Renal tumors US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Renal tumors. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
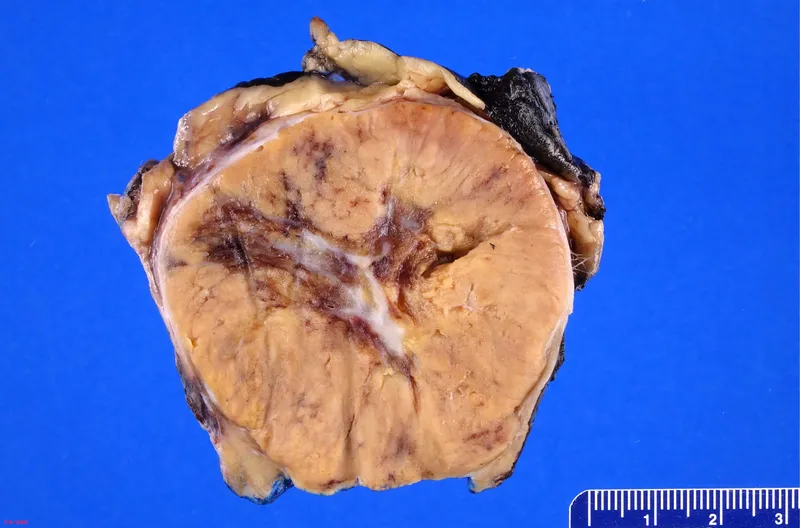
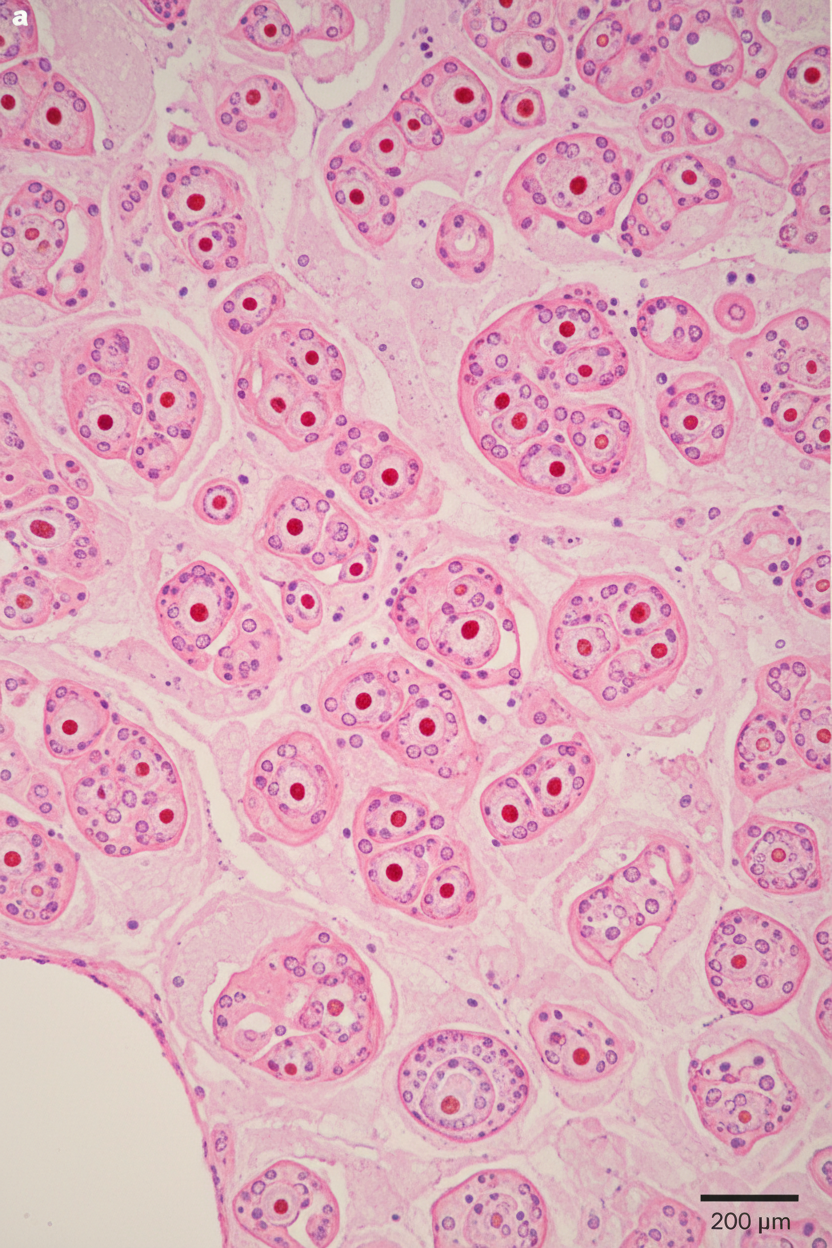
Renal tumors US Medical PG Question 1: A 57-year-old man comes to the physician with a 3-month history of right flank pain. Urinalysis shows 60 RBC/hpf. Renal ultrasound shows a 3 cm, well-defined mass in the upper pole of the right kidney. A photomicrograph of a section of the resected mass is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma
- B. Nephroblastoma
- C. Angiomyolipoma
- D. Oncocytoma (Correct Answer)
- E. Clear cell renal carcinoma
Renal tumors Explanation: ***Oncocytoma***
- Oncocytomas are characterized by cells with abundant, eosinophilic, granular cytoplasm due to numerous **mitochondria**, arranged in nests or cords.
- While typically benign, they can sometimes present with symptoms like **flank pain** and **hematuria**, mimicking renal cell carcinoma, which necessitates imaging and histology for definitive diagnosis.
*Chromophobe renal cell carcinoma*
- This tumor is characterized by cells with prominent cell membranes and pale, often reticulated cytoplasm, giving it a **"vegetable cell"** appearance, and is typically **CK7 positive**.
- Its cells are larger than oncocytoma cells and the cytoplasm is paler, not eosinophilic and granular.
*Nephroblastoma*
- Also known as Wilms tumor, it predominantly affects **children** (typically under 5 years old) and is characterized by a triphasic histology (blastemal, stromal, epithelial components).
- The patient's age (57 years old) makes nephroblastoma highly unlikely.
*Angiomyolipoma*
- This is a benign tumor composed of **blood vessels, smooth muscle, and mature adipose tissue**, which would be evident on imaging (fat content) and histology.
- While it can cause flank pain and hematuria, its microscopic appearance is distinct from the uniform, granular cells of an oncocytoma.
*Clear cell renal carcinoma*
- Characterized by cells with abundant **clear cytoplasm** due to dissolved lipids and glycogen, often arranged in nests and cords with a rich capillary network.
- The cytoplasm of oncocytoma cells is eosinophilic and granular, not clear.
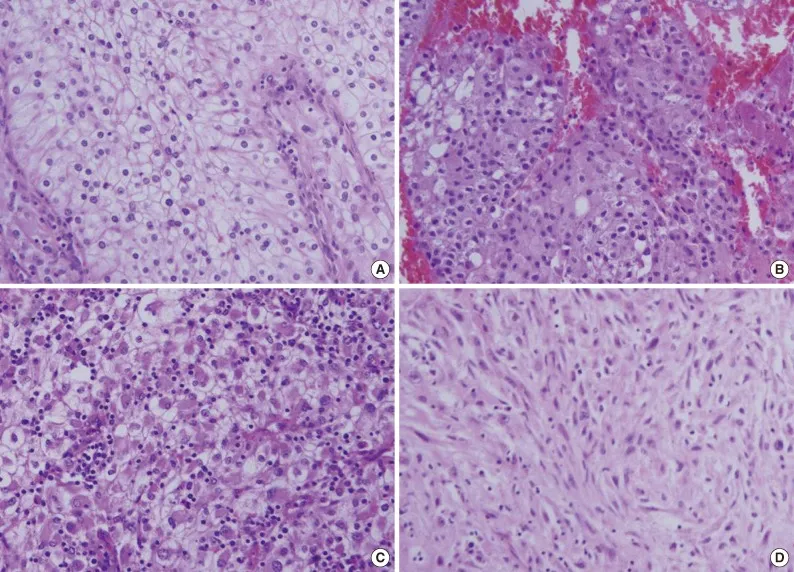
Renal tumors US Medical PG Question 2: A 69-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-week history of blood in the urine and fatigue. He also has had a 5.0-kg (11-lb) weight loss during the past month. Physical examination shows pallor and cachexia. A nontender right flank mass is palpated. A CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis shows a 5-cm right upper pole renal mass and several pulmonary lesions. A biopsy specimen of an affected area of the lung is obtained. A photomicrograph of the biopsy specimen is shown. Molecular evaluation of the specimen is most likely to show which of the following genetic changes?
- A. NF1 gene inactivation
- B. TSC1 gene insertion
- C. WT1 gene deletion
- D. PKD1 gene mutation
- E. VHL gene deletion (Correct Answer)
Renal tumors Explanation: ***VHL gene deletion***
- The clinical presentation of a **right flank mass** with **hematuria**, **weight loss**, and **pulmonary lesions** points to **renal cell carcinoma (RCC)**, which is further supported by the photomicrograph showing clear cells. The **VHL gene** is a tumor suppressor gene, and its inactivation (e.g., through deletion) is the most common genetic alteration in **clear cell RCC**.
- The image displays classic features of **clear cell RCC**, characterized by cells with **clear cytoplasm** due to abundant lipids and glycogen, arranged in **nests or cords with fine vascular networks**.
*NF1 gene inactivation*
- **NF1 gene inactivation** is associated with **neurofibromatosis type 1**, a genetic disorder that predisposes individuals to various tumors, including neurofibromas, optic gliomas, and pheochromocytomas, but not typically clear cell RCC.
- While patients with neurofibromatosis type 1 can develop kidney tumors, they are usually not clear cell RCC and the absence of other NF1 stigmata makes this less likely.
*TSC1 gene insertion*
- **TSC1 gene mutations** are linked to **tuberous sclerosis complex**, a genetic disorder characterized by tumor formation in multiple organs, including the brain, skin, heart, and kidneys (e.g., angiomyolipomas).
- While kidney tumors can occur, typical clear cell RCC is not the primary renal manifestation, and the image does not suggest angiomyolipoma.
*WT1 gene deletion*
- **WT1 gene deletion** is primarily associated with **Wilms' tumor (nephroblastoma)**, a childhood kidney cancer.
- This patient is 69 years old, making Wilms' tumor highly unlikely.
*PKD1 gene mutation*
- **PKD1 gene mutations** are responsible for **autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)**, a condition causing multiple cysts in the kidneys and other organs.
- While ADPKD can lead to kidney failure and may rarely be associated with RCC, the clinical presentation and microscopic image are not characteristic of ADPKD or its associated RCC type, which is often papillary RCC.
Renal tumors US Medical PG Question 3: A 4-year-old girl is being followed by the pediatric oncology team after her pediatrician found a palpable abdominal mass towards the right flank 2 weeks ago. Abdominal ultrasonography detected a solid mass in the right kidney without infiltration of the renal vein and inferior vena cava. The contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) confirmed the presence of a solitary mass in the right kidney surrounded by a pseudocapsule consisting of a rim of normal tissue, displacing it medially, and distorting the collecting system. No nodal involvement was detected. In which of the following chromosomes would you expect a genetic abnormality?
- A. Chromosome 13
- B. Chromosome 1
- C. Chromosome 3
- D. Chromosome 22
- E. Chromosome 11 (Correct Answer)
Renal tumors Explanation: ***Chromosome 11***
- This clinical presentation, particularly the **solitary renal mass** in a 4-year-old and the imaging findings of a **pseudocapsule** and displacement of the collecting system, is highly suggestive of **Wilms tumor (nephroblastoma)**.
- **Wilms tumor** is associated with genetic abnormalities, most notably mutations in the **WT1 gene** located on **chromosome 11p13**, and the **WT2 locus** on **chromosome 11p15.5**.
*Chromosome 13*
- Abnormalities on **chromosome 13** are primarily associated with **retinoblastoma**, linked to mutations in the **RB1 gene**.
- While retinoblastoma is a childhood cancer, its presentation involves ocular tumors, not renal masses.
*Chromosome 1*
- Genetic abnormalities on **chromosome 1** are implicated in various cancers and conditions, but they are not the primary or most characteristic genetic defect associated with **Wilms tumor**.
- Specific translocations or deletions on chromosome 1 can be seen in certain leukemias and lymphomas, which do not fit the clinical picture.
*Chromosome 3*
- **Chromosome 3** abnormalities are well-known in various malignancies, most notably **renal cell carcinoma (RCC)**, particularly the **von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) gene** at 3p25-26.
- RCC is typically a cancer of adulthood, and VHL disease presents with multiple organ system involvement, differing from a solitary renal mass in a young child.
*Chromosome 22*
- Abnormalities on **chromosome 22** are frequently associated with conditions like **neurofibromatosis type 2** (NF2 gene) and **DiGeorge syndrome** (22q11 deletion).
- The presentation of a renal mass in a child is not characteristic of genetic defects on chromosome 22.
Renal tumors US Medical PG Question 4: A newborn is brought to the pediatric clinic by his mother because she has noticed a swelling in the belly while dressing her baby. On physical examination, the newborn is found to have a non-tender upper abdominal mass. The clinician also noticed absent irises and undescended testes in this baby. A magnetic resonance image (MRI) scan of the abdomen shows a mass of intra-renal origin. Which 1 of the following genetic disorders is most probably the cause of this neonate’s symptoms and signs?
- A. WT-1 missense mutation
- B. Deletion 11-p-13 (Correct Answer)
- C. Duplication of 11-p-15
- D. Amplification of MYCN (N-myc) proto-oncogene
- E. Trisomy 18
Renal tumors Explanation: ***Deletion 11-p-13***
* This describes the genetic abnormality associated with **WAGR syndrome**, which stands for **Wilms tumor**, **Aniridia**, **Genitourinary anomalies** (like undescended testes), and **intellectual disability** (though not explicitly mentioned, it's part of the syndrome).
* The presence of a **nephroblastoma (Wilms tumor)**, **absent irises (aniridia)**, and **undescended testes** in a newborn strongly points to WAGR syndrome, caused by a deletion on chromosome 11 at band p13, affecting the *WT1* gene locus.
*WT-1 missense mutation*
* While *WT1* gene mutations are associated with Wilms tumor, a **missense mutation** specifically in *WT1* is more commonly linked to **Denys-Drash syndrome**, which presents with Wilms tumor, diffuse mesangial sclerosis (nephropathy), and male pseudohermaphroditism, but typically *not aniridia*.
* The constellation of symptoms including aniridia and undescended testes together with a Wilms tumor is more characteristic of a larger deletion encompassing *PAX6* (responsible for aniridia) and *WT1*.
*Duplication of 11-p-15*
* A **duplication of 11p15** is associated with **Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome**, which includes macrosomia, macroglossia, omphalocele, and an increased risk of Wilms tumor.
* However, Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome does *not* typically present with aniridia or undescended testes as core features.
*Amplification of MYCN (N-myc) proto-oncogene*
* **MYCN amplification** is a significant genetic alteration found in neuroblastoma, a common extracranial solid tumor of childhood, originating from neural crest cells.
* **Neuroblastoma** is distinct from Wilms tumor (which is intra-renal) and does not typically present with the specific features of aniridia or undescended testes as co-occurring symptoms.
*Trisomy 18*
* **Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)** is characterized by severe developmental delays, distinctive facial features, rocker-bottom feet, and various congenital anomalies affecting multiple organ systems (e.g., heart defects, kidney abnormalities, omphalocele).
* While kidney abnormalities can occur, **aniridia** and **isolated undescended testes combined with a Wilms tumor** are not classic features of Trisomy 18.
Renal tumors US Medical PG Question 5: A 75-year-old man comes to the physician because of abdominal pain and nausea over the past 2 weeks and a 1-month history of pain in his knees and hips. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 30 years. Physical examination shows decreased muscle strength. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 11.0 mg/dL
Serum
Creatinine 1.5 mg/dL
Calcium 12.2 mg/dL
Parathyroid hormone 115 pg/mL
Parathyroid hormone-related peptide elevated
Urine
Blood 2+
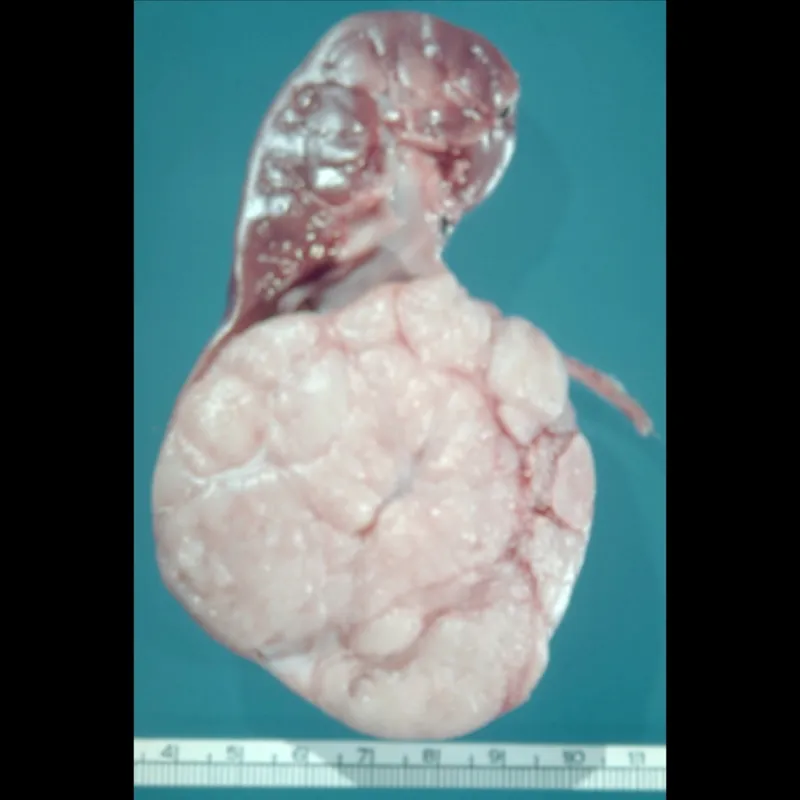
Ultrasonography of his abdomen shows a 6-cm mass in his right kidney. Nephrectomy is performed. A photograph of the resected specimen is shown. The patient's tumor most likely originated from which of the following locations?
- A. Collecting tubules
- B. Proximal convoluted tubules (Correct Answer)
- C. Glomerulus
- D. Renal pelvis
- E. Distal convoluted tubules
Renal tumors Explanation: ***Proximal convoluted tubules***
- The patient's symptoms (abdominal pain, nausea, bone pain, hypercalcemia, elevated PTHrP, renal mass, anemia, hematuria) are classic for **renal cell carcinoma (RCC)**, which typically arises from the **proximal convoluted tubules**.
- RCC often secretes **parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP)**, leading to **hypercalcemia** through paraneoplastic mechanisms.
- Note: In typical malignancy-associated hypercalcemia, PTHrP causes hypercalcemia which should **suppress** endogenous PTH via negative feedback; the elevated PTH shown here may represent concurrent primary hyperparathyroidism or laboratory timing issues.
*Collecting tubules*
- Tumors originating from the collecting tubules are rare and are known as **collecting duct carcinoma (Bellini duct carcinoma)**.
- These aggressive tumors typically present with **hematuria** and flank pain but are less commonly associated with paraneoplastic syndromes like PTHrP-induced hypercalcemia.
*Glomerulus*
- Tumors originating directly from the glomerulus, such as primary glomerular cancers, are exceedingly rare.
- Most glomerular pathologies are inflammatory or degenerative rather than primary neoplasms.
*Renal pelvis*
- Tumors in the renal pelvis are typically **urothelial carcinomas (transitional cell carcinomas)**, which arise from the urothelial lining.
- While they can present with hematuria and flank pain, they are less commonly associated with the paraneoplastic syndrome of hypercalcemia due to PTHrP secretion compared to RCC.
*Distal convoluted tubules*
- Tumors originating from the distal convoluted tubules are uncommon.
- **Oncocytomas**, a benign renal tumor, are thought to arise from the distal nephron or collecting ducts, but they do not typically cause paraneoplastic syndromes like hypercalcemia.
Renal tumors US Medical PG Question 6: A 1-year-old boy is brought to the physician for the evaluation of swelling around the eyelids. He was born at term after an uncomplicated pregnancy. He is at the 95th percentile for weight and 60th percentile for length. His blood pressure is 130/86 mm Hg. Physical examination shows an empty scrotal sac and a left-sided abdominal mass. Ophthalmologic examination shows no abnormalities. Urinalysis shows a proteinuria of 3+ and fatty casts. Abdominal ultrasound shows a hypervascular mass at the upper pole of the kidney. Which of the following best describes the pathogenesis of this patient's disease?
- A. Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α
- B. Increased expression of insulin-like growth factor 2
- C. Deficiency of 17α-hydroxylase
- D. Loss of function of zinc finger transcription factor
- E. Deletion of the WT1 gene on chromosome 11 (Correct Answer)
Renal tumors Explanation: ***Deletion of the WT1 gene on chromosome 11***
- This patient presents with the classic features of **Denys-Drash syndrome**: **gonadal dysgenesis** (**empty scrotal sac**), **renal disease** (**nephrotic syndrome** with proteinuria and fatty casts, hypertension), and **Wilms tumor**.
- **Denys-Drash syndrome** is caused by a **germline mutation** (often deletion) in the **WT1 tumor suppressor gene** located on **chromosome 11p13**. The WT1 gene encodes a zinc finger transcription factor critical for genitourinary development.
*Inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α*
- This is linked to some rare forms of **renal cell carcinoma**, particularly those associated with **VHL disease**, but not directly to **Wilms tumor** or the specific constellation of symptoms seen here.
- **HIF-1α** typically promotes angiogenesis and cell survival under hypoxic conditions, and its inhibition would generally not lead to tumor formation in this context.
*Increased expression of insulin-like growth factor 2*
- **IGF-2 overexpression** is associated with **Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome**, which also involves an increased risk of **Wilms tumor**, as well as other features like **macroglossia** and **hemihypertrophy**.
- While both conditions are linked to Wilms tumor and chromosome 11, the presence of **gonadal dysgenesis** and significant **renal disease** (nephrotic syndrome) strongly points to **Denys-Drash syndrome** rather than Beckwith-Wiedemann, which is a separate pathogenetic mechanism (often involving epigenetic changes in the 11p15.5 region).
*Deficiency of 17α-hydroxylase*
- This enzyme deficiency leads to **congenital adrenal hyperplasia** with features like **hypertension** and **gonadal dysgenesis** (due to impaired sex steroid synthesis) but *does not* cause **renal tumors** or **nephrotic syndrome**.
- The elevated blood pressure in 17α-hydroxylase deficiency is due to accumulation of mineralocorticoid precursors, distinct from the renal pathology here.
*Loss of function of zinc finger transcription factor*
- While the **WT1 gene** does encode a **zinc finger transcription factor**, this answer is too vague and non-specific. Multiple genes encode zinc finger transcription factors involved in various developmental and disease processes.
- The **correct and specific answer** is the **deletion of the WT1 gene on chromosome 11**, which precisely identifies the pathogenetic mechanism of Denys-Drash syndrome rather than using a generic functional description.
Renal tumors US Medical PG Question 7: A 32-year-old man presents to the emergency room for a generalized tonic-clonic seizure. After stabilizing the patient, a full radiologic evaluation reveals multiple contrast-enhancing lesions in the brain, lungs, and liver. According to his wife, he lost several pounds in the last few months. The medical history is relevant for cryptorchidism, with abdominal testes that were surgically transferred to the scrotum just before he turned 1-year old. His lab investigation reveals:
α-fetoprotein:
9 ng/mL (normal values < 10 ng/mL)
Human chorionic gonadotropin:
1,895 IU/L (normal values < 0.5 IU/L)
Which of the following microscopic features best describes the lesions seen in this patient's imaging study?
- A. Germ cells with well-defined borders, central nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and clear cytoplasm
- B. Mixture of primitive neuroectoderm, loose mesenchyme, and primitive glandular structures
- C. Intimate association of syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast cells (Correct Answer)
- D. Glomerulus-like structure with a mesoderm core, a central capillary, and lined with germ cells
- E. Cells with hyaline-like globules
Renal tumors Explanation: ***Intimate association of syncytiotrophoblast and cytotrophoblast cells***
- The combination of a **generalized tonic-clonic seizure** (suggesting brain metastasis), **multiple contrast-enhancing lesions** in brain, lungs, and liver, weight loss, history of **cryptorchidism**, and significantly **elevated human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)** (1,895 IU/L, normal < 0.5 IU/L) despite normal AFP, is highly indicative of a **choriocarcinoma**.
- **Choriocarcinomas** are characterized microscopically by an intimate admixture of **syncytiotrophoblast** and **cytotrophoblast cells** lacking chorionic villi. These tumors are highly aggressive and prone to widespread metastasis, particularly to the lungs, brain, and liver.
*Germ cells with well-defined borders, central nuclei, prominent nucleoli, and clear cytoplasm*
- This description is characteristic of **seminoma**, the most common germ cell tumor.
- While seminomas can spread, the extremely high hCG levels without elevated AFP and the rapid, widespread metastasis depicted are more typical of choriocarcinoma.
*Mixture of primitive neuroectoderm, loose mesenchyme, and primitive glandular structures*
- This description refers to the microscopic features of an **immature teratoma**.
- While immature teratomas can arise from germ cells, they typically do not produce such high levels of hCG, and their metastatic pattern is often different.
*Glomerulus-like structure with a mesoderm core, a central capillary, and lined with germ cells*
- This is the classic description of a **Schiller-Duval body**, which is pathognomonic for a **yolk sac tumor** (also known as endodermal sinus tumor).
- Yolk sac tumors are associated with elevated **alpha-fetoprotein (AFP)**, which is normal in this patient.
*Cells with hyaline-like globules*
- The presence of **hyaline-like globules** (containing AFP and/or alpha-1-antitrypsin) is also a feature seen in **yolk sac tumors**.
- As mentioned, the normal AFP level in this patient makes a yolk sac tumor less likely.
Renal tumors US Medical PG Question 8: A 59-year-old Caucasian man presents with a one-month history of left flank fullness and pain. The patient has stable angina, which is controlled with medications including atorvastatin, metoprolol, and aspirin. His vital signs are within normal limits. BMI is 32 kg/m2. Clinical examination reveals a 10 x 10-cm palpable mass in the left flank. Testicular examination indicates left varicocele. Laboratory parameters are as follows:
Urine
Blood 3+
WBC none
RBC 65/hpf without dysmorphic features
Abdominal CT scan confirms the presence of a large solid mass originating in the left kidney with impingement on the left renal vein. Based on the most likely diagnosis, which of the following is considered a risk factor in this patient?
- A. Obesity (Correct Answer)
- B. Varicocele
- C. Atorvastatin
- D. Lynch syndrome
- E. Caucasian race
Renal tumors Explanation: ***Obesity***
- This patient's **BMI of 32 kg/m2** indicates **obesity**, which is a well-established risk factor for **renal cell carcinoma (RCC)**, the most likely diagnosis given the clinical presentation (flank mass, hematuria, varicocele, and CT findings).
- Obesity is thought to increase RCC risk due to associated hormonal changes, such as increased **estrogen** and **insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1)**, and chronic inflammation.
*Varicocele*
- While a **left varicocele** is a clinical finding often associated with **renal cell carcinoma**, particularly on the left side due to impingement on the left renal vein, it is a **symptom/sign** of the disease, not a risk factor for its development.
- The varicocele develops because the tumor obstructs the **left renal vein**, leading to retrograde flow and dilation of the **gonadal vein**.
*Atorvastatin*
- **Atorvastatin**, a statin used to treat hyperlipidemia and prevent cardiovascular disease, has **no known association** with an increased risk of renal cell carcinoma.
- Some studies even suggest a potential **protective effect** of statins against certain cancers, but this is not definitively established for RCC, and certainly not a risk factor.
*Lynch syndrome*
- **Lynch syndrome** (hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer) is primarily associated with an increased risk of **colorectal cancer**, **endometrial cancer**, and other gastrointestinal/genitourinary cancers, but **not renal cell carcinoma**.
- Renal cell carcinoma is more commonly linked to other genetic syndromes like **Von Hippel-Lindau disease** or **hereditary papillary renal carcinoma**.
*Caucasian race*
- While there are some **racial disparities** in certain cancer incidences, the **Caucasian race itself is not considered a primary modifiable risk factor** for renal cell carcinoma.
- **African Americans** may have a slightly higher risk for RCC, but this is often attributed to socioeconomic factors and comorbidities rather than race as an independent biological risk factor.
Renal tumors US Medical PG Question 9: An obese 63-year-old man comes to the physician because of 3 episodes of red urine over the past week. He has also had recurrent headaches and intermittent blurry vision during the past month. He has benign prostatic hyperplasia. He works as an attendant at a gas station. The patient has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for the last 40 years. He does not drink alcohol. Current medications include tamsulosin. His temperature is 37.4°C (99.4°F), pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 152/95 mm Hg. Examination shows a flushed face. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. The abdomen is soft and non-tender. Digital rectal examination shows an enlarged prostate with no nodules. Urinalysis shows:
Blood 3+
Glucose negative
Protein negative
WBC 1-2/hpf
RBC 40-45/hpf
RBC casts none
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Nephrolithiasis
- B. Renal cell carcinoma (Correct Answer)
- C. Transitional cell bladder carcinoma
- D. IgA nephropathy
- E. Renal oncocytoma
Renal tumors Explanation: ***Correct: Renal cell carcinoma***
- This patient presents with **painless gross hematuria**, a common initial symptom of renal cell carcinoma, especially concerning in a long-term **smoker** with hypertension.
- The constellation of **headaches, blurry vision, and flushed face** could indicate paraneoplastic syndromes associated with RCC, such as **erythrocytosis (polycythemia)** causing facial flushing and hyperviscosity symptoms, or **hypertension due to renin secretion** by the tumor.
- RCC is strongly associated with **smoking** (major risk factor) and **obesity**.
*Incorrect: Nephrolithiasis*
- While nephrolithiasis can cause hematuria, it is typically associated with **severe, colicky flank pain** radiating to the groin, which is absent in this patient.
- The patient's other symptoms like headaches, blurry vision, and flushed face are not characteristic of nephrolithiasis.
*Incorrect: Transitional cell bladder carcinoma*
- Bladder cancer often presents with **painless gross hematuria**, similar to RCC.
- However, the additional symptoms of **headaches, blurry vision, flushed face, and hypertension in a long-term smoker** point more strongly towards a renal mass with **paraneoplastic effects** (polycythemia, renin secretion) rather than solely bladder involvement.
- Urothelial carcinoma is also associated with smoking but does not typically cause these systemic paraneoplastic manifestations.
*Incorrect: IgA nephropathy*
- IgA nephropathy is characterized by recurrent episodes of **gross hematuria**, often following an upper respiratory or gastrointestinal infection (synpharyngitic hematuria).
- Urinalysis would typically show **dysmorphic RBCs and RBC casts** (indicating glomerular bleeding), which are **absent** here.
- The non-glomerular hematuria pattern (no casts, no proteinuria) argues against this diagnosis.
*Incorrect: Renal oncocytoma*
- Renal oncocytomas are **benign renal tumors** that are often asymptomatic and discovered incidentally on imaging.
- While they can cause hematuria, they are **rarely associated with systemic symptoms** like headaches, blurry vision, hypertension, or flushed face.
- Unlike RCC, oncocytomas do **not produce paraneoplastic syndromes** (no erythropoietin or renin secretion).
Renal tumors US Medical PG Question 10: A 58-year-old woman with HbA1c of 10 % is referred to an ophthalmologist because of vision loss. An image of her retina is shown below, If this patient were to undergo renal biopsy, what will be the pathologic findings?
- A. Nodular glomerulosclerosis, mesangial expansion, and basement membrane thickening (Correct Answer)
- B. Scattered crescentic lesions with fibrin and plasma proteins
- C. Vascular intimal thickening and hyaline deposition
- D. Subepithelial immune complex deposits
- E. Wire-loop lesions and subendothelial deposits
Renal tumors Explanation: ***Nodular glomerulosclerosis, mesangial expansion, and basement membrane thickening***
- The patient's high HbA1c and vision loss (suggesting **diabetic retinopathy**) indicate **diabetes mellitus**. The classic renal pathology findings in **diabetic nephropathy** include **Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules** (nodular glomerulosclerosis), **mesangial expansion**, and **glomerular basement membrane thickening** [1].
- These changes are due to chronic hyperglycemia leading to advanced glycation end-product (AGE) accumulation and hemodynamic changes, causing **glomerular hypertrophy** and **sclerosis** [1].
*Scattered crescentic lesions with fibrin and plasma proteins*
- This describes **crescentic glomerulonephritis**, which is characteristic of rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN).
- While RPGN can cause kidney failure, it is not the primary renal manifestation of long-standing, uncontrolled diabetes.
*Vascular intimal thickening and hyaline deposition*
- This describes **hyaline arteriolosclerosis**, which is commonly seen in **hypertension** and **diabetes**, affecting afferent and efferent arterioles.
- While present in diabetic nephropathy, it is a vascular change and not the primary glomerular lesion that defines diabetic nephropathy.
*Subepithelial immune complex deposits*
- This is characteristic of **membranous nephropathy**, a common cause of nephrotic syndrome.
- It is an immune-mediated disease and not the typical renal pathology associated with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.
**References:**
[1] Kumar V, Abbas AK, et al.. Robbins and Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease. 9th ed. The Endocrine System, pp. 1121-1122.
More Renal tumors US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.