Research ethics and IRBs US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Research ethics and IRBs. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Research ethics and IRBs US Medical PG Question 1: A 42-year-old woman presents to the physician with symptoms of vague abdominal pain and bloating for several months. Test results indicate that she has ovarian cancer. Her physician attempts to reach her by phone multiple times but cannot reach her. Next of kin numbers are in her chart. According to HIPAA regulations, who should be the primary person the doctor discusses this information with?
- A. The patient's brother
- B. The patient's husband
- C. The patient's daughter
- D. All of the options
- E. The patient (Correct Answer)
Research ethics and IRBs Explanation: ***The patient***
- Under **HIPAA**, the patient has the **right to privacy** regarding their protected health information (PHI). Therefore, the physician must make all reasonable attempts to contact the patient directly to convey their diagnosis.
- Sharing sensitive medical information like a cancer diagnosis with anyone other than the patient, without their explicit consent, would be a **violation of HIPAA regulations**.
*The patient's brother*
- The patient's brother is not automatically authorized to receive her medical information, even if listed as **next of kin**, without the patient's explicit consent or a documented **healthcare power of attorney**.
- Discussing the diagnosis with the brother without the patient's direct consent would be a **breach of patient confidentiality**.
*The patient's husband*
- Even a spouse does not automatically have the right to access a patient's **PHI** without the patient's express permission, according to **HIPAA**.
- While often a trusted contact, without explicit consent, revealing the diagnosis to the husband would still violate the patient's **privacy rights**.
*The patient's daughter*
- Similar to other family members, the patient's daughter is not legally entitled to receive her mother's confidential medical information without explicit authorization or a medical **power of attorney**.
- The physician's primary responsibility is to the patient herself, ensuring her **privacy** is maintained.
*All of the options*
- According to **HIPAA**, sharing the patient's diagnosis with any family member without her explicit consent would be a **breach of confidentiality**.
- This option incorrectly assumes that **next of kin** automatically have the right to receive sensitive medical information.
Research ethics and IRBs US Medical PG Question 2: A 29-year-old man is admitted to the emergency department following a motorcycle accident. The patient is severely injured and requires life support after splenectomy and evacuation of a subdural hematoma. Past medical history is unremarkable. The patient’s family members, including wife, parents, siblings, and grandparents, are informed about the patient’s condition. The patient has no living will and there is no durable power of attorney. The patient must be put in an induced coma for an undetermined period of time. Which of the following is responsible for making medical decisions for the incapacitated patient?
- A. The spouse (Correct Answer)
- B. An older sibling
- C. Physician
- D. Legal guardian
- E. The parents
Research ethics and IRBs Explanation: ***The spouse***
- In the absence of a **living will** or **durable power of attorney**, the law typically designates the **spouse** as the primary decision-maker for an incapacitated patient.
- This hierarchy is established to ensure decisions are made by the individual most intimately connected and presumed to understand the patient's wishes.
*An older sibling*
- Siblings are generally further down the **hierarchy of surrogate decision-makers** than a spouse or parents.
- They would typically only be considered if higher-priority family members are unavailable or unwilling to make decisions.
*Physician*
- The physician's role is to provide medical care and guidance, not to make medical decisions for an incapacitated patient when family surrogates are available.
- Physicians only make decisions in **emergency situations** when no surrogate is immediately available and treatment is immediately necessary to save the patient's life or prevent serious harm.
*Legal guardian*
- A legal guardian is usually appointed by a **court** when there is no appropriate family member available or when there is a dispute among family members.
- In this scenario, with a spouse and other close family members present, a legal guardian would not be the first choice.
*The parents*
- While parents are close family members, they are typically considered **secondary to the spouse** in the hierarchy of surrogate decision-makers for an adult patient.
- They would usually only be the decision-makers if the patient were unmarried or the spouse were unavailable.
Research ethics and IRBs US Medical PG Question 3: A 19-year-old man presents to an orthopedic surgeon to discuss repair of his torn anterior cruciate ligament. He suffered the injury during a college basketball game 1 week ago and has been using a knee immobilizer since the accident. His past medical history is significant for an emergency appendectomy when he was 12 years of age. At that time, he said that he never wanted to have surgery again. At this visit, the physician explains the procedure to him in detail including potential risks and complications. The patient acknowledges and communicates his understanding of both the diagnosis as well as the surgery and decides to proceed with the surgery in 3 weeks. Afterward, he signs a form giving consent for the operation. Which of the following statements is true about this patient?
- A. He cannot provide consent because he lacks capacity
- B. He has the right to revoke his consent at any time (Correct Answer)
- C. His parents also need to give consent to this operation
- D. He did not need to provide consent for this procedure since it is obviously beneficial
- E. His consent is invalid because his decision is not stable over time
Research ethics and IRBs Explanation: ***He has the right to revoke his consent at any time***
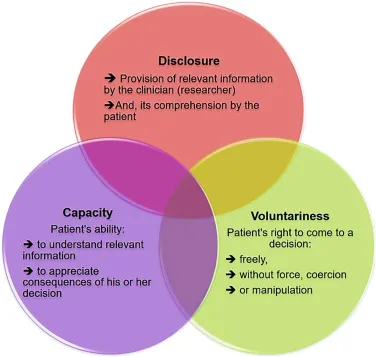
- **Informed consent** for medical procedures is an ongoing process, and a patient retains the right to **withdraw consent** at any point, even after initially signing the consent form.
- This right is a fundamental aspect of patient autonomy and ensures that medical interventions are only performed with a patient's current and willing agreement.
*He cannot provide consent because he lacks capacity*
- The patient is 19 years old, which in most jurisdictions (including the US where the age of majority is typically 18) means he is considered an **adult** and legally capable of providing his own consent.
- The scenario explicitly states he "communicates his understanding of both the diagnosis as well as the surgery," indicating he possesses the **mental capacity** to make an informed decision.
*His parents also need to give consent to this operation*
- As a 19-year-old, the patient has reached the **age of majority** and is legally entitled to make his own medical decisions, including consenting to surgery.
- Parental consent is generally required for minors (individuals under the age of majority), but not for adults like this patient.
*He did not need to provide consent for this procedure since it is obviously beneficial*
- Even for procedures that are clearly **beneficial**, informed consent is ethically and legally mandatory to uphold **patient autonomy** and ensure respect for individual rights.
- The concept of "obviously beneficial" does not negate the requirement for a patient's explicit agreement to a medical intervention.
*His consent is invalid because his decision is not stable over time*
- While the patient might have initially hated surgery at age 12, his current decision at age 19 to proceed with the ACL repair is based on current information and his mature understanding.
- The fact that his previous aversion to surgery has changed does not invalidate his current, well-informed decision; it simply indicates a change in perspective based on new circumstances and greater maturity.
Research ethics and IRBs US Medical PG Question 4: A 13-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after being involved in a motor vehicle accident in which he was a restrained passenger. He is confused and appears anxious. His pulse is 131/min, respirations are 29/min, and blood pressure is 95/49 mm Hg. Physical examination shows ecchymosis over the upper abdomen, with tenderness to palpation over the left upper quadrant. There is no guarding or rigidity. Abdominal ultrasound shows free intraperitoneal fluid and a splenic rupture. Intravenous fluids and vasopressors are administered. A blood transfusion and exploratory laparotomy are scheduled. The patient's mother arrives and insists that her son should not receive a blood transfusion because he is a Jehovah's Witness. The physician proceeds with the blood transfusion regardless of the mother's wishes. The physician's behavior is an example of which of the following principles of medical ethics?
- A. Autonomy
- B. Nonmaleficence
- C. Informed consent
- D. Justice
- E. Beneficence (Correct Answer)
Research ethics and IRBs Explanation: ***Beneficence***
- The physician prioritized the patient's immediate survival and well-being, which is the core principle of **beneficence** (acting in the best interest of the patient).
- In cases of life-threatening emergencies, especially with minors, the duty to preserve life often outweighs other considerations like parental wishes, particularly when the patient lacks the capacity for **informed refusal**.
*Autonomy*
- The physician’s action directly overrides the mother's wishes, which would be an infringement of surrogate autonomy for a minor.
- While patient autonomy is a fundamental principle, it was superseded by the immediate need to save the patient's life.
*Nonmaleficence*
- **Nonmaleficence** means "do no harm." While transfusions have risks, refusing one in this critical situation would cause more harm (death) than performing it.
- The physician acted to prevent immediate harm (death from hemorrhage), even if it meant overriding a family's wishes regarding the specific treatment method.
*Informed consent*
- **Informed consent** requires obtaining permission from a capacitated patient (or legal guardian for a minor) after explaining the risks and benefits of a treatment.
- In this emergency scenario, the patient is a minor and incapacitated, and the urgent need for a life-saving intervention (blood transfusion for a splenic rupture) did not allow for full informed consent or negotiation with the mother, who was refusing a life-saving measure.
*Justice*
- **Justice** refers to the fair and equitable distribution of healthcare resources and equal treatment, which is not the primary ethical concern in this personal patient-physician interaction.
- The scenario focuses on the individual patient's treatment decision, not broader societal resource allocation or fairness in access to care.
Research ethics and IRBs US Medical PG Question 5: A psychiatrist receives a call from a patient who expresses thoughts of harming his ex-girlfriend. The patient describes a detailed plan to attack her at her workplace. Which of the following represents the psychiatrist's most appropriate legal obligation?
- A. Warn the ex-girlfriend and notify law enforcement (Correct Answer)
- B. Only notify the patient's family
- C. Warn only law enforcement
- D. Maintain patient confidentiality
Research ethics and IRBs Explanation: ***Warn the ex-girlfriend and notify law enforcement***
- This scenario directly triggers the **"duty to warn"** and **"duty to protect"** principles, primarily stemming from the **Tarasoff v. Regents of the University of California** case.
- The psychiatrist has a legal obligation to take reasonable steps to protect the identifiable victim, which includes directly warning the intended victim and informing law enforcement.
*Only notify the patient's family*
- Notifying the patient's family alone does not fulfill the **legal obligation to protect** an identifiable third party from a serious threat of harm.
- While family involvement might be part of a comprehensive safety plan, it is insufficient as the sole action in this critical situation.
*Warn only law enforcement*
- While notifying law enforcement is a crucial step, the **Tarasoff duty** specifically mandates warning the **intended victim** directly (or those who can reasonably be expected to notify the victim).
- Relying solely on law enforcement might not ensure the immediate safety of the ex-girlfriend, especially if there's a delay in their response or ability to locate her.
*Maintain patient confidentiality*
- Patient confidentiality is a cornerstone of psychiatric practice, but it is **not absolute** when there is a serious and imminent threat of harm to an identifiable individual.
- The **duty to protect** a potential victim *outweighs* the duty to maintain confidentiality in such extreme circumstances.
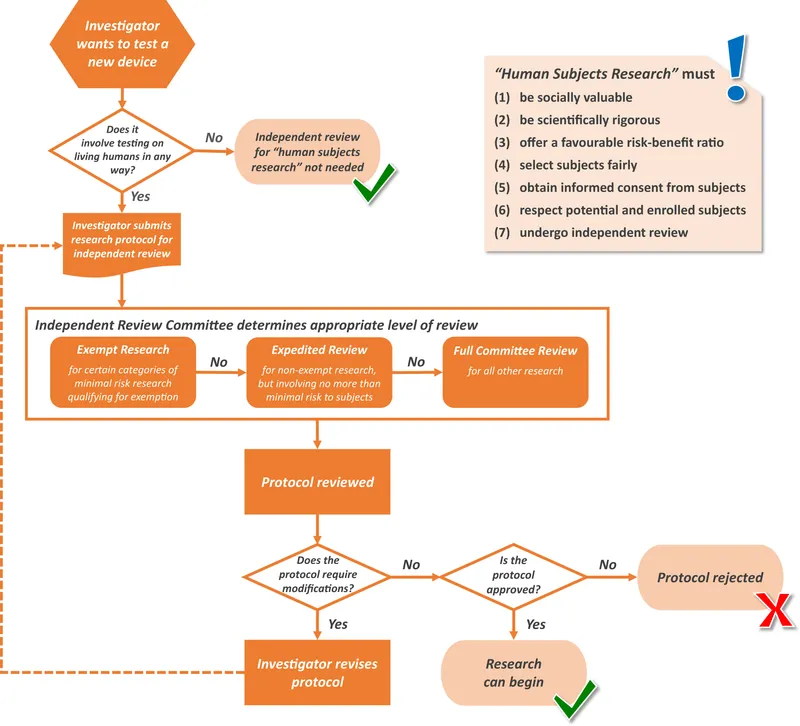
Research ethics and IRBs US Medical PG Question 6: A physician attempts to study cirrhosis in his state. Using a registry of admitted patients over the last 10 years at the local hospital, he isolates all patients who have been diagnosed with cirrhosis. Subsequently, he contacts this group of patients, asking them to complete a survey assessing their prior exposure to alcohol use, intravenous drug abuse, blood transfusions, personal history of cancer, and other medical comorbidities. An identical survey is given to an equal number of patients in the registry who do not carry a prior diagnosis of cirrhosis. Which of the following is the study design utilized by this physician?
- A. Randomized controlled trial
- B. Case-control study (Correct Answer)
- C. Cross-sectional study
- D. Cohort study
- E. Meta-analysis
Research ethics and IRBs Explanation: ***Case-control study***
- This study design **identifies subjects based on their outcome (cases with cirrhosis, controls without cirrhosis)** and then retrospectively investigates their past exposures.
- The physician selected patients with cirrhosis (cases) and patients without cirrhosis (controls), then assessed their prior exposures to risk factors like alcohol use and intravenous drug abuse.
*Randomized controlled trial*
- This design involves randomly assigning participants to an **intervention group** or a **control group** to assess the effect of an intervention.
- There is no intervention being tested or randomization occurring in this study; it is observational.
*Cross-sectional study*
- A cross-sectional study measures the **prevalence of disease and exposure at a single point in time** in a defined population.
- This study collects retrospective exposure data and compares two distinct groups (cases and controls), rather than assessing prevalence at one time point.
*Cohort study*
- A cohort study **follows a group of individuals over time** to see if their exposure to a risk factor is associated with the development of a disease.
- This study starts with the outcome (cirrhosis) and looks backward at exposures, which is the opposite direction of a cohort study.
*Meta-analysis*
- A meta-analysis is a statistical method that **combines the results of multiple independent studies** to produce a single, more powerful estimate of treatment effect or association.
- This is an original research study collecting new data, not a systematic review or synthesis of existing studies.
Research ethics and IRBs US Medical PG Question 7: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Research ethics and IRBs Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Research ethics and IRBs US Medical PG Question 8: During identification of severely decomposed remains, which of the following methods provides the most reliable means of positive identification?
- A. Birthmarks
- B. Facial features
- C. DNA analysis (Correct Answer)
- D. Personal effects
Research ethics and IRBs Explanation: ***DNA analysis***
- **DNA analysis** remains viable even in significantly degraded samples due to the stability and uniqueness of the genetic code, making it the most reliable method for positive identification of severely decomposed remains.
- It provides a definitive match that is **scientifically verifiable** and rarely subject to error when compared to ante-mortem samples or close relatives.
*Birthmarks*
- **Birthmarks** are soft tissue characteristics that often degrade or become indistinguishable in severely decomposed remains.
- Their presence and appearance can change over time or be obscured by **decomposition processes**, making them unreliable for identification in such cases.
*Facial features*
- **Facial features** rapidly deteriorate and distort after death, especially in severely decomposed remains, making visual recognition impossible.
- The soft tissues of the face are among the first to undergo **autolysis** and putrefaction.
*Personal effects*
- While **personal effects** (like jewelry or clothing) can provide circumstantial evidence, they do not offer positive identification of the individual's remains.
- These items can be easily lost, misplaced, or exchanged, and they do not directly identify the **biological individual**.
Research ethics and IRBs US Medical PG Question 9: A 32-year-old male asks his physician for information regarding a vasectomy. On further questioning, you learn that he and his wife have just had their second child and he asserts that they no longer wish to have additional pregnancies. You ask him if he has discussed a vasectomy with his wife to which he replies, "Well, not yet, but I'm sure she'll agree." What is the next appropriate step prior to scheduling the patient's vasectomy?
- A. Insist that the patient first discuss this procedure with his wife
- B. Telephone the patient's wife to inform her of the plan
- C. Refuse to perform the vasectomy
- D. Explain the risks and benefits of the procedure and request signed consent from the patient and his wife
- E. Explain the risks and benefits of the procedure and request signed consent from the patient (Correct Answer)
Research ethics and IRBs Explanation: ***Explain the risks and benefits of the procedure and request signed consent from the patient***
- A patient has the **right to make autonomous decisions** about their own medical care, including reproductive choices, regardless of their marital status or spousal approval.
- The physician's role is to ensure the patient is fully informed and provides **voluntary, uncoerced consent** after understanding the risks, benefits, and alternatives of the procedure.
*Insist that the patient first discuss this procedure with his wife*
- This option would be a **violation of patient autonomy** and confidentiality, as a married person has the right to make independent medical decisions.
- Requiring spousal consent for a procedure performed solely on one individual is not ethically or legally mandated and could be considered discriminatory.
*Telephone the patient's wife to inform her of the plan*
- This action would be a **breach of patient confidentiality**, as the patient's medical information, including his intent to have a vasectomy, cannot be shared with a third party, even a spouse, without explicit permission.
- Informing the wife without the husband's consent also undermines the patient's autonomy and right to privacy regarding his healthcare decisions.
*Refuse to perform the vasectomy*
- Refusing to perform the procedure simply because the patient has not discussed it with his wife would be **unethical and inconsistent with medical professionalism**, assuming the patient is competent and fully informed.
- A physician should not deny medically appropriate care based on a patient's marital dynamics or the presumed wishes of a spouse, as long as the patient's consent is valid.
*Explain the risks and benefits of the procedure and request signed consent from the patient and his wife*
- While it is advisable for a patient to discuss major life decisions with their spouse, requiring **spousal consent for a patient's own medical procedure** is not legally or ethically mandated for competent adults.
- Obtaining consent from both individuals is typically reserved for procedures affecting both parties directly or for those involving a surrogate decision-maker, not for an autonomous adult's personal medical choice.
Research ethics and IRBs US Medical PG Question 10: A 73-year-old man is admitted to the hospital for jaundice and weight loss. He is an immigrant from the Dominican Republic and speaks little English. A CT scan is performed showing a large mass at the head of the pancreas. When you enter the room to discuss these results with the patient, his daughter and son ask to speak with you outside of the patient's room. They express their desire to keep these results from their father. What is the appropriate response in this situation?
- A. Consult the hospital ethics committee
- B. Deliver the information in Spanish
- C. Respect the children's wishes to hold prognosis information
- D. Tell the children that you are obligated to tell the father
- E. Explore the reasoning behind the children's request (Correct Answer)
Research ethics and IRBs Explanation: ***Explore the reasoning behind the children's request***
- Understanding the family's cultural background, including beliefs about illness and communication, is crucial for navigating this sensitive situation.
- This approach allows the healthcare provider to assess whether the family's request stems from a protective desire rooted in their culture or a misunderstanding, which can inform the next steps.
*Consult the hospital ethics committee*
- While an ethics consultation may be necessary if an impasse is reached, it is not the immediate first step.
- Initial direct communication and exploration with the family are preferable to first understand the context before escalating to an ethics committee.
*Deliver the information in Spanish*
- This addresses the language barrier but does not resolve the ethical dilemma of withholding information from the patient at the family's request.
- Providing the information in Spanish without first understanding the family's wishes might violate their cultural norms or inadvertently cause distress.
*Respect the children's wishes to hold prognosis information*
- Respecting the children's wishes without understanding their rationale could violate the patient's right to **autonomy** and **informed consent**.
- In most Western medical ethics frameworks, the patient has the primary right to receive information about their health, even if it is distressing.
*Tell the children that you are obligated to tell the father*
- Immediately stating an obligation without understanding the family's perspective can come across as abrupt and culturally insensitive.
- This approach might create an adversarial dynamic, making it harder to build trust and find a mutually agreeable solution.
More Research ethics and IRBs US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.