Renal cystic diseases US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Renal cystic diseases. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Renal cystic diseases US Medical PG Question 1: A 42-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office with hematuria and right flank pain. He has no history of renal dialysis but has a history of recurrent urinary tract infections. You order an intravenous pyelogram, which reveals multiple cysts of the collecting ducts in the medulla. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Chronic renal failure
- B. Medullary sponge kidney (Correct Answer)
- C. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
- D. Simple retention cysts
- E. Acquired polycystic kidney disease
Renal cystic diseases Explanation: ***Medullary sponge kidney***
- This condition is characterized by **multiple cysts within the collecting ducts** in the renal medulla, often leading to **hematuria**, **flank pain**, and **recurrent UTIs** due to urinary stasis and stone formation.
- The intravenous pyelogram (IVP) finding of **"medullary blush"** or "bouquet of flowers" appearance due to contrast filling the dilated collecting ducts is classic for this diagnosis.
*Chronic renal failure*
- While chronic renal failure can present with hematuria and flank pain, it is a **consequence of various kidney diseases** and not a specific diagnosis for the described structural changes.
- This patient's presentation with specific imaging findings points to an underlying structural anomaly rather than just end-stage kidney dysfunction.
*Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)*
- ADPKD typically involves **numerous cysts throughout the entire kidney** (cortex and medulla), leading to massive kidney enlargement and progressive renal failure.
- The imaging findings in this case specifically describe cysts limited to the collecting ducts in the medulla, which is inconsistent with the widespread cystic involvement of ADPKD.
*Simple retention cysts*
- **Simple renal cysts are typically solitary or few** and generally benign, not forming multiple cysts specifically within the collecting ducts of the medulla.
- They also do not typically cause recurrent UTIs or significant hematuria unless they become very large or complicated.
*Acquired polycystic kidney disease*
- This condition is almost exclusively seen in patients with **long-standing end-stage renal disease** or on **dialysis**, which is explicitly denied in the patient's history.
- The cysts are usually small and scattered, located predominantly in the cortex, and not specifically limited to the medullary collecting ducts.
Renal cystic diseases US Medical PG Question 2: A 53-year-old male presents to your office for abdominal discomfort. The patient states he first noticed pain on his right flank several months ago, and it has been gradually getting worse. For the past week, he has also noticed blood in his urine. Prior to this episode, he has been healthy and does not take any medications. The patient denies fever, chills, and dysuria. He has a 40 pack-year smoking history. Vital signs are T 37 C, BP 140/90 mmHg, HR 84/min, RR 14/min, O2 98%. Physical exam is unremarkable. CBC reveals a hemoglobin of 17 and hematocrit of 51%, and urinalysis is positive for red blood cells, negative for leukocytes. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Pyelonephritis
- B. Renal oncocytoma
- C. Renal cell carcinoma (Correct Answer)
- D. Abdominal aortic aneurysm
- E. Polycystic kidney disease
Renal cystic diseases Explanation: ***Renal cell carcinoma***
- The classic triad of **flank pain**, **hematuria**, and a palpable abdominal mass (which may not always be present or detected on physical exam)
- **Erythrocytosis** (high hemoglobin and hematocrit) due to increased **erythropoietin** production by the tumor, and a significant **smoking history** are strong indicators.
*Pyelonephritis*
- This is an infection of the kidney, typically presenting with **fever**, **chills**, **dysuria**, and flank pain.
- The patient denies fever and chills, and the urinalysis is negative for leukocytes, making pyelonephritis unlikely.
*Renal oncocytoma*
- While it is a **renal tumor** that can cause flank pain or hematuria, it is typically **benign** and does not usually cause paraneoplastic syndromes like erythrocytosis.
- In the presence of erythrocytosis and a strong smoking history, a malignant cause like RCC is more probable.
*Abdominal aortic aneurysm*
- An AAA can cause abdominal or flank pain, but it would not typically cause **hematuria** or **erythrocytosis**.
- Rupture or dissection of an AAA presents as severe, acute pain and hemodynamic instability, which is not described.
*Polycystic kidney disease*
- This genetic disorder is characterized by multiple cysts in the kidneys, leading to pain, hematuria, and **renal failure over time**.
- While it can cause hematuria, it is less likely to present with new-onset erythrocytosis and in a patient with no previous medical history.
Renal cystic diseases US Medical PG Question 3: A 6-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician by his mother after he reported having red urine. He has never experienced this before and did not eat anything unusual before the episode. His past medical history is notable for sensorineural deafness requiring hearing aids. He is otherwise healthy and enjoys being in the 1st grade. His birth history was unremarkable. His temperature is 98.8°F (37.1°C), blood pressure is 145/85 mmHg, pulse is 86/min, and respirations are 18/min. On examination, he is a well-appearing boy in no acute distress. Cardiac, respiratory, and abdominal exams are normal. A urinalysis is notable for microscopic hematuria and mild proteinuria. This patient’s condition is most commonly caused by which of the following inheritance patterns?
- A. X-linked dominant
- B. Autosomal recessive
- C. Autosomal dominant
- D. X-linked recessive (Correct Answer)
- E. Mitochondrial inheritance
Renal cystic diseases Explanation: ***X-linked recessive***
- This is the **most common inheritance pattern** for **Alport syndrome**, accounting for approximately **80-85% of all cases**.
- This inheritance pattern is characteristic of **Alport syndrome**, which classically presents with **hematuria**, **sensorineural hearing loss**, and ocular abnormalities.
- The patient's presentation with **red urine (hematuria)** and a history of **sensorineural deafness** strongly points to **Alport syndrome**, which is primarily caused by **X-linked recessive** inheritance due to mutations in the *COL4A5* gene encoding the alpha-5 chain of type IV collagen.
- Males with the mutation are typically more severely affected, while female carriers may have variable manifestations.
*X-linked dominant*
- While Alport syndrome can manifest in females with an X-linked dominant-like pattern (due to mosaicism or severely affected carrier females), the **classic and most common inheritance** for severe forms in males is **X-linked recessive**.
- Conditions like **Fragile X syndrome** or **Vitamin D-resistant rickets** are examples of X-linked dominant conditions, but they do not typically present with the specific triad observed here.
*Autosomal recessive*
- An autosomal recessive form of **Alport syndrome** exists, but it accounts for only approximately **10-15% of cases** compared to the X-linked recessive form.
- While other conditions with **renal and auditory involvement** can be autosomal recessive (e.g., specific forms of branchio-oto-renal syndrome), the **combination of hematuria and sensorineural deafness with significant renal progression risk** in a male points most strongly to the X-linked form.
*Autosomal dominant*
- Alport syndrome also has an **autosomal dominant** form, which is typically due to mutations in *COL4A3* or *COL4A4* genes, but it accounts for only approximately **5% of cases** and is **less common** than the X-linked recessive form.
- The autosomal dominant form often presents with a **later onset** and a **more variable phenotype** with milder disease progression.
- While some forms of **polycystic kidney disease** are autosomal dominant and can cause hematuria, they typically involve cyst formation, which is not suggested by the clinical picture here.
*Mitochondrial inheritance*
- This inheritance pattern is associated with disorders affecting **energy production**, commonly involving multiple organ systems, including muscle, brain, and eye.
- While some mitochondrial disorders can affect the kidneys or cause hearing impairment, the **specific combination of hematuria and sensorineural deafness** as the primary presentation in this context is not characteristic of mitochondrial inheritance.
Renal cystic diseases US Medical PG Question 4: A female infant is born with a mutation in PKD1 on chromosome 16. An abdominal ultrasound performed shortly after birth would most likely reveal which of the following?
- A. Microscopic cysts
- B. Normal kidneys (Correct Answer)
- C. Adrenal atrophy
- D. Horseshoe kidney
- E. Bilateral kidney enlargement
Renal cystic diseases Explanation: ***Normal kidneys***
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), caused by a mutation in **PKD1 or PKD2**, typically presents with **cysts that develop later in life**, usually in adulthood.
- At birth, the kidneys of an infant with the ADPKD mutation are usually **structurally normal** and do not yet show macroscopic cyst formation on ultrasound.
*Microscopic cysts*
- While the genetic mutation is present, significant **macroscopic cyst formation** detectable by standard abdominal ultrasound does not typically occur at birth in ADPKD.
- The cysts develop and enlarge over decades, leading to symptoms later in adulthood.
*Adrenal atrophy*
- **Adrenal atrophy** is not a feature of polycystic kidney disease and is caused by other conditions like autoimmune diseases or prolonged corticosteroid use.
- The adrenal glands are distinct from the kidneys and are not directly affected by PKD1 mutations.
*Horseshoe kidney*
- **Horseshoe kidney** is a congenital anomaly where the kidneys are fused, usually at the lower poles, and is not associated with PKD1 mutations.
- This condition is a **developmental fusion defect** during embryogenesis.
*Bilateral kidney enlargement*
- Bilateral kidney enlargement due to multiple cysts is characteristic of **ADPKD in adulthood**, not at birth.
- Though ADPKD is a genetic condition, the **phenotypic expression (cyst growth)** progresses over time.
Renal cystic diseases US Medical PG Question 5: A 35-year-old male with a history of hypertension presents with hematuria and abdominal discomfort. Ultrasound and CT scan reveal large, bilateral cysts in all regions of the kidney. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Henoch-Schonlein purpura
- B. Diabetes mellitus
- C. Aortic stenosis
- D. Berger’s disease
- E. Polycystic kidney disease (Correct Answer)
Renal cystic diseases Explanation: ***Polycystic kidney disease***
- The presentation of **bilateral, large renal cysts** on imaging, along with **hematuria** and **hypertension** in a 35-year-old, is classic for **autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)**.
- ADPKD is a systemic disorder that can also cause cysts in other organs and is a leading cause of **end-stage renal disease**.
*Henoch-Schonlein purpura*
- This is a **small-vessel vasculitis** characterized by palpable purpura, arthritis, abdominal pain, and renal involvement (usually IgA nephropathy).
- It does not present with **large, bilateral renal cysts**.
*Diabetes mellitus*
- **Diabetic nephropathy** is a common complication causing progressive kidney damage and is a leading cause of kidney failure.
- However, it typically manifests as **proteinuria**, progressive decline in GFR, and eventually end-stage renal disease, not large renal cysts.
*Aortic stenosis*
- **Aortic stenosis** is a valvular heart disease impacting blood flow from the heart and is entirely unrelated to renal cysts or the described kidney pathology.
- While it can be associated with bleeding disorders (e.g., Heyde's syndrome), it does not directly cause **renal disease or cysts.**
*Berger’s disease*
- Also known as **IgA nephropathy**, Berger's disease is an immune-mediated glomerulonephritis, often presenting with recurrent **gross hematuria**, particularly after an upper respiratory infection.
- It involves inflammation of the glomeruli, not the development of **large renal cysts**.
Renal cystic diseases US Medical PG Question 6: A 40-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 4-week history of generalized weakness. He also reports increased urination and thirst. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. His only medication is metformin. Serum studies show:
Na+ 134 mEq/L
Cl- 110 mEq/L
K+ 5.6 mEq/L
HCO3- 19 mEq/L
Glucose 135 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.6 mg/dL
Urine pH is 5.1. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Impaired HCO3- reabsorption in the proximal tubule
- B. Decreased serum cortisol levels
- C. Impaired H+ secretion in the distal tubule
- D. Increased serum lactate levels
- E. Decreased serum aldosterone levels (Correct Answer)
Renal cystic diseases Explanation: ***Decreased serum aldosterone levels***
- The patient presents with **hyperkalemia** (K+ 5.6 mEq/L) and a **normal anion gap metabolic acidosis** (HCO3- 19 mEq/L, anion gap = Na - (Cl + HCO3) = 134 - (110 + 19) = 5 mEq/L), along with a relatively **acidic urine pH of 5.1**.
- **Aldosterone deficiency** (often seen in **hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism** associated with diabetes and chronic kidney disease) characteristically causes type 4 renal tubular acidosis, leading to impaired potassium and hydrogen excretion, thus presenting with hyperkalemia and a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis with low urine pH.
*Impaired HCO3- reabsorption in the proximal tubule*
- This describes **proximal (type 2) renal tubular acidosis (RTA)**, which typically presents with a **normal anion gap metabolic acidosis**, but usually causes **hypokalemia** due to increased distal potassium excretion.
- While it can cause an acidic urine, the predominant feature of hypokalemia is contrary to the patient's hyperkalemia.
*Impaired H+ secretion in the distal tubule*
- This describes **distal (type 1) renal tubular acidosis (RTA)**, which is characterized by an inability to acidify urine, resulting in a **urine pH > 5.5** in the presence of systemic acidosis.
- This contradicts the patient's **acidic urine pH of 5.1**, making type 1 RTA less likely.
*Increased serum lactate levels*
- **Lactic acidosis** is an **anion gap metabolic acidosis**, whereas this patient has a **normal anion gap metabolic acidosis**.
- While metformin can cause lactic acidosis, the calculated anion gap of 5 mEq/L is normal, ruling out this cause.
*Decreased serum cortisol levels*
- Decreased serum cortisol levels (e.g., in **adrenal insufficiency**) can lead to hyponatremia, hyperkalemia, and acidosis.
- However, the primary cause of the acidosis in adrenal insufficiency is usually due to the lack of mineralocorticoid effects (aldosterone), and the presentation here is more specifically aligned with a renal defect in hydrogen and potassium handling.
Renal cystic diseases US Medical PG Question 7: A 45-year-old woman presents to the office with a complaint of generalized weakness that has been getting worse over the last few months. She says that she just does not have the energy for her daily activities. She gets winded quite easily when she takes her dog for a walk in the evening. She says that her mood is generally ok and she gets together with her friends every weekend. She works as a teacher at a local elementary school and used to have frequent headaches while at work. Her husband is a commercial pilot and is frequently away for extended periods of time. Her only son is a sophomore in college and visits her every other week. She has had issues in the past with hypertension, but her blood pressure is currently well-controlled because she is compliant with her medication. She is currently taking atorvastatin and lisinopril. The blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, the pulse is 90/min, the temperature is 36.7°C (98.0°F), and the respirations are 16/min. On examination, she appears slightly pale and lethargic. Her ECG today is normal and recent lab work shows the following:
Serum creatinine 1.5 mg/dL
Estimated GFR 37.6 mL/min
Hemoglobin (Hb%) 9 mg/dL
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) 27 pg
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentration (MCHC) 36 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV) 85 fL
Reticulocyte count 0.1%
Erythrocyte count 2.5 million/mm3
Serum iron 160 μg/dL
Serum ferritin 150 ng/mL
Total iron binding capacity 105 μg/dL
Serum vitamin B12 254 pg/mL
Serum folic acid 18 ng/mL
Thyroid stimulating hormone 3.5 μU/mL
Which of the following will most likely help her?
- A. Start vitamin B12 with folic acid.
- B. Transfuse red blood cells.
- C. Start her on fluoxetine.
- D. Start her on erythropoietin. (Correct Answer)
- E. Start oral iron supplements.
Renal cystic diseases Explanation: ***Start her on erythropoietin.***
- This patient presents with symptoms of **anemia** (weakness, fatigue, dyspnea on exertion) and has laboratory findings consistent with **normocytic, normochromic anemia** (Hb 9 mg/dL, MCV 85 fL, MCH 27 pg, normal MCHC), a **low reticulocyte count (0.1%)**, and **chronic kidney disease (CKD)** stage 3 (GFR 37.6 mL/min).
- The combination of **CKD and anemia with appropriate iron stores** (normal serum iron and ferritin, low TIBC, high transferrin saturation) strongly suggests **anemia of chronic kidney disease**, which is caused by inadequate **erythropoietin (EPO) production** by the kidneys. Therefore, exogenous erythropoietin is the most appropriate treatment.
*Start vitamin B12 with folic acid.*
- The patient's **serum vitamin B12 (254 pg/mL)** and **folic acid (18 ng/mL)** levels are within normal limits, ruling out deficiencies of these vitamins as the cause of her anemia.
- Deficiencies in B12 or folate typically cause **macrocytic anemia** (elevated MCV), which is not observed in this patient (MCV 85 fL).
*Transfuse red blood cells.*
- While red blood cell transfusion can rapidly increase hemoglobin, it is typically reserved for **symptomatic severe anemia** or in situations requiring quick correction, for example, active bleeding.
- The patient's anemia, although symptomatic, is chronic, and her cardiovascular status, including a normal ECG and stable blood pressure, does not indicate an immediate life-threatening need for transfusion. **Long-term management** with erythropoietin is safer and more appropriate.
*Start her on fluoxetine.*
- The patient reports her **mood is generally okay**, and she actively socializes, making **depression less likely** as the primary cause of her generalized weakness or fatigue. Her fatigue is primarily due to anemia.
- While chronic illness can sometimes lead to depression, there's no strong indication for antidepressant therapy based on the provided symptoms.
*Start oral iron supplements.*
- The patient's **iron studies (serum iron 160 μg/dL, serum ferritin 150 ng/mL, total iron binding capacity 105 μg/dL)** indicate that she has **adequate iron stores** and is not iron deficient.
- Iron supplementation would not be beneficial and could be harmful if there is no iron deficiency.
Renal cystic diseases US Medical PG Question 8: A 70-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife because of lethargy, confusion, and nausea for the past 2 days. He has previously been healthy and has no past medical history. His only medications are a daily multivitamin and acetaminophen, which he takes daily for hip pain. Vital signs are within normal limits. He is disoriented to place and time but recognizes his wife. The remainder of his physical examination shows no abnormalities. Laboratory studies show a hemoglobin concentration of 9.1 g/dL, a serum calcium concentration of 14.7 mg/dL, and a serum creatinine of 2.2 mg/dL (previously 0.9 mg/dL). Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of this patient's condition?
- A. Increased serum levels of 1,25-hydroxyvitamin D
- B. Excessive consumption of calcium
- C. Excess PTH secretion from parathyroid glands
- D. Ectopic PTHrP release
- E. Overproliferation of plasma cells (Correct Answer)
Renal cystic diseases Explanation: ***Overproliferation of plasma cells***
- The patient presents with **hypercalcemia** (14.7 mg/dL), acute **kidney injury** (creatinine 2.2 mg/dL from 0.9 mg/dL), and **anemia** (hemoglobin 9.1 g/dL). These three findings, especially in an elderly patient, strongly suggest **multiple myeloma**, which is characterized by the overproliferation of plasma cells in the bone marrow.
- The overproliferation of plasma cells in multiple myeloma leads to the production of **osteoclast-activating factors**, resulting in increased bone resorption and subsequent hypercalcemia.
*Increased serum levels of 1,25-hydroxyvitamin D*
- While **elevated vitamin D levels** can cause hypercalcemia, it typically occurs due to excessive supplementation or granulomatous diseases (e.g., sarcoidosis). There is no history of either in this patient.
- This mechanism would not explain the accompanying **anemia** or **acute kidney injury** (beyond what hypercalcemia itself might induce), which are prominent features here.
*Excessive consumption of calcium*
- **Milk-alkali syndrome**, caused by excessive intake of calcium and absorbable alkali, can lead to hypercalcemia, metabolic alkalosis, and renal insufficiency.
- However, the patient's history does not indicate excessive calcium intake, and this etiology would not typically explain significant **anemia**.
*Excess PTH secretion from parathyroid glands*
- **Primary hyperparathyroidism** results in increased PTH, leading to hypercalcemia and often low or normal phosphate. While it can cause kidney stones and bone issues, it does not typically cause **anemia** or the rapid progression of kidney injury seen here.
- The patient's creatinine has doubled in a short period, which is more suggestive of an acute insult or a systemic disease like myeloma, rather than chronic changes from primary hyperparathyroidism.
*Ectopic PTHrP release*
- **Parathyroid hormone-related protein (PTHrP)** can be ectopically secreted by various malignancies (e.g., squamous cell carcinoma of the lung, renal cell carcinoma), leading to **humoral hypercalcemia of malignancy**.
- While this can cause **hypercalcemia** and related kidney issues, it typically does not directly cause **anemia** in the same way as multiple myeloma, where **bone marrow infiltration** by plasma cells directly suppresses hematopoiesis. The constellation of hypercalcemia, anemia, and acute kidney injury points more specifically to multiple myeloma.
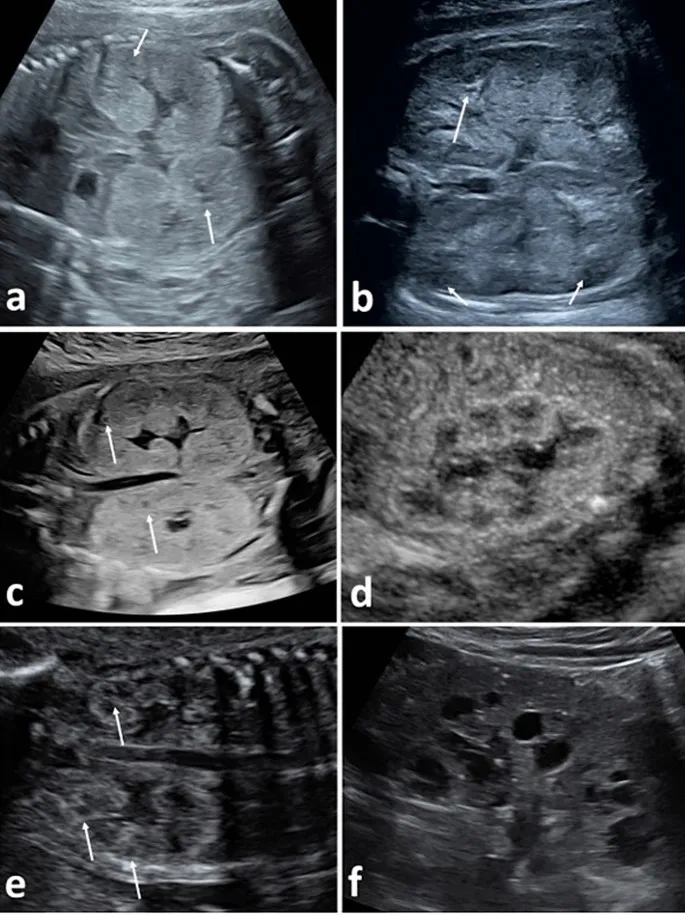
Renal cystic diseases US Medical PG Question 9: A 49-year-old man presents to your clinic with “low back pain”. When asked to point to the area that bothers him the most, he motions to both his left and right flank. He describes the pain as deep, dull, and aching for the past few months. His pain does not change significantly with movement or lifting heavy objects. He noted dark colored urine this morning. He has a history of hypertension managed with hydrochlorothiazide; however, he avoids seeing the doctor whenever possible. He drinks 3-4 beers on the weekends but does not smoke. His father died of a sudden onset brain bleed, and his mother has diabetes. In clinic, his temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 150/110 mmHg, pulse is 95/min, and respirations are 12/min. Bilateral irregular masses are noted on deep palpation of the abdomen. The patient has full range of motion in his back and has no tenderness of the spine or paraspinal muscles. Urine dipstick in clinic is notable for 3+ blood. Which chromosome is most likely affected by a mutation in this patient?
- A. Chromosome 6
- B. Chromosome 7
- C. Chromosome 4
- D. Chromosome 15
- E. Chromosome 16 (Correct Answer)
Renal cystic diseases Explanation: ***Chromosome 16***
- This patient's presentation with bilateral flank pain, hypertension, hematuria (dark urine with 3+ blood on dipstick), and palpable bilateral irregular abdominal masses is highly suggestive of **Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)**.
- The most common form of ADPKD, comprising about 85% of cases, is caused by mutations in the **PKD1 gene** located on **chromosome 16**.
*Chromosome 6*
- Mutations on chromosome 6 are associated with conditions such as **hemochromatosis (HFE gene)** and certain types of **human leukocyte antigen (HLA) linked diseases**, neither of which fits the patient's primary symptoms.
- There is no direct link between chromosome 6 mutations and the classic presentation of ADPKD.
*Chromosome 7*
- Mutations on chromosome 7 are linked to conditions like **Cystic Fibrosis (CFTR gene)** and **Williams-Beuren Syndrome**.
- While CFTR mutations can cause renal cysts in some atypical cases, it does not typically present with the extensive renal manifestations and palpable masses seen in ADPKD.
*Chromosome 4*
- Chromosome 4 harbors the **PKD2 gene**, which is responsible for approximately 15% of ADPKD cases (ADPKD type 2).
- While PKD2 mutations can cause ADPKD, they generally present with a milder phenotype and later onset compared to PKD1 mutations. Given this patient's classic presentation with significant bilateral masses and relatively younger age, PKD1 (chromosome 16) is more likely.
- Chromosome 4 is also associated with **Huntington's disease**.
*Chromosome 15*
- Mutations on chromosome 15 are linked to conditions such as **Marfan syndrome** and **Prader-Willi/Angelman syndromes**.
- These conditions have distinct clinical features that do not align with the patient's symptoms of significant renal pathology.
Renal cystic diseases US Medical PG Question 10: A 62-year-old man comes to the physician because of fatigue and decreased urine output for 2 weeks. He has not been to the physician for many years and takes no medications. Serum studies show a urea nitrogen concentration of 42 mg/dL and a creatinine concentration of 2.3 mg/dL. Urinalysis shows heavy proteinuria. A photomicrograph of a section of a kidney biopsy specimen is shown. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Amyloidosis
- B. Diabetes mellitus (Correct Answer)
- C. Dyslipidemia
- D. Fibromuscular dysplasia
- E. Severe hypertension
Renal cystic diseases Explanation: ***Diabetes mellitus***
- The kidney biopsy shows **diffuse glomerulosclerosis** with **Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules** (nodular mesangial sclerosis), which are pathognomonic for **diabetic nephropathy**.
- **Heavy proteinuria**, elevated BUN (42 mg/dL) and creatinine (2.3 mg/dL), along with the patient's age, are consistent with long-standing diabetes mellitus, even if previously undiagnosed.
- Diabetic nephropathy is the leading cause of end-stage renal disease in the United States.
*Amyloidosis*
- While amyloidosis can cause nephrotic syndrome and renal failure, the characteristic histology shows **extracellular amorphous deposits** that stain with **Congo red** and demonstrate apple-green birefringence under polarized light.
- The mesangial nodular pattern seen in diabetic nephropathy is distinct from the amyloid deposits seen in amyloidosis.
- Systemic amyloidosis typically presents with other organ involvement such as **cardiomyopathy**, **hepatosplenomegaly**, or **macroglossia**.
*Dyslipidemia*
- **Dyslipidemia** is a common comorbidity of nephrotic syndrome and diabetic nephropathy, but it is not a direct cause of the structural glomerular damage.
- It represents a metabolic consequence rather than the underlying etiology of the renal pathology.
*Fibromuscular dysplasia*
- **Fibromuscular dysplasia** affects the **renal arteries**, causing **renovascular hypertension** and renal ischemia.
- It typically presents with hypertension in young to middle-aged women and an abdominal bruit, not with heavy proteinuria and glomerular nodular sclerosis.
- The histology would show arterial wall changes, not glomerular pathology.
*Severe hypertension*
- **Severe hypertension** causes hypertensive nephrosclerosis with arteriolosclerosis and global glomerulosclerosis, but not the characteristic **nodular mesangial expansion** (Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules) seen in diabetic nephropathy.
- While hypertension commonly accompanies diabetic nephropathy, the specific histological findings of nodular glomerulosclerosis are pathognomonic for diabetes mellitus.
- Hypertensive nephrosclerosis shows arteriolar hyalinosis and ischemic changes, which differ from diabetic glomerular changes.
More Renal cystic diseases US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.