Brain tumors in children US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Brain tumors in children. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Brain tumors in children US Medical PG Question 1: A 13-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a 4-month history of worsening dizziness, nausea, and feeling clumsy. An MRI of the brain shows a well-demarcated, 4-cm cystic mass in the posterior fossa. The patient undergoes complete surgical resection of the mass. Pathologic examination of the surgical specimen shows parallel bundles of cells with eosinophilic, corkscrew-like processes. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Pinealoma
- B. Medulloblastoma
- C. Pilocytic astrocytoma (Correct Answer)
- D. Craniopharyngioma
- E. Ependymoma
Brain tumors in children Explanation: **Pilocytic astrocytoma**
- The clinical presentation of **posterior fossa symptoms** (dizziness, nausea, clumsiness) in a child, coupled with an **MRI showing a cystic mass**, is highly suggestive of pilocytic astrocytoma.
- Histologically, this tumor is characterized by **Rosenthal fibers** (eosinophilic, corkscrew-like processes) and **bipolar cells arranged in parallel bundles**.
*Pinealoma*
- Pinealomas typically present with symptoms related to compression of the **aqueduct of Sylvius** (hydrocephalus) or the **superior colliculus** (Parinaud's syndrome), such as impaired upward gaze.
- They are located in the **pineal region**, not the posterior fossa, and their histology is distinct from the described features.
*Medulloblastoma*
- Medulloblastomas are common **posterior fossa tumors** in children, often presenting with similar symptoms.
- However, they are typically **solid, poorly demarcated** masses on imaging, and their histology reveals **small, round blue cells** with **Homer-Wright rosettes**, not Rosenthal fibers.
*Craniopharyngioma*
- Craniopharyngiomas are typically located in the **suprasellar region**, causing symptoms like **visual field defects** (bitemporal hemianopsia) and **endocrine dysfunction**.
- While they can be cystic, their location and characteristic histology (e.g., **wet keratin**, calcifications) differentiate them from the given case.
*Ependymoma*
- Ependymomas commonly arise from the **ventricular system**, especially the **fourth ventricle** in children, and can cause hydrocephalus and posterior fossa symptoms.
- Histologically, they are characterized by **perivascular pseudorosettes** and true rosettes, lacking the described corkscrew-like processes.
Brain tumors in children US Medical PG Question 2: A previously healthy 10-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department for the evaluation of one episode of vomiting and severe headache since this morning. His mother says he also had difficulty getting dressed on his own. He has not had any trauma. The patient appears nervous. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 100/min, and blood pressure is 185/125 mm Hg. He is confused and oriented only to person. Ophthalmic examination shows bilateral optic disc swelling. There is an abdominal bruit that is best heard at the right costovertebral angle. A complete blood count is within normal limits. Which of the following is most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
- A. Serum IGF-I level
- B. Oral sodium loading test
- C. Echocardiography
- D. CT angiography (Correct Answer)
- E. High-dose dexamethasone suppression test
Brain tumors in children Explanation: ***CT angiography***
- The patient presents with **malignant hypertension** (BP 185/125 mmHg, confusion, optic disc swelling) and an **abdominal bruit** especially at the **right costovertebral angle**, pointing strongly towards **renovascular hypertension** due to **renal artery stenosis**.
- **CT angiography** is the most appropriate imaging modality to confirm **renal artery stenosis** by visualizing the renal arteries and identifying any narrowing.
*Serum IGF-I level*
- This test is used to screen for **growth hormone disorders** like **acromegaly** or **gigantism**, which are not indicated by the patient's symptoms.
- The patient's presentation is focused on acute severe hypertension and neurological changes, rather than chronic growth disturbances.
*Oral sodium loading test*
- This test is used to confirm the diagnosis of **primary aldosteronism**, where **aldosterone levels** fail to suppress after a sodium load.
- While primary aldosteronism can cause hypertension, it typically doesn't present with an **abdominal bruit** or the acute, severe neurological symptoms seen here.
*Echocardiography*
- **Echocardiography** assesses the heart's structure and function, which could show signs of **hypertensive heart disease** (e.g., left ventricular hypertrophy) due to long-standing uncontrolled hypertension.
- However, it does not identify the underlying cause of the hypertension in this acute setting, especially when an **abdominal bruit** suggests a vascular origin.
*High-dose dexamethasone suppression test*
- This test is used to differentiate between **Cushing's disease** (pituitary ACTH-dependent) and other causes of **Cushing's syndrome** (e.g., ectopic ACTH production, adrenal tumor) due to excess cortisol.
- The patient's symptoms are inconsistent with Cushing's syndrome, and the **abdominal bruit** points away from this diagnosis.
Brain tumors in children US Medical PG Question 3: A previously healthy 4-year-old girl is brought to the physician for evaluation of a 3-week history of recurrent vomiting and difficulty walking. Examination shows a broad-based gait and bilateral optic disc swelling. An MRI shows an intracranial tumor. A ventriculoperitoneal shunt is placed, and surgical excision of the tumor is performed. A photomicrograph of a section of the tumor is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Medulloblastoma (Correct Answer)
- B. Hemangioblastoma
- C. Glioblastoma multiforme
- D. Oligodendroglioma
- E. Pinealoma
Brain tumors in children Explanation: ***Medulloblastoma***
- This is the most common **malignant brain tumor** in children, typically arising in the **cerebellum** and presenting with **ataxia** (broad-based gait) and signs of **hydrocephalus** (vomiting, optic disc swelling) due to obstruction of CSF flow.
- Histologically, medulloblastomas are characterized by small, round blue cells with **high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio**, often forming **Homer-Wright rosettes**, indicating their primitive neuroectodermal origin.
*Hemangioblastoma*
- These are typically **benign tumors** of vascular origin, most commonly found in the **cerebellum** of adults and associated with **von Hippel-Lindau disease**.
- Histologically, they consist of foamy stromal cells and a dense capillary network, which is distinct from the provided image.
*Glioblastoma multiforme*
- This is the most common and aggressive primary brain tumor in **adults**, primarily affecting the cerebral hemispheres.
- Histologically, it is characterized by **astrocytic cells** with pleomorphism, high mitotic activity, **necrosis** with pseudopalisading, and vascular proliferation, which is not depicted in the image.
*Oligodendroglioma*
- These are typically found in the **cerebral hemispheres** of adults and are characterized by a **"fried egg"** appearance due to perinuclear halos and a capillary network with a **"chicken wire"** pattern.
- Their incidence in children is much lower, and the presented image is not consistent with this histology.
*Pinealoma*
- Tumors of the **pineal gland** can occur in children but often present with symptoms related to compression of the tectum (**Parinaud syndrome**) or hydrocephalus due to aqueductal compression.
- The most common pineal tumor is a **germinoma**, which has a different histological appearance (large round cells with prominent nucleoli amidst a lymphocytic infiltrate).
Brain tumors in children US Medical PG Question 4: A 10-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents because of a dull persistent headache beginning that morning. He has nausea and has vomited twice. During the past four days, the patient has had left-sided ear pain and fever, but his parents did not seek medical attention. He is from Thailand and is visiting his relatives in the United States for the summer. There is no personal or family history of serious illness. He is at the 45th percentile for height and 40th percentile for weight. He appears irritable. His temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 110/min, and blood pressure is 98/58 mm Hg. The pupils are equal and reactive to light. Lateral gaze of the left eye is limited. The left tympanic membrane is erythematous with purulent discharge. There is no nuchal rigidity. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Intravenous ceftriaxone and clindamycin therapy
- B. Lumbar puncture
- C. MRI of the brain (Correct Answer)
- D. Intravenous cefazolin and metronidazole therapy
- E. Cranial burr hole evacuation
Brain tumors in children Explanation: ***MRI of the brain***
- The patient's presentation with **headache**, **nausea**, **vomiting**, recent **ear infection** (otitis media), **fever**, and **abducens nerve palsy** (limited lateral gaze of the left eye) is highly suggestive of an intracranial complication, such as a **brain abscess** or **epidural abscess**, secondary to the uncontrolled otitis media.
- An MRI of the brain is the **most sensitive and specific imaging modality** for detecting intracranial abscesses, which are critical to diagnose promptly due to their potential for surgical drainage and targeted antibiotic therapy.
*Intravenous ceftriaxone and clindamycin therapy*
- While broad-spectrum antibiotics are necessary, they should be initiated **after establishing a definitive diagnosis and ruling out conditions requiring immediate surgical intervention**.
- Without imaging, there's a risk of delaying crucial surgical management for a contained abscess or empyema.
*Lumbar puncture*
- A lumbar puncture is **contraindicated** in the presence of focal neurological deficits (like **abducens nerve palsy**) and symptoms of **increased intracranial pressure** (headache, nausea, vomiting), as it carries a significant risk of **herniation** if there's a mass lesion.
- Imaging should always precede LP in such cases.
*Intravenous cefazolin and metronidazole therapy*
- Cefazolin has **poor penetration into the CNS**, making it an inadequate choice for suspected intracranial infection.
- While metronidazole targets anaerobes common in brain abscesses, the overall regimen is not optimal, and imaging is still the priority.
*Cranial burr hole evacuation*
- This is a definitive surgical treatment for a brain abscess but should only be performed **after the abscess has been localized and characterized by imaging**.
- Performing a burr hole without prior imaging would be a blind procedure and is not the appropriate next step in diagnosis and management.
Brain tumors in children US Medical PG Question 5: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the physician because his parents are concerned about his early sexual development. He has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. His brother was diagnosed with testicular cancer 5 years ago and underwent a radical orchiectomy. The patient is at the 85th percentile for height and 70th percentile for weight. Examination shows greasy facial skin. There is coarse axillary hair. Pubic hair development is at Tanner stage 3 and testicular development is at Tanner stage 2. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. An x-ray of the wrist shows a bone age of 10 years. Basal serum luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone are elevated. An MRI of the brain shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Leuprolide therapy (Correct Answer)
- B. Testicular ultrasound
- C. Cortisol supplementation
- D. Radiation therapy
- E. Observation
Brain tumors in children Explanation: ***Leuprolide therapy***
- This patient presents with **central precocious puberty** (CPP), indicated by elevated **basal LH and FSH levels** in the context of advanced bone age, Tanner stage 3 pubic hair, and Tanner stage 2 testicular development at a young age.
- **Leuprolide** is a GnRH analog that, when given continuously, downregulates the pituitary's GnRH receptors, suppressing gonadotropin release and halting pubertal progression. This is the appropriate treatment for CPP.
*Testicular ultrasound*
- While useful for evaluating testicular size and consistency, it is typically performed when there is suspicion of **peripheral precocious puberty** (e.g., Leydig cell tumor) with low LH/FSH or significant testicular asymmetry, which is not the primary presentation here.
- The elevated basal LH and FSH values indicate a **central origin** of puberty, making a testicular ultrasound less immediately relevant as a *next step* compared to directly addressing the central hormonal drive.
*Cortisol supplementation*
- This would be indicated for conditions causing **adrenal insufficiency**, such as **congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH)** with salt-wasting or Addison's disease.
- CAH typically presents with virilization and advanced bone age but would show **low LH/FSH** (due to peripheral androgen excess) and elevated adrenal androgens (e.g., DHEA-S, 17-hydroxyprogesterone), which are not described.
*Radiation therapy*
- This is a treatment for **malignant tumors**, often used in cases of brain tumors.
- The MRI of the brain showed **no abnormalities**, ruling out a pituitary or hypothalamic tumor as the cause of CPP in this case, thus making radiation therapy inappropriate.
*Observation*
- **Observation** alone is inappropriate given the significant **advancement of bone age** (10 years in a 7-year-old) and clear signs of central precocious puberty.
- Untreated CPP can lead to **compromised adult height potential** due to premature epiphyseal fusion and psychosocial issues, necessitating intervention.
Brain tumors in children US Medical PG Question 6: An 18-month-old boy is brought to the physician for a well-child examination. His mother is concerned because he is unable to walk on his own. He has been increasingly irritable over the past month, has been feeding poorly, and has had multiple episodes of vomiting. His immunizations are up-to-date. He is at the 50th percentile for height, 40th percentile for weight, and 98th percentile for head circumference. He appears lethargic. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows a bulging anterior fontanelle. The child is unable to stand without support and falls if he attempts to walk. Muscle tone is increased and deep tendon reflexes are 4+ in the lower extremities. Examination of the back is unremarkable. An MRI of the brain shows symmetrical enlargement of all four ventricles. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment in this patient?
- A. Cerebral aqueductoplasty
- B. Acetazolamide therapy
- C. Ventriculoperitoneal shunt (Correct Answer)
- D. Furosemide therapy
- E. Serial lumbar punctures
Brain tumors in children Explanation: ***Ventriculoperitoneal shunt***
- The patient presents with symptoms and signs of **hydrocephalus** (e.g., rapidly increasing head circumference, bulging fontanelle, vomiting, irritability, gait disturbance, hypertonia, hyperreflexia). An MRI showing **symmetrical enlargement of all four ventricles** confirms communicating hydrocephalus.
- A **ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt** is the most appropriate long-term treatment for symptomatic hydrocephalus, diverting CSF from the ventricles to the peritoneal cavity.
*Cerebral aqueductoplasty*
- This procedure is indicated for **aqueductal stenosis**, which causes **obstructive (non-communicating) hydrocephalus**, where only the ventricles proximal to the obstruction are dilated (e.g., third and lateral ventricles).
- The MRI in this case shows **symmetrical enlargement of all four ventricles**, indicating **communicating hydrocephalus**, making aqueductoplasty unsuitable.
*Acetazolamide therapy*
- **Acetazolamide** is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor that can reduce CSF production, typically used in cases of **idiopathic intracranial hypertension** or as a temporary measure in some forms of hydrocephalus.
- However, in a symptomatic infant with significant hydrocephalus and rapid head growth, medical therapy alone is usually insufficient for long-term management and does not address the underlying CSF drainage issue.
*Furosemide therapy*
- **Furosemide**, a loop diuretic, can also reduce CSF production but is generally not considered a primary treatment for hydrocephalus, especially in symptomatic infants.
- Its effects on CSF reduction are often transient and not as robust as surgical intervention for established hydrocephalus with neurological deficits.
*Serial lumbar punctures*
- **Serial lumbar punctures** can temporarily relieve pressure in **communicating hydrocephalus**, especially in neonates or patients awaiting shunt placement.
- However, they are not a long-term solution for symptomatic hydrocephalus in an older infant with ongoing symptoms and a need for definitive management and are associated with risks of infection and discomfort.
Brain tumors in children US Medical PG Question 7: A 12-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after he vomited and said he was having double vision in school. He also says that he has been experiencing morning headaches, nausea, and dizziness over the last month. He has no past medical history and is not taking any medications. Physical exam reveals a broad-based gait, dysmetria on finger-to-nose testing, and nystagmus. Both serum and urine toxicology are negative, and radiography reveals a solid mass in the midline cerebellum that enhances after contrast administration. Biopsy of this lesion reveals cells of primitive neuroectodermal origin. Which of the following would most likely be seen on histology of this lesion?
- A. Rosettes with small blue cells (Correct Answer)
- B. Rosenthal fibers
- C. Tooth enamel-like calcification
- D. Foamy cells and high vascularity
- E. Perivascular pseudorosettes
Brain tumors in children Explanation: ***Rosettes with small blue cells***
- The description of a **midline cerebellar mass** in a child, presenting with signs of **increased intracranial pressure (headaches, vomiting, double vision)** and **cerebellar dysfunction (broad-based gait, dysmetria, nystagmus)**, is classic for **medulloblastoma**.
- **Medulloblastomas** are primitive neuroectodermal tumors (PNETs) known for their distinctive histology of **small, round, blue cells** forming **Homer-Wright rosettes**.
*Rosenthal fibers*
- **Rosenthal fibers** are eosinophilic, corkscrew-shaped structures that are characteristic histological features of **pilocytic astrocytomas**.
- While pilocytic astrocytomas can be cerebellar and common in children, the question describes a "solid mass of primitive neuroectodermal origin" rather than the typical cystic lesion with mural nodule associated with pilocytic astrocytomas, and the aggressive presentation points away from pilocytic astrocytoma.
*Tooth enamel-like calcification*
- **Tooth enamel-like calcification** is a pathognomonic feature of **craniopharyngiomas**, which are typically supratentorial (in the sellar region) and cause symptoms related to pituitary dysfunction and optic chiasm compression, not cerebellar dysfunction.
- The location and symptoms provided in the vignette do not match the typical presentation of a craniopharyngioma.
*Foamy cells and high vascularity*
- **Foamy cells and high vascularity** are characteristic features of **hemangioblastomas**, which are typically seen in adults, often associated with **von Hippel-Lindau disease**, and are more commonly located in the cerebellum.
- However, the patient's age (12-year-old) and the description of cells of "primitive neuroectodermal origin" do not align with the typical presentation or origin of hemangioblastomas.
*Perivascular pseudorosettes*
- **Perivascular pseudorosettes** are the classic histological finding in **ependymomas**, another common pediatric brain tumor.
- While ependymomas can occur in the posterior fossa, they typically arise from the floor of the fourth ventricle and are not described as having primitive neuroectodermal origin in the same way medulloblastomas are, and the specific rosettes formed by medulloblastomas are Homer-Wright rosettes.
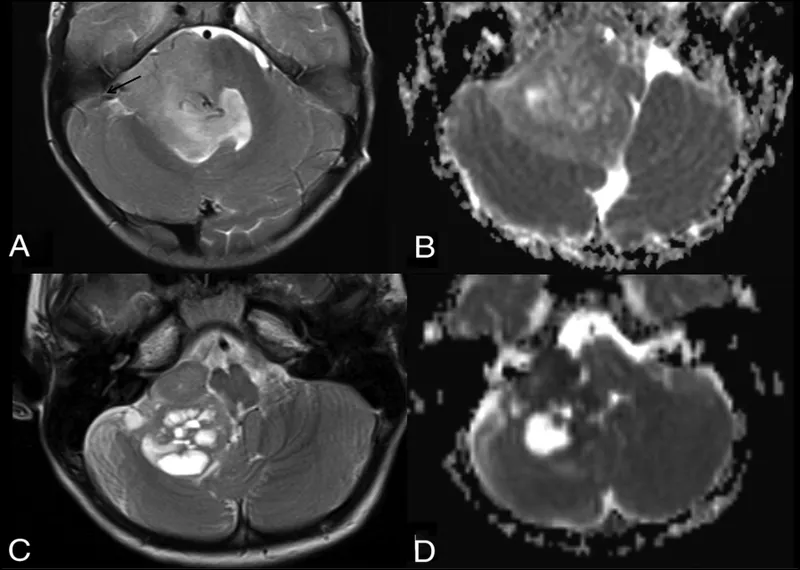
Brain tumors in children US Medical PG Question 8: A 10-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents due to 2 months of a progressively worsening headache. The headaches were initially infrequent and her parents attributed them to stress from a recent move. However, over the last week the headaches have gotten significantly worse and she had one episode of vomiting this morning when she woke up. Her medical history is remarkable for a hospitalization during infancy for bacterial meningitis. On physical exam, the patient has difficulty looking up. The lower portion of her pupil is covered by the lower eyelid and there is sclera visible below the upper eyelid. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Ependymoma
- B. Medulloblastoma
- C. Craniopharyngioma
- D. Pinealoma (Correct Answer)
- E. Pituitary Adenoma
Brain tumors in children Explanation: ***Pinealoma***
- The constellation of a progressively worsening headache, vomiting, and difficulty looking up (Parinaud's syndrome or **dorsal midbrain syndrome**) with **hydrocephalus** visible on MRI points strongly to a **pineal region tumor** that compresses the **tectal plate** and obstructs CSF flow. The visible sclera below the upper eyelid is due to **retraction of the upper eyelids**, a component of Parinaud's syndrome.
- The MRI shows significant **ventricular dilation**, particularly of the lateral and third ventricles, indicating **obstructive hydrocephalus**, which is consistent with a mass in the pineal region compressing the **cerebral aqueduct**.
*Ependymoma*
- Ependymomas most commonly occur in the **fourth ventricle** in children and can cause hydrocephalus by obstructing CSF flow at that level.
- However, typical symptoms would be more associated with **cerebellar dysfunction** (ataxia, nystagmus), and Parinaud's syndrome is not characteristic.
*Medulloblastoma*
- Medulloblastomas are highly malignant **cerebellar tumors** in children, typically arising from the vermis, and often cause **ataxia**, truncal instability, and hydrocephalus due to fourth ventricle obstruction.
- While they cause hydrocephalus and headaches, they do not typically present with Parinaud's syndrome.
*Craniopharyngioma*
- Craniopharyngiomas are **suprasellar tumors** that originate from Rathke's pouch remnants and can cause headaches, visual field defects (**bitemporal hemianopsia**), and **endocrine dysfunction** (e.g., growth delays, diabetes insipidus).
- They are typically located anteriorly, compressing the **optic chiasm** and hypothalamus, not directly obstructing the cerebral aqueduct to cause Parinaud's syndrome.
*Pituitary Adenoma*
- Pituitary adenomas are rare in children and typically cause symptoms related to **hormonal overproduction** or compression of adjacent structures, such as **visual field defects** (bitemporal hemianopsia).
- While large adenomas can cause headaches, they are not typically associated with **Parinaud's syndrome** or rapid-onset **obstructive hydrocephalus** in this manner.
Brain tumors in children US Medical PG Question 9: An inconsolable mother brings her 2-year-old son to the emergency room after finding a large amount of bright red blood in his diaper, an hour ago. She states that for the past week her son has been having crying fits while curling his legs towards his chest in a fetal position. His crying resolves either after vomiting or passing fecal material. Currently, the child is in no apparent distress. Physical examination with palpation in the gastric region demonstrates no acute findings. X-ray of the abdominal area demonstrates no acute findings. His current temperature is 36.5°C (97.8°F), heart rate is 93/min, blood pressure is 100/64 mm Hg, and respiratory rate is 26/min. His weight is 10.8 kg (24.0 lb), and height is 88.9 cm (35.0 in). Laboratory tests show the following:
RBC count 5 million/mm3
Hematocrit 36%
Hemoglobin 12 g/dL
WBC count 6,000/mm3
Mean corpuscular volume 78 fL
What is the most likely underlying embryological cause predisposing to this condition?
- A. Failure of the vitelline duct to close (Correct Answer)
- B. Failure of the vitelline duct to open
- C. Elevated anti-mitochondrial antibodies
- D. Problem with bilirubin conjugation
- E. Problem with bilirubin uptake
Brain tumors in children Explanation: ***Failure of the vitelline duct to close***
- The clinical presentation of a 2-year-old with recurrent episodes of abdominal pain, crying spells (curling legs to chest), and the passage of bright red blood in the diaper is highly suggestive of **intussusception**. This can be transiently relieved when the "curled" bowel straightens itself out, or gas/fecal matter is passed. The presence of **bright red blood** (often referred to as **currant jelly stools** when mixed with mucus) further supports this diagnosis, indicating ischemic bowel.
- In children, intussusception is often idiopathic, but in a small percentage of cases, especially in older infants and children, an **anatomical lead point** can cause it. The most common anatomical lead point is a **Meckel's diverticulum**, which results from the **incomplete obliteration of the vitelline duct** (also known as the omphalomesenteric duct) during embryological development. The diverticulum can act as a foreign body that then telescopes into the adjacent bowel, causing intussusception.
*Failure of the vitelline duct to open*
- The vitelline duct should normally regress and disappear. Therefore, a "failure to open" is not a recognized embryological anomaly or pathology.
- Problems related to the vitelline duct involve either its **incomplete closure** (leading to Meckel's diverticulum, vitelline cysts, or fistulas) or other abnormal remnants, not a failure to open.
*Elevated anti-mitochondrial uptake*
- This option refers to **anti-mitochondrial antibodies (AMAs)**, which are characteristic markers for **primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)**, an autoimmune disease primarily affecting the liver.
- PBC is an adult-onset condition and is not associated with intussusception or the gastrointestinal symptoms described in the child.
*Problem with bilirubin conjugation*
- Issues with **bilirubin conjugation** primarily manifest as different types of **jaundice** (e.g., Crigler-Najjar syndrome, Gilbert's syndrome) due to the accumulation of unconjugated bilirubin.
- These conditions do not cause abdominal pain, intussusception, or bloody stools.
*Problem with bilirubin uptake*
- Problems with **bilirubin uptake** by hepatocytes also lead to **unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia** and jaundice.
- This condition is unrelated to acute abdominal emergencies like intussusception or gastrointestinal bleeding.
Brain tumors in children US Medical PG Question 10: A 25-year-old man comes to the physician because of right-sided painless scrotal swelling that he noticed yesterday while taking a shower. He is currently sexually active with two female partners and uses condoms inconsistently. He immigrated to the US from Argentina 2 years ago. His immunization records are unavailable. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for the last 5 years. He is 170 cm (5 ft 7 in) tall and weighs 70 kg (154 lb); BMI is 24.2 kg/m2. He appears healthy and well nourished. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 72/min, and blood pressure is 125/75 mm Hg. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Cardiac examination shows no abnormalities. The abdomen is soft with dull lower abdominal discomfort. Testicular examination shows a solid mass in the right testis that is firm and nontender. A light held behind the scrotum does not shine through. The mass is not reduced when the patient is in a supine position. The remainder of the physical examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Testicular tumor (Correct Answer)
- B. Testicular torsion
- C. Scrotal hernia
- D. Hydrocele testis
- E. Orchitis
Brain tumors in children Explanation: ***Testicular tumor***
- A **painless, firm, and nontender solid mass** in the testis that does not transilluminate and is not reducible is highly suspicious for a testicular tumor.
- The patient's age (25 years old) is within the typical demographic for **testicular cancer**, and the recent discovery further supports this diagnosis.
*Testicular torsion*
- Characterized by **sudden onset of severe pain**, scrotal swelling, and tenderness, often associated with nausea and vomiting.
- The patient in this case presents with a **painless** mass, which makes testicular torsion unlikely.
*Scrotal hernia*
- A hernia typically presents as a **reducible mass** that may increase in size with maneuvers like coughing, and it often transilluminates.
- The mass described here is **not reducible** and does not transilluminate, ruling out a simple scrotal hernia.
*Hydrocele testis*
- A hydrocele is a collection of fluid in the tunica vaginalis, which typically presents as a **painless, soft, and transilluminating** scrotal swelling.
- The mass in this patient is described as **solid** and does not transilluminate, making hydrocele unlikely.
*Orchitis*
- Orchitis is an **inflammation of the testis**, which usually presents with pain, tenderness, swelling, and sometimes fever.
- The patient's mass is explicitly described as **painless** and nontender, which is inconsistent with orchitis.
More Brain tumors in children US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.