Restrictive lung diseases US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Restrictive lung diseases. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Restrictive lung diseases US Medical PG Question 1: A 61-year-old male presents to your office with fever and dyspnea on exertion. He has been suffering from chronic, non-productive cough for 1 year. You note late inspiratory crackles on auscultation. Pulmonary function tests reveal an FEV1/FVC ratio of 90% and an FVC that is 50% of the predicted value. Which of the following would you most likely see on a biopsy of this patient's lung?
- A. Arteriovenous malformations
- B. Hyaline membranes
- C. Charcot-Leyden crystals
- D. Subpleural cystic enlargement (Correct Answer)
- E. Linear immunofluorescence along alveolar basement membranes
Restrictive lung diseases Explanation: ***Subpleural cystic enlargement***
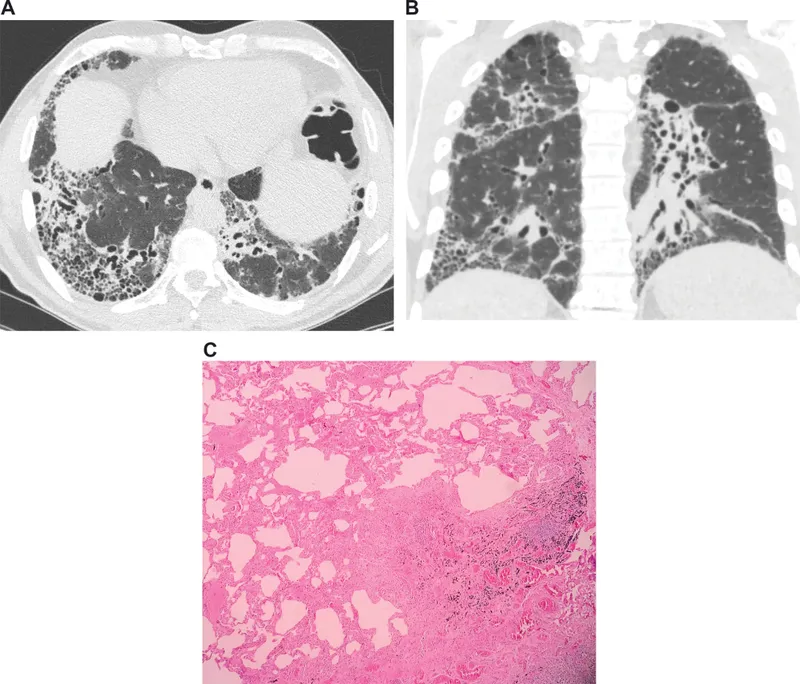
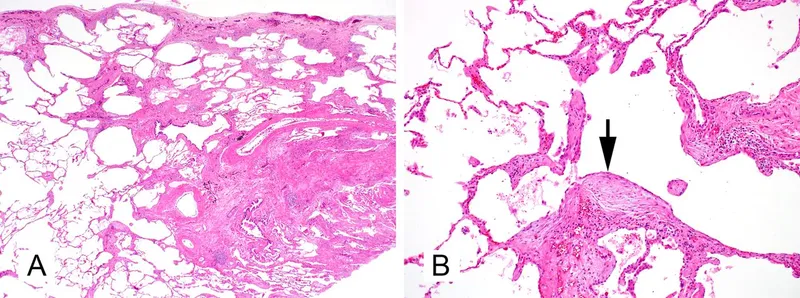
- The patient's presentation with **dyspnea, non-productive cough, late inspiratory crackles**, and **restrictive lung disease** (normal FEV1/FVC ratio of 90% with reduced FVC of 50%) is highly suggestive of **pulmonary fibrosis**.
- **Subpleural cystic enlargement** (honeycombing) is the characteristic histological finding in advanced pulmonary fibrosis, particularly in the **usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP)** pattern seen in **idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF)**.
- The chronic, progressive nature (1-year history) and the restrictive PFT pattern make this the most likely biopsy finding.
*Arteriovenous malformations*
- These are abnormal vascular connections between arteries and veins that can cause **hypoxemia** and are typically associated with **hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Osler-Weber-Rendu disease)**.
- They do not explain the restrictive PFT pattern or the typical presentation of chronic progressive fibrosis with late inspiratory crackles.
*Linear immunofluorescence along alveolar basement membranes*
- This finding on **direct immunofluorescence** with **IgG deposition** is characteristic of **Goodpasture syndrome** (anti-GBM disease), which causes pulmonary hemorrhage and rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis.
- This condition presents with **hemoptysis** and **acute renal failure**, not chronic non-productive cough, and would show an obstructive or mixed pattern if hemorrhage were present.
*Hyaline membranes*
- **Hyaline membranes** are proteinaceous material lining alveoli seen in **acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)** or **diffuse alveolar damage (DAD)**.
- The patient's **chronic 1-year symptoms** and restrictive PFTs indicate chronic interstitial lung disease, not acute lung injury.
*Charcot-Leyden crystals*
- **Charcot-Leyden crystals** are formed from breakdown of **eosinophils** and are found in conditions with eosinophilic inflammation, such as **asthma** or **eosinophilic pneumonia**.
- While these conditions can cause cough and dyspnea, they would typically show an **obstructive pattern** (reduced FEV1/FVC) in asthma, not the restrictive pattern seen here.
Restrictive lung diseases US Medical PG Question 2: A 35-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of progressive fatigue, shortness of breath, and pain in her knees and ankles. Her temperature is 37.6°C (99.7°F). Physical examination shows mild hepatomegaly and tender, red nodules on her shins. There are purple, indurated lesions on her nose, nasolabial fold, and cheeks. A biopsy of the liver shows scattered aggregations of multinucleated giant cells with cytoplasmic inclusions and eosinophilic, needle-shaped structures arranged in a star-like pattern. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Hypereosinophilic syndrome
- B. Hemochromatosis
- C. Sarcoidosis (Correct Answer)
- D. Serum sickness
- E. Systemic lupus erythematosus
Restrictive lung diseases Explanation: ***Sarcoidosis***
- The constellation of **fatigue**, **dyspnea**, **polyarthritis**, **hepatomegaly**, **erythema nodosum** (tender, red nodules on shins), and facial lesions consistent with **lupus pernio** (purple, indurated lesions on nose, nasolabial fold, and cheeks) strongly points to multisystem involvement characteristic of sarcoidosis.
- The liver biopsy findings of **scattered aggregations of multinucleated giant cells with cytoplasmic inclusions** and **eosinophilic, needle-shaped structures arranged in a star-like pattern** describes **non-caseating granulomas** with **asteroid bodies** and **Schaumann bodies**, which are pathognomonic for sarcoidosis.
*Hypereosinophilic syndrome*
- This syndrome is characterized by **persistent eosinophilia** (>1.5 x 10^9/L for >6 months) and organ damage due to eosinophil infiltration, but the biopsy findings and specific skin lesions presented are not typical.
- While it can affect multiple organs, including the skin and heart, it would not typically present with the described granulomatous features or lupus pernio.
*Hemochromatosis*
- Hemochromatosis is an **iron overload disorder** leading to iron deposition in various organs, causing fatigue, arthralgia, and hepatomegaly, but the skin lesions described and the specific biopsy findings of granulomas are not characteristic.
- The classic skin presentation in hemochromatosis is generally a **bronze pigmentation**, not the nodular lesions or lupus pernio described.
*Serum sickness*
- Serum sickness is a **Type III hypersensitivity reaction** typically manifesting with fever, rash (often urticarial), arthralgia, and lymphadenopathy, usually arising 7-14 days after exposure to certain agents (e.g., antitoxins, medications).
- It does not cause the specific granulomatous liver changes or chronic skin lesions like erythema nodosum or lupus pernio seen in this patient.
*Systemic lupus erythematosus*
- SLE is a **multisystem autoimmune disease** that can present with fatigue, arthralgia, and skin manifestations, but the classical skin lesions are often malar rash or discoid lupus, and the liver biopsy findings of non-caseating granulomas are not typical.
- While lupus can affect the liver, it usually manifests as autoimmune hepatitis or fatty liver, not the specific granulomatous pathology seen here.
Restrictive lung diseases US Medical PG Question 3: A 60-year-old woman presents to the clinic with a 3-month history of shortness of breath that worsens on exertion. She also complains of chronic cough that has lasted for 10 years. Her symptoms are worsened even with light activities like climbing up a flight of stairs. She denies any weight loss, lightheadedness, or fever. Her medical history is significant for hypertension, for which she takes amlodipine daily. She has a 70-pack-year history of cigarette smoking and drinks 3–4 alcoholic beverages per week. Her blood pressure today is 128/84 mm Hg. A chest X-ray shows flattening of the diaphragm bilaterally. Physical examination is notable for coarse wheezing bilaterally. Which of the following is likely to be seen with pulmonary function testing?
- A. Decreased FEV1: FVC and decreased total lung capacity
- B. Normal FEV1: FVC and decreased total lung capacity
- C. Increased FEV1: FVC and decreased total lung capacity
- D. Decreased FEV1: FVC and increased total lung capacity (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased FEV1: FVC and normal total lung capacity
Restrictive lung diseases Explanation: ***Decreased FEV1:FVC ratio and increased total lung capacity***
- This patient's symptoms (shortness of breath on exertion, chronic cough, 70-pack-year smoking history, coarse wheezing, and diaphragmatic flattening on X-ray) are highly suggestive of **Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)**, specifically **emphysema**, an obstructive lung disease.
- In COPD, there is airflow limitation, causing a **decreased FEV1:FVC ratio** (typically <0.70). Over time, air trapping occurs due to damaged alveoli and loss of elastic recoil, leading to an **increased total lung capacity (TLC)** and residual volume.
*Decreased FEV1:FVC ratio and decreased total lung capacity*
- A **decreased FEV1:FVC ratio** indicates an **obstructive lung disease**.
- However, a **decreased total lung capacity (TLC)** is characteristic of a **restrictive lung disease**, which does not align with the patient's presentation typical of COPD/emphysema.
*Normal FEV1:FVC ratio and decreased total lung capacity*
- A **normal FEV1:FVC ratio** is inconsistent with the patient's strong history of smoking and symptoms suggestive of airflow obstruction.
- A **decreased total lung capacity (TLC)** indicates a restrictive lung disease, which is not the primary diagnosis here.
*Increased FEV1:FVC ratio and decreased total lung capacity*
- An **increased FEV1:FVC ratio** is not physiologically possible in significant lung disease and is therefore incorrect.
- A **decreased total lung capacity (TLC)** would point towards a restrictive pattern not seen in generalized emphysema.
*Increased FEV1:FVC ratio and normal total lung capacity*
- An **increased FEV1:FVC ratio** is not a characteristic finding in any lung disease and is therefore incorrect.
- A **normal total lung capacity** would not be expected in advanced emphysema where air trapping is prominent.
Restrictive lung diseases US Medical PG Question 4: A 60-year-old man presents with breathlessness for the past 3 months. His symptoms have been getting progressively worse during this time. He denies any history of cough, fever, or chest pain. He works at a local shipyard and is responsible for installing the plumbing aboard the vessels. His past medical history is significant for hypertension for which he takes metoprolol every day. He denies smoking and any illicit drug use. His pulse is 74/min, respiratory rate is 14/min, blood pressure is 130/76 mm Hg, and temperature is 36.8°C (98.2°F). Physical examination is significant for fine bibasilar crackles at the end of inspiration without digital clubbing. Which of the following additional findings would most likely be present in this patient?
- A. Increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure
- B. Increased residual lung volume
- C. Reduced FEV1/FVC ratio
- D. Decreased diffusing capacity of CO (Correct Answer)
- E. Decreased pulmonary arterial pressure
Restrictive lung diseases Explanation: ***Decreased diffusing capacity of CO***
- This patient's occupation at a **shipyard**, progressive dyspnea, and bibasilar crackles without clubbing, along with normal vital signs, are highly suggestive of **asbestosis**, a type of **interstitial lung disease (ILD)**.
- ILDs cause **fibrosis of the alveolar-capillary membrane**, leading to impaired gas exchange and a characteristic **reduction in DLCO (diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide)**. This is a hallmark of parenchymal lung disease.
*Increased pulmonary capillary wedge pressure*
- An elevated **pulmonary capillary wedge pressure (PCWP)** indicates **left-sided heart failure** or **pulmonary venous hypertension**.
- While dyspnea can be a symptom of heart failure, the patient's normal blood pressure and absence of cardiac-specific symptoms or signs point away from primary cardiac pathology.
*Increased residual lung volume*
- **Increased residual lung volume** is a characteristic finding in **obstructive lung diseases** such as **COPD** and **asthma**, where there is air trapping due to airflow limitation.
- The patient's presentation with progressive dyspnea and bibasilar crackles is more consistent with a **restrictive lung disorder** like asbestosis, which typically causes **decreased lung volumes**.
*Reduced FEV1/FVC ratio*
- A **reduced FEV1/FVC ratio** is the hallmark of **obstructive lung diseases**, indicating airflow limitation.
- In **restrictive lung diseases** like asbestosis, both FEV1 and FVC are typically reduced proportionally, often resulting in a **normal or even increased FEV1/FVC ratio**.
*Decreased pulmonary arterial pressure*
- **Pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP)** is typically **normal or increased** in patients with interstitial lung disease due to **hypoxic vasoconstriction** and vascular remodeling.
- A decreased PAP would be an unusual and atypical finding in such a patient and is not associated with this clinical picture.
Restrictive lung diseases US Medical PG Question 5: A 68-year-old man presents to the office with progressive shortness of breath and cough. A chest X-ray shows prominent hilar lymph nodes and scattered nodular infiltrates. Biopsy of the latter reveals noncaseating granulomas. This patient most likely has a history of exposure to which of the following?
- A. Asbestos
- B. Silica
- C. Coal dust
- D. Beryllium (Correct Answer)
- E. Organic dust
Restrictive lung diseases Explanation: ***Beryllium***
- **Chronic beryllium disease** (CBD) is characterized by **noncaseating granulomas** in the lungs, similar to sarcoidosis, and is associated with occupational exposure to beryllium.
- Exposure typically occurs in workers involved in aerospace, ceramics, and electronics manufacturing.
*Asbestos*
- Exposure to **asbestos** is primarily associated with **asbestosis**, which features diffuse interstitial fibrosis, and an increased risk of mesothelioma and lung cancer.
- While it causes lung disease, it does not typically present with noncaseating granulomas as the primary pathological finding.
*Silica*
- **Silicosis** results from inhaling **crystalline silica** and is characterized by nodular opacities, often with “egg-shell” calcifications in hilar lymph nodes, and fibrotic nodules, but not noncaseating granulomas.
- The granulomas in silicosis are typically fibrotic and hyalinized, lacking the noncaseating appearance.
*Coal dust*
- Inhalation of **coal dust** leads to **coal worker's pneumoconiosis** (CWP), which can range from simple CWP with small nodular opacities to progressive massive fibrosis (PMF).
- The pathology involves **macrophage accumulation** laden with coal dust, leading to fibrosis, rather than forming noncaseating granulomas.
*Organic dust*
- Exposure to **organic dusts** (e.g., from molds, animal proteins, cotton) can lead to **hypersensitivity pneumonitis**, characterized by diffuse inflammation of the lung interstitium and airways.
- While granulomas can sometimes be seen in hypersensitivity pneumonitis, they are often poorly formed and are not the defining feature of the occupational lung disease that aligns with the described clinical picture with prominent nodular infiltrates and noncaseating granulomas, which is more characteristic of beryllium.
Restrictive lung diseases US Medical PG Question 6: A previously healthy 64-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a dry cough and progressively worsening shortness of breath for the past 2 months. She has not had fever, chills, or night sweats. She has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for the past 45 years. She appears thin. Examination of the lung shows a prolonged expiratory phase and end-expiratory wheezing. Spirometry shows decreased FEV1:FVC ratio (< 70% predicted), decreased FEV1, and a total lung capacity of 125% of predicted. The diffusion capacity of the lung (DLCO) is decreased. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Bronchiectasis
- B. Interstitial lung disease
- C. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (Correct Answer)
- D. Hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- E. Bronchial asthma
Restrictive lung diseases Explanation: ***Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease***
- The patient's long history of **smoking (45 pack-years)**, **prolonged expiratory phase**, and **end-expiratory wheezing** are classic signs of airway obstruction.
- Spirometry findings of a **decreased FEV1:FVC ratio** (< 70% predicted), **decreased FEV1**, **increased total lung capacity (TLC)**, and **decreased DLCO** are all highly indicative of **emphysema**, a subtype of COPD.
*Bronchiectasis*
- While it shares symptoms like cough and SOB, **bronchiectasis** is characterized by permanent **dilatation of bronchi** and profuse, chronic **sputum production**, which is not mentioned here.
- Spirometry typically shows **obstructive patterns**, but the marked increase in TLC and decreased DLCO are more specific to emphysema.
*Interstitial lung disease*
- This condition primarily causes a **restrictive lung pattern**, meaning a decreased TLC and normal or increased FEV1:FVC ratio.
- The patient's **increased TLC** and **obstructive spirometry** rule out a purely restrictive process.
*Hypersensitivity pneumonitis*
- This is an inflammatory response to inhaled antigens, often presenting with **recurrent episodes** of fever, chills, and cough, and can lead to restrictive physiology.
- The patient lacks a history of specific **antigen exposure** and presents with an obstructive pattern and increased TLC.
*Bronchial asthma*
- While asthma shares obstructive features like wheezing and a decreased FEV1:FVC ratio, it is characterized by **reversibility** of airway obstruction and typically does not cause a significantly **elevated TLC** or **decreased DLCO** in uncomplicated cases.
- The patient's long smoking history points away from asthma as the primary diagnosis.
Restrictive lung diseases US Medical PG Question 7: A 41-year-old woman presents to urgent care with complaints of a new rash. On review of systems, she endorses ankle pain bilaterally. Otherwise, she has no additional localized complaints. Physical examination reveals numerous red subcutaneous nodules overlying her shins, bilaterally. Complete blood count shows leukocytes 7,300, Hct 42.0%, Hgb 14.0 g/dL, mean corpuscular volume (MCV) 88 fL, and platelets 209. Chest radiography demonstrates bilateral hilar adenopathy with clear lungs. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Yersiniosis
- B. Coccidioidomycosis
- C. Histoplasmosis
- D. Chlamydophila pneumoniae
- E. Sarcoidosis (Correct Answer)
Restrictive lung diseases Explanation: ***Sarcoidosis***
- The combination of **erythema nodosum** (red subcutaneous nodules on shins), **bilateral hilar adenopathy**, and **ankle arthralgia** (ankle pain) in a young woman is highly characteristic of **Lofgren's syndrome**, a common acute presentation of sarcoidosis.
- While other conditions can cause hilar adenopathy or erythema nodosum, the triad presented makes sarcoidosis the most likely diagnosis.
*Yersiniosis*
- Can cause **erythema nodosum** and arthralgia, but **bilateral hilar adenopathy** is not a typical feature of *Yersinia* infection.
- Often associated with **gastrointestinal symptoms** (e.g., diarrhea) which are not mentioned here.
*Coccidioidomycosis*
- Can cause **erythema nodosum** and affect the lungs, but typically presents with **pulmonary infiltrates** or **nodules**, not just isolated bilateral hilar adenopathy.
- Endemic to specific geographic regions (e.g., southwestern US), which is not specified but relevant for exposure.
*Histoplasmosis*
- Can cause **hilar adenopathy** and **erythema nodosum**, especially in acute disseminated forms.
- However, it's more common in individuals exposed to **bird or bat droppings** (Ohio and Mississippi River valleys), and a fungal infection would likely present with more systemic symptoms or specific lung findings beyond just hilar adenopathy.
*Chlamydophila pneumoniae*
- This atypical bacterial infection can cause respiratory symptoms and, rarely, reactive arthritis or erythema nodosum.
- However, **bilateral hilar adenopathy** is not a typical prominent feature of *Chlamydophila pneumoniae* infection.
Restrictive lung diseases US Medical PG Question 8: A 49-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 4-month history of a dry cough and shortness of breath on exertion. She also reports recurrent episodes of pain, stiffness, and swelling in her wrist and her left knee over the past 6 months. She had two miscarriages at age 24 and 28. Physical examination shows pallor, ulcerations on the palate, and annular hyperpigmented plaques on the arms and neck. Fine inspiratory crackles are heard over bilateral lower lung fields on auscultation. Which of the following additional findings is most likely in this patient?
- A. Increased airway resistance
- B. Decreased A-a gradient
- C. Decreased right atrial pressure
- D. Decreased diffusing capacity (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased lung compliance
Restrictive lung diseases Explanation: ***Decreased diffusing capacity***
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)**, including recurrent miscarriages, joint pain, oral ulcers, skin lesions (annular hyperpigmented plaques), and pulmonary involvement (dry cough, dyspnea, crackles).
- **Interstitial lung disease (ILD)**, a common pulmonary manifestation of SLE, leads to **fibrosis** of the alveolar-capillary membrane, thereby **decreasing the diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO)**.
*Increased airway resistance*
- Increased airway resistance is characteristic of **obstructive lung diseases** like asthma or COPD, which primarily involve narrowing of the airways.
- The patient's presentation with **inspiratory crackles** and symptoms of restrictive disease (shortness of breath on exertion, dry cough) is not consistent with increased airway resistance.
*Decreased A-a gradient*
- A **decreased alveolar-arterial (A-a) gradient** indicates efficient gas exchange and is typically seen in healthy individuals or in conditions causing hypoventilation without intrinsic lung disease.
- In conditions like pulmonary fibrosis or ILD, there is impaired gas exchange leading to an **increased A-a gradient**.
*Decreased right atrial pressure*
- **Decreased right atrial pressure** would typically signify reduced venous return or normal cardiac function.
- Given the patient's respiratory symptoms and potential for pulmonary hypertension secondary to ILD, an **increased right atrial pressure** would be more likely due to increased pulmonary vascular resistance.
*Increased lung compliance*
- **Increased lung compliance** is seen in conditions where the lung tissue becomes more distensible, such as **emphysema**, due to destruction of elastic fibers.
- **Interstitial lung disease** and pulmonary fibrosis, as suggested by the patient's symptoms and signs, lead to **decreased lung compliance** due to stiffening of the lung tissue.
Restrictive lung diseases US Medical PG Question 9: A 62-year-old man presents to the emergency department for evaluation of a 2-year history of increasing shortness of breath. He also has an occasional nonproductive cough. The symptoms get worse with exertion. The medical history is significant for hypertension and he takes chlorthalidone. He is a smoker with a 40-pack-year smoking history. On physical examination, the patient is afebrile; the vital signs include: blood pressure 125/78 mm Hg, pulse 90/min, and respiratory rate 18/min. The body mass index (BMI) is 31 kg/m2. The oxygen saturation is 94% at rest on room air. A pulmonary examination reveals decreased breath sounds bilaterally, but is otherwise normal with no wheezes or crackles. The remainder of the examination is unremarkable. A chest radiograph shows hyperinflation of both lungs with mildly increased lung markings, but no focal findings. Based on this clinical presentation, which of the following is most likely?
- A. Decreased total lung capacity
- B. Increased DLCO
- C. Metabolic acidosis
- D. FEV1/FVC of 80% with an FEV1 of 82%
- E. FEV1/FVC of 65% (Correct Answer)
Restrictive lung diseases Explanation: ***FEV1/FVC of 65%***
- This patient's symptoms (shortness of breath, nonproductive cough, worsening with exertion), significant smoking history (40-pack-years), and chest X-ray findings (**hyperinflation**, mildly increased lung markings) are highly suggestive of **Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)**, particularly **emphysema** given the hyperinflation and decreased breath sounds.
- COPD is characterized by **airflow limitation** that is not fully reversible, which is reflected by a **reduced FEV1/FVC ratio** (typically < 0.7 or < 70%).
*Decreased total lung capacity*
- **Decreased total lung capacity (TLC)** is characteristic of **restrictive lung diseases**, where lung expansion is limited (e.g., pulmonary fibrosis, interstitial lung disease).
- COPD, and especially emphysema, typically presents with **increased TLC** due to air trapping and hyperinflation, not decreased TLC.
*Increased DLCO*
- **Increased DLCO** (diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide) can be seen in conditions like **pulmonary hemorrhage** or **asthma**.
- In COPD, particularly emphysema, there is destruction of alveolar-capillary membranes, leading to a **decreased DLCO** due to impaired gas exchange.
*Metabolic acidosis*
- **Metabolic acidosis** is not a primary or direct feature of uncomplicated COPD. While severe respiratory failure in later stages might lead to some acid-base disturbances, directly attributing metabolic acidosis as a defining characteristic is incorrect.
- COPD primarily causes **respiratory acidosis** due to CO2 retention in advanced stages.
*FEV1/FVC of 80% with an FEV1 of 82%*
- An **FEV1/FVC ratio of 80%** (or 0.8) and an **FEV1 of 82%** of predicted values are within the normal range and indicate **normal spirometry**.
- This would rule out significant airflow obstruction, which is central to the diagnosis of COPD.
Restrictive lung diseases US Medical PG Question 10: A 31 year-old African-American female presents with painful shin nodules, uveitis, and calcified hilar lymph nodes. A transbronchial biopsy of the lung would most likely show which of the following histologies?
- A. Golden-brown fusiform rods
- B. Inflammation, fibrosis and cyst formation that is most prominent in subpleural regions
- C. Non-caseating granulomas (Correct Answer)
- D. Silica particles (birefringent) surrounded by collagen
- E. Patchy interstitial lymphoid infiltrate into walls of alveolar units
Restrictive lung diseases Explanation: ***Non-caseating granulomas***
- The constellation of **erythema nodosum** (painful shin nodules), **uveitis**, and **hilar lymphadenopathy** in an African-American female is highly characteristic of **sarcoidosis**.
- **Sarcoidosis** is pathologically defined by the presence of **non-caseating granulomas** in affected tissues, which would be visible on a transbronchial biopsy.
*Golden-brown fusiform rods*
- These are **ferruginous bodies**, characteristic of **asbestosis**, which is not supported by the patient's presentation.
- Asbestosis would typically involve a history of **asbestos exposure** and present with **pleural plaques** or **interstitial fibrosis**.
*Inflammation, fibrosis and cyst formation that is most prominent in subpleural regions*
- This description is more indicative of **pulmonary Langerhans cell histiocytosis**, a rare disease usually associated with **smoking**.
- It does not align with the patient's specific systemic manifestations like uveitis or erythema nodosum.
*Silica particles (birefringent) surrounded by collagen*
- This describes the histological findings of **silicosis**, an occupational lung disease resulting from exposure to **silica dust**.
- Silicosis is not typically associated with uveitis or erythema nodosum.
*Patchy interstitial lymphoid infiltrate into walls of alveolar units*
- This pattern can be seen in various interstitial lung diseases, but it is not specific for sarcoidosis.
- It could be found in conditions like **lymphoid interstitial pneumonia**, which does not fit the overall clinical picture.
More Restrictive lung diseases US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.