Demyelinating diseases US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Demyelinating diseases. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Demyelinating diseases US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old woman presents with a 3-month history of intermittent blurred vision and problems walking. The patient states that she often feels “pins and needles” in her legs that cause her problems when she’s walking. The patient is afebrile, and her vital signs are within normal limits. An autoimmune disorder is suspected. Which of the following findings would most likely be present in this patient?
- A. Damaged myelin sheath and myelin-producing cells (Correct Answer)
- B. Absence of interneurons
- C. Destruction of blood-brain barrier
- D. Degeneration of anterior horn cells
- E. Decreased cerebrospinal fluid due to destruction of cells
Demyelinating diseases Explanation: ***Damaged myelin sheath and myelin-producing cells***
- The patient's symptoms of intermittent **blurred vision** (optic neuritis), **problems walking** (ataxia, spasticity), and **paresthesias** ("pins and needles") are classical presentations of Multiple Sclerosis (MS).
- MS is characterized by multifocal areas of inflammation and **demyelination** in the central nervous system, where the **myelin sheath** surrounding axons is damaged, and the **oligodendrocytes** (myelin-producing cells) are attacked.
- This demyelination disrupts saltatory conduction, leading to the varied and intermittent neurological symptoms.
*Absence of interneurons*
- The absence of **interneurons** is typically associated with conditions like **spinal muscular atrophy** or certain **neuropathies**, which present with different clinical features (e.g., muscle weakness, atrophy) than those described.
- While interneurons are crucial for neuronal communication, their absence doesn't explain the *intermittent* and multifocal symptoms seen in this case.
*Destruction of blood-brain barrier*
- While **blood-brain barrier (BBB) breakdown** does occur in MS, it is a *consequence* of the inflammatory process rather than the primary *pathological finding* that directly explains the neurological symptoms.
- BBB destruction allows inflammatory cells to enter the CNS, contributing to demyelination, but the core issue remains the myelin damage itself.
*Degeneration of anterior horn cells*
- **Anterior horn cell degeneration** is the hallmark of **amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)** and **spinal muscular atrophy**, presenting with progressive muscle weakness, atrophy, and fasciculations.
- These conditions lack the sensory symptoms (paresthesias) and visual disturbances seen in this patient, and typically show a progressive rather than intermittent course.
*Decreased cerebrospinal fluid due to destruction of cells*
- **Decreased CSF volume** is not a characteristic feature of MS; in fact, CSF analysis often shows increased protein and **oligoclonal bands**.
- The destruction of cells in MS primarily affects myelin and oligodendrocytes, not cells responsible for CSF production or volume regulation.
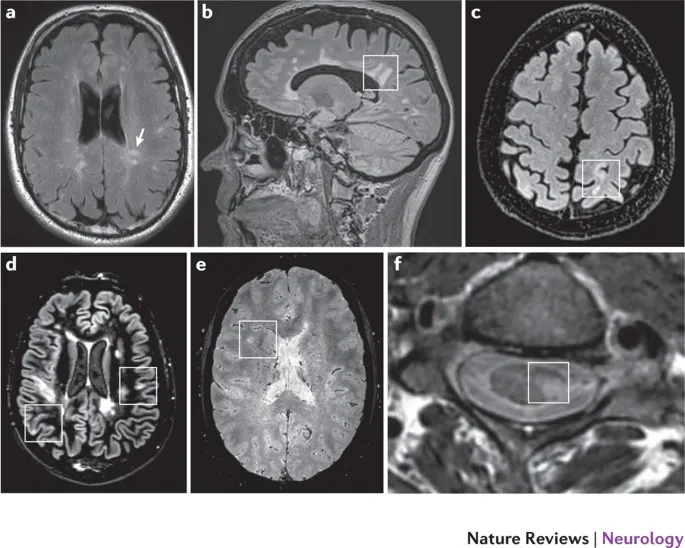
Demyelinating diseases US Medical PG Question 2: A 29-year-old woman presents with progressive vision loss in her right eye and periorbital pain for 5 days. She says that she has also noticed weakness, numbness, and tingling in her left leg. Her vital signs are within normal limits. Neurological examination shows gait imbalance, positive Babinski reflexes, bilateral spasticity, and exaggerated deep tendon reflexes in the lower extremities bilaterally. FLAIR MRI is obtained and is shown in the image. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient’s condition?
- A. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- B. Multiple sclerosis (Correct Answer)
- C. Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
- D. Lead intoxication
- E. Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL)
Demyelinating diseases Explanation: ***Multiple sclerosis***
- This patient's presentation with **optic neuritis** (vision loss, periorbital pain), disseminated neurological symptoms (**weakness, numbness, tingling in the left leg**, gait imbalance, spasticity, exaggerated DTRs, Babinski reflexes), and multifocal white matter lesions on MRI (FLAIR image would show **Dawson's fingers** or juxtacortical/infratentorial lesions) is highly characteristic of **multiple sclerosis**.
- The symptoms are **disseminated in space and time**, meaning different neurological deficits occurring at different locations in the CNS at different times, as suggested by the right eye and left leg involvement.
*Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis*
- Primarily a **motor neuron disease** affecting both upper and lower motor neurons, causing progressive muscle weakness, atrophy, and fasciculations.
- It does not typically involve **sensory deficits** (numbness, tingling), **optic neuritis**, or extensive white matter lesions on MRI.
*Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL)*
- A genetic (NOTCH3 gene) small vessel disease causing recurrent **strokes, migraine with aura**, and progressive cognitive decline, typically starting in middle age.
- While it causes white matter abnormalities on MRI, it does not typically present with **inflammatory demyelination** causing optic neuritis or the diverse neurological relapses seen in MS.
*Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis*
- This is a monophasic, immune-mediated demyelinating disorder that typically occurs **after an infection or vaccination**.
- It often has a more **acute and severe onset** with encephalopathy, and while it causes multifocal white matter lesions, it is typically a single event rather than relapsing-remitting course seen in MS.
*Lead intoxication*
- Lead poisoning can cause a variety of neurological symptoms, including **peripheral neuropathy** (motor and sensory), **encephalopathy**, and cognitive impairment.
- It does not typically cause **optic neuritis**, demyelinating lesions in the CNS, or the specific pattern of neurological deficits characteristic of MS.
Demyelinating diseases US Medical PG Question 3: An 80-year-old woman is brought to the physician by her 2 daughters for worsening memory loss. They report that their mother is increasingly forgetful about recent conversations and events. She is unable to remember her appointments and commitments she has made. 3 years ago, the patient was moved into an elder care facility because she was often getting lost on her way home and forgetting to take her medications. The patient reports that she is very socially active at her new home and has long conversations with the other residents about her adventures as an air hostess during her youth. Which of the following cerebral pathologies is most likely present in this patient?
- A. Lewy bodies
- B. Lacunar infarcts
- C. Intracytoplasmic vacuoles
- D. Neurofibrillary tangles (Correct Answer)
- E. Demyelination
Demyelinating diseases Explanation: ***Neurofibrillary tangles***
- The patient's presentation with **progressive memory loss** affecting recent events, getting lost, and forgetting medications, while largely preserving long-term memory (recalling youth as an air hostess and engaging in conversations), is highly characteristic of **Alzheimer's disease**.
- **Neurofibrillary tangles**, composed of hyperphosphorylated tau protein, along with **amyloid plaques**, are the hallmark pathological findings in Alzheimer's disease.
*Lewy bodies*
- **Lewy bodies** are characteristic of **Lewy body dementia** or Parkinson's disease with dementia, which typically present with prominent **fluctuations in cognition**, recurrent **visual hallucinations**, and parkinsonism.
- While memory loss can occur, the dominant features in this case point away from Lewy body pathology.
*Lacunar infarcts*
- **Lacunar infarcts** are associated with **vascular dementia**, which often presents with a more **step-wise decline** in cognitive function, focal neurological deficits, and evidence of cerebrovascular disease on imaging.
- The patient's gradual and progressive memory loss is less typical of lacunar infarcts as the primary cause.
*Intracytoplasmic vacuoles*
- **Intracytoplasmic vacuoles** are characteristic of **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease** (spongiform encephalopathy), which is a rapidly progressive and fatal neurodegenerative disorder with distinct neurological symptoms such as myoclonus and ataxia, not fitting this patient's profile.
- The disease course is typically much faster than the 3-year progression described.
*Demyelination*
- **Demyelination** is the hallmark of conditions like **multiple sclerosis**, which primarily affects younger individuals and typically presents with a range of neurological deficits, including motor, sensory, and visual disturbances, that often relapse and remit.
- It does not typically present as a primary, progressive memory disorder in an 80-year-old in this manner.
Demyelinating diseases US Medical PG Question 4: A 63-year-old man presents to the clinic concerned about numbness and weakness in his bilateral shoulders and arms for the past 8 weeks. The symptoms started when he fell from scaffolding at work and landed on his back. Initial workup was benign and he returned to normal duty. However, his symptoms have progressively worsened since the fall. He denies fever, back pain, preceding vomiting, and diarrhea. He has a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, ischemic heart disease, and a 48-pack-year cigarette smoking history. He takes atorvastatin, hydrochlorothiazide, lisinopril, labetalol, and metformin. His blood pressure is 132/82 mm Hg, the pulse is 72/min, and the respiratory rate is 15/min. All cranial nerves are intact. Muscle strength is reduced in the upper limbs (4/5 bilaterally) but normal in the lower limbs. Perception of sharp stimuli and temperature is reduced on his shoulders and upper arms. The vibratory sense is preserved. Sensory examination is normal in the lower limbs. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Anterior cord syndrome
- B. Central cord syndrome (Correct Answer)
- C. Guillain-Barre syndrome
- D. Vitamin B12 deficiency
- E. Pontine infarction
Demyelinating diseases Explanation: ***Central cord syndrome***
- This syndrome typically results from a **hyperextension injury** in patients with pre-existing cervical spinal stenosis, leading to damage to the central gray matter and surrounding tracts.
- It classically presents with greater **motor weakness in the upper extremities** than in the lower extremities, and a **"cape-like" distribution of sensory loss** (impaired pain and temperature sensation) over the shoulders and arms due to spinothalamic tract involvement, as seen in this patient.
*Anterior cord syndrome*
- This syndrome is characterized by **paraplegia/quadriplegia**, dissociated sensory loss (loss of **pain and temperature sensation**), and bowel/bladder dysfunction below the level of the lesion.
- It spares **proprioception and vibratory sensation** since the posterior columns remain intact, which is not fully consistent with the patient's presentation of primarily sensory symptoms in the upper limbs with normal strength.
*Guillain-Barre syndrome*
- This is an **acute demyelinating polyneuropathy** that typically presents with **progressive, ascending weakness** and often **areflexia**, usually following an infection.
- The patient's symptoms are primarily sensory, descending, and lack significant weakness or preceding infection, making this diagnosis less likely.
*Vitamin B12 deficiency*
- This deficiency can cause **subacute combined degeneration** of the spinal cord, affecting the **posterior columns** (vibratory and proprioception loss) and **corticospinal tracts** (weakness, spasticity).
- The patient primarily has loss of pain and temperature sensation with preserved vibratory sense and normal strength, which is inconsistent with B12 deficiency.
*Pontine infarction*
- A pontine infarction would present with a constellation of cranial nerve deficits, motor weakness (hemiparesis or quadriplegia), and cerebellar signs due to its location in the brainstem.
- The patient has intact cranial nerves, normal muscle strength, and specific sensory deficits limited to the shoulders and arms, which does not align with a brainstem stroke.
Demyelinating diseases US Medical PG Question 5: A 35-year-old woman with a history of Crohn disease presents for a follow-up appointment. She says that lately, she has started to notice difficulty walking. She says that some of her friends have joked that she appears to be walking as if she was drunk. Past medical history is significant for Crohn disease diagnosed 2 years ago, managed with natalizumab for the past year because her intestinal symptoms have become severe and unresponsive to other therapies. On physical examination, there is gait and limb ataxia present. Strength is 4/5 in the right upper limb. A T1/T2 MRI of the brain is ordered and is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sCJD)
- B. West Nile encephalitis
- C. Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD)
- D. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE)
- E. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) (Correct Answer)
Demyelinating diseases Explanation: ***Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)***
- This patient's history of **Crohn's disease** managed with **natalizumab** (a monoclonal antibody targeting α4-integrin) significantly increases the risk for **PML**, especially with new onset **ataxia** and **gait disturbance**. MRI findings would likely show multifocal, asymmetric white matter lesions without mass effect or enhancement.
- PML is caused by the **JC virus**, which reactivates in immunocompromised individuals, leading to demyelination and neurological deficits.
*Sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sCJD)*
- While sCJD presents with rapidly progressive **dementia**, **myoclonus**, and **ataxia**, it typically affects older individuals and is not directly linked to immunosuppression or natalizumab use.
- MRI findings in sCJD commonly show **cortical ribboning** or **basal ganglia hyperintensity** on DWI/FLAIR, which differs from PML's white matter lesions.
*West Nile encephalitis*
- This is an acute **viral infection** transmitted by mosquitoes, presenting with fever, headache, altered mental status, and sometimes movement disorders.
- It would typically have an **acute onset** and often characteristic seasonal and geographic patterns, which are not described here.
*Variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD)*
- vCJD is linked to the consumption of **bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)**-contaminated products and typically affects younger individuals with prominent psychiatric symptoms and sensory disturbances before neurological decline.
- It does not have a direct association with immunosuppressive therapy like natalizumab.
*Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE)*
- SSPE is a rare, progressive neurological disorder that occurs years after a **measles infection**, primarily affecting children and young adults.
- Symptoms include intellectual deterioration, seizures, and myoclonus, but it is not associated with Crohn's disease, natalizumab, or the typical MRI findings for PML.
Demyelinating diseases US Medical PG Question 6: A 38-year-old woman comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. Two years ago, she was diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. Three weeks ago, she was admitted and treated for right lower leg weakness with high-dose methylprednisone for 5 days. She has had 4 exacerbations over the past 6 months. Current medications include interferon beta and a multivitamin. Her temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 116/74 mm Hg. Examination shows pallor of the right optic disk. Neurologic examination shows no focal findings. She is anxious about the number of exacerbations and repeated hospitalizations. She is counseled about the second-line treatment options available to her. She consents to treatment with natalizumab. However, she has read online about its adverse effects and is concerned. This patient is at increased risk for which of the following complications?
- A. Tuberculosis
- B. Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone
- C. Parkinsonism
- D. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (Correct Answer)
- E. Aplastic anemia
Demyelinating diseases Explanation: ***Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy***
- **Natalizumab** is a monoclonal antibody that blocks the binding of leukocytes to endothelial cells, preventing their entry into the central nervous system. This immunosuppressive effect increases the risk of **progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)**, especially in patients who are positive for the **JC virus**.
- PML is a serious and often fatal opportunistic infection of the brain caused by the **JC virus**, which demyelinates axons and leads to severe neurological deficits.
*Tuberculosis*
- While some immunosuppressants can reactivate **latent tuberculosis**, natalizumab is not typically associated with an increased risk of TB compared to other immunomodulatory drugs like TNF-alpha inhibitors.
- The mechanism of action of natalizumab (alpha-4 integrin blocker) does not directly impede the immune response responsible for containing mycobacterial infections to the same extent as other treatments.
*Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone*
- **SIADH** is not a known adverse effect of natalizumab.
- SIADH is characterized by excessive secretion of **antidiuretic hormone**, leading to hyponatremia, and is often associated with certain medications (e.g., SSRIs, carbamazepine) or underlying conditions like malignancy or pulmonary disease.
*Parkinsonism*
- Parkinsonism involves symptoms like **bradykinesia**, rigidity, and tremor, and is a neurodegenerative disorder.
- There is **no evidence** suggesting a causal link between natalizumab treatment and the development of Parkinsonism.
*Aplastic anemia*
- **Aplastic anemia** is a rare but severe condition where the bone marrow fails to produce blood cells.
- This adverse effect is not associated with natalizumab; it is more commonly linked to certain **chemotherapeutic agents**, radiation, or specific antimicrobial drugs like chloramphenicol.
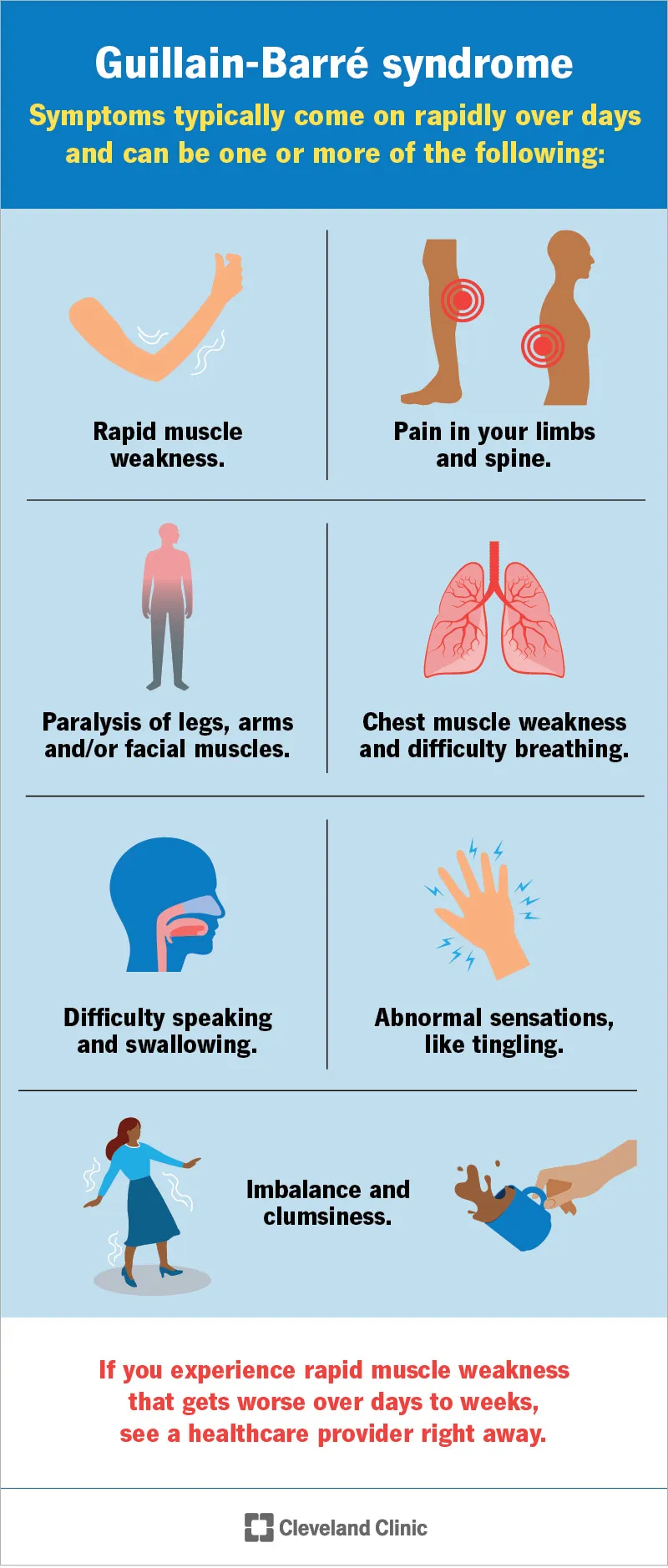
Demyelinating diseases US Medical PG Question 7: A 28-year-old man presents to the emergency department with lower extremity weakness. He was in his usual state of health until 10 days ago. He then began to notice his legs were “tiring out” during his workouts. This progressed to difficulty climbing the stairs to his apartment. He has asthma and uses albuterol as needed. He has no significant surgical or family history. He smokes marijuana daily but denies use of other recreational drugs. He is sexually active with his boyfriend of 2 years. He has never traveled outside of the country but was camping 3 weeks ago. He reports that he had diarrhea for several days after drinking unfiltered water from a nearby stream. On physical examination, he has 1/5 strength in his bilateral lower extremities. He uses his arms to get up from the chair. Achilles and patellar reflexes are absent. A lumbar puncture is performed, and results are as shown below:
Cerebral spinal fluid:
Color: Clear
Pressure: 15 cm H2O
Red blood cell count: 0 cells/µL
Leukocyte count: 3 cells/ µL with lymphocytic predominance
Glucose: 60 mg/dL
Protein: 75 mg/dL
A culture of the cerebral spinal fluid is pending. Which of the following is the part of the management for the patient’s most likely diagnosis?
- A. Aspirin
- B. Intravenous methylprednisolone
- C. Plasmapheresis (Correct Answer)
- D. Doxycycline
- E. Azithromycin
Demyelinating diseases Explanation: ***Plasmapheresis***
- The patient exhibits classic signs of **Guillain-Barré Syndrome (GBS)**: **ascending paralysis** starting in the lower extremities, progression over days to weeks, and **areflexia**.
- The **CSF findings** of **elevated protein** with normal cell count (**albuminocytologic dissociation**) are characteristic of GBS. Plasmapheresis is a first-line treatment, as it removes pathogenic autoantibodies from the plasma.
*Aspirin*
- **Aspirin** is an antiplatelet agent used for cardiovascular disease prevention or acute ischemic events.
- It has no role in the treatment of GBS, which is an autoimmune demyelinating polyneuropathy.
*Intravenous methylprednisolone*
- While corticosteroids like **methylprednisolone** are used for some autoimmune conditions, they have been shown to be **ineffective** and potentially harmful in GBS.
- The primary treatments for GBS are **intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG)** and **plasmapheresis**.
*Doxycycline*
- **Doxycycline** is a broad-spectrum antibiotic commonly used for bacterial infections like Lyme disease, rickettsial infections, and some STIs.
- It is not indicated for the autoimmune pathophysiology of GBS.
*Azithromycin*
- **Azithromycin** is a macrolide antibiotic frequently used for respiratory tract infections and certain sexually transmitted infections.
- It has no therapeutic benefit in the management of GBS.
Demyelinating diseases US Medical PG Question 8: A 43-year-old man presents to the emergency department following a work-related accident in which both arms were amputated. The patient lost a substantial amount of blood prior to arrival, and his bleeding is difficult to control due to arterial damage and wound contamination with debris. His complete blood count (CBC) is significant for a hemoglobin (Hgb) level of 5.3 g/dL. The trauma surgery resident initiates the massive transfusion protocol and orders whole blood, O negative, which she explains is the universal donor. The patient receives 6 units of O negative blood prior to admission. He subsequently develops fever, chills, hematuria, and pulmonary edema. Several hours later, the patient goes into hemodynamic shock requiring the emergent administration of vasopressors. Of the following options, which hypersensitivity reaction occurred?
- A. Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction
- B. Combined type 1 and type 4 hypersensitivity reaction
- C. Type 3 hypersensitivity reaction
- D. Type 2 hypersensitivity reaction (Correct Answer)
- E. Type 4 hypersensitivity reaction
Demyelinating diseases Explanation: ***Type 2 hypersensitivity reaction***
- This scenario describes an **acute hemolytic transfusion reaction (AHTR)**, a classic example of a **Type II hypersensitivity reaction**. The recipient's antibodies (IgM) recognize and bind to antigens on the transfused red blood cells, leading to their destruction (hemolysis) via complement activation and cellular mechanisms.
- Symptoms like **fever, chills, hematuria (due to hemoglobinuria)**, and subsequent **shock** are characteristic of AHTR, even with O negative blood if other minor blood group antigens (e.g., Kell, Duffy) are incompatible or if the patient developed antibodies against these from previous transfusions or pregnancies.
*Type 1 hypersensitivity reaction*
- This type involves **IgE-mediated mast cell degranulation** and is associated with allergic reactions such as anaphylaxis, asthma, and hives.
- While anaphylaxis can cause shock, the systemic symptoms of **hemolysis and hematuria** are not characteristic of a Type 1 reaction.
*Combined type 1 and type 4 hypersensitivity reaction*
- This combination is uncommon in an acute transfusion setting and does not align with the presented symptoms.
- Type 1 is immediate allergic, and Type 4 is delayed cell-mediated, neither fully explaining the hemolytic features observed.
*Type 3 hypersensitivity reaction*
- This reaction involves the formation of **immune complexes** (antigen-antibody complexes) that deposit in tissues, leading to inflammation and damage (e.g., serum sickness, lupus nephritis).
- While immune complexes can cause systemic symptoms, the prominent hemolytic features and immediate presentation of a transfusion reaction are more indicative of Type 2.
*Type 4 hypersensitivity reaction*
- This is a **delayed type hypersensitivity** reaction mediated by **T cells**, taking 24-72 hours or longer to develop (e.g., contact dermatitis, tuberculin skin test).
- The acute onset of symptoms following transfusion makes a Type 4 reaction highly unlikely.
Demyelinating diseases US Medical PG Question 9: A 67-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of fatigue and worsening back and abdominal pain. During this period, she has also had excessive night sweats and a 4.6-kg (10-lb) weight loss. She has had swelling of the neck for 3 days. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows a 4-cm, supraclavicular, nontender, enlarged and fixed lymph node. The spleen is palpated 2 cm below the left costal margin. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.4 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume 87 μm3
Leukocyte count 5,200/mm3
Platelet count 190,000/mm3
Serum
Lactate dehydrogenase 310 U/L
A CT scan of the thorax and abdomen shows massively enlarged paraaortic, axillary, mediastinal, and cervical lymph nodes. Histopathologic examination of an excised cervical lymph node shows lymphocytes with a high proliferative index that stain positive for CD20. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Hairy cell leukemia
- B. Adult T-cell lymphoma
- C. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (Correct Answer)
- D. Marginal zone lymphoma
- E. Follicular lymphoma
Demyelinating diseases Explanation: ***Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma***
- The patient presents with **B symptoms** (fever, night sweats, weight loss), rapid progression, generalized **lymphadenopathy** (cervical, supraclavicular, paraaortic, axillary, mediastinal), **splenomegaly**, and elevated **LDH**.
- **Histopathologic examination** showing lymphocytes with a **high proliferative index** and positive **CD20 staining** confirms a B-cell lymphoma with aggressive features, highly characteristic of DLBCL.
*Hairy cell leukemia*
- This condition typically presents with **splenomegaly** and **pancytopenia**, but **lymphadenopathy** is rare and often absent.
- The characteristic "hairy cells" are identified by specific markers (CD103, CD123, CD25), and a **high proliferative index** is not a feature.
*Adult T-cell lymphoma*
- This lymphoma is associated with **HTLV-1 infection** and often presents with hypercalcemia, skin lesions, and generalized lymphadenopathy, but it is a **T-cell lymphoma**.
- The **CD20 positivity** in the histology rules out a T-cell lineage lymphoma.
*Marginal zone lymphoma*
- This is an **indolent B-cell lymphoma** that typically progresses slowly and is often associated with chronic inflammation or autoimmune diseases.
- The patient's aggressive symptoms, rapid progression, significant **B symptoms**, and **high proliferative index** are not consistent with indolent lymphoma.
*Follicular lymphoma*
- This is also an **indolent B-cell lymphoma** characterized by a follicular growth pattern and usually presents with painless lymphadenopathy.
- The rapid onset of symptoms, significant **B symptoms**, and elevated **LDH** indicate an aggressive lymphoma, which is not typical of follicular lymphoma.
Demyelinating diseases US Medical PG Question 10: A 61-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a constant, dull headache and generalized body pains for the past 8 months. She has also had difficulty hearing from her left side, which started a month after the onset of the headaches. Five months ago, she had surgery to correct a fracture of the right femur that occurred without a fall or any significant trauma. Five years ago, she underwent a total thyroidectomy for localized thyroid carcinoma. She takes levothyroxine and calcium supplements, which she started after menopause. Physical examination reveals a prominent forehead and irregular, tender skull surface. Bony tenderness is present over bilateral hip and knee joints, with decreased range of motion of the right hip joint and increased anterior curvature of both tibias. Laboratory studies show a highly elevated level of alkaline phosphatase, with vitamin D, calcium and PTH levels within normal limits. A plain x-ray of the head is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Mixed lytic and sclerotic lesions (Correct Answer)
- B. Periosteal trabeculations with radiolucent marrow hyperplasia
- C. Generalized dense, sclerotic bone
- D. Multiple, well-defined, punched out lytic lesions
- E. Lytic lesions with no sclerotic margin
Demyelinating diseases Explanation: ***Mixed lytic and sclerotic lesions***
- The patient's symptoms (headache, hearing loss, pathological fracture, bony pain, prominent forehead, enlarged skull, increased tibial curvature, and elevated alkaline phosphatase with normal calcium and PTH) are classic for **Paget's disease of bone**.
- **Paget's disease** is characterized by disorganized bone remodeling, which radiographically appears as a mixture of osteolytic (bone destruction) and osteosclerotic (bone formation) lesions, often described as a "cotton wool" appearance in the skull.
*Periosteal trabeculations with radiolucent marrow hyperplasia*
- This finding is more characteristic of conditions like **myelofibrosis**, where there is marrow replacement and extramedullary hematopoiesis, leading to bony changes.
- While Paget's can affect bone structure, it primarily involves remodeling within the bone itself rather than periosteal trabeculations and marrow hyperplasia as a primary radiological feature.
*Generalized dense, sclerotic bone*
- **Osteopetrosis** (Albers-Schönberg disease) is characterized by excessively dense, brittle bones due to defective osteoclast function, leading to generalized sclerosis.
- The clinical presentation with mixed lytic and sclerotic phases, hearing loss, and characteristic bone deformities points away from uniform bone sclerosis.
*Multiple, well-defined, punched out lytic lesions*
- This finding is most suggestive of **multiple myeloma**, a plasma cell malignancy that causes discrete areas of bone destruction without much osteoblastic (bone-forming) activity.
- The patient's symptoms, particularly the prominent forehead, increased tibial curvature, and highly elevated alkaline phosphatase, are not typical of multiple myeloma.
*Lytic lesions with no sclerotic margin*
- This pattern can be seen in aggressive **metastatic bone disease** (e.g., from renal cell carcinoma or thyroid carcinoma, although the patient had a thyroidectomy 5 years ago for localized cancer, making widespread metastases less likely to present this way).
- While Paget's does have lytic phases, the entire clinical picture and the eventual mixed lytic-sclerotic appearance differentiate it from purely lytic, unsclerofed lesions of aggressive metastatic disease.
More Demyelinating diseases US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.