Congenital CNS malformations US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Congenital CNS malformations. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Congenital CNS malformations US Medical PG Question 1: A 32-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 1, at 14-weeks' gestation comes to the physician for a prenatal visit. Routine first trimester screening shows increased nuchal translucency, decreased β-hCG concentration, and decreased levels of pregnancy-associated plasma protein A. Amniocentesis shows trisomy of chromosome 13. This fetus is at increased risk for which of the following?
- A. Duodenal atresia
- B. Cutis aplasia (Correct Answer)
- C. Cystic hygroma
- D. Optic glioma
- E. Prominent occiput
Congenital CNS malformations Explanation: ***Cutis aplasia***
- **Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)** is characterized by **cutis aplasia**, which is a congenital absence of skin, typically on the scalp.
- Other common features of Trisomy 13 include **midline defects**, microphthalmia, cleft lip/palate, polydactyly, and severe intellectual disability.
*Duodenal atresia*
- **Duodenal atresia** is strongly associated with **Trisomy 21 (Down syndrome)**, not Trisomy 13.
- It presents with a "double bubble" sign on imaging due to dilation of the stomach and proximal duodenum.
*Cystic hygroma*
- **Cystic hygromas**, which are lymphatic malformations, are a common finding in **Turner syndrome (XO)** and **Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)**.
- While increased nuchal translucency is noted, a cystic hygroma itself is not a specific finding for Trisomy 13.
*Optic glioma*
- **Optic gliomas** are tumors of the optic nerve most frequently associated with **neurofibromatosis type 1**, an autosomal dominant disorder.
- They are not a characteristic finding of Trisomy 13.
*Prominent occiput*
- A **prominent occiput** is a classic feature of **Trisomy 18 (Edwards syndrome)**.
- This condition is also associated with rocker-bottom feet, micrognathia, and clenched hands with overlapping fingers.
Congenital CNS malformations US Medical PG Question 2: A 21-year-old G3P2 woman presents to her obstetrician at 6 weeks gestation for routine prenatal care. Her past medical history includes obesity and gestational diabetes. She has had two spontaneous vaginal deliveries at term. One infant was macrosomic with hypoglycemia, but otherwise, she has had no complications. Her physician informs her that she must start taking a multivitamin with folic acid daily. The defect that folic acid supplementation protects against arises in tissue that is derived from which germ cell layer?
- A. Mesoderm
- B. Notochord
- C. Endoderm
- D. Mesenchyme
- E. Ectoderm (Correct Answer)
Congenital CNS malformations Explanation: ***Ectoderm***
- Folic acid supplementation primarily prevents **neural tube defects**, such as **spina bifida** and **anencephaly**.
- The **neural tube**, which forms the brain and spinal cord, is derived from the **ectoderm**.
*Mesoderm*
- The **mesoderm** gives rise to structures like muscle, bone, connective tissue, and the cardiovascular system.
- Defects in mesodermal development are not primarily prevented by folic acid supplementation.
*Notochord*
- The **notochord** is a transient embryonic structure that induces the formation of the neural plate from the ectoderm.
- While critical for nervous system development, it is not a germ cell layer itself, and defects in its development are not directly prevented by folic acid.
*Endoderm*
- The **endoderm** forms the lining of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts, as well as glands like the thyroid and pancreas.
- Anomalies of these internal organs are not the primary target of folic acid supplementation.
*Mesenchyme*
- **Mesenchyme** is embryonic connective tissue, largely derived from the mesoderm, but can also come from neural crest (ectoderm).
- It differentiates into connective tissues, blood, and lymphatic vessels; neural tube defects are not considered mesenchymal in origin.
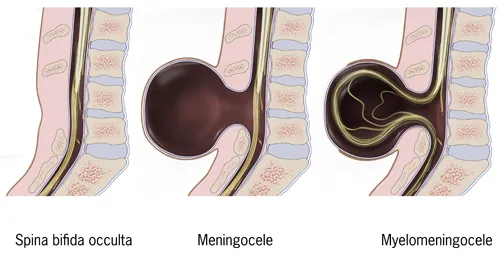
Congenital CNS malformations US Medical PG Question 3: A 29-year-old primigravid woman at 18 weeks’ gestation comes to the physician for her first prenatal visit. She works as a paralegal and lives with her husband. Her current pregnancy was unexpected, and she did not take any prenatal medications or supplements. Physical examination shows a uterus 2 inches above the umbilicus. The concentration of α-fetoprotein in the maternal serum and concentrations of both α-fetoprotein and acetylcholinesterase in the amniotic fluid are elevated. Ultrasonography of the uterus shows an increased amniotic fluid volume. The fetus most likely has which of the following conditions?
- A. Anencephaly (Correct Answer)
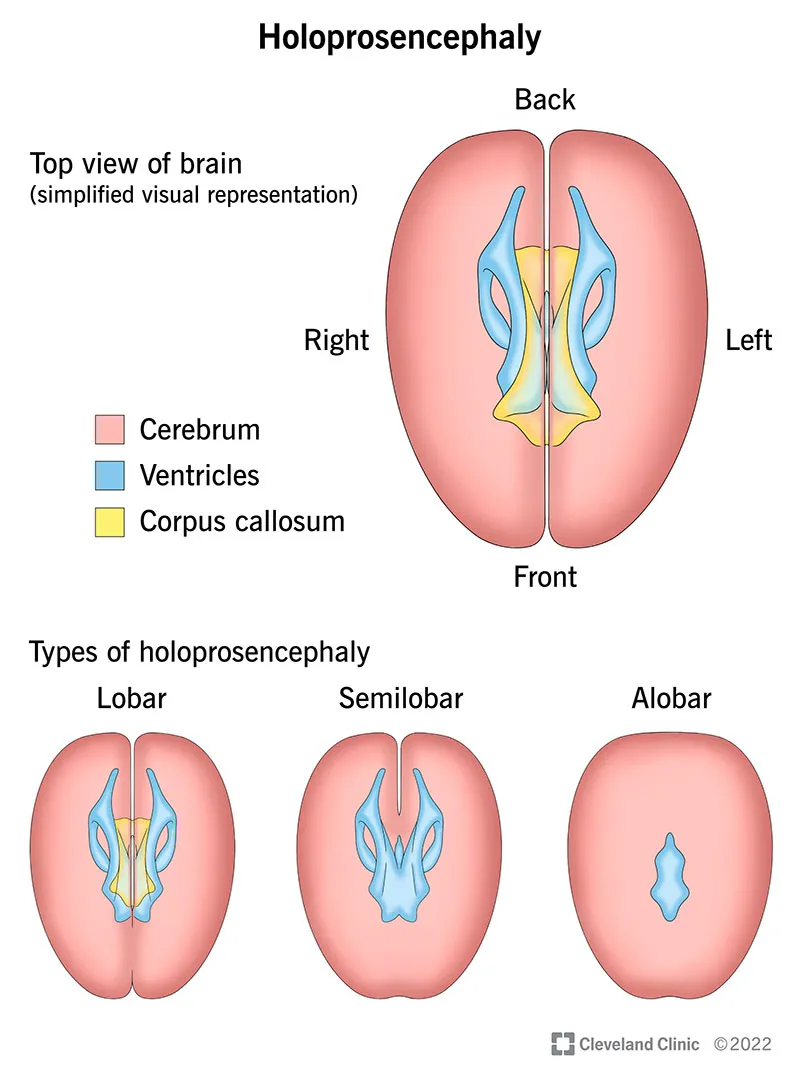
- B. Holoprosencephaly
- C. Spina bifida occulta
- D. Myelomeningocele
- E. Lissencephaly
Congenital CNS malformations Explanation: ***Anencephaly***
- **Elevated maternal serum α-fetoprotein (MSAFP)** and **amniotic fluid α-fetoprotein (AFAFP)**, along with elevated **acetylcholinesterase (AChE)** in amniotic fluid, are classic markers for **open neural tube defects**. Anencephaly, characterized by the **absence of a major portion of the brain and skull**, is an open neural tube defect.
- The **increased amniotic fluid volume (polyhydramnios)** is due to the fetus's inability to swallow amniotic fluid, a common finding in anencephaly.
*Holoprosencephaly*
- This condition involves incomplete separation of the **prosencephalon (forebrain)**, leading to **severe facial abnormalities** and brain malformations.
- While it is a severe brain malformation, it is typically a **closed neural tube defect** or a developmental anomaly not involving an open lesion, and therefore, it is usually not associated with elevated MSAFP, AFAFP, or AChE.
*Spina bifida occulta*
- This is the **mildest form of spina bifida**, involving a small gap in the vertebrae without protrusion of the spinal cord or meninges.
- It is a **closed neural tube defect** and is typically asymptomatic, often not associated with elevated MSAFP or AFAFP levels.
*Myelomeningocele*
- While a **myelomeningocele** is an **open neural tube defect** that would cause elevated MSAFP, AFAFP, and AChE, it is characterized by the protrusion of the spinal cord and meninges through a vertebral defect.
- The primary characteristic of anencephaly (absence of a major portion of the brain/skull) better fits the severe degree of neural tube defect suggested by the findings, particularly the polyhydramnios due to absent swallowing reflex.
*Lissencephaly*
- This is a brain malformation characterized by a **lack of gyri and sulci**, resulting in a smooth brain surface.
- It is a brain development defect, not an **open neural tube defect**, and as such, it is not associated with elevated MSAFP, AFAFP, or AChE.
Congenital CNS malformations US Medical PG Question 4: A 58-year-old man comes to the physician because of burning pain in his neck and arms for a year. He has also had paresthesias in his hands during this period. He has had increasing weakness in both hands during the past 3 months. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypercholesterolemia, and hypertension. He was involved in a motor vehicle collision 3 years ago. Current medications include metformin, sitagliptin, enalapril, atorvastatin, and aspirin. He has had 7 sexual partners in his lifetime; he uses condoms inconsistently. He is oriented to time, place, and person. Vital signs are within normal limits. The pupils are equal and reactive to light. Examination of the upper extremities shows decreased muscle strength, absent reflexes, and decreased hand grip with fasciculations bilaterally. Sensation to temperature and pain is absent over the chest and bilateral upper arms. Vibration and joint position sensations are present in the upper limbs. Cranial nerve examination shows no focal findings. Examination of the lower extremities show no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Brown-Séquard syndrome
- B. Tabes dorsalis
- C. Multiple sclerosis
- D. Syringomyelia (Correct Answer)
- E. Cervical disk prolapse
Congenital CNS malformations Explanation: ***Syringomyelia***
- This condition is characterized by a central canal cavitation (syrinx) in the spinal cord, leading to damage to the **spinothalamic tracts** (loss of pain and temperature sensation) and anterior horn cells (weakness, fasciculations, absent reflexes). The **'cape-like' distribution** of sensory loss over the chest and arms, along with hand weakness, is classic.
- The sensation loss to temperature and pain over the chest and bilateral upper arms with preserved vibration and joint position sensation in upper limbs is a **dissociated sensory loss**, a hallmark of syringomyelia, as the dorsal columns (responsible for vibration and proprioception) are typically spared.
*Brown-Séquard syndrome*
- This syndrome results from **hemitransaction of the spinal cord**, causing ipsilateral loss of motor function and proprioception/vibration sensation, and contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation below the lesion.
- The patient's symptoms of **bilateral sensory loss** and **bilateral weakness** do not fit this unilateral lesion pattern.
*Tabes dorsalis*
- This is a late manifestation of **syphilis**, primarily affecting the posterior columns of the spinal cord (dorsal columns), leading to loss of **proprioception and vibration sensation**, along with ataxia and shooting pains.
- The patient presents with loss of pain and temperature sensation, not primarily proprioception and vibration, and has **motor weakness with fasciculations**, which are not typical for tabes dorsalis.
*Multiple sclerosis*
- MS is characterized by **demyelination in the central nervous system**, presenting with diverse neurological symptoms that often wax and wane, affecting multiple areas of the brain and spinal cord.
- While it can cause sensory and motor deficits, the **dissociated sensory loss** (pain/temperature vs. vibration/proprioception) in a "cape-like" distribution with prominent fasciculations points away from MS.
*Cervical disk prolapse*
- A cervical disk prolapse typically causes **radicular pain and neurological deficits** (motor weakness, sensory loss, reflex changes) in a dermatomal or myotomal distribution corresponding to the compressed nerve root.
- While it can cause arm pain and weakness, the **bilateral, "cape-like" dissociated sensory loss** over the chest and arms is not characteristic of a single or multiple cervical nerve root compressions.
Congenital CNS malformations US Medical PG Question 5: A 6-year-old boy is brought in for evaluation by his adopted mother due to trouble starting 1st grade. His teacher has reported that he has been having trouble focusing on tasks and has been acting out while in class. His family history is unknown as he was adopted 2 years ago. His temperature is 36.2°C (97.2°F), pulse is 80/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure 110/70 mm Hg. Visual inspection of the boy's face shows a low set nasal bridge, a smooth philtrum, and small lower jaw. Which of the following findings would also likely be found on physical exam?
- A. Cataracts
- B. Congenital deafness
- C. Holosystolic murmur (Correct Answer)
- D. Limb hypoplasia
- E. Wide notched teeth
Congenital CNS malformations Explanation: **Holosystolic murmur**
- The child exhibits classic features of **fetal alcohol syndrome** (FAS), including the distinctive facial anomalies (low set nasal bridge, smooth philtrum, small lower jaw) and developmental/behavioral issues (trouble focusing, acting out).
- Up to 50% of children with FAS develop **congenital heart defects**, with **ventricular septal defects (VSDs)** being the most common, which are characterized by a **holosystolic murmur** at the lower left sternal border.
*Cataracts*
- **Cataracts** are not a typical feature of fetal alcohol syndrome but are often associated with congenital infections such as **rubella** or **cytomegalovirus**.
- While some genetic syndromes can include cataracts, they are not a primary finding for the constellation of symptoms observed here.
*Congenital deafness*
- **Congenital deafness** is not a hallmark of fetal alcohol syndrome; rather, it is commonly associated with congenital infections like **rubella**, **CMV**, or genetic syndromes such as **CHARGE syndrome**.
- Children with FAS may have hearing problems due to recurrent ear infections, but not typically congenital deafness.
*Limb hypoplasia*
- **Limb hypoplasia** is typically seen in conditions like **thalidomide embryopathy** or certain genetic syndromes, such as **Roberts syndrome**.
- While growth restriction is common in FAS, significant limb hypoplasia as described is not a characteristic feature.
*Wide notched teeth*
- **Wide notched teeth**, also known as **Hutchinson teeth**, are pathognomonic for **congenital syphilis**.
- This finding is unrelated to fetal alcohol syndrome, and the patient's other symptoms do not suggest congenital syphilis.
Congenital CNS malformations US Medical PG Question 6: A 47-year-old man presents to you with gradual loss of voice and difficulty swallowing for the past couple of months. The difficulty of swallowing is for both solid and liquid foods. His past medical history is insignificant except for occasional mild headaches. Physical exam also reveals loss of taste sensation on the posterior third of his tongue and palate, weakness in shrugging his shoulders, an absent gag reflex, and deviation of the uvula away from the midline. MRI scanning was suggested which revealed a meningioma that was compressing some cranial nerves leaving the skull. Which of the following openings in the skull transmit the affected cranial nerves?
- A. Jugular foramen (Correct Answer)
- B. Foramen rotundum
- C. Foramen spinosum
- D. Foramen ovale
- E. Foramen lacerum
Congenital CNS malformations Explanation: ***Jugular foramen***
- The symptoms described—loss of voice, difficulty swallowing, loss of taste on the posterior third of the tongue, absent gag reflex, and uvula deviation—point to impairment of **cranial nerves IX (glossopharyngeal), X (vagus), XI (accessory)**, which all exit the skull via the **jugular foramen**.
- The **vagus nerve** (CN X) is responsible for voice and swallowing (via innervation of the pharynx and larynx), the **glossopharyngeal nerve** (CN IX) for taste from the posterior third of the tongue and the gag reflex, and the **accessory nerve** (CN XI) for shoulder shrugging (trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles).
- Note: Loss of taste on the palate may involve CN VII (facial nerve) fibers, but the dominant clinical picture with absent gag reflex, uvula deviation, dysphagia, and dysphonia clearly indicates jugular foramen pathology.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **foramen rotundum** transmits the **maxillary nerve (V2)**, a branch of the trigeminal nerve.
- Damage to V2 would primarily cause sensory deficits in the midface and upper teeth, which are not described in this patient.
*Foramen spinosum*
- The **foramen spinosum** transmits the **middle meningeal artery** and the **meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve (V3)**.
- Injury here would not explain the constellation of symptoms related to voice, swallowing, taste, or shoulder movement.
*Foramen ovale*
- The **foramen ovale** transmits the **mandibular nerve (V3)**, the **accessory meningeal artery**, and occasionally the superficial petrosal nerve.
- Damage to V3 would result in sensory loss to the lower face and motor deficits in the muscles of mastication, which are not reported.
*Foramen lacerum*
- The **foramen lacerum** is filled with cartilage in vivo and does not typically transmit major neurovascular structures directly through its aperture.
- The **internal carotid artery** passes superior to it, and some small nerves may traverse its vicinity, but not the specific cranial nerves indicated by the patient's symptoms.
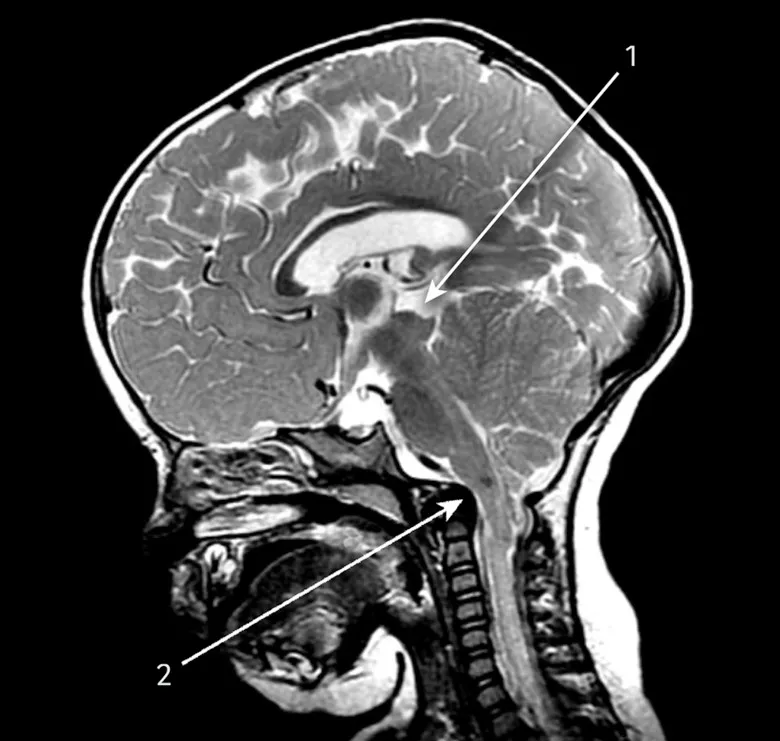
Congenital CNS malformations US Medical PG Question 7: A 4-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a progressive headache and neck pain for 2 weeks. During this period, he has had multiple episodes of dizziness and tingling sensations in his arms and hands. A year ago, he underwent closed reduction of a dislocated shoulder that he suffered after a fall. He underwent surgical removal of a sac-like protuberance on his lower back, soon after being born. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 80/min, and blood pressure is 100/80 mm Hg. His neck is supple. Neurological examination shows sensorineural hearing loss bilaterally and normal gross motor function. Fundoscopy reveals bilateral optic disk swelling. An MRI of the brain is shown. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Brachial plexus injury
- B. Vestibular schwannoma
- C. Chiari II malformation (Correct Answer)
- D. Medulloblastoma
- E. Intraventricular hemorrhage
Congenital CNS malformations Explanation: ***Chiari II malformation***
- The patient's history of surgical removal of a "sac-like protuberance" on his lower back soon after birth suggests a **myelomeningocele**, which is strongly associated with Chiari II malformation.
- Symptoms like progressive headache, neck pain, dizziness, tingling in arms/hands, bilateral optic disk swelling (indicating **increased intracranial pressure**), and sensorineural hearing loss are consistent with brainstem and cranial nerve compression common in Chiari II.
*Brachial plexus injury*
- This typically presents with acute, localized weakness, numbness, or pain in the arm and hand **due to nerve damage**, often following trauma like a dislocated shoulder.
- It would not explain the **progressive headache**, optic disc swelling, or the patient's congenital history of a lower back malformation.
*Vestibular schwannoma*
- This tumor primarily affects the **vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)**, causing **unilateral hearing loss**, tinnitus, and balance issues.
- It would not typically present with bilateral hearing loss, increased intracranial pressure symptoms (like optic disc swelling), or be linked to a congenital spinal defect.
*Medulloblastoma*
- While a **medulloblastoma** can cause symptoms of increased intracranial pressure (headache, optic disc swelling) and sometimes dizziness, it is a **malignant brain tumor**.
- It does not explain the patient's history of a congenital spinal defect (myelomeningocele) or the specific tingling sensations in the arms and hands in the context of brainstem compression.
*Intraventricular hemorrhage*
- This usually occurs in **neonates, especially premature infants**, and presents with acute neurological deficits, apnea, bradycardia, or seizures.
- It is unlikely to present as progressive headache and neck pain in a 4-year-old and does not account for the congenital spinal defect or chronic symptoms.
Congenital CNS malformations US Medical PG Question 8: A 10-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents due to 2 months of a progressively worsening headache. The headaches were initially infrequent and her parents attributed them to stress from a recent move. However, over the last week the headaches have gotten significantly worse and she had one episode of vomiting this morning when she woke up. Her medical history is remarkable for a hospitalization during infancy for bacterial meningitis. On physical exam, the patient has difficulty looking up. The lower portion of her pupil is covered by the lower eyelid and there is sclera visible below the upper eyelid. A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Ependymoma
- B. Medulloblastoma
- C. Craniopharyngioma
- D. Pinealoma (Correct Answer)
- E. Pituitary Adenoma
Congenital CNS malformations Explanation: ***Pinealoma***
- The constellation of a progressively worsening headache, vomiting, and difficulty looking up (Parinaud's syndrome or **dorsal midbrain syndrome**) with **hydrocephalus** visible on MRI points strongly to a **pineal region tumor** that compresses the **tectal plate** and obstructs CSF flow. The visible sclera below the upper eyelid is due to **retraction of the upper eyelids**, a component of Parinaud's syndrome.
- The MRI shows significant **ventricular dilation**, particularly of the lateral and third ventricles, indicating **obstructive hydrocephalus**, which is consistent with a mass in the pineal region compressing the **cerebral aqueduct**.
*Ependymoma*
- Ependymomas most commonly occur in the **fourth ventricle** in children and can cause hydrocephalus by obstructing CSF flow at that level.
- However, typical symptoms would be more associated with **cerebellar dysfunction** (ataxia, nystagmus), and Parinaud's syndrome is not characteristic.
*Medulloblastoma*
- Medulloblastomas are highly malignant **cerebellar tumors** in children, typically arising from the vermis, and often cause **ataxia**, truncal instability, and hydrocephalus due to fourth ventricle obstruction.
- While they cause hydrocephalus and headaches, they do not typically present with Parinaud's syndrome.
*Craniopharyngioma*
- Craniopharyngiomas are **suprasellar tumors** that originate from Rathke's pouch remnants and can cause headaches, visual field defects (**bitemporal hemianopsia**), and **endocrine dysfunction** (e.g., growth delays, diabetes insipidus).
- They are typically located anteriorly, compressing the **optic chiasm** and hypothalamus, not directly obstructing the cerebral aqueduct to cause Parinaud's syndrome.
*Pituitary Adenoma*
- Pituitary adenomas are rare in children and typically cause symptoms related to **hormonal overproduction** or compression of adjacent structures, such as **visual field defects** (bitemporal hemianopsia).
- While large adenomas can cause headaches, they are not typically associated with **Parinaud's syndrome** or rapid-onset **obstructive hydrocephalus** in this manner.
Congenital CNS malformations US Medical PG Question 9: A 2-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his mother for evaluation of severe abdominal pain that began one hour ago. On examination, the patient is afebrile and has diffuse rebound tenderness with acute epigastric pain. A stool guaiac test is positive. A small bowel perforation is suspected. What is the embryologic structure that is the underlying cause of this patient’s presentation?
- A. Fibrous cord remnant
- B. Anal membrane
- C. Vermiform appendix
- D. Cloaca
- E. Vitelline duct (Correct Answer)
Congenital CNS malformations Explanation: ***Vitelline duct***
- The symptoms of **severe abdominal pain**, rebound tenderness, epigastric pain, and **positive stool guaiac** (indicating bleeding) in a 2-year-old suggest a bleeding **Meckel's diverticulum**, which is a remnant of the **vitelline duct**.
- **Meckel's diverticulum** is the most common congenital anomaly of the GI tract, often containing **ectopic gastric or pancreatic tissue** that can lead to ulceration, bleeding, or perforation.
*Fibrous cord remnant*
- While a fibrous cord remnant can be associated with the **vitelline duct**, it typically presents with **intestinal obstruction (volvulus or intussusception)** rather than perforation and bleeding from ectopic mucosa.
- A fibrous cord is a potential complication of a persistent **vitelline duct**, but it is not the underlying embryologic structure responsible for ectopic tissue or bleeding.
*Anal membrane*
- The **anal membrane** is involved in the development of the **anus and rectum**.
- Persistence of the **anal membrane** would lead to **anal atresia** or stenosis, causing symptoms of difficult defecation or obstruction, not abdominal pain and perforation like in this case.
*Vermiform appendix*
- The **vermiform appendix** is a lymphoid organ arising from the **cecum**.
- While **appendicitis** can cause severe abdominal pain and perforation, a positive stool guaiac and presentation with ectopic gastric tissue leading to ulceration are not characteristic features.
*Cloaca*
- The **cloaca** is a common embryologic structure that divides into the **urogenital sinus** and the **anorectal canal**.
- Abnormalities of the **cloaca** typically result in complex **anomalies of the urogenital and GI tracts**, such as persistent cloaca with a single perineal opening, not an isolated perforation with bleeding.
Congenital CNS malformations US Medical PG Question 10: An 8-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician because his mother is concerned about recent behavioral changes. His mother states that she has started to notice that he is slurring his speech and seems to be falling more than normal. On exam, the pediatrician observes the boy has pes cavus, hammer toes, and kyphoscoliosis. Based on these findings, the pediatrician is concerned the child has a trinucleotide repeat disease. Which of the following trinucleotide repeats is this child most likely to possess?
- A. CTG
- B. GAA (Correct Answer)
- C. CGG
- D. CAG
- E. GCC
Congenital CNS malformations Explanation: ***GAA***
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **Friedreich's ataxia**, an autosomal recessive neurodegenerative disorder.
- The presented symptoms of **ataxia** (slurred speech, falling), **pes cavus**, **hammer toes**, and **kyphoscoliosis** are classic features of Friedreich's ataxia.
*CTG*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **myotonic dystrophy type 1**, an autosomal dominant disorder.
- While it causes muscle weakness, it is characterized by **myotonia** (delayed muscle relaxation), cataracts, and frontal baldness, which are not described here.
*CGG*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **fragile X syndrome**, an X-linked dominant disorder.
- Fragile X syndrome primarily causes intellectual disability, behavioral issues (e.g., autism spectrum disorder), and characteristic facial features, but not the specific neurological and orthopedic findings seen in this patient.
*CAG*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with several neurodegenerative diseases, including **Huntington's disease**, spinocerebellar ataxias, and **dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy**.
- Huntington's disease, for example, presents with chorea, cognitive decline, and psychiatric symptoms, differing from the patient's presentation.
*GCC*
- This trinucleotide repeat is associated with **fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS)**.
- FXTAS typically affects older adult carriers of premutation alleles for fragile X, presenting with intention tremor and gait ataxia, not the early childhood onset and specific orthopedic deformities seen here.
More Congenital CNS malformations US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.