Neurodegenerative diseases US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Neurodegenerative diseases. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
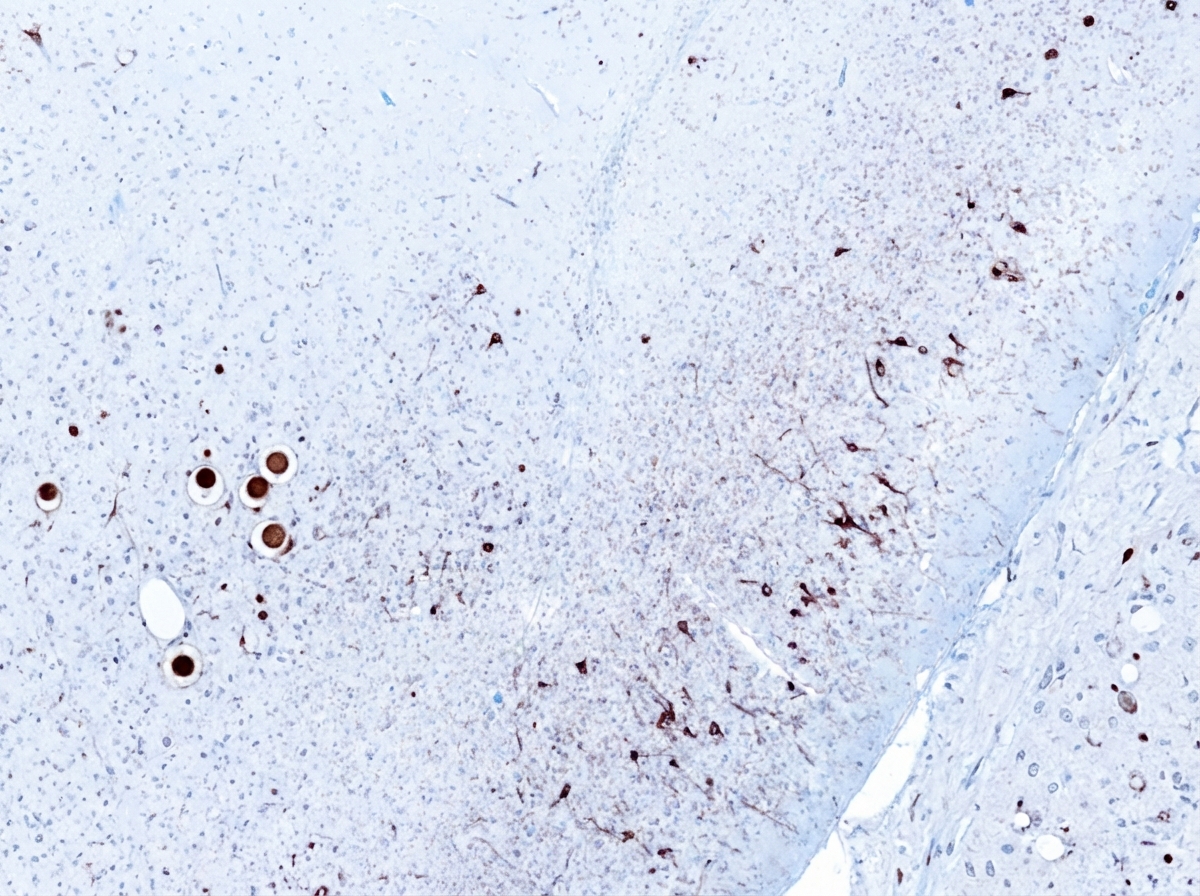
Neurodegenerative diseases US Medical PG Question 1: An 81-year-old man is brought to the physician by his daughter after he was found wandering on the street. For the last 3 months, he often has a blank stare for several minutes. He also claims to have seen strangers in the house on several occasions who were not present. He has hypertension and hyperlipidemia, and was diagnosed with Parkinson disease 8 months ago. His current medications include carbidopa-levodopa, hydrochlorothiazide, and atorvastatin. His blood pressure is 150/85 mm Hg. He has short-term memory deficits and appears confused and disheveled. Examination shows bilateral muscle rigidity and resting tremor in his upper extremities. He has a slow gait with short steps. Microscopic examination of the cortex of a patient with the same condition is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Vascular dementia
- B. Lewy body dementia (Correct Answer)
- C. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- D. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
- E. Frontotemporal dementia
Neurodegenerative diseases Explanation: ***Lewy body dementia***
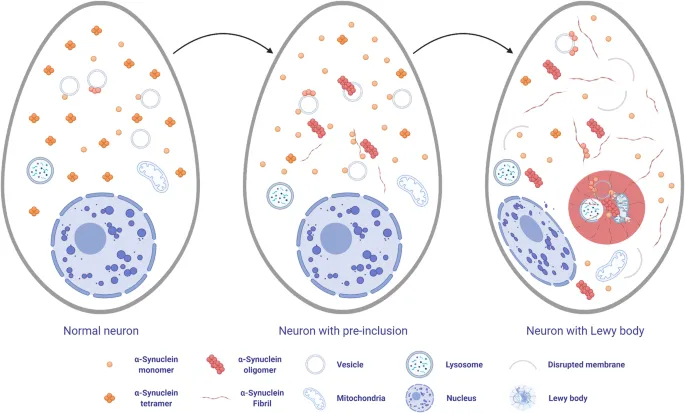
- This patient presents with a classic triad of **dementia**, **Parkinsonism** (rigidity, tremor, slow gait), and **fluctuating cognition** (blank stares, confusion) with **visual hallucinations** (seeing strangers).
- The presence of **Lewy bodies** in the cortex (**alpha-synuclein** aggregates) on microscopic examination is pathognomonic for Lewy body dementia, which can manifest as dementia with Lewy bodies or Parkinson's disease dementia.
*Vascular dementia*
- Characterized by **stepwise cognitive decline** and focal neurological deficits, often with a history of stroke or significant vascular risk factors, although hypertension and hyperlipidemia are present, they do not explain the visual hallucinations or prominent Parkinsonism.
- While memory deficits can occur, the prominent motor symptoms, fluctuating cognition, and visual hallucinations are not typical features differentiating it from Lewy body dementia.
*Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease*
- This rapidly progressive dementia is associated with **myoclonus**, ataxia, and other neurological signs, but generally progresses much faster than described here.
- The **pathology involves spongiform changes** in the brain, not Lewy bodies.
*Normal pressure hydrocephalus*
- Classic triad includes **gait disturbance**, **urinary incontinence**, and **dementia**, often responsive to shunting.
- While gait disturbance is present, the prominent visual hallucinations, fluctuating cognition, and rigidity are not characteristic.
*Frontotemporal dementia*
- Primarily affects personality, behavior, and language, with relative sparing of memory in early stages.
- It does not typically present with the prominent **Parkinsonian features** and **visual hallucinations** seen in this patient.
Neurodegenerative diseases US Medical PG Question 2: An 80-year-old woman is brought to the physician by her 2 daughters for worsening memory loss. They report that their mother is increasingly forgetful about recent conversations and events. She is unable to remember her appointments and commitments she has made. 3 years ago, the patient was moved into an elder care facility because she was often getting lost on her way home and forgetting to take her medications. The patient reports that she is very socially active at her new home and has long conversations with the other residents about her adventures as an air hostess during her youth. Which of the following cerebral pathologies is most likely present in this patient?
- A. Lewy bodies
- B. Lacunar infarcts
- C. Intracytoplasmic vacuoles
- D. Neurofibrillary tangles (Correct Answer)
- E. Demyelination
Neurodegenerative diseases Explanation: ***Neurofibrillary tangles***
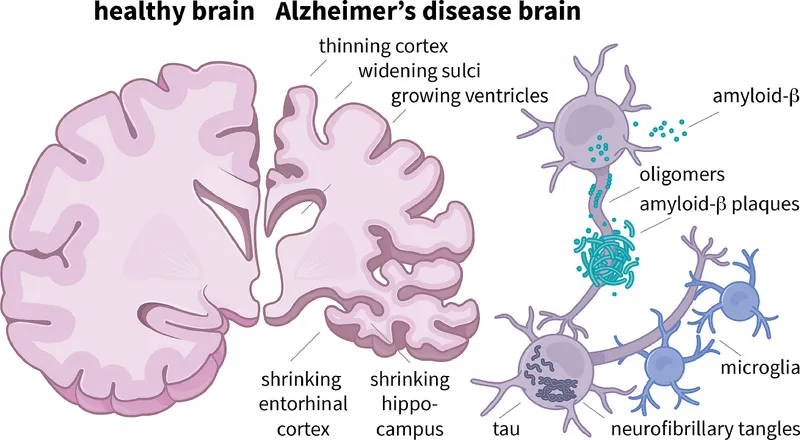
- The patient's presentation with **progressive memory loss** affecting recent events, getting lost, and forgetting medications, while largely preserving long-term memory (recalling youth as an air hostess and engaging in conversations), is highly characteristic of **Alzheimer's disease**.
- **Neurofibrillary tangles**, composed of hyperphosphorylated tau protein, along with **amyloid plaques**, are the hallmark pathological findings in Alzheimer's disease.
*Lewy bodies*
- **Lewy bodies** are characteristic of **Lewy body dementia** or Parkinson's disease with dementia, which typically present with prominent **fluctuations in cognition**, recurrent **visual hallucinations**, and parkinsonism.
- While memory loss can occur, the dominant features in this case point away from Lewy body pathology.
*Lacunar infarcts*
- **Lacunar infarcts** are associated with **vascular dementia**, which often presents with a more **step-wise decline** in cognitive function, focal neurological deficits, and evidence of cerebrovascular disease on imaging.
- The patient's gradual and progressive memory loss is less typical of lacunar infarcts as the primary cause.
*Intracytoplasmic vacuoles*
- **Intracytoplasmic vacuoles** are characteristic of **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease** (spongiform encephalopathy), which is a rapidly progressive and fatal neurodegenerative disorder with distinct neurological symptoms such as myoclonus and ataxia, not fitting this patient's profile.
- The disease course is typically much faster than the 3-year progression described.
*Demyelination*
- **Demyelination** is the hallmark of conditions like **multiple sclerosis**, which primarily affects younger individuals and typically presents with a range of neurological deficits, including motor, sensory, and visual disturbances, that often relapse and remit.
- It does not typically present as a primary, progressive memory disorder in an 80-year-old in this manner.
Neurodegenerative diseases US Medical PG Question 3: A 70-year-old woman is brought to the office after her nurse noticed her being apathetic, easily distracted, and starting to urinate in bed. Her medical history is relevant for hypertension, under control with medication. Physical examination reveals a blood pressure of 138/76 mm Hg, a heart rate of 70/min, and a respiratory rate 14/min and regular. On neurological examination, she has a broad-based shuffling gait, and increased muscle tone in her limbs that is reduced by distracting the patient. There is decreased coordination with exaggerated deep tendon reflexes, decreased attention and concentration, and postural tremor. Which of the following additional features would be expected to find in this patient?
- A. Degeneration of the substantia nigra pars compacta
- B. Caudate head atrophy
- C. Accumulation of Lewy bodies in cortical cells
- D. Dilation of the ventricular system (Correct Answer)
- E. Accumulation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the cerebral cortex
Neurodegenerative diseases Explanation: ***Dilation of the ventricular system***
- The patient presents with a classic triad of **gait apraxia** (broad-based, shuffling gait), **dementia** (apathy, distractibility, decreased attention and concentration), and **urinary incontinence**, which are the hallmark symptoms of **Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus (NPH)**. NPH is characterized by **ventricular dilation without increased intracranial pressure**.
- Other features like **increased muscle tone that reduces with distraction** (frontal release sign), **exaggerated deep tendon reflexes**, and **postural tremor** further support the diagnosis of NPH, as these are often seen due to involvement of frontal lobe pathways secondary to ventricular enlargement.
*Degeneration of the substantia nigra pars compacta*
- This is characteristic of **Parkinson's disease**, which typically presents with a rest tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability, but not typically with prominent early dementia and urinary incontinence in this combined clinical picture.
- While Parkinson's can cause gait disturbance, the specific combination of symptoms (dementia, incontinence, and gait apraxia) points away from primary Parkinson's as the most likely diagnosis.
*Caudate head atrophy*
- **Caudate head atrophy** is a hallmark finding in **Huntington's disease**, which is characterized by chorea, psychiatric symptoms, and progressive cognitive decline.
- The patient's symptoms, particularly the broad-based shuffling gait and urinary incontinence, are inconsistent with the typical presentation of Huntington's disease.
*Accumulation of Lewy bodies in cortical cells*
- This is a pathological feature of **Lewy body dementia (LBD)**. While LBD presents with dementia and Parkinsonian features, it also typically includes **recurrent visual hallucinations** and **fluctuations in attention and alertness**, which are not specified in this patient's presentation.
- The patient's dominant features of gait apraxia and urinary incontinence along with dementia are more indicative of NPH.
*Accumulation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the cerebral cortex*
- These are the pathological hallmarks of **Alzheimer's disease**, which primarily presents with progressive memory loss, executive dysfunction, and other cognitive deficits.
- While dementia is a feature in this patient, the prominent gait disturbance and urinary incontinence are not typical early or dominant features of Alzheimer's disease.
Neurodegenerative diseases US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old man with no significant medical history begins to have memory loss and personality changes. Rapidly, over the next few months his symptoms increase in severity. He experiences a rapid mental deterioration associated with sudden, jerking movements, particularly in response to being startled. He has gait disturbances as well. Eventually, he lapses into a coma and dies approximately ten months after the onset of symptoms. Which of the following would most likely be seen on autopsy of the brain in this patient?
- A. Neurofibrillary tangles
- B. Amyloid plaques
- C. Spongiform changes (Correct Answer)
- D. Vascular lesions
- E. Lewy bodies
Neurodegenerative diseases Explanation: ***Spongiform changes***
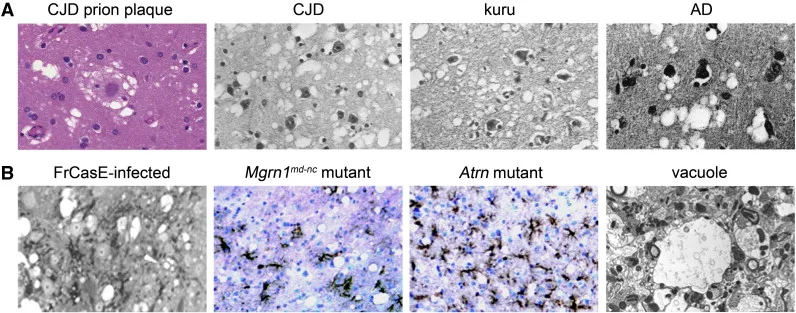
- This patient's **rapidly progressive dementia**, associated with **myoclonus (jerking movements)** and **gait disturbances**, culminating in death within months, is highly suggestive of **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)**.
- CJD is characterized by the accumulation of abnormally folded prion proteins (PrPSc), leading to **spongiform degeneration** (vacuolation) of neurons and neuropil, **neuronal loss**, and **astrogliosis** in the brain.
*Neurofibrillary tangles*
- **Neurofibrillary tangles**, composed primarily of hyperphosphorylated **tau protein**, are a hallmark of **Alzheimer's disease**.
- Alzheimer's disease typically has a much **slower progression** over several years, unlike the rapid deterioration seen in this patient.
*Amyloid plaques*
- **Amyloid plaques**, formed by the extracellular deposition of **beta-amyloid protein**, are also characteristic features of **Alzheimer's disease**.
- Like neurofibrillary tangles, amyloid plaques are associated with a chronic, progressive course of dementia, not the **rapidly fatal trajectory** described.
*Vascular lesions*
- **Vascular lesions**, such as infarcts or hemorrhages, are the underlying pathology in **vascular dementia**.
- While vascular dementia can cause cognitive decline, its presentation often involves **step-wise deterioration** and may be associated with focal neurological deficits, which are not the primary features here.
*Lewy bodies*
- **Lewy bodies**, which are intracellular cytoplasmic inclusions of **alpha-synuclein protein**, are characteristic of **Lewy body dementia** and **Parkinson's disease**.
- Lewy body dementia presents with fluctuating cognition, visual hallucinations, and parkinsonism, but typically does not show the **rapid progression** and prominent myoclonus seen in CJD.
Neurodegenerative diseases US Medical PG Question 5: An 81-year-old woman presents to your office accompanied by her husband. She has been doing well except for occasional word finding difficulty. Her husband is concerned that her memory is worsening over the past year. Recently, she got lost twice on her way home from her daughter’s house, was unable to remember her neighbor’s name, and could not pay the bills like she usually did. She has a history of hypertension and arthritis. She has no significant family history. Her medications include a daily multivitamin, hydrochlorothiazide, and ibuprofen as needed. Physical exam is unremarkable. Which of the following is associated with an increased risk of this patient’s disease?
- A. Presenilin-2
- B. ApoE2
- C. ApoE4 (Correct Answer)
- D. Female gender
- E. Advanced age (>85 years)
Neurodegenerative diseases Explanation: ***Correct: ApoE4***
- The patient's symptoms (progressive memory loss, getting lost on familiar routes, difficulty with routine tasks like paying bills) in an 81-year-old suggest **Alzheimer's disease**.
- The **ApoE4 allele** is a well-established genetic risk factor for **late-onset Alzheimer's disease**, significantly increasing the likelihood (3-fold increased risk for one allele, 12-fold for two alleles) and often lowering the age of onset.
- ApoE4 is the **most specific and discriminating risk factor** among the options provided.
*Incorrect: Presenilin-2*
- **Presenilin-2** mutations are associated with **early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease**, which typically manifests before age 65 and often has a strong family history.
- This patient is 81 years old and has no significant family history, making early-onset familial AD unlikely.
*Incorrect: ApoE2*
- The **ApoE2 allele** is actually associated with a **decreased risk** of Alzheimer's disease.
- It is thought to be protective due to its more efficient clearance of amyloid beta peptides from the brain.
*Incorrect: Female gender*
- While **female gender** is indeed a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease (women have approximately 2:1 higher lifetime risk even after adjusting for longevity), it is less specific than ApoE4 as a discriminating answer.
- All patients have a biological sex, but only some carry the ApoE4 allele, making ApoE4 a more useful clinical and epidemiological marker.
*Incorrect: Advanced age (>85 years)*
- **Advanced age** is actually the strongest non-modifiable risk factor for Alzheimer's disease, with incidence doubling every 5 years after age 65.
- However, in the context of this question, **ApoE4 is the better answer** because it represents a specific genetic risk factor that can be tested and is directly associated with disease pathogenesis, whereas advanced age is a universal demographic factor that applies to all individuals who live long enough.
Neurodegenerative diseases US Medical PG Question 6: A 68-year-old man is brought to the physician by his wife because she is concerned about his speech being irregular. Specifically, she says that over the last 8 months, her husband has been saying increasingly nonsensical statements at home. In addition, he is no longer able to perform basic verbal tasks such as ordering from a menu or giving directions even though he was an English teacher prior to retirement. She also reports that he has recently started attempting to kiss strangers and urinate in public. Finally, she has also noticed that he has been frequently binge eating sweets even though he was previously very conscientious about his health. When asked about these activities, the patient does not have insight into his symptoms. Which of the following would most likely be seen in this patient?
- A. Intracellular hyperphosphorylated tau proteins
- B. Alpha-synuclein
- C. Large intracellular vacuoles
- D. Perivascular inflammation
- E. Hyperphosphorylated tau inclusion bodies (Correct Answer)
Neurodegenerative diseases Explanation: ***Hyperphosphorylated tau inclusion bodies***
- The patient's symptoms of **disinhibition** (kissing strangers, public urination), **personality changes** (binge eating sweets), and **progressive language dysfunction** are characteristic of **frontotemporal dementia (FTD)**.
- FTD has heterogeneous pathology: approximately **40-50% of cases** involve **tau pathology** (forming Pick bodies and neurofibrillary tangles), while 50-60% show **TDP-43 pathology**.
- The term **"inclusion bodies"** specifically refers to the aggregated, pathological deposits visible microscopically, making this the most precise answer.
- Tau pathology is particularly associated with **Pick's disease**, a subtype of FTD characterized by **Pick bodies** (spherical tau inclusions).
*Intracellular hyperphosphorylated tau proteins*
- This describes the **same pathological process** as the correct answer but is **less specific**.
- While technically accurate for tau-positive FTD cases, the term lacks the specificity of "inclusion bodies," which denotes the characteristic aggregated form seen on microscopy.
- In pathology, precision matters: stating "inclusion bodies" indicates you recognize the specific morphological finding.
*Alpha-synuclein*
- **Alpha-synuclein** aggregates (Lewy bodies) are characteristic of **Lewy body dementia** and **Parkinson's disease dementia**.
- These conditions typically present with **fluctuating cognition**, **visual hallucinations**, **parkinsonism**, and **REM sleep behavior disorder**.
- The prominent behavioral disinhibition and language dysfunction without parkinsonian features point away from synucleinopathies.
*Large intracellular vacuoles*
- **Spongiform change** (vacuolation) with prion protein accumulation is pathognomonic for **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)**.
- CJD presents with **rapidly progressive dementia** (weeks to months), **myoclonus**, **ataxia**, and periodic sharp waves on EEG.
- The **gradual 8-month progression** and absence of myoclonus make prion disease unlikely.
*Perivascular inflammation*
- **Perivascular lymphocytic infiltration** indicates **inflammatory or infectious CNS disease**, such as **vasculitis** or **viral encephalitis**.
- This patient's **chronic, insidious progression** over 8 months without acute features argues against an inflammatory process.
Neurodegenerative diseases US Medical PG Question 7: A 33-year-old man presents to his physician with a 3-year history of gradually worsening tics and difficulty walking. He was last seen by the physician 5 years ago for anxiety, and he has been buying anti-anxiety medications from an internet website without a prescription as he cannot afford to pay for doctor’s visits. Now, the patient notes that his anxiety is somewhat controlled, but motor difficulties are making it difficult for him to work and socialize. Family history is unobtainable as his parents died in an accident when he was an infant. He grew up in foster care and was always a bright child. An MRI of the brain is ordered; it shows prominent atrophy of the caudate nucleus. Repeats of which of the following trinucleotides are most likely responsible for this patient’s disorder?
- A. CCG
- B. CTG
- C. CGG
- D. CAG (Correct Answer)
- E. GAA
Neurodegenerative diseases Explanation: ***CAG***
- The clinical presentation of **worsening tics**, **difficulty walking** (suggesting motor dysfunction), and the MRI finding of **caudate nucleus atrophy** are classic signs of **Huntington's disease**.
- **Huntington's disease** is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder caused by an unstable expansion of **CAG trinucleotide repeats** within the *HTT* gene.
*CCG*
- Expansions of **CCG repeats** are associated with conditions like **fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS)**.
- While FXTAS involves neurological symptoms, the specific presentation of prominent tics and caudate atrophy points more strongly to Huntington's.
*CTG*
- **CTG trinucleotide repeat** expansions are characteristic of **myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1)**.
- Myotonic dystrophy primarily manifests with muscle weakness, myotonia, and cataracts, which are not the primary presenting symptoms here.
*CGG*
- Expansions of **CGG repeats** are the genetic basis of **Fragile X syndrome**, the most common inherited cause of intellectual disability.
- While Fragile X syndrome can have neurological features, it typically presents with developmental delay and distinctive physical features, rather than adult-onset tics and caudate atrophy.
*GAA*
- An expansion of **GAA trinucleotide repeats** is responsible for **Friedreich's ataxia**.
- Friedreich's ataxia is characterized by progressive ataxia, dysarthria, and loss of proprioception, which differ from the motor tics and specific caudate atrophy seen in this patient.
Neurodegenerative diseases US Medical PG Question 8: A 52-year-old man presents with 2 months of diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fatigue. He reports a weight loss of 4 kg (8 lb). He also says his joints have been hurting recently, as well. Past medical history is unremarkable. Review of systems is significant for problems with concentration and memory. Physical examination is unremarkable. A GI endoscopy is performed with a biopsy of the small bowel. Which of the following histologic finding would most likely be seen in this patient?
- A. PAS positive macrophages (Correct Answer)
- B. Non-caseating granulomas in the small intestine
- C. Absence of nerves in the myenteric plexus
- D. Blunting of the villi
- E. Crypt hyperplasia with increased intraepithelial lymphocytes
Neurodegenerative diseases Explanation: **PAS positive macrophages**
- The clinical presentation with **diarrhea**, abdominal pain, weight loss, joint pain, and **neurological symptoms** (problems with concentration and memory) is classic for **Whipple's disease**.
- **Whipple's disease** is caused by the bacterium **Tropheryma whipplei**, which is characterized histologically by **foamy macrophages** in the lamina propria that stain **positive with Periodic Acid-Schiff (PAS)** due to undigested bacterial cell wall material.
*Non-caseating granulomas in the small intestine*
- **Non-caseating granulomas** are characteristic of **Crohn's disease**, which typically presents with abdominal pain, diarrhea, and weight loss, but **neurological symptoms** are not a primary feature.
- While Crohn's disease can cause joint pain (arthritis), the combination of GI and neurological symptoms points away from it.
*Absence of nerves in the myenteric plexus*
- An **absence of nerves in the myenteric plexus** is the hallmark of **Hirschsprung's disease**, which is a congenital disorder primarily affecting neonates and infants, causing intestinal obstruction and chronic constipation.
- This finding is inconsistent with the patient's age and presenting symptoms of diarrhea and neurological issues.
*Blunting of the villi*
- **Villi blunting** is characteristic of **celiac disease** (gluten-sensitive enteropathy), which presents with malabsorption symptoms like diarrhea, weight loss, and abdominal pain.
- However, **celiac disease** typically does not involve **neurological symptoms** like concentration and memory problems as a prominent feature, and the PAS-positive macrophages are specific to Whipple's.
*Crypt hyperplasia with increased intraepithelial lymphocytes*
- **Crypt hyperplasia** and **increased intraepithelial lymphocytes (IELs)** are seen in various small bowel pathologies, including **celiac disease** and **microscopic colitis**.
- While these findings suggest intestinal inflammation, they are not specific to **Whipple's disease** and do not account for the characteristic neurological involvement.
Neurodegenerative diseases US Medical PG Question 9: A 35-year-old woman presents with headaches and seizures. MRI shows a well-circumscribed, calcified frontal lobe mass. Histology reveals oligodendroglioma with 1p/19q codeletion and IDH1 mutation. She undergoes gross total resection. Two years later, surveillance MRI shows a new enhancing nodule at the resection margin. Biopsy shows increased mitotic activity, microvascular proliferation, and retained 1p/19q codeletion but new CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion. What is the most critical factor in determining management strategy?
- A. The tumor has progressed to anaplastic oligodendroglioma requiring combined chemoradiation with temozolomide and RT
- B. CDKN2A/B deletion indicates transformation to glioblastoma requiring maximal therapy
- C. Retained 1p/19q codeletion predicts continued chemosensitivity to PCV regimen (Correct Answer)
- D. Loss of IDH1 mutation suggests new primary tumor requiring re-resection only
- E. Microvascular proliferation mandates anti-angiogenic therapy with bevacizumab
Neurodegenerative diseases Explanation: ***Retained 1p/19q codeletion predicts continued chemosensitivity to PCV regimen***
- The preservation of **1p/19q codeletion** in a recurrent tumor is the strongest predictor of clinical response to alkylating chemotherapy, specifically the **PCV (Procarbazine, Lomustine, Vincristine)** regimen.
- While the tumor shows histological progression, the underlying molecular subtype remains an **oligodendroglioma**, which generally carries a better prognosis and higher chemosensitivity than non-codeleted gliomas.
*The tumor has progressed to anaplastic oligodendroglioma requiring combined chemoradiation with temozolomide and RT*
- While the histology suggests a higher grade, the standard of care for 1p/19q codeleted tumors frequently favors **PCV** over **Temozolomide** due to more robust long-term survival data from clinical trials like RTOG 9402.
- Grading alone does not dictate management as much as the **molecular profile** does in modern neuro-oncology guidelines.
*CDKN2A/B deletion indicates transformation to glioblastoma requiring maximal therapy*
- Under the current WHO classification, **glioblastoma** is defined as an **IDH-wildtype** tumor; since this tumor has an **IDH1 mutation**, it cannot be classified as a glioblastoma.
- **CDKN2A/B homozygous deletion** is a marker of high-grade malignancy (WHO Grade 4) in IDH-mutant astrocytomas, but its presence in an **oligodendroglioma** does not change the lineage-defining 1p/19q status.
*Loss of IDH1 mutation suggests new primary tumor requiring re-resection only*
- **IDH1 mutations** are early, trunk events in gliomagenesis and are almost never
Neurodegenerative diseases US Medical PG Question 10: A 55-year-old man presents with progressive supranuclear gaze palsy, axial rigidity, and frequent falls. MRI shows midbrain atrophy with hummingbird sign. He dies 7 years later. Autopsy reveals globose neurofibrillary tangles in the basal ganglia and brainstem. Tau immunostaining shows 4-repeat tau predominance. His brother had similar symptoms. Genetic testing reveals a MAPT mutation. How does this change the pathogenic understanding and potential therapeutic approach?
- A. It suggests prion-like propagation requiring anti-aggregation compounds
- B. It demonstrates autoimmune etiology requiring immunosuppression
- C. It reveals mitochondrial dysfunction requiring coenzyme Q10 supplementation
- D. It confirms primary tauopathy amenable to tau-directed antisense oligonucleotide therapy (Correct Answer)
- E. It indicates concurrent alpha-synuclein pathology requiring dual-target therapy
Neurodegenerative diseases Explanation: ***It confirms primary tauopathy amenable to tau-directed antisense oligonucleotide therapy***
- The presence of **MAPT mutations** and **4-repeat (4R) tau** predominance confirms that tau dysfunction is the primary driver of the neurodegenerative process in this **Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP)** phenotype.
- Targeting the underlying genetic cause with **antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs)** can reduce the expression of toxic tau protein, offering a disease-modifying approach rather than just symptomatic relief.
*It suggests prion-like propagation requiring anti-aggregation compounds*
- While **prion-like seeding** occurs in tauopathies, the discovery of a **MAPT mutation** specifically points to a genetic production error rather than isolated misfolding propagation.
- **Anti-aggregation compounds** are a general strategy, but they do not address the primary genetic driver identified by the mutation in this specific case.
*It demonstrates autoimmune etiology requiring immunosuppression*
- **PSP** and related **tauopathies** are degenerative proteinopathies, not autoimmune conditions, and show no response to **immunosuppressive therapy**.
- The **hummingbird sign** and **globose tangles** are classic markers of protein deposition, not inflammatory-mediated demyelination or vasculitis.
*It reveals mitochondrial dysfunction requiring coenzyme Q10 supplementation*
- Although some **mitochondrial deficit** is seen in neurodegeneration, it is a downstream effect and not the primary cause identified by a **MAPT mutation**.
- **Coenzyme Q10** has failed to show significant disease-modifying efficacy in clinical trials for primary tauopathies like **PSP**.
*It indicates concurrent alpha-synuclein pathology requiring dual-target therapy*
- The **MAPT mutation** and **4R tau** findings are specific to tauopathies; **alpha-synuclein** is the hallmark of synucleinopathies like **Parkinson’s disease** or **Multiple System Atrophy (MSA)**.
- Clinical features like the **hummingbird sign** (midbrain atrophy) and **axial rigidity** without resting tremors strongly favor a pure tau pathology over a dual-pathology state.
More Neurodegenerative diseases US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.