Acute tubular necrosis US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Acute tubular necrosis. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Acute tubular necrosis US Medical PG Question 1: A 78-year-old man dies suddenly from complications of acute kidney failure. An autopsy is performed and microscopic evaluation of the kidneys shows pale, swollen cells in the proximal convoluted tubules. Microscopic evaluation of the liver shows similar findings. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of these findings?
- A. Double-stranded DNA breakage
- B. Impaired Na+/K+-ATPase pump activity (Correct Answer)
- C. Free radical formation
- D. Cytochrome C release
- E. Cytoplasmic triglyceride accumulation
Acute tubular necrosis Explanation: ***Impaired Na+/K+-ATPase pump activity***
- **Acute kidney failure** leads to **hypoxia** and ATP depletion, which impairs the function of the **Na+/K+-ATPase pump** on the cell membrane.
- Failure of this pump results in **intracellular accumulation of sodium** and water, causing **cellular swelling** and pallor as seen in the kidneys and liver.
*Double-stranded DNA breakage*
- This is primarily associated with **apoptosis** or **radiation injury**, which would lead to nuclear fragmentation and cellular death rather than simple cellular swelling.
- While cell death can occur in acute kidney failure, the initial changes described (pale, swollen cells) are characteristic of **reversible cell injury** before extensive DNA damage.
*Free radical formation*
- **Free radical formation** (oxidative stress) can cause cellular injury, but it primarily leads to **lipid peroxidation of membranes** and damage to proteins and DNA, not directly to the widespread intracellular water accumulation described.
- While part of the injury cascade, it's not the most direct mechanism for the initial gross and microscopic findings of swelling.
*Cytochrome C release*
- **Cytochrome C release** from mitochondria is a critical step in the **intrinsic pathway of apoptosis**, leading to programmed cell death.
- The findings described (pale, swollen cells) are more indicative of **reversible cellular injury** or early necrosis, prior to the widespread activation of apoptosis.
*Cytoplasmic triglyceride accumulation*
- **Cytoplasmic triglyceride accumulation** (steatosis or fatty change) is often seen in conditions like **alcoholic liver disease** or **metabolic syndrome**.
- While it can be a sign of cellular injury, it does not directly explain the generalized "pale, swollen cells" observed in both the kidneys and liver following acute kidney failure, which points to water influx.
Acute tubular necrosis US Medical PG Question 2: An 84-year-old man is brought to the physician by the staff of a group home where he resides because of worsening confusion and decreased urinary output. His nurse reports that the patient has not been drinking much for the last 3 days. Examination shows a decreased skin turgor and dry oral mucosa. His pulse is 105/min and blood pressure is 100/65 mm Hg. His serum creatinine is 3.1 mg/dL and a urea nitrogen is 42 mg/dL. Urine studies show multiple brownish granular casts. Which of the following processes is most likely involved in the pathogenesis of this patient's condition?
- A. Immune complex deposition in mesangium
- B. Leukocytic infiltration of renal interstitium
- C. Necrosis of renal papillae
- D. Necrosis of tubular epithelial cells (Correct Answer)
- E. Disruption of glomerular podocytes
Acute tubular necrosis Explanation: ***Necrosis of tubular epithelial cells***
- The patient presents with classic signs of **acute kidney injury (AKI)**, including confusion, decreased urinary output, decreased skin turgor, dry oral mucosa, tachycardia, hypotension, elevated creatinine (3.1 mg/dL), and urea nitrogen (42 mg/dL).
- The presence of **brownish granular casts** in the urine is highly suggestive of **acute tubular necrosis (ATN)**, secondary to ischemia caused by severe dehydration and hypoperfusion.
*Immune complex deposition in mesangium*
- This typically points to a **glomerular pathology**, such as IgA nephropathy or post-infectious glomerulonephritis.
- These conditions would usually present with **hematuria** and **proteinuria**, not necessarily brownish granular casts or the acute dehydration found here.
*Leukocytic infiltration of renal interstitium*
- This finding is characteristic of **acute interstitial nephritis**, which is often caused by drug hypersensitivity or infection.
- The clinical presentation with dehydration and granular casts is not typical for acute interstitial nephritis.
*Necrosis of renal papillae*
- **Renal papillary necrosis** is often associated with analgesic abuse, sickle cell disease, diabetes, or obstruction.
- While it can cause AKI, it typically presents with **flank pain** and **hematuria**, and the urine sediment would show ghost cells or fragments of necrotic papillae, not specifically brownish granular casts.
*Disruption of glomerular podocytes*
- **Podocyte disruption** is seen in primary glomerular diseases like minimal change disease or focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.
- These conditions primarily cause **nephrotic syndrome** (heavy proteinuria, edema), which is not the main presentation here.
Acute tubular necrosis US Medical PG Question 3: Nine days after being treated for a perforated gastric ulcer and sepsis, a 78-year-old woman develops decreased urinary output and malaise. She required emergency laparotomy and was subsequently treated in the intensive care unit for sepsis. Blood cultures grew Pseudomonas aeruginosa. The patient was treated with ceftazidime and gentamicin. She has type 2 diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, and osteoarthritis of the hips. Prior to admission, her medications were insulin, ramipril, and ibuprofen. Her temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 80/min, and blood pressure is 115/75 mm Hg. Examination shows a healing surgical incision in the upper abdomen. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin count 14 g/dL
Leukocyte count 16,400 mm3
Segmented neutrophils 60%
Eosinophils 2%
Lymphocytes 30%
Monocytes 6%
Platelet count 260,000 mm3
Serum
Na+ 137 mEq/L
Cl- 102 mEq/L
K+ 5.1 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 25 mg/dL
Creatinine 4.2 mg/dL
Fractional excretion of sodium is 2.1%. Which of the following findings on urinalysis is most likely associated with this patient's condition?
- A. RBC casts
- B. WBC casts
- C. Waxy casts
- D. Muddy brown casts (Correct Answer)
- E. Pigmented casts
Acute tubular necrosis Explanation: ***Muddy brown casts***
- The patient's presentation with **decreased urinary output**, **malaise**, and significantly **elevated creatinine** (4.2 mg/dL) after recent sepsis and treatment with nephrotoxic drugs (gentamicin) strongly suggests **acute tubular necrosis (ATN)**.
- **Muddy brown casts** are pathognomonic for **acute tubular necrosis**, indicating damage to the renal tubules.
*RBC casts*
- **Red blood cell (RBC) casts** are indicative of **glomerulonephritis** or severe glomerular damage, which is not suggested by the clinical picture.
- While the patient has hypertension and diabetes, her current acute kidney injury (AKI) is more consistent with ATN given the recent sepsis and aminoglycoside use.
*WBC casts*
- **White blood cell (WBC) casts** are characteristic of **pyelonephritis** (kidney infection) or **interstitial nephritis**.
- Although she had sepsis, there is no direct evidence of pyelonephritis, and interstitial nephritis would present differently.
*Waxy casts*
- **Waxy casts** are associated with **chronic kidney disease** and indicate severe, longstanding tubular atrophy and urine stasis.
- While she has risk factors for chronic kidney disease (diabetes, hypertension), her acute decline points to an acute process like ATN, making waxy casts less likely as the primary finding.
*Pigmented casts*
- **Pigmented casts** (e.g., myoglobin casts in rhabdomyolysis or hemoglobin casts in hemolysis) are seen in conditions involving the release of large amounts of pigments into the bloodstream.
- While sepsis can cause hemolysis or muscle breakdown, **muddy brown casts** specifically refer to the granular, pigmented casts seen in ATN due to damaged tubular cells and heme pigments. "Pigmented casts" is a broader term, and "muddy brown casts" is more specific to ATN.
Acute tubular necrosis US Medical PG Question 4: A 53-year-old woman presents to her physician for evaluation of sudden onset respiratory distress for the past few hours. The past medical history includes a myocardial infarction 2 years ago. The vital signs include a blood pressure 70/40 mm Hg, pulse 92/min, respiratory rate 28/min, and SpO2 92% on room air. The physical examination reveals bilateral basal crepitations on auscultation. The echocardiogram reveals an ejection fraction of 34%. She is admitted to the medical floor and started on furosemide. The urine output in 24 hours is 400 mL. The blood urea nitrogen is 45 mg/dL and the serum creatinine is 1.85 mg/dL. The fractional excretion of sodium is 2.4%. Urinalysis revealed muddy brown granular casts. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the abnormal urinalysis?
- A. Acute interstitial nephritis
- B. Acute tubular necrosis (Correct Answer)
- C. Acute pyelonephritis
- D. Chronic kidney disease
- E. Acute glomerulonephritis
Acute tubular necrosis Explanation: ***Acute tubular necrosis***
- The presence of **muddy brown granular casts** on urinalysis is pathognomonic for **acute tubular necrosis (ATN)**, indicating damage to the renal tubules.
- The patient's history of **cardiogenic shock** (low BP 70/40 mm Hg, respiratory distress, low SpO2, low ejection fraction of 34%) led to **renal hypoperfusion** and ischemic tubular injury.
- The **fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) of 2.4%** (>2%) is characteristic of **intrinsic renal injury** (ATN), as damaged tubules cannot effectively reabsorb sodium.
- **Oliguria** (400 mL/24 hours), elevated **BUN (45 mg/dL)** and **creatinine (1.85 mg/dL)** further support acute kidney injury from ATN.
*Acute interstitial nephritis*
- This condition is typically associated with **drug hypersensitivity** (e.g., NSAIDs, antibiotics, PPIs) or **infections** and is characterized by inflammatory infiltrate in the renal interstitium.
- Urinalysis typically shows **white blood cell casts** and **eosinophiluria**, not muddy brown granular casts.
*Acute pyelonephritis*
- This is an **infection of the kidney** parenchyma, usually caused by bacterial ascension from the urinary tract.
- Symptoms often include **fever, flank pain, dysuria**, and urinalysis reveals **leukocyturia** (white blood cells) and **bacterial casts**, not muddy brown granular casts.
*Chronic kidney disease*
- While the patient has elevated creatinine and BUN, **chronic kidney disease (CKD)** develops over months to years and is characterized by persistent kidney damage or decreased function.
- Urinalysis in CKD often shows **broad waxy casts** and typically does not present with such **acute, sudden onset** of severe renal dysfunction with muddy brown granular casts.
*Acute glomerulonephritis*
- This condition involves inflammation of the glomeruli and typically presents with **hematuria, proteinuria, and red blood cell casts** (dysmorphic RBCs).
- The patient's clinical picture, including the absence of significant hematuria and the presence of **muddy brown granular casts**, does not fit acute glomerulonephritis.
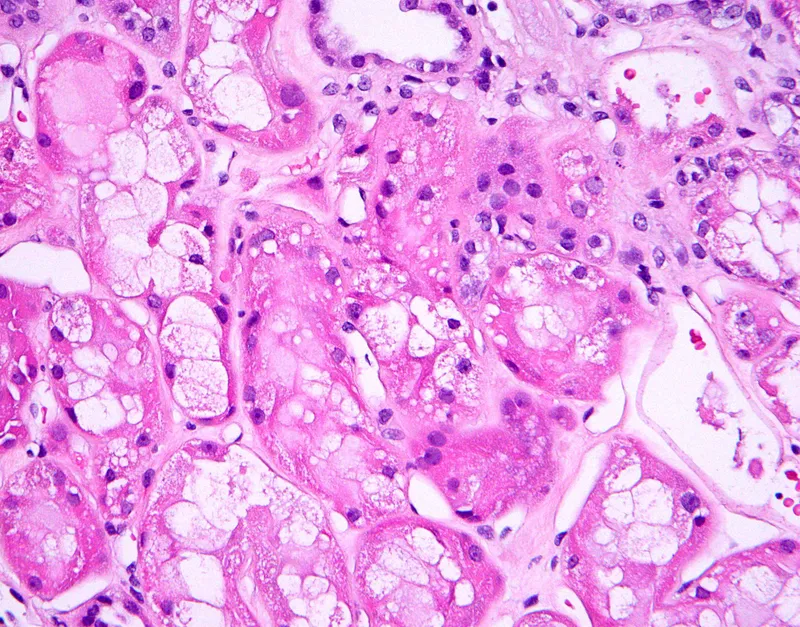
Acute tubular necrosis US Medical PG Question 5: A 53-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife because of a 1-day history of headache, blurry vision, and confusion. His wife also says that he hasn't urinated in the past 24 hours. Despite appropriate measures, the patient dies shortly after admission. A photomicrograph of a section of the kidney obtained at autopsy is shown. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the findings indicated by the arrow?
- A. Mycotic aneurysm
- B. Atherosclerotic plaque rupture
- C. Necrotizing vasculitis
- D. Chronic hyperglycemia
- E. Severe hypertension (Correct Answer)
Acute tubular necrosis Explanation: ***Severe hypertension***
- The image likely shows **hyperplastic arteriolosclerosis** ("onion-skinning") or **fibrinoid necrosis** of arterioles, which are characteristic pathological changes seen in severe, **malignant hypertension**.
- This type of severe vascular damage explains the rapid onset of headache, blurry vision (hypertensive retinopathy), confusion (hypertensive encephalopathy), and acute kidney injury (lack of urination) due to widespread microvascular ischemia and organ dysfunction.
*Mycotic aneurysm*
- A **mycotic aneurysm** is an infected aneurysm, typically caused by bacterial endocarditis or other sources of bacteremia.
- While it can lead to stroke or organ ischemia, the histological image features are not consistent with an infectious process or an aneurysm, but rather with diffuse microvascular injury.
*Atherosclerotic plaque rupture*
- **Atherosclerotic plaque rupture** causes acute ischemic events by forming a thrombus on the ruptured plaque, typically in larger arteries.
- The presented clinical picture and histological findings (likely small arteriolar damage) are not typical of large vessel atherosclerosis.
*Necrotizing vasculitis*
- **Necrotizing vasculitis** involves inflammation and necrosis of vessel walls, which can lead to organ damage, but it's typically an autoimmune or inflammatory process.
- Although there may be some vascular necrosis in malignant hypertension (fibrinoid necrosis), the primary driver here is the sustained high pressure rather than a specific vasculitic syndrome.
*Chronic hyperglycemia*
- **Chronic hyperglycemia** leads to diabetic microangiopathy, characterized by **hyaline arteriolosclerosis** (protein deposition in vessel walls) and capillary basement membrane thickening.
- These changes develop slowly over years and would not explain the acute, severe presentation described, nor do they typically present with the "onion-skinning" appearance of severe hypertension.
Acute tubular necrosis US Medical PG Question 6: A 39-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department in a semi-unconscious state by her neighbor who saw her lose consciousness. There was no apparent injury on the primary survey. She is not currently taking any medications. She has had loose stools for the past 3 days and a decreased frequency of urination. No further history could be obtained. The vital signs include: blood pressure 94/62 mm Hg, temperature 36.7°C (98.0°F), pulse 105/min, and respiratory rate 10/min. The skin appears dry. Routine basic metabolic panel, urine analysis, urine osmolality, and urine electrolytes are pending. Which of the following lab abnormalities would be expected in this patient?
- A. Serum blood urea nitrogen/creatinine (BUN/Cr) > 20 (Correct Answer)
- B. Urine osmolality < 350 mOsm/kg
- C. Fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) > 2%
- D. Urine Na+ > 40 mEq/L
- E. Serum creatinine < 1 mg/dL
Acute tubular necrosis Explanation: ***Serum blood urea nitrogen/creatinine (BUN/Cr) > 20***
- The patient presents with classic signs of **hypovolemia**, including hypotension, tachycardia, dry skin, and decreased urine output, likely due to significant fluid loss from diarrheal illness. This state leads to **prerenal azotemia**.
- In prerenal azotemia, the kidneys reabsorb more water and urea to conserve fluid, leading to a disproportionate rise in BUN compared to creatinine, resulting in a **BUN/Cr ratio typically > 20:1**.
*Urine osmolality < 350 mOsm/kg*
- This value indicates the kidney is actively excreting dilute urine, which would be expected in conditions like **diabetes insipidus** or **excessive fluid intake**.
- In response to hypovolemia, the kidneys attempt to conserve water, leading to the excretion of **highly concentrated urine**, with osmolality typically **> 500 mOsm/kg**.
*Fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) > 2%*
- An FENa > 2% suggests **intrinsic renal damage** (acute tubular necrosis) where the kidneys cannot effectively reabsorb sodium.
- In prerenal azotemia, the kidneys are structurally intact and actively conserve sodium to maintain circulating volume, leading to an **FENa < 1%**.
*Urine Na+ > 40 mEq/L*
- A urine sodium concentration above 40 mEq/L is observed in **intrinsic kidney injury** or during **diuretic use**, where sodium reabsorption is impaired.
- With hypovolemia, the kidneys avidly reabsorb sodium, striving to restore volume. This results in a **low urine sodium concentration**, typically **< 20 mEq/L**.
*Serum creatinine < 1 mg/dL*
- While a serum creatinine < 1 mg/dL *could* be normal for some individuals, in the context of significant dehydration and prerenal azotemia, one would expect a **rise in serum creatinine** alongside BUN.
- The patient's condition, characterized by hypovolemia and decreased renal perfusion, leads to **elevated serum creatinine**.
Acute tubular necrosis US Medical PG Question 7: A 32-year-old man is brought to the Emergency Department after 3 consecutive days of diarrhea, fatigue and weakness. His stool has been soft and mucoid, with no blood stains. The patient just came back from a volunteer mission in Guatemala, where he remained asymptomatic. His personal medical history is unremarkable. Today his blood pressure is 98/60 mm Hg, pulse is 110/min, respiratory rate is 19/min, and his body temperature is 36.7°C (98.1°F). On physical exam, he has sunken eyes, dry mucosa, mild diffuse abdominal tenderness, and hyperactive bowel sounds. Initial laboratory tests are shown below:
Serum creatinine (SCr) 1.8 mg/dL
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) 50 mg/dL
Serum sodium 132 mEq/L
Serum potassium 3.5 mEq/L
Serum chloride 102 mEq/L
Which of the following phenomena would you expect in this patient?
- A. Low urine osmolality, high FeNa+, high urine Na+
- B. High urine osmolality, high fractional excretion of sodium (FeNa+), high urine Na+
- C. Low urine osmolality, high FeNa+, low urine Na+
- D. High urine osmolality, low FeNa+, low urine Na+ (Correct Answer)
- E. Low urine osmolality, low FeNa+, high urine Na+
Acute tubular necrosis Explanation: ***High urine osmolality, low FeNa+, low urine Na+***
- The patient exhibits signs of **dehydration** (hypotension, tachycardia, sunken eyes, dry mucosa) and **acute kidney injury (AKI)** with elevated BUN and creatinine, particularly a **BUN/creatinine ratio of 27.8** (50/1.8). These findings point to **prerenal AKI** due to hypovolemia from diarrhea.
- In prerenal AKI, the kidneys attempt to conserve water and sodium to restore intravascular volume. This leads to **increased ADH** secretion and **aldosterone**, resulting in **high urine osmolality** (concentrated urine), **low fractional excretion of sodium (FeNa+)** (<1%), and **low urine sodium concentration** (<20 mEq/L).
*Low urine osmolality, high FeNa+, high urine Na+*
- This pattern is typical of **acute tubular necrosis (ATN)**, an intrinsic cause of AKI, where tubular damage impairs the kidney's ability to concentrate urine and reabsorb sodium.
- The context of dehydration and prerenal state makes ATN less likely as the initial primary pathology compared to the body's compensatory mechanisms during hypovolemia.
*High urine osmolality, high fractional excretion of sodium (FeNa+), high urine Na+*
- This combination is generally contradictory. High urine osmolality suggests water conservation, while high FeNa+ and urine Na+ indicate sodium wasting, which would typically be seen in diuretic use or specific renal tubular disorders, not uncompensated hypovolemia.
- In prerenal AKI, the body actively reabsorbs sodium to expand volume, leading to low rather than high FeNa+ and urine Na+.
*Low urine osmolality, high FeNa+, low urine Na+*
- This combination is inconsistent. High FeNa+ and low urine Na+ do not usually occur together in a state of hypovolemia. If FeNa+ is high, it implies significant sodium excretion, which would typically be accompanied by higher urine Na+.
- Low urine osmolality also suggests impaired concentrating ability, which is not characteristic of the compensatory mechanisms in prerenal AKI.
*Low urine osmolality, low FeNa+, high urine Na+*
- This combination is also contradictory. Low urine osmolality with low FeNa+ and high urine Na+ does not align with typical kidney responses to dehydration or specific AKI etiologies.
- Low FeNa+ and high urine Na+ are conflicting, as low FeNa+ implies sodium conservation, while high urine Na+ indicates sodium excretion.
Acute tubular necrosis US Medical PG Question 8: A 49-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with bloody stool and malaise. She developed a fever and acute left lower quadrant abdominal pain earlier in the day. She has had 2 bowel movements with bright red blood. Her past medical history is notable for hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. She takes lovastatin, hydrochlorothiazide, metformin, glyburide, and aspirin. Her temperature is 102.9°F (39.4°C), blood pressure is 101/61 mmHg, pulse is 110/min, and respirations are 22/min. On exam, she is fully alert and oriented. She is tender in the left lower quadrant. A computerized tomography (CT) scan is performed demonstrating acute diverticulitis. She is admitted and started on broad-spectrum antibiotics. 48 hours later, her urine output is significantly decreased. Her abdominal pain has improved but she has started vomiting and appears confused. She has new bilateral lower extremity edema and decreased breath sounds at the lung bases. Laboratory analysis upon admission and 48 hours later is shown below:
Admission:
Hemoglobin: 11.9 g/dl
Hematocrit: 34%
Leukocyte count: 11,500/mm^3
Platelet count: 180,000/ mm^3
Serum:
Na+: 141 mEq/L
Cl-: 103 mEq/L
K+: 4.5 mEq/L
HCO3-: 23 mEq/L
BUN: 21 mg/dL
Glucose: 110 mg/dL
Creatinine: 0.9 mg/dL
48 hours later:
Hemoglobin: 10.1 g/dl
Hematocrit: 28%
Leukocyte count: 11,500 cells/mm^3
Platelet count: 195,000/ mm^3
Serum:
Na+: 138 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
K+: 5.1 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
BUN: 30 mg/dL
Glucose: 120 mg/dL
Creatinine: 2.1 mg/dL
Which of the following findings would most likely be seen on urine microscopy?
- A. Waxy casts
- B. Muddy brown casts (Correct Answer)
- C. White blood cell casts
- D. Fatty casts
- E. Hyaline casts
Acute tubular necrosis Explanation: ***Muddy brown casts***
- The patient's presentation with **acute kidney injury** (creatinine rising from 0.9 to 2.1 mg/dL in 48 hours) along with signs of **sepsis** (fever, hypotension, altered mental status, decreased urine output) strongly suggests **acute tubular necrosis (ATN)**, a common cause of intrinsic renal failure.
- **Muddy brown casts** composed of degenerating renal tubular epithelial cells and granular material are pathognomonic for **acute tubular necrosis** and indicate significant tubular damage.
*Waxy casts*
- **Waxy casts** are typically associated with **chronic renal failure** and advanced renal disease, indicating prolonged tubular stasis and severe urine flow reduction.
- While the patient has acute kidney injury, her history does not suggest pre-existing chronic kidney disease to this extent.
*White blood cell casts*
- **White blood cell casts** are characteristic of **interstitial nephritis** or **pyelonephritis**, indicating inflammation or infection within the kidney parenchyma.
- Although the patient has a possible infection (diverticulitis, sepsis), the rapid decline in renal function with a clear rise in creatinine points more directly to ATN rather than primarily interstitial inflammation.
*Fatty casts*
- **Fatty casts** are typically seen in **nephrotic syndrome**, a condition characterized by massive proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and significant edema.
- The patient's symptoms are more consistent with acute kidney injury due to sepsis, and there is no information to suggest nephrotic-range proteinuria.
*Hyaline casts*
- **Hyaline casts** can be found in **healthy individuals** from concentrated urine or after exercise and are non-specific, indicating only mild tubular protein aggregation.
- They are not indicative of significant renal pathology like ATN and would not explain the patient's acute and severe renal deterioration.
Acute tubular necrosis US Medical PG Question 9: A 53-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with severe chest pain radiating to the back. She was diagnosed with acute aortic dissection. A few hours into the resuscitation, she was having oliguria. Laboratory findings show a serum creatinine level of 5.3 mg/dL. Which of the following casts are most likely to be seen on urinalysis?
- A. RBC casts
- B. Fatty casts
- C. Muddy brown casts (Correct Answer)
- D. Waxy casts
- E. Hyaline casts
Acute tubular necrosis Explanation: ***Muddy brown casts***
- **Acute tubular necrosis (ATN)**, likely caused by **renal hypoperfusion** in the context of an aortic dissection, is characterized by the presence of **muddy brown granular casts** in urinalysis. The significantly elevated **creatinine (5.3 mg/dL)** and **oliguria** support a diagnosis of acute kidney injury with ATN.
- These casts are pathognomonic for ATN and are formed from shed **epithelial cells** and debris accumulating in the renal tubules.
*RBC casts*
- **Red blood cell (RBC) casts** are indicative of **glomerulonephritis** or other causes of **glomerular injury**, which are not directly suggested by the presentation of aortic dissection and subsequent oliguria.
- While hematuria can occur in various renal conditions, the presence of **RBC casts** points to bleeding originating from the glomerulus, which is a different pathology than ATN.
*Fatty casts*
- **Fatty casts** are typically associated with **nephrotic syndrome**, a condition characterized by significant proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and edema.
- There is no clinical information to suggest nephrotic syndrome in this patient, whose acute renal failure is likely due to hypoperfusion.
*Waxy casts*
- **Waxy casts** are generally indicative of **chronic kidney disease** and highly advanced, severe tubular damage, representing a later stage of kidney injury.
- While the patient has acute kidney injury, the timeline and acute nature of the insult make muddy brown casts more likely than waxy casts.
*Hyaline casts*
- **Hyaline casts** are composed primarily of Tamm-Horsfall mucoprotein, a normal protein secreted by renal tubule cells.
- These casts can be seen in normal urine, especially after exercise or dehydration, and are not specific for any particular kidney pathology or acute kidney injury.
Acute tubular necrosis US Medical PG Question 10: A 29-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 2-day history of intermittent dark urine and mild flank pain. She has also had a cough, sore throat, and runny nose for the past 5 days. She has not had dysuria. She takes no medications. She has no known allergies. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F). Examination of the back shows no costovertebral angle tenderness. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.4 g/dL
Leukocyte count 8,000/mm3
Platelet count 200,000/mm3
Serum
Na+ 135 mEq/L
K+ 4.9 mEq/L
Cl- 101 mEq/L
HCO3- 22 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 18 mg/dL
Creatinine 1.1 mg/dL
Urine
Color yellow
Blood 3+
Protein 1+
Leukocyte esterase negative
An ultrasound of the kidney and bladder shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Ischemic tubular injury
- B. Urothelial neoplasia
- C. Renal papillary necrosis
- D. Renal glomerular damage (Correct Answer)
- E. Interstitial renal inflammation
Acute tubular necrosis Explanation: ***Renal glomerular damage***
- The patient's symptoms (dark urine, mild flank pain) occurring shortly after an **upper respiratory infection** (cough, sore throat, runny nose) are highly suggestive of **acute glomerulonephritis**.
- The urinalysis showing **hematuria (blood 3+) and proteinuria (protein 1+)** in the absence of dysuria or bacterial infection (leukocyte esterase negative, no CVA tenderness) points to glomerular inflammation as the cause of kidney involvement.
*Ischemic tubular injury*
- This condition typically presents with signs of **acute kidney injury**, such as elevated creatinine and blood urea nitrogen (BUN), which are not significantly altered here.
- Urinalysis usually shows **muddy brown casts** and signs of tubular damage, rather than prominent hematuria and proteinuria alone.
*Urothelial neoplasia*
- While it can cause painless hematuria, it is less likely to present with concurrent **flu-like symptoms** and the rapid onset described.
- Urothelial neoplasms are more common in older individuals or those with specific risk factors (e.g., smoking), and an **ultrasound revealed no abnormalities**.
*Renal papillary necrosis*
- This is typically seen in patients with **analgesic nephropathy**, sickle cell disease, or diabetes, none of which are indicated here.
- It often leads to **gross hematuria** and passage of tissue fragments, and can be associated with severe pain, but the clinical picture does not fit this diagnosis.
*Interstitial renal inflammation*
- Acute interstitial nephritis is often caused by **drug reactions** or infections and is characterized by a significant inflammatory infiltrate in the renal interstitium.
- While it can cause flank pain and hematuria, it more commonly presents with **fever, rash, and eosinophiluria**, and less often with prominent proteinuria like glomerulonephritis.
More Acute tubular necrosis US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.