this time. He was born at 37 weeks gestation by cesarean delivery. The delivery was complicated by an omphalocele and macrosomia. During infancy and into early childhood, he struggled to breathe and eat due to an enlarged tongue. Growth and development were mostly normal with mild uneven growth of his body. He has one uncle that had similar symptoms and is alive and well. The child is up to date on all vaccines and is meeting developmental goals. He enjoys school and playing with his friends. His heart rate of 90/min, respiratory rate of 22/min, blood pressure of 110/65 mm Hg, and temperature of 36.9°C (98.4°F). Overall the child appears healthy. Physical exam findings include known hemihypertrophy of the right side along with a mildly enlarged tongue. This patient is at increased risk of developing which of the following?
- A. Sudden infant death syndrome
- B. Scoliosis
- C. Alzheimer's disease
- D. Diabetes mellitus
- E. Wilms tumor (Correct Answer)
Cancer predisposition syndromes Explanation: ***Wilms tumor***
- The constellation of **macrosomia**, **omphalocele**, **macroglossia**, and **hemihypertrophy** in a child points to **Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome (BWS)**.
- Children with BWS have a significantly increased risk of developing childhood cancers, most notably **Wilms tumor** (nephroblastoma) and **hepatoblastoma**.
*Sudden infant death syndrome*
- While macrosomia can be associated with some complications, **SIDS** is not a primary or significantly increased risk for children with BWS past infancy.
- SIDS is typically defined as the sudden, unexplained death of an infant younger than one year of age.
*Scoliosis*
- **Scoliosis** is a curvature of the spine that can occur in some genetic syndromes, but it is not a hallmark or particularly increased risk feature of BWS.
- **Hemihypertrophy** in BWS can cause limb length discrepancies, which might indirectly lead to scoliosis, but it's not a direct cancer risk associated with the syndrome.
*Alzheimer's disease*
- **Alzheimer's disease** is a neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects older adults and is not associated with childhood syndromes like BWS.
- There is no known genetic link between BWS and an increased risk of early-onset or childhood Alzheimer's.
*Diabetes mellitus*
- While individuals with BWS can have issues with **hypoglycemia** in infancy due to **pancreatic islet cell hyperplasia**, they are not typically at an increased risk of developing **type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus** later in childhood.
- The initial hypoglycemia usually resolves over time.
Cancer predisposition syndromes US Medical PG Question 2: A 33-year-old woman comes to the physician 1 week after noticing a lump in her right breast. Fifteen years ago, she was diagnosed with osteosarcoma of her left distal femur. Her father died of an adrenocortical carcinoma at the age of 41 years. Examination shows a 2-cm, firm, immobile mass in the lower outer quadrant of the right breast. A core needle biopsy of the mass shows adenocarcinoma. Genetic analysis in this patient is most likely to show a defect in which of the following genes?
- A. BRCA1
- B. KRAS
- C. TP53 (Correct Answer)
- D. Rb
- E. PTEN
Cancer predisposition syndromes Explanation: ***TP53***
- This patient's presentation with **early-onset breast cancer**, a history of **osteosarcoma** at a young age, and a father's death from **adrenocortical carcinoma** at 41 years strongly suggests **Li-Fraumeni syndrome**.
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder caused by a germline mutation in the **tumor suppressor gene TP53**, increasing the risk for multiple primary cancers at a young age.
*BRCA1*
- While **BRCA1 mutations** are associated with an increased risk of breast and ovarian cancer, they are not typically linked to osteosarcoma or adrenocortical carcinoma.
- The constellation of cancers in this patient is more indicative of Li-Fraumeni syndrome than solely a BRCA1-related cancer syndrome.
*KRAS*
- **KRAS** is an oncogene commonly mutated in several cancers, including pancreatic, colorectal, and lung cancer, but is not primarily associated with either Li-Fraumeni syndrome or the specific tumors seen in this family history.
- Mutations in KRAS are typically somatic mutations acquired during a person's lifetime, not germline mutations causing inherited cancer syndromes like the one suggested here.
*Rb*
- Mutations in the **retinoblastoma (Rb) gene** are associated with retinoblastoma and an increased risk of osteosarcoma, but not typically with adrenocortical carcinoma or breast cancer as part of a classic inherited syndrome.
- The combination of breast cancer, osteosarcoma, and adrenocortical carcinoma points more specifically to TP53.
*PTEN*
- **PTEN mutations** are associated with Cowden syndrome, which increases the risk for breast cancer, thyroid cancer, and endometrial cancer, along with benign growths.
- However, Cowden syndrome does not typically include osteosarcoma or adrenocortical carcinoma as prominent features, making PTEN less likely than TP53 for this specific family history.
Cancer predisposition syndromes US Medical PG Question 3: A 3-year-old male child is found to have a disease involving DNA repair. Specifically, he is found to have a defect in the endonucleases involved in the nucleotide excision repair of pyrimidine dimers. Which of the following is a unique late-stage complication of this child's disease?
- A. Telangiectasia
- B. Colorectal cancer
- C. Malignant melanoma (Correct Answer)
- D. Lymphomas
- E. Endometrial cancer
Cancer predisposition syndromes Explanation: **Malignant melanoma**
- The described condition is **xeroderma pigmentosum**, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by a defect in **nucleotide excision repair (NER)**, specifically the inability to remove **pyrimidine dimers** caused by **UV radiation**.
- This severely impaired DNA repair leads to an extreme predisposition to **UV-induced skin cancers**, including basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas, and, most aggressively, **malignant melanoma**, which is a unique and life-threatening late-stage complication.
*Telangiectasia*
- **Telangiectasias** are dilated small blood vessels that appear on the skin or mucous membranes and can be associated with various conditions.
- While skin abnormalities are prevalent in xeroderma pigmentosum due to sun damage, **melanoma** is a more specific and severe late-stage complication directly resulting from the DNA repair defect.
*Colorectal cancer*
- **Colorectal cancer** is typically associated with other DNA repair defects, such as those in the **mismatch repair system**, as seen in conditions like **Lynch syndrome**.
- It is not a primary or most significant late-stage complication of xeroderma pigmentosum, which is primarily characterized by skin cancers.
*Lymphomas*
- **Lymphomas** are cancers of the lymphatic system, often linked to immune deficiencies or specific genetic translocations.
- While individuals with genetic syndromes can have increased cancer risks, **lymphoma** is not the hallmark late-stage complication of xeroderma pigmentosum; skin cancers are the predominant concern.
*Endometrial cancer*
- **Endometrial cancer** is a gynecological cancer often associated with hormonal factors or genetic predispositions like Lynch syndrome, which involves mismatch repair defects.
- This type of cancer is not a characteristic or unique late-stage complication of xeroderma pigmentosum, whose pathology is centered on **UV-induced DNA damage** and subsequent skin malignancies.
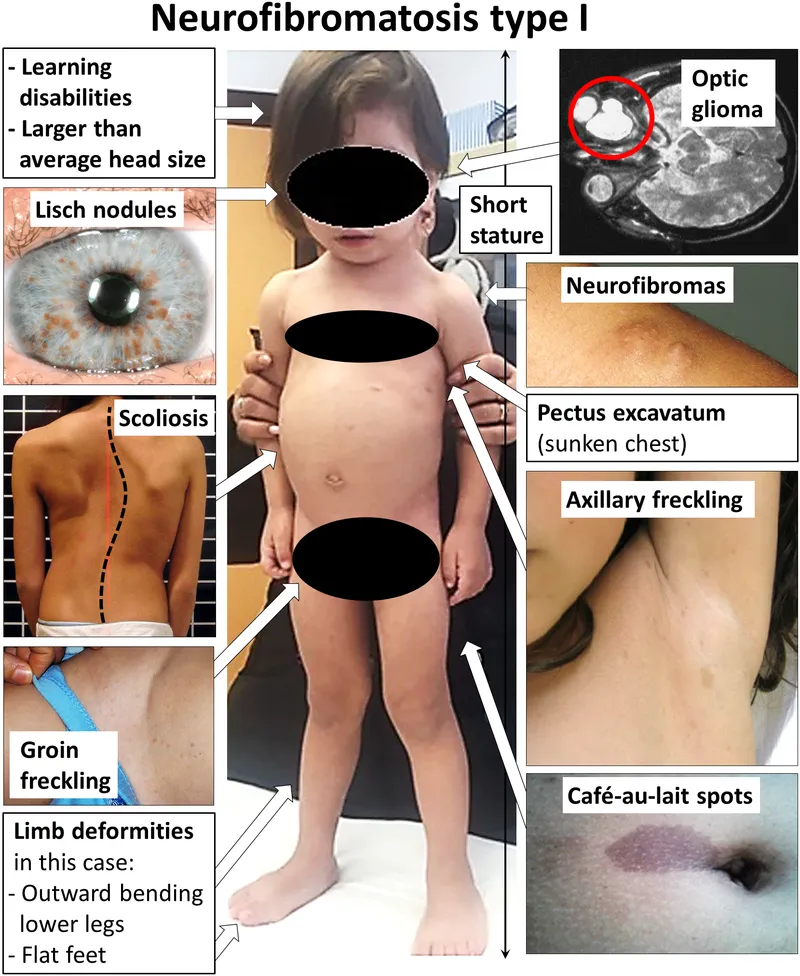
Cancer predisposition syndromes US Medical PG Question 4: A 16-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician by his mother because she is concerned about the “spots” on his abdomen and back. The patient’s mother reports that there are several “light spots” on the patient’s trunk that have been slowly increasing in number. The lesions are not painful nor pruritic. The patient’s mother is worried because her nephew had vitiligo. The patient reports that he feels “fine,” but reports occasional headaches and increasing difficulty with seeing the board at school. In addition to the patient’s cousin having vitiligo, the patient’s paternal grandfather and uncle have bilateral deafness, and his mother has systemic lupus erythematous. On physical examination, there are multiple, discrete, 2-3 cm hypopigmented macules on the chest, abdomen, back, and posterior shoulders. Which of the following head and neck computed tomography findings is the patient most likely to develop?
- A. Subependymal hamartomas
- B. Optic nerve glioma
- C. Bilateral vestibular schwannomas (Correct Answer)
- D. Cerebral atrophy
- E. Thyroid nodule
Cancer predisposition syndromes Explanation: ***Bilateral vestibular schwannomas***
- The family history of **bilateral deafness** in the paternal grandfather and uncle is highly suggestive of **Neurofibromatosis type 2 (NF2)**, which is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern.
- **NF2** is characterized by the development of **bilateral vestibular schwannomas** (acoustic neuromas), which typically present with progressive hearing loss, tinnitus, and balance problems in the second or third decade of life.
- The patient's headaches and vision difficulties may represent early CNS manifestations of NF2 (meningiomas, cataracts, or other tumors).
- Unlike NF1, **skin findings in NF2 are minimal** - café-au-lait spots are rare and usually fewer than 6. The hypopigmented macules described here are atypical for NF2 but the strong family history makes this the most likely diagnosis.
*Subependymal hamartomas*
- These are characteristic findings in **Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC)**, which presents with hypopigmented **ash-leaf spots**, seizures, developmental delay, and facial angiofibromas.
- TSC does not typically present with a family history of bilateral deafness, which is the key distinguishing feature pointing toward NF2 in this case.
*Optic nerve glioma*
- **Optic nerve gliomas** are associated with **Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)**, which presents with multiple café-au-lait spots (≥6, and these are **hyperpigmented**, not hypopigmented), axillary/inguinal freckling, Lisch nodules, and neurofibromas.
- NF1 does not typically cause bilateral deafness, making this diagnosis less likely given the family history.
*Cerebral atrophy*
- **Cerebral atrophy** is a nonspecific finding seen in various neurodegenerative disorders, aging, or conditions causing chronic brain injury.
- It is not a characteristic or primary finding in any of the neurocutaneous syndromes suggested by this clinical presentation.
*Thyroid nodule*
- **Thyroid nodules** are common in the general population but are not specifically associated with the constellation of symptoms presented here.
- There is no direct link between NF2 and an increased risk of thyroid nodules.
Cancer predisposition syndromes US Medical PG Question 5: An investigator is studying DNA repair processes in an experimental animal. The investigator inactivates a gene encoding a protein that physiologically excises nucleotides from damaged, bulky, helix-distorting DNA strands. A patient with a similar defect in this gene is most likely to present with which of the following findings?
- A. Ataxic gait and facial telangiectasias
- B. Malignant breast and ovarian growths
- C. Leukocoria and a painful bone mass
- D. Colorectal and endometrial cancers
- E. Dry skin and increased photosensitivity (Correct Answer)
Cancer predisposition syndromes Explanation: ***Dry skin and increased photosensitivity***
- The description of excising **nucleotides from damaged, bulky, helix-distorting DNA strands** points to a defect in **Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER)**.
- Patients with defects in NER, such as those with **xeroderma pigmentosum**, are highly susceptible to UV-induced DNA damage, leading to **dry skin, increased photosensitivity**, and a high risk of skin cancers.
*Ataxic gait and facial telangiectasias*
- This constellation of symptoms is characteristic of **ataxia-telangiectasia**, a disorder caused by mutations in the **ATM gene**, which is involved in **DNA double-strand break repair**.
- While a DNA repair defect, it's not primarily linked to the excision of bulky, helix-distorting DNA strands.
*Malignant breast and ovarian growths*
- These cancers are commonly associated with mutations in the **BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes**, which play crucial roles in **homologous recombination repair of DNA double-strand breaks**.
- This type of repair is distinct from the excision of bulky, helix-distorting DNA strands described in the question.
*Leukocoria and a painful bone mass*
- **Leukocoria** can indicate **retinoblastoma**, linked to mutations in the **RB1 tumor suppressor gene**, which regulates the cell cycle but isn't primarily a DNA repair gene.
- A painful bone mass could suggest **osteosarcoma**, which is sometimes seen in retinoblastoma patients but not directly related to the specific DNA repair defect described.
*Colorectal and endometrial cancers*
- These cancers are hallmarks of **Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer - HNPCC)**, which is caused by defects in **Mismatch Repair (MMR)** genes (e.g., MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2).
- Mismatch repair corrects errors that arise during DNA replication, which is different from excising bulky, helix-distorting DNA damage.
Cancer predisposition syndromes US Medical PG Question 6: A 27-year-old man presents to the emergency department with painless yellowing of his skin. The patient states he is generally healthy and has no past medical history. He smokes 2 packs of cigarettes per day and was recently treated for a urinary tract infection with a single dose of ceftriaxone followed by a 7 day course of ciprofloxacin. He recently returned from a 3 day hiking trip and is an avid vegan. His only other medical history is a mild cough for the past few days. His temperature is 97.5°F (36.4°C), blood pressure is 122/82 mmHg, pulse is 85/min, respirations are 15/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam reveals an abdomen which is non-tender. Mild scleral icterus and sublingual jaundice is noted. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this patient’s symptoms?
- A. Ceftriaxone administration
- B. Carotenoid consumption
- C. Pancreatic cancer
- D. Gilbert syndrome (Correct Answer)
- E. Crigler-Najjar syndrome
Cancer predisposition syndromes Explanation: ***Gilbert syndrome***
- The patient presents with **painless jaundice** and **scleral icterus** but is otherwise healthy, which is typical for Gilbert syndrome. Stressors like a recent **hiking trip** or mild illness can precipitate episodes of visible jaundice in individuals with this condition.
- Gilbert syndrome is a common, benign, inherited disorder characterized by intermittent episodes of **unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia** due to reduced activity of the hepatic enzyme **UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT1A1)**.
*Ceftriaxone administration*
- While ceftriaxone can rarely cause biliary sludge or cholelithiasis, leading to obstructive jaundice, the patient's symptoms are mild and **painless**, and ceftriaxone typically causes an **elevated direct bilirubin**, not unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia.
- The patient's presentation with mild, intermittent jaundice is not characteristic of significant **biliary obstruction** that would be related to ceftriaxone.
*Carotenoid consumption*
- Excessive consumption of **carotenoids** can cause **carotenemia**, leading to yellowing of the skin, especially on the palms and soles, but it **does not cause scleral icterus** or sublingual jaundice.
- The patient's **vegan diet** might suggest high carotenoid intake, but the presence of scleral icterus rules out carotenemia as the primary cause of the generalized yellowing.
*Pancreatic cancer*
- Pancreatic cancer in a 27-year-old is extremely rare and typically presents with **obstructive jaundice** (elevated direct bilirubin), often accompanied by other symptoms such as **weight loss**, **abdominal pain**, or **dark urine**.
- The patient's good general health, normal vitals, and lack of other systemic symptoms make pancreatic cancer highly unlikely.
*Crigler-Najjar syndrome*
- Crigler-Najjar syndrome is a rare, severe genetic disorder causing **severe unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia** due to near-total absence (Type I) or significantly reduced (Type II) **UGT1A1 activity**.
- Type I typically presents in **neonates** with severe jaundice and **kernicterus**, while Type II presents later but is generally more symptomatic and persistent than what is described in this patient, who has mild, intermittent jaundice.
Cancer predisposition syndromes US Medical PG Question 7: A 75-year-old gentleman is brought to the ED with confusion that started earlier this morning. His family notes that he was complaining of feeling weak last night and also had a slight tremor at the time. He is afebrile and he has no known chronic medical conditions. Physical exam reveals a cooperative but confused gentleman. His mucous membranes are moist, he has no focal neurological deficits, and his skin turgor is within normal limits. His lab results are notable for:
Serum Na+: 123 mEq/L
Plasma osmolality: 268 mOsm/kg
Urine osmolality: 349 mOsm/kg
Urine Na+: 47 mEq/L
Which of the following malignancies is most likely to be responsible for this patient's presentation?
- A. Gastric adenocarcinoma
- B. Small cell lung cancer (Correct Answer)
- C. Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- D. Non-seminomatous germ cell tumor
- E. Rib osteosarcoma
Cancer predisposition syndromes Explanation: ***Small cell lung cancer***
- This patient's laboratory values (hyponatremia, low plasma osmolality, and inappropriately high urine osmolality with elevated urine sodium) are classic for the **Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH)**.
- **Small cell lung cancer** is the most common malignancy associated with paraneoplastic SIADH due to its ability to ectopically produce ADH.
*Gastric adenocarcinoma*
- While gastric adenocarcinomas can cause paraneoplastic syndromes, SIADH is an **uncommon** paraneoplastic manifestation of this type of cancer.
- Other paraneoplastic syndromes, such as **Trousseau's syndrome** (migratory thrombophlebitis), are more classically associated with gastric adenocarcinoma.
*Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma*
- Esophageal cancer, including squamous cell carcinoma, is **rarely associated** with SIADH.
- Its paraneoplastic manifestations are less defined and not prominent for ADH production.
*Non-seminomatous germ cell tumor*
- Germ cell tumors, particularly non-seminomatous types, are more commonly associated with paraneoplastic syndromes involving **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)** or **alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)** production.
- While some germ cell tumors *can* release ADH, it is **not a primary cause** of SIADH compared to small cell lung cancer.
*Rib osteosarcoma*
- Osteosarcoma is a primary bone tumor and is **not typically associated** with paraneoplastic syndromes like SIADH.
- Its primary clinical manifestations are related to local bone destruction and metastasis.
Cancer predisposition syndromes US Medical PG Question 8: A 19-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of blood-speckled stools and a protruding rectal mass. He has no abdominal pain, altered bowel habits, or fever. His mother has inflammatory bowel disease. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows multiple, small, hyperpigmented maculae on the lips, buccal mucosa, palms, and soles. The abdomen is soft with no organomegaly. Rectal examination shows a 4-cm pedunculated polyp with superficial excoriations on the mucosa. A colonoscopy shows 14 polyps. A biopsy shows hamartomatous mucosal polyps. This patient's diagnosis is most likely?
- A. Crohn's disease
- B. Juvenile polyposis syndrome
- C. Ulcerative colitis
- D. Familial adenomatous polyposis
- E. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (Correct Answer)
Cancer predisposition syndromes Explanation: ***Peutz-Jeghers syndrome***
- The presence of **multiple hamartomatous polyps** in the gastrointestinal tract, coupled with **hyperpigmented macules** on the lips, buccal mucosa, palms, and soles, is pathognomonic for Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
- This condition carries an increased risk of various cancers, including colorectal, breast, gastric, and pancreatic cancers.
*Crohn's disease*
- While Crohn's disease can cause bloody stools and rectal involvement, it is characterized by **chronic inflammation**, often with **skip lesions** and **granulomas**, and does not present with mucocutaneous hyperpigmented macules or hamartomatous polyps.
- Symptoms typically include abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss, which are absent here.
*Juvenile polyposis syndrome*
- This syndrome is characterized by **multiple juvenile polyps**, primarily in the colon, but it does **not involve the characteristic mucocutaneous hyperpigmentation** seen in Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
- The polyps are typically inflammatory rather than purely hamartomatous in the same way as Peutz-Jeghers.
*Familial adenomatous polyposis*
- This condition is characterized by hundreds to thousands of **adenomatous polyps** in the colon and rectum, with a very high risk of colorectal cancer.
- It does **not typically involve hamartomatous polyps** or the mucocutaneous pigmented lesions seen in this patient.
*Ulcerative colitis*
- Ulcerative colitis is characterized by **continuous inflammation** of the colon and rectum, typically causing bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, and tenesmus.
- It is an inflammatory bowel disease and does **not involve the presence of hamartomatous polyps** or mucocutaneous hyperpigmentation.
Cancer predisposition syndromes US Medical PG Question 9: A 75-year-old man comes to his primary care physician because he has been having diarrhea and difficulty breathing. The diarrhea has been intermittent with frequent watery stools that occur along with abdominal cramps. Furthermore, the skin on his face and upper chest feels hot and changes color in episodes lasting from a few minutes to hours. Finally, the patient complains of loss of appetite and says that he has unexpectedly lost 20 pounds over the last two months. Based on clinical suspicion, magnetic resonance imaging is obtained showing a small mass in this patient's lungs. Which of the following is associated with the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. It also arises in the GI tract (Correct Answer)
- B. Stains positive for vimentin
- C. Has keratin pearls and intercellular bridges
- D. Most common lung cancer in non-smokers and females
- E. Contains psammoma bodies
Cancer predisposition syndromes Explanation: ***Correct: It also arises in the GI tract***
- The patient's symptoms (diarrhea, flushing, difficulty breathing, weight loss) are highly suggestive of **carcinoid syndrome**, often caused by a **neuroendocrine tumor (NET)** in the lung or gastrointestinal tract that metastasizes to the liver.
- While a lung mass is identified here, **carcinoid tumors** (a type of NET) most commonly originate in the **gastrointestinal tract** (especially the appendix, small intestine, and rectum), making this option strongly associated with the likely cause.
- Carcinoid syndrome typically occurs when liver metastases allow serotonin and other vasoactive substances to bypass hepatic metabolism and enter systemic circulation.
*Incorrect: Stains positive for vimentin*
- **Vimentin** is an intermediate filament typically found in **mesenchymal cells** and is often positive in sarcomas, lymphomas, and melanomas.
- Neuroendocrine tumors, including carcinoid, typically stain positive for **chromogranin** and **synaptophysin**, not vimentin.
*Incorrect: Has keratin pearls and intercellular bridges*
- **Keratin pearls** and **intercellular bridges** are characteristic histological features of **squamous cell carcinoma**, which is a type of non-small cell lung cancer.
- While the patient has a lung mass, his symptoms of carcinoid syndrome point away from squamous cell carcinoma and towards a neuroendocrine tumor.
*Incorrect: Most common lung cancer in non-smokers and females*
- **Adenocarcinoma** is the most common type of lung cancer, particularly prevalent in non-smokers and females.
- However, adenocarcinoma does not typically cause carcinoid syndrome, which is a key clinical presentation in this case.
*Incorrect: Contains psammoma bodies*
- **Psammoma bodies** are concentric, laminated calcified structures seen in certain tumors, such as papillary thyroid carcinoma, meningioma, and serous papillary ovarian cancer.
- They are not characteristic features of neuroendocrine tumors or carcinoid tumors.
Cancer predisposition syndromes US Medical PG Question 10: A 40-year-old man presents with a painless firm mass in the right breast. Examination shows retraction of the nipple and the skin is fixed to the underlying mass. The axillary nodes are palpable. Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding the above condition?
- A. Lobular cancer is the most common breast cancer in males (Correct Answer)
- B. BRCA2 mutations are associated with increased risk
- C. These are positive for estrogen receptor
- D. Endocrine therapy plays an important role in treatment
- E. Gynecomastia may be caused by certain medications
Cancer predisposition syndromes Explanation: ***Lobular cancer is the most common breast cancer in males***
- This statement is **FALSE** and is the correct answer. The most common type of breast cancer in males is **invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC)**, accounting for about 80-90% of cases.
- **Invasive lobular carcinoma** is rare in men because men have very few lobules in their breast tissue.
*Gynecomastia may be caused by certain medications*
- This statement is **TRUE**. Medications such as spironolactone, cimetidine, finasteride, antipsychotics, and anabolic steroids can cause gynecomastia.
- However, the clinical presentation described (firm mass, nipple retraction, skin fixation, axillary nodes) is consistent with **malignancy**, not gynecomastia.
*BRCA2 mutations are associated with increased risk*
- This statement is **TRUE**. Male breast cancer is strongly associated with **BRCA2 mutations** (and less commonly BRCA1), which are hereditary.
- Men with BRCA2 mutations have a 5-10% lifetime risk of developing breast cancer, compared to less than 0.1% in the general male population.
*These are positive for estrogen receptor*
- This statement is **TRUE**. A vast majority (over 90%) of male breast cancers are **estrogen receptor (ER) positive**, which makes them responsive to endocrine therapy.
- This high rate of ER positivity is even greater than in female breast cancers.
*Endocrine therapy plays an important role in treatment*
- This statement is **TRUE**. Given the high prevalence of ER positivity (over 90%), endocrine therapy such as **tamoxifen** or aromatase inhibitors is a cornerstone of treatment for male breast cancer.
- Endocrine therapy is used in both adjuvant and metastatic settings for hormone receptor-positive disease.
More Cancer predisposition syndromes US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.