Female reproductive pathology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Female reproductive pathology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Female reproductive pathology US Medical PG Question 1: A 63-year-old woman, gravida 0, para 0 comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of abdominal distension, constipation, and weight loss. She has a history of endometriosis. Pelvic examination shows a nontender, irregular, left adnexal mass. Her serum level of CA-125 is elevated. Serum concentrations of human chorionic gonadotropin and alpha-fetoprotein are within the reference ranges. Microscopic examination of the mass is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Large undifferentiated germ cells with clear cytoplasm
- B. Spindle-shaped stromal cells along with signet ring cells
- C. Small, round cells that form Call-Exner bodies
- D. Atypical epithelial cells along with psammoma bodies (Correct Answer)
- E. Flattened, cuboidal cells along with Schiller-Duval bodies
Female reproductive pathology Explanation: ***Atypical epithelial cells along with psammoma bodies***
- This constellation of symptoms (abdominal distension, weight loss, constipation, adnexal mass), along with **elevated CA-125** and a history of **endometriosis** in a postmenopausal woman, is highly suggestive of **epithelial ovarian cancer**, particularly **serous cystadenocarcinoma**.
- **Psammoma bodies** (concentric calcifications) are characteristic findings in **serous papillary carcinomas**, including those originating from the ovary.
*Large undifferentiated germ cells with clear cytoplasm*
- This describes **dysgerminoma**, a **germ cell tumor** of the ovary.
- While dysgerminomas can cause adnexal masses and abdominal symptoms, they typically present in **younger women** and often lead to elevated **LDH** levels, not primary CA-125 elevation.
*Spindle-shaped stromal cells along with signet ring cells*
- **Signet ring cells** are characteristic of **Krukenberg tumors**, which are metastatic carcinomas (most commonly from the GI tract) to the ovary.
- While metastasis is possible, the primary symptoms and elevated CA-125 point more directly toward a primary epithelial ovarian cancer.
*Small, round cells that form Call-Exner bodies*
- This describes **granulosa cell tumors**, which are **sex cord-stromal tumors** of the ovary.
- These tumors can produce hormones (e.g., estrogen), leading to symptoms like abnormal uterine bleeding, and may have elevated **inhibin** levels, rather than primarily CA-125.
*Flattened, cuboidal cells along with Schiller-Duval bodies*
- This describes **yolk sac tumors** (endodermal sinus tumors), another type of **germ cell tumor**.
- These tumors typically occur in **younger individuals** and are associated with a significant elevation of **alpha-fetoprotein**, which is explicitly stated as being within reference range in this patient.
Female reproductive pathology US Medical PG Question 2: A 39-year-old woman, gravida 3, para 2, at 32 weeks' gestation comes to the emergency department 1 hour after the sudden onset of severe abdominal pain and nausea. She has had one episode of nonbloody vomiting. Pregnancy has been uncomplicated, except for a blood pressure measurement of 150/90 mm Hg on her last prenatal visit. Her first child was delivered vaginally; her second child was delivered by lower segment transverse cesarean section because of a nonreassuring fetal heart rate. She appears anxious and pale. Her temperature is 36.1°C (96°F), pulse is 115/min, and blood pressure is 92/65 mm Hg. Extremities are cool and clammy. Pelvic examination shows a rigid, tender uterus. The cervix is 30% effaced and 1 cm dilated; the vertex is at -1 station. The fetal heart rate is 100/min. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Ruptured vasa previa
- B. Placenta accreta
- C. Abruptio placentae (Correct Answer)
- D. Ruptured uterus
- E. Placenta previa
Female reproductive pathology Explanation: ***Abruptio placentae***
- The sudden onset of **severe abdominal pain**, **uterine rigidity and tenderness**, maternal hypovolemic shock (tachycardia, hypotension, cool and clammy extremities), and **fetal bradycardia** are classic signs of **abruptio placentae**.
- **Hypertension** (150/90 mm Hg) is a risk factor, and a prior **cesarean section** may slightly increase the risk as well, although the primary risk factor here is hypertension.
*Ruptured vasa previa*
- **Vasa previa** typically presents with **painless vaginal bleeding** when membranes rupture, accompanied by rapid fetal deterioration due to fetal blood loss, and would not cause severe maternal abdominal pain and shock.
- The bleeding in vasa previa originates from fetal vessels, leading to a profound impact on fetal heart rate *before* significant maternal symptoms.
*Placenta accreta*
- **Placenta accreta** is typically diagnosed prenatally via ultrasound or suspected at delivery due to difficulty with placental separation. It does not usually present with acute, severe abdominal pain and hypovolemic shock during pregnancy.
- Patients with placenta accreta are at high risk for significant hemorrhage *after* delivery of the fetus, but before placental delivery.
*Ruptured uterus*
- While a prior **cesarean section** is a risk factor for uterine rupture, the presentation of **rigid and tender uterus** is more characteristic of abruptio placentae. Uterine rupture often involves a **sudden cessation of contractions**, palpable fetal parts outside the uterus, and often severe, sharp pain, but not typically a rigid uterus.
- The fetal heart rate in uterine rupture often shows a **sudden, profound deceleration** or absence, but the specific finding of a rigid, tender uterus with ongoing severe pain points away from frank rupture.
*Placenta previa*
- **Placenta previa** typically presents with **painless vaginal bleeding** in the second or third trimester.
- It does not usually cause severe abdominal pain, uterine tenderness, or maternal hypovolemic shock unless accompanied by abruptio placentae, which is the more dominant and acute finding here.
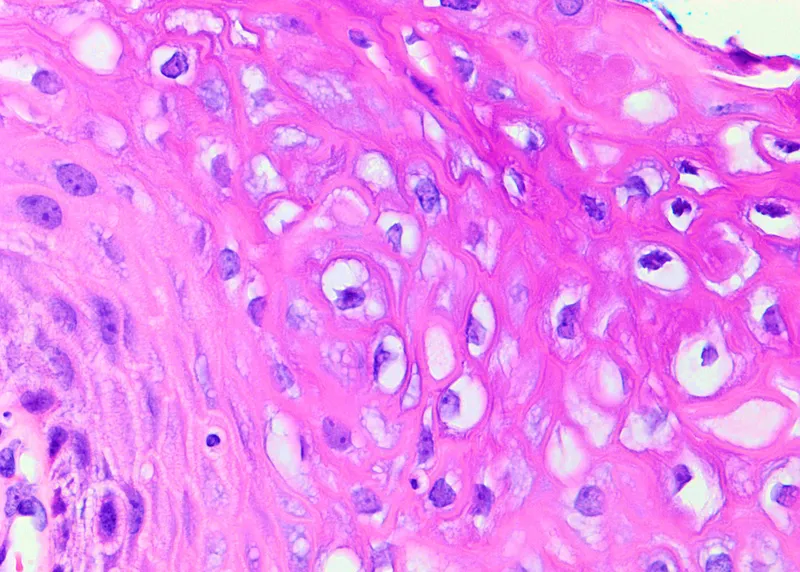
Female reproductive pathology US Medical PG Question 3: A 42-year-old woman comes to the physician for the evaluation of a 1-month history of dull lower abdominal pain, decreased appetite, and a 5-kg (11-lb) weight loss. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Pelvic ultrasonography shows bilateral ovarian enlargement and free fluid in the rectouterine pouch. Biopsy specimens from the ovaries show multiple, round, mucin-filled cells with flat, peripheral nuclei. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Decreased TSH levels
- B. Gastric wall thickening (Correct Answer)
- C. Dark blue peritoneal spots
- D. Increased testosterone levels
- E. Elevated β-hCG levels
Female reproductive pathology Explanation: ***Gastric wall thickening***
- The description of **bilateral ovarian enlargement** with **mucin-filled cells** and **flat, peripheral nuclei** (**signet ring cells**) on biopsy is characteristic of **Krukenberg tumors**, which are metastatic ovarian tumors.
- The most common primary site for **Krukenberg tumors** is the **stomach**, implying that further evaluation would likely reveal **gastric wall thickening** or a mass consistent with the primary gastric adenocarcinoma.
*Decreased TSH levels*
- **Decreased TSH levels** are associated with **hyperthyroidism**, which typically presents with symptoms like weight loss (often with increased appetite), heat intolerance, and palpitations, none of which are specifically indicated as primary symptoms or directly linked to the ovarian findings described.
- While weight loss is present, it's alongside **decreased appetite**, which is atypical for primary hyperthyroidism, and the ovarian pathology points to a metastatic malignancy rather than an endocrine disorder.
*Dark blue peritoneal spots*
- **Dark blue peritoneal spots** are characteristic of **endometriosis**, specifically **peritoneal endometriosis**, where endometrial tissue is found outside the uterus.
- This condition presents with pelvic pain, dysmenorrhea, and infertility, but does not involve mucin-filled **signet ring cells** in ovarian biopsies or typically cause significant systemic symptoms like unexplained weight loss and decreased appetite in the same manner as a metastatic malignancy.
*Increased testosterone levels*
- **Increased testosterone levels** can be seen in conditions like **polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)** or **androgen-producing ovarian tumors** (e.g., Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors).
- These conditions are not associated with the histological finding of **signet ring cells** in ovarian biopsies or the systemic symptoms of weight loss and decreased appetite described in this patient.
*Elevated β-hCG levels*
- **Elevated β-hCG levels** are primarily associated with **pregnancy** or **gestational trophoblastic disease** (e.g., hydatidiform mole, choriocarcinoma) and some germ cell tumors.
- While some ovarian tumors can produce β-hCG, the specific histological findings of **signet ring cells** point strongly towards a metastatic adenocarcinoma, not a condition typically characterized by β-hCG elevation.
Female reproductive pathology US Medical PG Question 4: A 40-year-old woman visits your office with her pathology report after being subjected to total abdominal hysterectomy a month ago. She explains that she went through this procedure after a long history of lower abdominal pain that worsened during menses and heavy menstrual bleeding. She is a mother of 5 children, and they are all delivered by cesarean section. The pathology gross examination report and microscopic examination report from the specimen from surgery describes an enlarged, globular uterus with invading clusters of endometrial tissue within the myometrium. What is the most likely diagnosis for this patient?
- A. Endometrial hyperplasia
- B. Uterine leiomyoma
- C. Uterine adenomyosis (Correct Answer)
- D. Endometrial polyp
- E. Endometrial carcinoma
Female reproductive pathology Explanation: ***Uterine adenomyosis***
- The pathology findings of an **enlarged, globular uterus** with **invading clusters of endometrial tissue within the myometrium** are classic for adenomyosis.
- The clinical history of **dysmenorrhea** (lower abdominal pain worsening during menses) and **menorrhagia** (heavy menstrual bleeding) along with multiparity and prior C-sections are risk factors for adenomyosis.
*Endometrial hyperplasia*
- This condition involves **proliferation of endometrial glands** within the uterine cavity, not invasion into the myometrium.
- While it can cause abnormal uterine bleeding, it does not typically result in an **enlarged, globular uterus** due to myometrial involvement.
*Uterine leiomyoma*
- Also known as **fibroids**, these are **benign smooth muscle tumors** of the uterus, which can cause uterine enlargement and heavy bleeding.
- However, they are distinct masses and do not involve "invading clusters of endometrial tissue within the myometrium" as described in the pathology.
*Endometrial polyp*
- These are **localised overgrowths of endometrial tissue** projecting into the uterine cavity, often causing abnormal bleeding.
- They are typically small and do not cause an **enlarged, globular uterus** or evidence of myometrial invasion.
*Endometrial carcinoma*
- This is a **malignant proliferation of endometrial glands**, which can invade the myometrium in advanced stages.
- While it can cause abnormal uterine bleeding, the description of "invading clusters of endometrial tissue within the myometrium" without mention of malignancy favors a benign condition like adenomyosis, especially in the context of the patient's age and history.
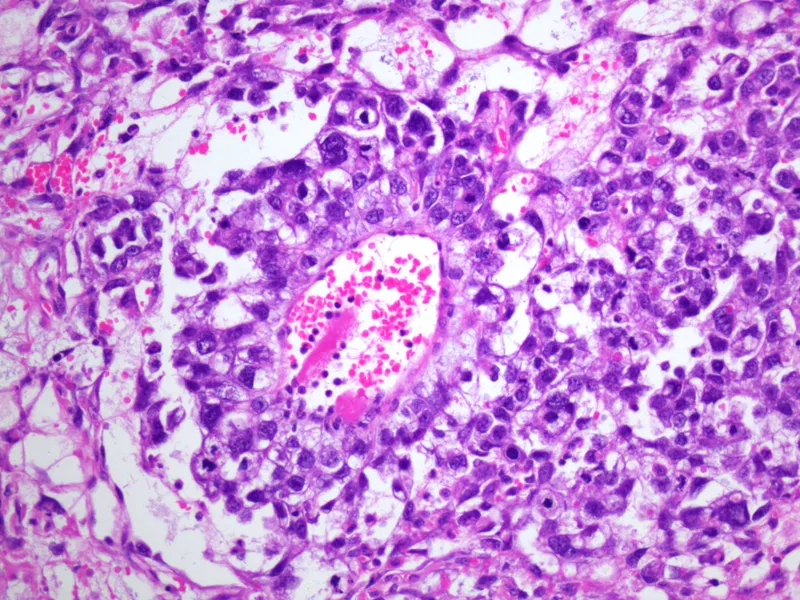
Female reproductive pathology US Medical PG Question 5: A 36-year-old woman comes to the physician for an annual pelvic examination and Pap smear. Her last Pap smear was 3 years ago. She has been sexually active with multiple male partners and takes an oral contraceptive. She has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 10 years. Pelvic examination shows no abnormalities. A photomicrograph of cervical cells from the Pap smear specimen is shown. Cells similar to the one indicated by the arrow are most likely to be seen in which of the following conditions?
- A. Condylomata acuminata (Correct Answer)
- B. Bacterial vaginosis
- C. Trichomoniasis
- D. Genital herpes
- E. Syphilitic chancre
Female reproductive pathology Explanation: ***Condylomata acuminata***
- The image likely depicts a **koilocyte**, a key indicator of **Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection**, which causes condylomata acuminata.
- Koilocytes are characterized by **perinuclear cytoplasmic vacuolization** and nuclear atypia, directly linked to HPV.
*Bacterial vaginosis*
- Characterized by a **shift in vaginal flora**, presenting with "clue cells" (vaginal epithelial cells covered in bacteria) and discharge, not koilocytes.
- While common, bacterial vaginosis does not cause the **cytopathic changes** seen with HPV infection.
*Trichomoniasis*
- Caused by the **protozoan parasite** *Trichomonas vaginalis*, leading to a frothy, green-yellow discharge and cervical inflammation (strawberry cervix).
- Diagnosis involves identifying the **motile trichomonads** on wet mount, not koilocytes on a Pap smear.
*Genital herpes*
- Caused by **herpes simplex virus (HSV)**, resulting in painful vesicular lesions that ulcerate.
- Cytologic findings include **multinucleated giant cells** with nuclear molding and intranuclear inclusions, distinctly different from koilocytes.
*Syphilitic chancre*
- A primary lesion of syphilis caused by **_Treponema pallidum_**, presenting as a painless ulcer.
- Diagnosis is made by **darkfield microscopy** or serologic tests; cytology is not used to identify syphilitic chancres.
Female reproductive pathology US Medical PG Question 6: A 17-year-old girl comes to the emergency department with a 5-day history of severe abdominal pain, cramping, nausea, and vomiting. She also has pain with urination. She is sexually active with one male partner, and they use condoms inconsistently. She experienced a burning pain when she last had sexual intercourse 3 days ago. Menses occur at regular 28-day intervals and last 5 days. Her last menstrual period was 3 weeks ago. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 83/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. Physical examination shows abdominal tenderness in the lower quadrants. Pelvic examination shows cervical motion tenderness and purulent cervical discharge. Laboratory studies show a leukocyte count of 15,000/mm3 and an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 100 mm/h. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Ectopic pregnancy
- B. Ovarian cyst rupture
- C. Pyelonephritis
- D. Appendicitis
- E. Pelvic inflammatory disease (Correct Answer)
Female reproductive pathology Explanation: ***Pelvic inflammatory disease***
- The constellation of **lower abdominal pain, fever, cervical motion tenderness, purulent cervical discharge, leukocytosis, and elevated ESR** in a sexually active young woman strongly indicates PID.
- The history of **pain during intercourse and inconsistent condom use** increases the risk for sexually transmitted infections, which are common causes of PID.
*Ectopic pregnancy*
- While it can cause unilateral abdominal pain and tenderness, it's typically associated with **amenorrhea** and **vaginal spotting**, neither of which is present, and would not cause purulent discharge or fever this high.
- A **positive pregnancy test** would be expected, but none is mentioned, and her last menstrual period was 3 weeks ago, making pregnancy less likely as a cause of such severe symptoms.
*Ovarian cyst rupture*
- Characterized by **sudden-onset, sharp, unilateral abdominal pain** which may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting, but generally **lacks fever, purulent cervical discharge, cervical motion tenderness, or leukocytosis** as prominent features.
- The symptoms in the case, particularly the signs of infection, are inconsistent with a simple cyst rupture.
*Pyelonephritis*
- Typically presents with **flank pain, fever, dysuria, and CVA tenderness**, often with urinary symptoms like frequency or urgency.
- While dysuria is present, the **prominent cervical motion tenderness and purulent cervical discharge** make pyelonephritis less likely as the primary diagnosis, although a co-infection is possible.
*Appendicitis*
- Causes periumbilical pain that migrates to the **right lower quadrant**, often with anorexia, nausea, fever, and leukocytosis, but **lacks the genitourinary symptoms** such as dysuria, cervical motion tenderness, and purulent cervical discharge.
- The patient's pain is described as lower quadrant, which can be diffuse with PID.
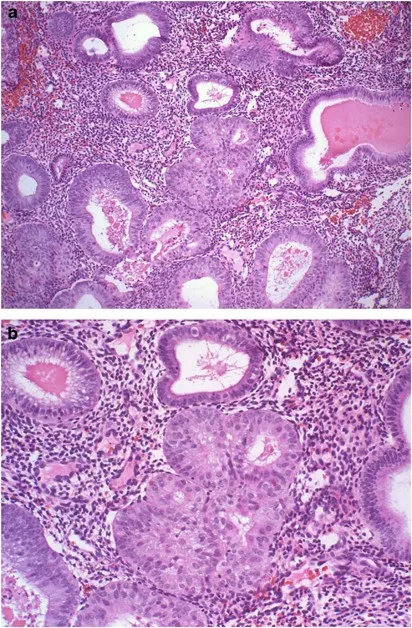
Female reproductive pathology US Medical PG Question 7: A 55-year-old postmenopausal woman comes to the physician for a screening Pap smear. She has no history of serious illness. Her last Pap smear was 10 years ago and showed no abnormalities. She has smoked one-half pack of cigarettes daily for 20 years and drinks 3 bottles of wine per week. She is sexually active with multiple male partners and uses condoms inconsistently. Her paternal grandmother had ovarian cancer and her maternal aunt had breast cancer. Pelvic examination shows multiple red, fleshy polypoid masses on the anterior vaginal wall. A biopsy is obtained and histology shows large cells with abundant clear cytoplasm. Which of the following is the most significant risk factor for this diagnosis?
- A. Family history of breast and ovarian cancer
- B. Human papillomavirus infection
- C. Alcohol consumption
- D. Diethylstilbestrol exposure in utero (Correct Answer)
- E. Cigarette smoking
Female reproductive pathology Explanation: ***Diethylstilbestrol exposure in utero***
- The patient's presentation with **clear cell carcinoma of the vagina**, characterized by **red, fleshy polypoid masses** and **large cells with abundant clear cytoplasm**, is highly suggestive of this diagnosis.
- **In utero exposure to diethylstilbestrol (DES)** is a classic and significant risk factor for the development of clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina and cervix.
*Family history of breast and ovarian cancer*
- While a family history of breast and ovarian cancer may indicate an increased risk for other gynecological cancers (e.g., BRCA mutations), it is **not directly linked** to clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina.
- This family history points more towards **hereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndromes**, not the specific pathology described.
*Human papillomavirus infection*
- **HPV infection** is a major risk factor for most cases of **squamous cell carcinoma of the vagina and cervix**, and also increases the risk of adenocarcinoma of the cervix.
- However, HPV is **not a primary risk factor for clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina**, which has a distinct etiology.
*Alcohol consumption*
- While excessive **alcohol consumption** can be associated with an increased risk of certain cancers, it is **not a specific or significant risk factor** for clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina.
- It generally contributes to a broad range of cancers rather than specific rare forms.
*Cigarette smoking*
- **Cigarette smoking** is a well-established risk factor for **squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix and vagina**, among other cancers.
- However, it is **not a recognized significant risk factor** for the development of **clear cell adenocarcinoma of the vagina**.
Female reproductive pathology US Medical PG Question 8: A 21-year-old female presents to her primary care doctor for prenatal counseling before attempting to become pregnant for the first time. She is an avid runner, and the physician notes her BMI of 17.5. The patient complains of chronic fatigue, which she attributes to her busy lifestyle. The physician orders a complete blood count that reveals a Hgb 10.2 g/dL (normal 12.1 to 15.1 g/dL) with an MCV 102 µm^3 (normal 78 to 98 µm^3). A serum measurement of a catabolic derivative of methionine returns elevated. Which of the following complications is the patient at most risk for if she becomes pregnant?
- A. Placenta abruptio (Correct Answer)
- B. Placenta previa
- C. Placenta accreta
- D. Neural tube defects
- E. Gestational diabetes
Female reproductive pathology Explanation: **Placenta abruptio**
* The patient presents with several risk factors for **placental abruption**, including **low BMI**, **anemia** (Hgb 10.2), and **elevated homocysteine** (indicated by elevated catabolic derivative of methionine, implying **folate or B12 deficiency**, which leads to high homocysteine).
* **Anemia** and **folate deficiency** are associated with an increased risk of placental abruption.
*Placenta previa*
* **Placenta previa** is characterized by the placenta covering the cervical os, typically associated with risk factors like **previous C-section**, **multiparity**, and **advanced maternal age**.
* The patient's profile (first pregnancy, young) does not align with the typical risk factors for placenta previa.
*Placenta accreta*
* **Placenta accreta** involves abnormal placental adherence to the uterine wall, most commonly linked to **prior uterine surgery** (especially C-sections) and **placenta previa**.
* The patient has no history of uterine surgery, making placenta accreta an unlikely primary risk.
*Neural tube defects*
* **Neural tube defects** are associated with **folate deficiency**, which is likely present given the **macrocytic anemia** (MCV 102) and elevated homocysteine.
* However, the question asks for the complication the patient is *most* at risk for due to her overall profile including her low BMI and anemia, and while NTDs are a risk, the combination of factors points more strongly to placental abruption.
*Gestational diabetes*
* **Gestational diabetes** is linked to risk factors like **obesity**, **family history of diabetes**, and **advanced maternal age**.
* The patient's **low BMI** (17.5) and young age make gestational diabetes an unlikely significant risk.
Female reproductive pathology US Medical PG Question 9: A 68-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. Over the past six months, he has had an increase in the frequency of his bowel movements and occasional bloody stools. He has hypertension, coronary artery disease, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 40 years. His current medications include aspirin, lisinopril, and salmeterol. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 75/min, and blood pressure is 128/75 mm Hg. The lungs are clear to auscultation. Cardiac examination shows no murmurs, rubs, or gallops. The abdomen is soft with no organomegaly. Digital rectal examination shows a large internal hemorrhoid. Test of the stool for occult blood is positive. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the management of this patient?
- A. Capsule endoscopy
- B. Rubber band ligation
- C. Hemorrhoidectomy
- D. Barium enema
- E. Colonoscopy (Correct Answer)
Female reproductive pathology Explanation: ***Colonoscopy***
- This patient presents with **changes in bowel habits** (increased frequency) and **rectal bleeding** (bloody stools, positive fecal occult blood test), which are classic alarm symptoms for **colorectal cancer**.
- A **colonoscopy** is the most appropriate next step because it allows for direct visualization of the entire colon, biopsy of suspicious lesions, and removal of polyps, which is crucial for diagnosing or ruling out colorectal cancer and other colon pathologies.
*Capsule endoscopy*
- **Capsule endoscopy** is primarily used to evaluate the **small bowel** for obscure GI bleeding, Crohn's disease, or small bowel tumors.
- It is **not effective** for evaluating the colon as it cannot be controlled to visualize the colonic lining thoroughly and cannot perform biopsies.
*Rubber band ligation*
- **Rubber band ligation** is a procedure used to treat **hemorrhoids**, particularly problematic internal hemorrhoids.
- While the patient has an internal hemorrhoid, his new onset of bowel changes and bloody stools warrants a more comprehensive evaluation to rule out other serious conditions like **colorectal cancer** before attributing symptoms solely to hemorrhoids, especially given his age and risk factors.
*Hemorrhoidectomy*
- **Hemorrhoidectomy** is a surgical procedure for treating severe or refractory hemorrhoids.
- Similar to rubber band ligation, performing a hemorrhoidectomy without a prior **colonoscopy** would be inappropriate given the patient's alarm symptoms, as it might delay the diagnosis of a more serious underlying condition.
*Barium enema*
- A **barium enema** is a radiological study that can identify large polyps or masses in the colon, but it has **lower sensitivity** than colonoscopy, especially for smaller lesions.
- It **does not allow for biopsy** of suspicious areas or removal of polyps, which limits its diagnostic and therapeutic utility compared to colonoscopy for these symptoms.
Female reproductive pathology US Medical PG Question 10: A 54-year-old woman comes to the physician because of an ulcer on her left ankle for 6 years. She has had multiple ulcers over her left lower extremity during this period that have subsided with wound care and dressing. She has type 2 diabetes mellitus and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Current medications include metformin, sitagliptin, and omeprazole. She appears anxious. She is 162 cm (5 ft 4 in) tall and weighs 89 kg (196 lb); BMI is 34 kg/m2. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows a 7.5-cm (3-in) ulcer with elevated, indurated margins and a necrotic floor above the left medial malleolus. There are multiple dilated, tortuous veins along the left lower extremity. There is 2+ pretibial edema of the lower extremities bilaterally. The skin around the left ankle appears darker than the right and there are multiple excoriation marks. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management of this patient's current condition?
- A. Trendelenburg test
- B. Punch biopsy (Correct Answer)
- C. Digital subtraction angiography
- D. Perthes test
- E. CT scan of the left leg
Female reproductive pathology Explanation: ***Punch biopsy***
- A 6-year history of a non-healing **ulcer with elevated, indurated margins and a necrotic floor** is highly suspicious for **Marjolin's ulcer**, a type of squamous cell carcinoma arising in chronic wounds.
- A **punch biopsy** is the most appropriate next step to obtain a tissue diagnosis and confirm or rule out malignancy.
*Trendelenburg test*
- The Trendelenburg test assesses **venous valve competence** in superficial veins.
- While this patient has signs of **venous insufficiency** (dilated veins, edema, skin changes), the primary concern is the non-healing, suspicious ulcer, for which biopsy is more urgent.
*Digital subtraction angiography*
- Digital subtraction angiography is used to visualize **arterial blood flow** and diagnose peripheral artery disease.
- Although the patient has diabetes, there are no classic signs of significant arterial insufficiency (e.g., claudication, cold limb, diminished pulses), and the ulcer characteristics are more suggestive of malignancy or venous etiology.
*Perthes test*
- The Perthes test evaluates the **patency of deep veins** and the function of communicating veins by assessing changes in superficial venous distension after exercise with a tourniquet.
- Similar to the Trendelenburg test, it focuses on venous hemodynamics, which is secondary to the suspicion of malignancy in a chronic, non-healing ulcer.
*CT scan of the left leg*
- A CT scan can assess the **extent of soft tissue destruction or bone involvement** if malignancy is suspected or confirmed.
- However, it is not the initial diagnostic step for determining the nature of the ulcer itself; a **tissue biopsy** is required for definitive diagnosis.
More Female reproductive pathology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.