CNS infections US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for CNS infections. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
CNS infections US Medical PG Question 1: A 41-year-old male with a history of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia is found to have multiple ring-enhancing lesions on brain CT. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's abnormal scan?
- A. Protozoa (Correct Answer)
- B. Virus
- C. Neoplasm
- D. Bacteria
- E. Prion
CNS infections Explanation: ***Protozoa***
- The patient's history of **Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia** (PJP) suggests an **immunocompromised state**, likely due to HIV/AIDS.
- In such patients, **ring-enhancing brain lesions** are highly characteristic of **cerebral toxoplasmosis**, an opportunistic infection caused by the protozoan *Toxoplasma gondii*.
*Virus*
- While viruses like **CMV** or **JC virus** (causing PML) can affect the brain in immunocompromised patients, they typically present with different imaging features (e.g., non-enhancing lesions in PML) and are less likely to cause multiple ring-enhancing lesions.
- Though HIV can cause **HIV encephalopathy**, it typically involves **diffuse atrophy** and **white matter changes**, rather than distinct ring-enhancing lesions.
*Neoplasm*
- **Primary central nervous system lymphoma (PCNSL)** can present with ring-enhancing lesions, especially in HIV-positive individuals.
- However, given the association with PJP, **infectious etiologies** like toxoplasmosis are generally more common as the initial diagnosis for multiple ring-enhancing lesions in this patient population.
*Bacteria*
- **Bacterial brain abscesses** can cause ring-enhancing lesions but are less common in disseminated opportunistic infections in HIV/AIDS compared to protozoal or fungal infections.
- They also typically present with a more **acute inflammatory picture** and may be preceded by a source of bacterial infection (e.g., endocarditis, sinusitis) not mentioned here.
*Prion*
- **Prion diseases** (e.g., Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease) cause rapidly progressive dementia and characteristic EEG and MRI findings (e.g., cortical ribboning, basal ganglia hyperintensity) that do not typically include multiple ring-enhancing lesions.
- They are also not associated with the immunocompromised state indicated by PJP.
CNS infections US Medical PG Question 2: A 15-year-old boy is brought to the Emergency department by ambulance from school. He started the day with some body aches and joint pain but then had several episodes of vomiting and started complaining of a terrible headache. The school nurse called for emergency services. The boy was born at 39 weeks gestation via spontaneous vaginal delivery. He is up to date on all vaccines and is meeting all developmental milestones. Past medical history is noncontributory. He is a good student and enjoys sports. At the hospital, his blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, heart rate is 105/min, respiratory rate is 21/min, and his temperature is 38.9°C (102.0°F). On physical exam, he appears drowsy with neck stiffness and sensitivity to light. Kernig’s sign is positive. An ophthalmic exam is performed followed by a lumbar puncture. An aliquot of cerebrospinal fluid is sent to microbiology. A gram stain shows gram-negative diplococci. A smear is prepared on blood agar and grows round, smooth, convex colonies with clearly defined edges. Which of the following would identify the described pathogen?
- A. Oxidase-positive and ferments glucose and maltose (Correct Answer)
- B. Oxidase-positive test and ferments glucose only
- C. Catalase-negative and oxidase-positive
- D. No growth on Thayer-Martin medium
- E. Growth in anaerobic conditions
CNS infections Explanation: ***Oxidase-positive and ferments glucose and maltose***
- The patient's symptoms (fever, headache, neck stiffness, sensitivity to light, positive Kernig's sign) are classic for **meningitis**, and the CSF showing **gram-negative diplococci** points to *Neisseria meningitidis*.
- *Neisseria meningitidis* is identified by its positive **oxidase test** and its ability to ferment both **glucose and maltose**.
*Oxidase-positive test and ferments glucose only*
- This description corresponds to *Neisseria gonorrhoeae*, which primarily causes **gonorrhea** and occasionally meningitis due to disseminated infection but is less common in this age group and presentation.
- While *Neisseria gonorrhoeae* is also an **oxidase-positive gram-negative diplococcus**, it specifically ferments only *glucose*, not maltose.
*Catalase-negative and oxidase-positive*
- While *Neisseria meningitidis* is **oxidase-positive**, stating it is "catalase-negative" is incorrect; *Neisseria* species are actually **catalase-positive**.
- This option incorrectly describes a general metabolic property that would rule out *Neisseria meningitidis*.
*No growth on Thayer-Martin medium*
- Thayer-Martin medium is a **selective medium** specifically designed to isolate pathogenic *Neisseria species* by inhibiting the growth of commensal bacteria and fungi.
- Therefore, *Neisseria meningitidis* would **grow well** on Thayer-Martin medium, making "no growth" an incorrect identifier.
*Growth in anaerobic conditions*
- *Neisseria meningitidis* is an **obligate aerobe**, meaning it requires oxygen for growth.
- It would **not grow** in anaerobic conditions, making this statement false for identifying the described pathogen.
CNS infections US Medical PG Question 3: An 81-year-old man is brought to the physician by his daughter after he was found wandering on the street. For the last 3 months, he often has a blank stare for several minutes. He also claims to have seen strangers in the house on several occasions who were not present. He has hypertension and hyperlipidemia, and was diagnosed with Parkinson disease 8 months ago. His current medications include carbidopa-levodopa, hydrochlorothiazide, and atorvastatin. His blood pressure is 150/85 mm Hg. He has short-term memory deficits and appears confused and disheveled. Examination shows bilateral muscle rigidity and resting tremor in his upper extremities. He has a slow gait with short steps. Microscopic examination of the cortex of a patient with the same condition is shown. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Vascular dementia
- B. Lewy body dementia (Correct Answer)
- C. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- D. Normal pressure hydrocephalus
- E. Frontotemporal dementia
CNS infections Explanation: ***Lewy body dementia***
- This patient presents with a classic triad of **dementia**, **Parkinsonism** (rigidity, tremor, slow gait), and **fluctuating cognition** (blank stares, confusion) with **visual hallucinations** (seeing strangers).
- The presence of **Lewy bodies** in the cortex (**alpha-synuclein** aggregates) on microscopic examination is pathognomonic for Lewy body dementia, which can manifest as dementia with Lewy bodies or Parkinson's disease dementia.
*Vascular dementia*
- Characterized by **stepwise cognitive decline** and focal neurological deficits, often with a history of stroke or significant vascular risk factors, although hypertension and hyperlipidemia are present, they do not explain the visual hallucinations or prominent Parkinsonism.
- While memory deficits can occur, the prominent motor symptoms, fluctuating cognition, and visual hallucinations are not typical features differentiating it from Lewy body dementia.
*Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease*
- This rapidly progressive dementia is associated with **myoclonus**, ataxia, and other neurological signs, but generally progresses much faster than described here.
- The **pathology involves spongiform changes** in the brain, not Lewy bodies.
*Normal pressure hydrocephalus*
- Classic triad includes **gait disturbance**, **urinary incontinence**, and **dementia**, often responsive to shunting.
- While gait disturbance is present, the prominent visual hallucinations, fluctuating cognition, and rigidity are not characteristic.
*Frontotemporal dementia*
- Primarily affects personality, behavior, and language, with relative sparing of memory in early stages.
- It does not typically present with the prominent **Parkinsonian features** and **visual hallucinations** seen in this patient.
CNS infections US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old patient presents with rapidly progressive dementia, myoclonus, and ataxia over 3 months. Laboratory studies, including serum vitamin B12 (cyanocobalamin), thyroxine (T4), and thyroid-stimulating hormone concentrations, are within normal limits. A lumbar puncture is performed. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Increased 14-3-3 protein concentration (Correct Answer)
- B. Antiganglioside GM1 antibodies
- C. Anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies
- D. Increased α-synuclein protein concentration
- E. Oligoclonal bands
CNS infections Explanation: ***Increased 14-3-3 protein concentration***
- The constellation of **rapidly progressive dementia**, **myoclonus**, and **ataxia** over 3 months with normal routine labs is highly suggestive of **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)**.
- An **elevated 14-3-3 protein concentration** in the CSF is a **classic diagnostic marker** for CJD, reflecting rapid neuronal destruction and included in the **WHO diagnostic criteria**.
- This is the most characteristic CSF finding in CJD, with high sensitivity and specificity.
*Oligoclonal bands*
- **Oligoclonal bands** are indicative of intrathecal antibody production and are characteristic of **inflammatory or demyelinating conditions** such as **multiple sclerosis** and **CNS infections**.
- They are **NOT typically found in prion diseases** like CJD, which involve protein misfolding rather than immune-mediated inflammation.
*Increased α-synuclein protein concentration*
- **Alpha-synuclein accumulation** is characteristic of **synucleinopathies** such as Parkinson's disease, Lewy body dementia, and multiple system atrophy.
- While these can involve dementia and motor symptoms, they typically have a **slower progression** and different symptom profile than the rapid course seen in CJD.
*Antiganglioside GM1 antibodies*
- **Anti-ganglioside GM1 antibodies** are primarily associated with autoimmune **motor neuropathies**, particularly **multifocal motor neuropathy** and some forms of Guillain-Barré syndrome.
- They are not typically associated with rapidly progressive dementia or CJD.
*Anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase antibodies*
- **Anti-glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) antibodies** are primarily associated with **stiff-person syndrome** and certain types of **autoimmune encephalitis**.
- While these conditions can present with neurological symptoms, the clinical picture of rapidly progressive dementia with myoclonus and ataxia is not typical for GAD antibody-mediated disorders.
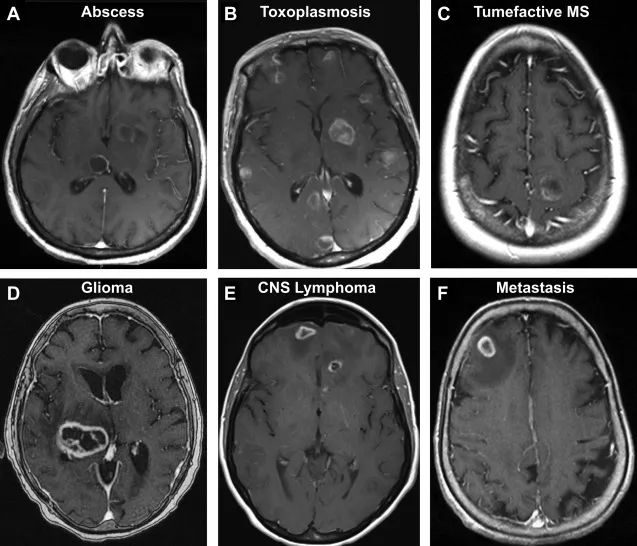
CNS infections US Medical PG Question 5: A 52-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of headaches, vertigo, and changes to his personality for the past few weeks. He was diagnosed with HIV 14 years ago and was started on antiretroviral therapy at that time. Medical records from one month ago indicate that he followed his medication schedule inconsistently. Since then, he has been regularly taking his antiretroviral medications and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. His vital signs are within normal limits. Neurological examination shows ataxia and apathy. Mini-Mental State Examination score is 15/30. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 12.5 g/dL
Leukocyte count 8400/mm3
Segmented neutrophils 80%
Eosinophils 1%
Lymphocytes 17%
Monocytes 2%
CD4+ T-lymphocytes 90/μL
Platelet count 328,000/mm3
An MRI of the brain with contrast shows a solitary ring-enhancing lesion involving the corpus callosum and measuring 4.5 cm in diameter. A lumbar puncture with subsequent cerebrospinal fluid analysis shows slight pleocytosis, and PCR is positive for Epstein-Barr virus DNA. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. CNS lymphoma (Correct Answer)
- B. AIDS dementia
- C. Glioblastoma
- D. Bacterial brain abscess
- E. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
CNS infections Explanation: ***CNS lymphoma***
- The patient's **immunosuppressed state (CD4 count 90/µL)** and the **solitary ring-enhancing lesion in the corpus callosum** are highly suggestive of CNS lymphoma.
- The **positive Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) DNA in CSF** is a strong indicator, as primary CNS lymphoma in HIV-positive patients is often associated with EBV infection.
*AIDS dementia*
- Characterized by **widespread cortical atrophy** and demyelination rather than a solitary, well-defined mass.
- While associated with cognitive decline, it doesn't typically present with a **mass lesion** or **EBV DNA in CSF**.
*Glioblastoma*
- More commonly presents as an **irregularly enhancing mass** in immunocompetent individuals and is less common in HIV patients with low CD4 counts.
- **EBV DNA in CSF** is not a feature of glioblastoma.
*Bacterial brain abscess*
- Usually presents with **fever, seizures, and focal neurological deficits**, and often multiple lesions.
- There is no mention of fever or a clear source of bacterial infection, and **EBV DNA in CSF** is not typical.
*Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy*
- Typically presents with **non-enhancing white matter lesions** without mass effect.
- Caused by the **JC virus (JCV)**, not EBV, and does not show ring enhancement.
CNS infections US Medical PG Question 6: A 13-year-old girl is brought to the physician because of worsening fever, headache, photophobia, and nausea for 2 days. One week ago, she returned from summer camp. She has received all age-appropriate immunizations. Her temperature is 39.1°C (102.3°F). She is oriented to person, place, and time. Physical examination shows a maculopapular rash. There is rigidity of the neck; forced flexion of the neck results in involuntary flexion of the knees and hips. Cerebrospinal fluid studies show:
Opening pressure 120 mm H2O
Appearance Clear
Protein 47 mg/dL
Glucose 68 mg/dL
White cell count 280/mm3
Segmented neutrophils 15%
Lymphocytes 85%
Which of the following is the most likely causal organism?
- A. Echovirus (Correct Answer)
- B. Listeria monocytogenes
- C. Streptococcus pneumoniae
- D. Herpes simplex virus
- E. Neisseria meningitidis
CNS infections Explanation: ***Echovirus***
- The patient's symptoms (fever, headache, photophobia, maculopapular rash, neck rigidity) along with CSF findings of **lymphocytic pleocytosis**, **normal glucose**, and **moderately elevated protein** are highly suggestive of **aseptic meningitis**.
- **Enteroviruses**, such as Echovirus, are the most common cause of **viral (aseptic) meningitis**, especially in children and during summer months, fitting the patient's age and recent summer camp attendance.
*Listeria monocytogenes*
- This organism typically causes meningitis in **neonates, elderly, or immunocompromised individuals**, which does not fit this healthy 13-year-old girl.
- While it can cause lymphocytic pleocytosis, it is less likely given the patient's age and presentation.
*Streptococcus pneumoniae*
- This is a common cause of **bacterial meningitis**, characterized by **PMN predominance (neutrophilic pleocytosis)**, **low CSF glucose**, and **markedly elevated CSF protein**, which are not seen in this case.
- The patient is also described as having received all age-appropriate immunizations, likely including the pneumococcal vaccine.
*Herpes simplex virus*
- HSV can cause aseptic meningitis or encephalitis, but it often presents with **focal neurological deficits** or **seizures** in cases of encephalitis, which are absent here.
- While it can cause lymphocytic pleocytosis, the maculopapular rash is less typical for HSV meningitis compared to enteroviruses.
*Neisseria meningitidis*
- This typically causes **bacterial meningitis** with characteristic CSF findings of **neutrophilic pleocytosis**, **low glucose**, and **high protein**.
- Although it can cause a rash (petechial or purpuric), the CSF profile and absence of petechiae make bacterial meningitis less likely.
CNS infections US Medical PG Question 7: A 67-year-old man presents to the emergency department with confusion. The patient is generally healthy, but his wife noticed him becoming progressively more confused as the day went on. The patient is not currently taking any medications and has no recent falls or trauma. His temperature is 102°F (38.9°C), blood pressure is 126/64 mmHg, pulse is 120/min, respirations are 17/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam is notable for a confused man who cannot participate in a neurological exam secondary to his confusion. No symptoms are elicited with flexion of the neck and jolt accentuation of headache is negative. Initial laboratory values are unremarkable and the patient's chest radiograph and urinalysis are within normal limits. An initial CT scan of the head is unremarkable. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. CT angiogram of the head and neck
- B. Vancomycin, ceftriaxone, ampicillin, and dexamethasone
- C. Acyclovir (Correct Answer)
- D. PCR of the cerebrospinal fluid
- E. MRI of the head
CNS infections Explanation: ***Acyclovir***
- This patient presents with **acute confusion and fever** without an obvious infectious source, negative meningeal signs, and normal initial imaging, highly suggestive of **herpes simplex encephalitis (HSE)**.
- HSE is a **medical emergency** with high mortality (70-80%) if untreated, but mortality drops to 20-30% with early acyclovir therapy.
- **Empiric acyclovir must be started immediately** upon clinical suspicion of HSE, **without waiting for diagnostic confirmation**.
- Standard management includes obtaining CSF for PCR **concurrently** with starting acyclovir, but treatment should never be delayed for diagnostic testing.
- The best next step in **management** is initiating acyclovir; CSF PCR is obtained for confirmation but does not delay treatment.
*PCR of the cerebrospinal fluid*
- **CSF PCR for HSV** is the gold standard **diagnostic test** for HSE with high sensitivity (96%) and specificity (99%).
- While lumbar puncture should be performed to obtain CSF for PCR, this is a **diagnostic step** that should be done **concurrently** with starting acyclovir, not instead of it.
- The question asks for best next step in **management**, not diagnosis—acyclovir therapy takes precedence.
- Delaying acyclovir while awaiting diagnostic confirmation significantly increases morbidity and mortality.
*Vancomycin, ceftriaxone, ampicillin, and dexamethasone*
- This broad-spectrum antibiotic regimen is empiric therapy for **bacterial meningitis** and should be considered in patients with fever and altered mental status.
- However, the **absence of meningeal signs** (negative nuchal rigidity, negative jolt accentuation) makes bacterial meningitis less likely.
- In practice, when HSE is suspected but bacterial meningitis cannot be excluded, both antimicrobial regimens may be initiated empirically, but the primary concern here is HSE given the clinical presentation.
*MRI of the head*
- **MRI with FLAIR sequences** is highly sensitive for HSE and typically shows **temporal lobe involvement** (especially medial temporal lobes).
- However, MRI findings may be **normal early in the disease course** (first 48-72 hours).
- MRI is useful for supporting the diagnosis but should **not delay empiric acyclovir therapy**.
- Obtaining MRI before treatment would be inappropriate given the time-sensitive nature of HSE.
*CT angiogram of the head and neck*
- CT angiography evaluates vascular structures and is indicated for suspected **stroke, aneurysm, or vascular dissection**.
- This patient lacks focal neurological deficits, signs of acute stroke, or vascular risk factors that would prioritize vascular imaging.
- The presentation with fever and diffuse encephalopathy points toward an infectious/inflammatory process rather than a vascular etiology.
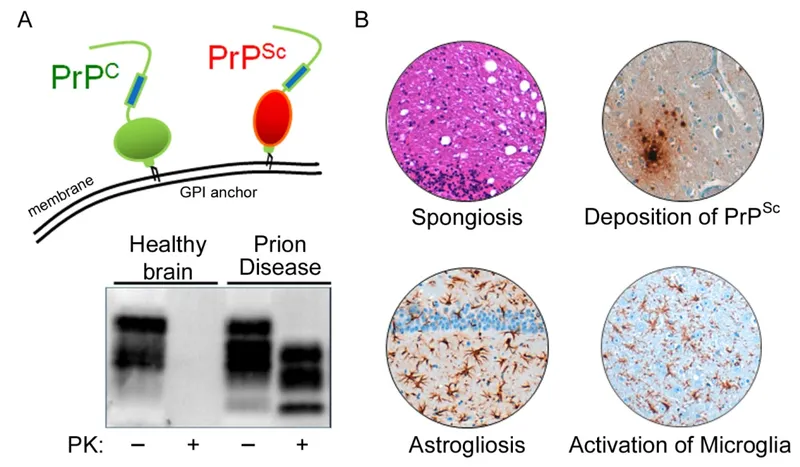
CNS infections US Medical PG Question 8: A 65-year-old man with no significant medical history begins to have memory loss and personality changes. Rapidly, over the next few months his symptoms increase in severity. He experiences a rapid mental deterioration associated with sudden, jerking movements, particularly in response to being startled. He has gait disturbances as well. Eventually, he lapses into a coma and dies approximately ten months after the onset of symptoms. Which of the following would most likely be seen on autopsy of the brain in this patient?
- A. Neurofibrillary tangles
- B. Amyloid plaques
- C. Spongiform changes (Correct Answer)
- D. Vascular lesions
- E. Lewy bodies
CNS infections Explanation: ***Spongiform changes***
- This patient's **rapidly progressive dementia**, associated with **myoclonus (jerking movements)** and **gait disturbances**, culminating in death within months, is highly suggestive of **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)**.
- CJD is characterized by the accumulation of abnormally folded prion proteins (PrPSc), leading to **spongiform degeneration** (vacuolation) of neurons and neuropil, **neuronal loss**, and **astrogliosis** in the brain.
*Neurofibrillary tangles*
- **Neurofibrillary tangles**, composed primarily of hyperphosphorylated **tau protein**, are a hallmark of **Alzheimer's disease**.
- Alzheimer's disease typically has a much **slower progression** over several years, unlike the rapid deterioration seen in this patient.
*Amyloid plaques*
- **Amyloid plaques**, formed by the extracellular deposition of **beta-amyloid protein**, are also characteristic features of **Alzheimer's disease**.
- Like neurofibrillary tangles, amyloid plaques are associated with a chronic, progressive course of dementia, not the **rapidly fatal trajectory** described.
*Vascular lesions*
- **Vascular lesions**, such as infarcts or hemorrhages, are the underlying pathology in **vascular dementia**.
- While vascular dementia can cause cognitive decline, its presentation often involves **step-wise deterioration** and may be associated with focal neurological deficits, which are not the primary features here.
*Lewy bodies*
- **Lewy bodies**, which are intracellular cytoplasmic inclusions of **alpha-synuclein protein**, are characteristic of **Lewy body dementia** and **Parkinson's disease**.
- Lewy body dementia presents with fluctuating cognition, visual hallucinations, and parkinsonism, but typically does not show the **rapid progression** and prominent myoclonus seen in CJD.
CNS infections US Medical PG Question 9: A 40-year-old man presents to the office with complaints of epigastric discomfort for the past 6 months. He adds that the discomfort is not that bothersome as it does not interfere with his daily activities. He does not have any other complaints at the moment. The past medical history is insignificant. He is a non-smoker and does not consume alcohol. He recently came back from a trip to South America where he visited a relative who owned a sheep farm. On physical examination, he has a poorly palpable epigastric non-tender mass with no organomegaly. The hepatitis B and C serology are negative. The liver CT scan and MRI are shown. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Echinococcosis (Correct Answer)
- B. Liver abscess
- C. Hepatocellular carcinoma
- D. Tuberculosis
- E. Hemangioma
CNS infections Explanation: ***Echinococcosis (Correct Answer)***
- The patient's history of travel to **South America** and contact with a **sheep farm** is highly suggestive of exposure to *Echinococcus granulosus*, the causative agent of hydatid disease.
- The **CT scan image** shows a large, well-defined cyst with a **calcified wall** and internal septations, consistent with the characteristic appearance of a **hydatid cyst** in the liver.
- This presentation is classic for **hepatic echinococcosis**: chronic indolent course, epidemiological exposure, and pathognomonic imaging findings.
*Liver abscess (Incorrect)*
- Liver abscesses typically present with more acute symptoms such as **fever, chills, and significant pain**, which are absent in this case.
- Imaging usually reveals a **hypo-dense lesion** with a rim of enhancement, possibly gas formation, and less commonly a calcified wall.
*Hepatocellular carcinoma (Incorrect)*
- This patient lacks typical risk factors for HCC, such as **chronic hepatitis B or C infection** (serology is negative) or cirrhosis.
- HCC imaging typically shows an **enhancing mass** that washes out on delayed phases, without the calcified, multi-loculated appearance seen here.
*Tuberculosis (Incorrect)*
- Hepatic tuberculosis typically presents with fever, weight loss, and multiple **small, hypo-dense lesions** on imaging, often with an associated pulmonary or extra-pulmonary focus.
- The single, large, calcified cystic lesion seen on imaging is not characteristic of hepatic tuberculosis.
*Hemangioma (Incorrect)*
- Hepatic hemangiomas are benign vascular tumors that often present as **incidental findings** and are typically asymptomatic.
- On CT scans, they show characteristic **peripheral nodular enhancement** that fills in centripetally on delayed phases, which is different from the calcified cyst observed.
CNS infections US Medical PG Question 10: A 43-year-old male visits the emergency room around 4 weeks after getting bitten by a bat during a cave diving trip. After cleansing the wound with water, the patient reports that he felt well enough not to seek medical attention immediately following his trip. He does endorse feeling feverish in the past week but a new onset of photophobia and irritability led him to seek help today. What would the post-mortem pathology report show if the patient succumbs to this infection?
- A. Howell-Jolly bodies
- B. Heinz bodies
- C. Psammoma bodies
- D. Pick bodies
- E. Negri bodies (Correct Answer)
CNS infections Explanation: ***Negri bodies***
- This patient's symptoms (fever, photophobia, irritability) and history of a bat bite point to rabies. **Negri bodies** are eosinophilic inclusions found in the cytoplasm of hippocampal and Purkinje cells in cases of rabies.
- They are **pathognomonic** for rabies infection and represent viral nucleocapsid proteins.
*Howell-Jolly bodies*
- These are **nuclear remnants** found in red blood cells that indicate impaired splenic function or asplenia.
- They are not associated with viral infections like rabies and are observed in conditions like sickle cell disease or after splenectomy.
*Heinz bodies*
- **Heinz bodies** are inclusions within red blood cells composed of denatured hemoglobin.
- They are typically seen in conditions involving **oxidative stress** to red blood cells, such as G6PD deficiency or alpha-thalassemia, not rabies.
*Psammoma bodies*
- These are **calcified, laminated, concentric spherules** found in some tumors (e.g., papillary thyroid carcinoma, meningioma, serous ovarian cystadenocarcinoma).
- They are a marker of specific neoplastic conditions and have no relevance to viral infections.
*Pick bodies*
- **Pick bodies** are aggregates of tau protein found in neurons, characteristic of **Pick's disease**, a type of frontotemporal dementia.
- They are neurodegenerative markers and are unrelated to infectious diseases.
More CNS infections US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.