Congenital renal anomalies US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Congenital renal anomalies. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Congenital renal anomalies US Medical PG Question 1: A newborn infant is resuscitated and transferred to the neonatal intensive care unit. The infant has notable limb deformities as well as low-set ears and a flattened nose. He was born at 34 weeks gestation to a healthy mother who received regular obstetric follow-up. Resuscitation was notable for difficulty maintaining oxygenation in the newborn. Despite appropriate interventions, the infant is still struggling to maintain adequate oxygenation. Which of the following is most likely the cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. PKD1 gene mutation
- B. Cystic dilation of the collecting ducts in the kidney (Correct Answer)
- C. Chromosomal abnormality
- D. Maternal diabetes
- E. Failure to administer betamethasone
Congenital renal anomalies Explanation: ***Cystic dilation of the collecting ducts in the kidney***
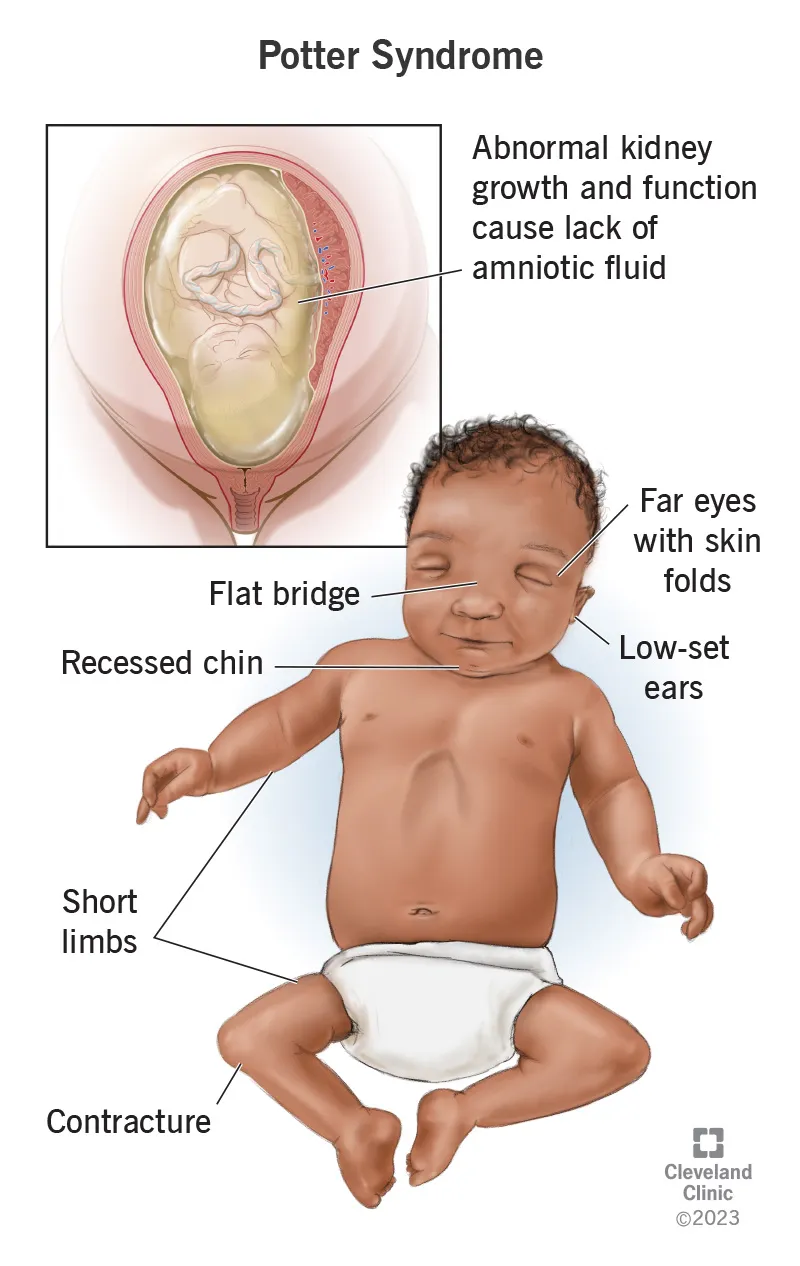
- This finding is characteristic of **autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD)**, which leads to **Potter sequence/Potter syndrome**.
- **Potter sequence** results from severe **oligohydramnios** (often due to bilateral renal disease causing inadequate urine production), leading to:
- **Pulmonary hypoplasia** (lungs cannot expand properly without adequate amniotic fluid)
- **Characteristic facial features** (Potter facies): low-set ears, flattened nose, recessed chin
- **Limb deformities** (positional abnormalities from mechanical compression in utero)
- The **persistent difficulty maintaining oxygenation despite appropriate interventions** is the key clinical clue - this indicates **structural pulmonary hypoplasia**, not simply respiratory distress from prematurity or other causes that would respond to treatment.
- Potter sequence is the most likely diagnosis given this specific constellation of findings.
*Chromosomal abnormality*
- While **trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)** or **trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)** can present with multiple congenital anomalies including facial dysmorphisms and limb deformities, they typically have additional characteristic findings (cardiac defects, rocker-bottom feet, holoprosencephaly, etc.).
- The **specific triad** of Potter facies + limb deformities + **refractory respiratory distress due to pulmonary hypoplasia** is pathognomonic for Potter sequence, not chromosomal abnormalities.
- Chromosomal abnormalities would not typically cause the severe oligohydramnios that leads to pulmonary hypoplasia.
*Maternal diabetes*
- Maternal diabetes can cause **macrosomia**, **hypoglycemia**, **respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)**, and rarely congenital anomalies (cardiac, neural tube defects).
- It does not cause the specific pattern of **Potter facies** (low-set ears, flattened nose) and **limb deformities** seen in Potter sequence.
- The mother is described as healthy with regular obstetric follow-up, making uncontrolled diabetes unlikely.
*PKD1 gene mutation*
- **PKD1 mutation** causes **autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)**, which typically presents in **adulthood** with hypertension, flank pain, and progressive renal failure.
- While rare severe cases can present in utero, PKD1 mutation does not cause the **cystic dilation of collecting ducts** - that finding is specific to **ARPKD** (associated with PKHD1 gene mutation).
- ADPKD involves cysts throughout the cortex and medulla, not specifically in collecting ducts.
*Failure to administer betamethasone*
- **Betamethasone** is given to mothers at risk of preterm delivery (before 34 weeks) to accelerate **fetal lung maturity** and reduce the severity of **respiratory distress syndrome (RDS)**.
- While this infant is preterm (34 weeks) and has respiratory distress, betamethasone failure would cause RDS due to **surfactant deficiency**, which typically **responds to surfactant administration and respiratory support**.
- This does not explain the **structural pulmonary hypoplasia** (indicated by refractory oxygenation issues) or the **facial and limb deformities**.
- Betamethasone is typically given before 34 weeks; at 34 weeks, the benefit is limited.
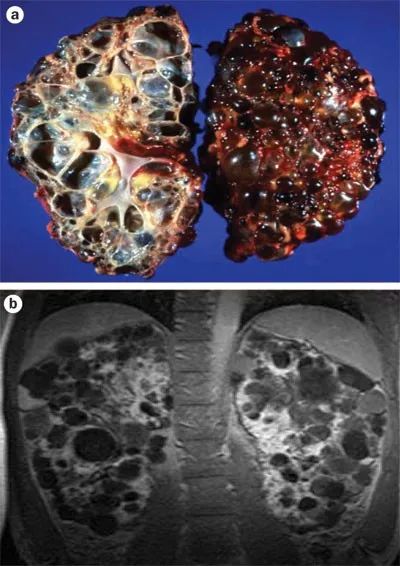
Congenital renal anomalies US Medical PG Question 2: A 41-year-old man presents to the emergency department because of brownish discoloration of his urine for the last several days. The review of symptoms includes complaints of increasing abdominal girth, early satiety, and difficulty breathing on exertion. The past medical history includes essential hypertension for 19 years. The medication list includes lisinopril and hydrochlorothiazide. He had a right inguinal hernia repair when he was a teenager. He smokes 20–30 cigarettes daily for the last 21 years, and drinks alcohol socially. His father died of a hemorrhagic stroke at the age of 69 years. The vital signs include: temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), blood pressure 131/88 mm Hg, and pulse 82/min. The physical examination is positive for a palpable right upper quadrant mass. The abdominal ultrasound shows multiple bilateral kidney cysts and hepatic cysts. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Simple kidney cyst
- B. Renal cell carcinoma
- C. Medullary sponge kidney
- D. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (Correct Answer)
- E. Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome
Congenital renal anomalies Explanation: ***Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease***
- The presence of **multiple bilateral kidney cysts** and **hepatic cysts**, along with symptoms like **increasing abdominal girth**, **early satiety**, and **hypertension** in a 41-year-old man, is highly characteristic of **autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)**.
- The **brownish discoloration of urine** suggests potential bleeding into a cyst or a urinary tract infection, common complications of ADPKD.
*Simple kidney cyst*
- A simple kidney cyst is typically **solitary, unilateral**, and usually asymptomatic.
- It does not explain the **multiplicity of cysts**, **bilateral involvement**, the presence of hepatic cysts, or the associated systemic symptoms.
*Renal cell carcinoma*
- While renal cell carcinoma can present with a palpable mass and hematuria (brownish urine), it typically manifests as a **single, solid mass** rather than **multiple bilateral cystic lesions**.
- Renal cell carcinoma is not associated with widespread hepatic cysts as seen in this patient.
*Medullary sponge kidney*
- This condition involves **dilation of the collecting ducts** in the renal pyramids and is often asymptomatic, though it can lead to **recurrent kidney stones** and urinary tract infections.
- It presents with **normal renal cortex** and does not typically involve multiple large cysts or hepatic cysts.
*Von Hippel-Lindau syndrome*
- This genetic disorder is characterized by the development of **cysts and tumors** in various organs, including the kidneys (**renal cell carcinoma**), pancreas, and central nervous system.
- While it can cause renal cysts, the primary renal manifestation is often **clear cell renal cell carcinoma**, and the clinical picture in this patient, particularly the widespread hepatic cysts and the absence of other typical VHL findings, makes it less likely than ADPKD.
Congenital renal anomalies US Medical PG Question 3: A 27-year-old female in her 20th week of pregnancy presents for a routine fetal ultrasound screening. An abnormality of the right fetal kidney is detected. It is determined that the right ureteropelvic junction has failed to recanalize. Which of the following findings is most likely to be seen on fetal ultrasound:
- A. Renal cysts
- B. Duplicated ureter
- C. Bilateral renal agenesis
- D. Pelvic kidney
- E. Unilateral hydronephrosis (Correct Answer)
Congenital renal anomalies Explanation: ***Unilateral hydronephrosis***
- Failure of the **ureteropelvic junction (UPJ)** to recanalize leads to an obstruction of urine flow from the **renal pelvis** into the ureter.
- This obstruction causes a buildup of urine in the renal pelvis and calyces, a condition known as **hydronephrosis**, which will be unilateral as only the right kidney is affected.
*Renal cysts*
- **Renal cysts** are typically associated with conditions like polycystic kidney disease or multicystic dysplastic kidney, which involve abnormal development of renal parenchyma, not specifically a UPJ obstruction.
- While hydronephrosis can sometimes lead to cystic changes if severe and prolonged, in the initial stages of a UPJ obstruction detected on fetal ultrasound, **hydronephrosis** itself is the primary and most likely finding.
*Duplicated ureter*
- A **duplicated ureter** is a distinct congenital anomaly involving the formation of two ureters draining a single kidney or separate renal moieties.
- It does not directly result from the failure of **ureteropelvic junction recanalization**.
*Bilateral renal agenesis*
- **Bilateral renal agenesis** means both kidneys failed to develop, which would lead to severe oligohydramnios and is incompatible with sustained fetal life.
- The question describes an abnormality only in the **right kidney**, making bilateral agenesis incorrect.
*Pelvic kidney*
- A **pelvic kidney** (renal ectopia) occurs when the kidney fails to ascend from the pelvis to its normal lumbar position.
- This is a positional anomaly and is not directly caused by a failure of **ureteropelvic junction recanalization**.
Congenital renal anomalies US Medical PG Question 4: A 14-year-old girl comes to the physician for exertional leg pain. The pain began last week when she started jogging to lose weight. She is at the 5th percentile for height and 80th percentile for weight. Physical examination shows a broad neck with bilateral excess skin folds that extend to the shoulders, as well as a low-set hairline and ears. There is an increased carrying angle when she fully extends her arms at her sides. Pulses are palpable in all extremities; lower leg pulses are delayed. Which of the following additional findings is most likely in this patient?
- A. Triphalangeal thumb
- B. Absent uterus
- C. Horseshoe adrenal gland
- D. Ovarian dysgenesis (Correct Answer)
- E. Mitral valve prolapse
Congenital renal anomalies Explanation: ***Ovarian dysgenesis***
- The patient's presentation with **short stature** (5th percentile for height), **webbed neck**, low-set hairline and ears, and increased carrying angle are classic features of **Turner syndrome (45,XO)**.
- **Ovarian dysgenesis (streak gonads)** is a hallmark of Turner syndrome, leading to **primary amenorrhea** and **infertility**, which would be a likely additional finding as she approaches puberty.
*Triphalangeal thumb*
- A triphalangeal thumb is a feature associated with conditions like **Fanconi anemia** or **Holt-Oram syndrome**, which have different constellations of anomalies (e.g., bone marrow failure, cardiac defects).
- These syndromes do not typically present with the specific phenotypic features of **webbed neck** or **increased carrying angle** seen in this patient.
*Absent uterus*
- An absent uterus, or **Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome**, presents with normal ovaries and female secondary sexual characteristics despite the lack of a uterus.
- This condition does not explain the patient's **short stature**, **webbed neck**, or **cardiovascular findings** (delayed lower leg pulses suggestive of coarctation of the aorta), which are classic for Turner syndrome.
*Horseshoe adrenal gland*
- A **horseshoe adrenal gland** is a rare congenital anomaly, often noted incidentally, and is not specifically associated with Turner syndrome or the patient's observed phenotypic features.
- While kidney anomalies (e.g., horseshoe kidney) are common in Turner syndrome, adrenal abnormalities generally are not a prominent feature.
*Mitral valve prolapse*
- Although **cardiac defects** are common in Turner syndrome, the most frequent are **bicuspid aortic valve** and **coarctation of the aorta**, suggested by the delayed lower leg pulses.
- While mitral valve prolapse can occur in the general population, it is not as specifically or commonly associated with Turner syndrome as **aortic anomalies**.
Congenital renal anomalies US Medical PG Question 5: A female infant is born with a mutation in PKD1 on chromosome 16. An abdominal ultrasound performed shortly after birth would most likely reveal which of the following?
- A. Microscopic cysts
- B. Normal kidneys (Correct Answer)
- C. Adrenal atrophy
- D. Horseshoe kidney
- E. Bilateral kidney enlargement
Congenital renal anomalies Explanation: ***Normal kidneys***
- Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), caused by a mutation in **PKD1 or PKD2**, typically presents with **cysts that develop later in life**, usually in adulthood.
- At birth, the kidneys of an infant with the ADPKD mutation are usually **structurally normal** and do not yet show macroscopic cyst formation on ultrasound.
*Microscopic cysts*
- While the genetic mutation is present, significant **macroscopic cyst formation** detectable by standard abdominal ultrasound does not typically occur at birth in ADPKD.
- The cysts develop and enlarge over decades, leading to symptoms later in adulthood.
*Adrenal atrophy*
- **Adrenal atrophy** is not a feature of polycystic kidney disease and is caused by other conditions like autoimmune diseases or prolonged corticosteroid use.
- The adrenal glands are distinct from the kidneys and are not directly affected by PKD1 mutations.
*Horseshoe kidney*
- **Horseshoe kidney** is a congenital anomaly where the kidneys are fused, usually at the lower poles, and is not associated with PKD1 mutations.
- This condition is a **developmental fusion defect** during embryogenesis.
*Bilateral kidney enlargement*
- Bilateral kidney enlargement due to multiple cysts is characteristic of **ADPKD in adulthood**, not at birth.
- Though ADPKD is a genetic condition, the **phenotypic expression (cyst growth)** progresses over time.
Congenital renal anomalies US Medical PG Question 6: A 49-year-old man presents to your clinic with “low back pain”. When asked to point to the area that bothers him the most, he motions to both his left and right flank. He describes the pain as deep, dull, and aching for the past few months. His pain does not change significantly with movement or lifting heavy objects. He noted dark colored urine this morning. He has a history of hypertension managed with hydrochlorothiazide; however, he avoids seeing the doctor whenever possible. He drinks 3-4 beers on the weekends but does not smoke. His father died of a sudden onset brain bleed, and his mother has diabetes. In clinic, his temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 150/110 mmHg, pulse is 95/min, and respirations are 12/min. Bilateral irregular masses are noted on deep palpation of the abdomen. The patient has full range of motion in his back and has no tenderness of the spine or paraspinal muscles. Urine dipstick in clinic is notable for 3+ blood. Which chromosome is most likely affected by a mutation in this patient?
- A. Chromosome 6
- B. Chromosome 7
- C. Chromosome 4
- D. Chromosome 15
- E. Chromosome 16 (Correct Answer)
Congenital renal anomalies Explanation: ***Chromosome 16***
- This patient's presentation with bilateral flank pain, hypertension, hematuria (dark urine with 3+ blood on dipstick), and palpable bilateral irregular abdominal masses is highly suggestive of **Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPKD)**.
- The most common form of ADPKD, comprising about 85% of cases, is caused by mutations in the **PKD1 gene** located on **chromosome 16**.
*Chromosome 6*
- Mutations on chromosome 6 are associated with conditions such as **hemochromatosis (HFE gene)** and certain types of **human leukocyte antigen (HLA) linked diseases**, neither of which fits the patient's primary symptoms.
- There is no direct link between chromosome 6 mutations and the classic presentation of ADPKD.
*Chromosome 7*
- Mutations on chromosome 7 are linked to conditions like **Cystic Fibrosis (CFTR gene)** and **Williams-Beuren Syndrome**.
- While CFTR mutations can cause renal cysts in some atypical cases, it does not typically present with the extensive renal manifestations and palpable masses seen in ADPKD.
*Chromosome 4*
- Chromosome 4 harbors the **PKD2 gene**, which is responsible for approximately 15% of ADPKD cases (ADPKD type 2).
- While PKD2 mutations can cause ADPKD, they generally present with a milder phenotype and later onset compared to PKD1 mutations. Given this patient's classic presentation with significant bilateral masses and relatively younger age, PKD1 (chromosome 16) is more likely.
- Chromosome 4 is also associated with **Huntington's disease**.
*Chromosome 15*
- Mutations on chromosome 15 are linked to conditions such as **Marfan syndrome** and **Prader-Willi/Angelman syndromes**.
- These conditions have distinct clinical features that do not align with the patient's symptoms of significant renal pathology.
Congenital renal anomalies US Medical PG Question 7: A 4-year-old male is accompanied by his mother to the pediatrician. His mother reports that over the past two weeks, the child has had intermittent low grade fevers and has been more lethargic than usual. The child’s past medical history is notable for myelomeningocele complicated by lower extremity weakness as well as bowel and bladder dysfunction. He has been hospitalized multiple times at an outside facility for recurrent urinary tract infections. The child is in the 15th percentile for both height and weight. His temperature is 100.7°F (38.2°C), blood pressure is 115/70 mmHg, pulse is 115/min, and respirations are 20/min. Physical examination is notable for costovertebral angle tenderness that is worse on the right. Which of the following would most likely be found on biopsy of this patient’s kidney?
- A. Replacement of renal parenchyma with foamy histiocytes
- B. Tubular colloid casts with diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate (Correct Answer)
- C. Diffusely necrotic papillae with dystrophic calcification
- D. Mononuclear and eosinophilic infiltrate
- E. Destruction of the proximal tubule and medullary thick ascending limb
Congenital renal anomalies Explanation: ***Tubular colloid casts with diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate***
- The patient's history of **myelomeningocele**, recurrent **urinary tract infections (UTIs)**, and current symptoms (fever, lethargy, CVA tenderness) strongly suggest **chronic pyelonephritis**.
- **Chronic pyelonephritis** is characterized histologically by **tubular atrophy**, interstitial fibrosis, and a **lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate**, often with "thyroidization" of the tubules where they are dilated and filled with colloid casts.
*Replacement of renal parenchyma with foamy histiocytes*
- This description is characteristic of **xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis**, a severe and rare form of chronic pyelonephritis.
- While possible given chronic UTIs, the more general and common finding in chronic pyelonephritis is a diffuse lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate, not necessarily dominant foamy histiocytes.
*Diffusely necrotic papillae with dystrophic calcification*
- This finding is most consistent with **renal papillary necrosis**.
- Renal papillary necrosis is typically associated with conditions like **analgesic nephropathy**, **sickle cell disease**, or severe acute pyelonephritis, but not the primary histological change in chronic pyelonephritis as described.
*Mononuclear and eosinophilic infiltrate*
- A prominent **eosinophilic infiltrate** in the kidney is often seen in **acute interstitial nephritis**, which can be drug-induced.
- While chronic inflammation involves mononuclear cells, the specific mention of eosinophils makes this less likely to be the primary finding in chronic pyelonephritis from recurrent UTIs.
*Destruction of the proximal tubule and medullary thick ascending limb*
- Destruction of specific tubular segments, particularly the **proximal tubule**, is characteristic of acute tubular necrosis (ATN).
- While chronic pyelonephritis leads to tubular atrophy and damage, the primary description here points to an acute injury rather than the chronic inflammatory changes expected.
Congenital renal anomalies US Medical PG Question 8: A child presents with rachitic changes in the limbs that are not responding to Vitamin D supplementation. Investigations reveal the following results:
- Calcium: $9.5 \mathrm{mg} / \mathrm{dl}$
- Phosphorus: $1.6 \mathrm{mg} / \mathrm{dl}$
- Alkaline phosphatase (ALP): 814 IU
- Serum PTH: $24.2 \mathrm{pg} / \mathrm{ml}$
- Serum electrolytes, creatinine, and blood gases: Normal.
What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Hypophosphatemic rickets (Correct Answer)
- B. Vitamin D-dependent rickets type 2
- C. Vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1
- D. Chronic renal failure
- E. Vitamin D deficiency rickets
Congenital renal anomalies Explanation: ***Hypophosphatemic rickets***
- The combination of **rachitic changes** not responding to Vitamin D, **low serum phosphorus (1.6 mg/dl)**, and **normal calcium and PTH levels** strongly points to hypophosphatemic rickets, a condition characterized by impaired renal phosphate reabsorption.
- The **elevated alkaline phosphatase** indicates increased bone turnover as the body tries to mineralize bone despite phosphate deficiency.
*Vitamin D-dependent rickets type 2*
- This condition involves resistance to **1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D**, leading to **hypocalcemia** and elevated PTH, none of which are present here.
- It would also typically show an inadequate response to Vitamin D, but the primary biochemical derangement is different.
*Vitamin D-dependent rickets type 1*
- This type is caused by a defect in **1-alpha-hydroxylase**, leading to an inability to convert 25-hydroxyvitamin D to its active form, resulting in **hypocalcemia** and elevated PTH, which are not observed.
- It would also show a poor response to standard Vitamin D supplementation.
*Vitamin D deficiency rickets*
- This is the most common form of rickets caused by inadequate Vitamin D intake or synthesis, presenting with **hypocalcemia**, **elevated PTH**, and **low phosphorus**.
- However, it typically responds well to Vitamin D supplementation, unlike the presentation here, and would show elevated PTH levels.
*Chronic renal failure*
- Chronic renal failure would present with **elevated creatinine**, and typically leads to **secondary hyperparathyroidism** (elevated PTH), **hyperphosphatemia**, and metabolic acidosis, none of which are suggested by the provided lab results.
- The serum electrolytes, creatinine, and blood gases are explicitly stated as normal.
Congenital renal anomalies US Medical PG Question 9: A 6-year-old girl comes with her parents to the physician's office to initiate care with a new physician. The patient was recently adopted and her parents do not know her birth history; however, she has had some issues with fatigue. They were told by the adoption agency that the patient has required blood transfusions for "low blood count" in the past but they are not aware of the reason for these transfusions. Her temperature is 37.8°C (99.8°F), blood pressure is 110/84 mmHg, and pulse is 95/min. Physical examination is notable for conjunctival pallor, pale skin, and mild splenomegaly. A complete blood count is taken in the office with the following results:
Hemoglobin: 6.8 g/dL
Leukocyte count: 5,000/mm^3
Platelet count: 190,000/mm^3
Peripheral smear shows spherocytes and further analysis reveals rigid red blood cells. The most likely cause of this patient's symptoms has which of the following modes of inheritance?
- A. Autosomal recessive
- B. Autosomal dominant (Correct Answer)
- C. Mitochondrial inheritance
- D. X-linked dominant
- E. X-linked recessive
Congenital renal anomalies Explanation: ***Autosomal dominant***
- The clinical picture of severe **anemia** requiring transfusions, **splenomegaly**, and peripheral smear findings of **spherocytes** and rigid red blood cells is highly suggestive of **hereditary spherocytosis**.
- **Hereditary spherocytosis** is caused by defects in red blood cell membrane proteins (e.g., spectrin, ankyrin), and the **most common mode of inheritance** for this condition is **autosomal dominant** (approximately 75% of cases).
*Autosomal recessive*
- While approximately **25%** of hereditary spherocytosis cases result from **autosomal recessive inheritance** or de novo mutations, the majority (~75%) follow an autosomal dominant pattern.
- The severity of presentation alone does not distinguish between inheritance patterns; both can present with severe anemia requiring transfusions.
- Other common red blood cell disorders, such as **sickle cell anemia** and **beta-thalassemia**, are autosomal recessive, but their characteristic findings (e.g., sickle cells, target cells) are not described here.
*Mitochondrial inheritance*
- **Mitochondrial disorders** primarily affect organs with high energy demands (e.g., muscles, brain) and do not typically cause isolated hemolytic anemia with spherocytes.
- This mode of inheritance involves genes located in the **mitochondrial DNA** and is passed down exclusively from the mother.
*X-linked dominant*
- **X-linked dominant** disorders affect both males and females (though often more severely in males) and do not fit the typical presentation or known genetic basis of hereditary spherocytosis.
- Examples include **Rett syndrome** and **incontinentia pigmenti**.
*X-linked recessive*
- **X-linked recessive** disorders, such as **G6PD deficiency** or **hemophilia**, are more common in males and have distinct clinical and laboratory features that do not match the patient's presentation of hereditary spherocytosis.
- While **G6PD deficiency** can cause hemolytic anemia, it is typically triggered by oxidative stress and does not primarily involve spherocytes or chronic splenomegaly in the same manner.
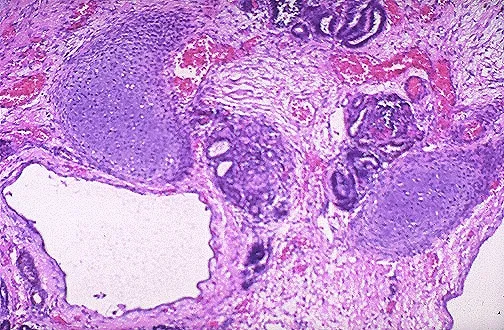
Congenital renal anomalies US Medical PG Question 10: An 82-year-old woman presents to the emergency department because of excruciating right flank pain and fever for the past 2 days. She states that she is having trouble urinating. Her past medical history is unremarkable. A urinalysis is performed and comes back positive for leukocytes and gram-negative bacilli. A contrast computed tomography of the abdomen is performed and reveals a large retroperitoneal mass compressing the right ureter, leading to hydronephrosis of the right kidney. The mass is excised. Histopathologic evaluation of the mass is shown in the image below, and it is determined to be malignant. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Rhabdomyosarcoma
- B. Leiomyosarcoma
- C. Lipoma
- D. Teratoma
- E. Liposarcoma (Correct Answer)
Congenital renal anomalies Explanation: ***Liposarcoma***
- The **most common primary malignant retroperitoneal tumor** in adults, particularly in elderly patients
- Characteristically presents as a **large retroperitoneal mass** causing compressive symptoms such as hydronephrosis
- **Histopathological features** include pleomorphic lipoblasts with varying degrees of differentiation (well-differentiated, dedifferentiated, myxoid, or pleomorphic subtypes)
- The clinical presentation of an elderly patient with a malignant retroperitoneal mass strongly suggests this diagnosis
*Rhabdomyosarcoma*
- Primarily a **pediatric malignancy**, most common in children and young adults under 20 years old
- Most frequently arises in the **head and neck, genitourinary tract, or extremities**, not typically retroperitoneal
- Histologically shows skeletal muscle differentiation with rhabdomyoblasts, not lipoblastic features
*Leiomyosarcoma*
- More commonly found in the **uterus, gastrointestinal tract, or blood vessels**
- While it can occur in the retroperitoneum, it is **less common** than liposarcoma in this location
- Histologically demonstrates **smooth muscle differentiation** with spindle cells, not the lipoblastic features characteristic of the described mass
*Lipoma*
- A **benign tumor** composed of mature adipose tissue without cellular atypia
- Would not present as a **malignant mass** on histopathologic evaluation
- Generally asymptomatic and slow-growing; unlikely to cause severe symptoms like excruciating pain or obstructive hydronephrosis
*Teratoma*
- Contains tissue derived from **all three germ layers** (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm)
- More commonly associated with **gonadal or midline structures** (ovaries, testes, mediastinum)
- Rare in the retroperitoneum in elderly patients; histology would show diverse tissue types rather than predominantly lipoblastic features
More Congenital renal anomalies US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.