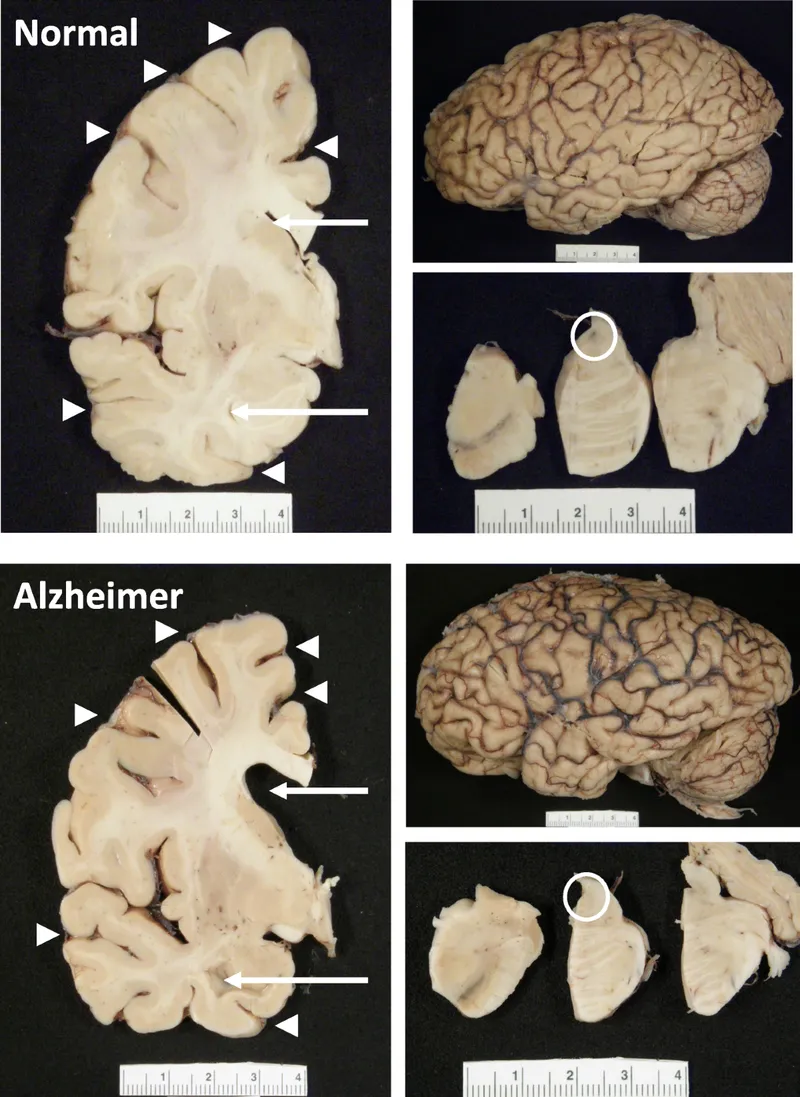
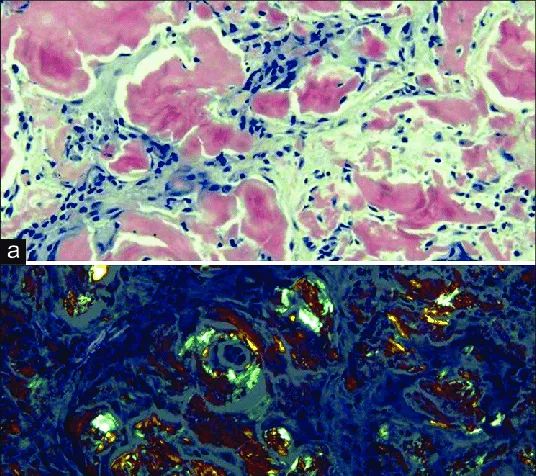
Alzheimer's disease pathology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Alzheimer's disease pathology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Alzheimer's disease pathology US Medical PG Question 1: A 70-year-old man with a long-standing history of diabetes mellitus type 2 and hypertension presents with complaints of constant wrist and shoulder pain. Currently, the patient undergoes hemodialysis 2 to 3 times a week and is on the transplant list for a kidney. The patient denies any recent traumas. Which of the following proteins is likely to be increased in his plasma, causing the patient’s late complaints?
- A. Amyloid precursor protein
- B. Amyloid A (AA)
- C. β2-microglobulin (Correct Answer)
- D. Transthyretin (TTR)
- E. Ig light chains
Alzheimer's disease pathology Explanation: **β2-microglobulin**
- The patient's presentation with **chronic wrist and shoulder pain**, particularly in the setting of **long-term hemodialysis for end-stage renal disease (ESRD)**, is highly suggestive of **dialysis-related amyloidosis (DRA)**.
- **β2-microglobulin** is a small protein that is normally filtered by the kidneys. In ESRD patients on hemodialysis, it accumulates and forms amyloid deposits, primarily in joint capsules, synovium, and bones.
*Amyloid precursor protein*
- **Amyloid precursor protein (APP)** is primarily associated with **Alzheimer's disease**, where its proteolytic cleavage leads to the formation of amyloid-beta plaques in the brain.
- It is not directly implicated in joint pain or musculoskeletal amyloidosis in the context of renal failure.
*Amyloid A (AA)*
- **Amyloid A (AA)** is the protein responsible for **secondary (reactive) amyloidosis**, which is typically associated with chronic inflammatory conditions like rheumatoid arthritis or chronic infections.
- While the patient has some chronic conditions (diabetes, hypertension), his joint pain is more characteristic of dialysis-related amyloidosis, not systemic inflammation-induced AA amyloidosis.
*Transthyretin (TTR)*
- **Transthyretin (TTR)** is associated with **familial amyloid polyneuropathy** and **senile systemic amyloidosis (SSA)**, causing heart failure or carpal tunnel syndrome, but it is not directly linked to dialysis-related amyloidosis.
- The patient's symptoms are more indicative of the specific type of amyloidosis seen in ESRD.
*Ig light chains*
- **Immunoglobulin (Ig) light chains** are involved in **primary (AL) amyloidosis**, which is caused by a plasma cell dyscrasia.
- While AL amyloidosis can affect various organs, including joints, the patient's history of ESRD and hemodialysis makes **β2-microglobulin amyloidosis** the most specific and likely cause of his musculoskeletal symptoms.
Alzheimer's disease pathology US Medical PG Question 2: A 45-year-old man is brought to the hospital by his daughter with complaints of wide-based gait. His daughter reveals that he was sitting silently in the examination chair with a blank face. In addition, he was frequently talking to the empty chairs and told that his friends are sitting there. He has been forgetting many small things recently. On physical examination, fine movements are seen at resting condition that disappears when he is asked to drink water. A stepwise slowness in movement is also seen in his upper limb. Which of the following is most likely to be observed in the histological specimen of this patient?
- A. Spongiform changes in cortex
- B. Neuritic plaques in cortex
- C. Lewy bodies in affected neurons (Correct Answer)
- D. Tau protein aggregates in cortex
- E. Neurofibrillary tangles in hippocampus
Alzheimer's disease pathology Explanation: ***Lewy bodies in affected neurons***
- The patient's symptoms of **wide-based gait**, **cognitive decline** (forgetting things, talking to empty chairs), **psychotic features** (visual hallucinations), and **motor symptoms** (resting tremor, bradykinesia) are highly suggestive of **Lewy body dementia** (LBD).
- **Lewy bodies**, which are abnormal aggregates of **alpha-synuclein protein**, are the characteristic histological finding in neurons of individuals with LBD, found in both **cortical areas** (defining feature of LBD) and **substantia nigra**.
- The presence of early prominent visual hallucinations with parkinsonism and cognitive fluctuations is pathognomonic for Lewy body dementia.
*Spongiform changes in cortex*
- This finding is characteristic of **prion diseases**, such as **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease** (CJD), which typically present with rapidly progressive dementia and myoclonus.
- While CJD involves cognitive decline, the presence of resting tremor, visual hallucinations, and a more gradual progression with parkinsonian features makes spongiform changes unlikely.
*Neuritic plaques in cortex*
- **Neuritic plaques**, composed of **amyloid-beta protein**, are a hallmark of **Alzheimer's disease**.
- Although Alzheimer's disease causes cognitive decline, the prominent early motor symptoms (resting tremor, wide-based gait, bradykinesia) and early visual hallucinations are not typical features of Alzheimer's disease.
*Tau protein aggregates in cortex*
- **Tau protein aggregates** (neurofibrillary tangles) are another key histological feature of **Alzheimer's disease** and certain **tauopathies** like **frontotemporal dementia** and **progressive supranuclear palsy**.
- While associated with dementia, they do not explain the unique combination of early parkinsonian motor features and prominent visual hallucinations seen in this patient.
*Neurofibrillary tangles in hippocampus*
- **Neurofibrillary tangles** composed of hyperphosphorylated **tau protein** in the hippocampus are characteristic of **Alzheimer's disease** and correlate with memory impairment.
- However, Alzheimer's disease does not typically present with early parkinsonism, resting tremor, or prominent visual hallucinations as seen in this patient with Lewy body dementia.
Alzheimer's disease pathology US Medical PG Question 3: A 36-year-old woman is brought to the emergency room by her husband for “weird behavior" for the past several weeks. He reports that her right arm has been moving uncontrollably in a writhing movement and that she has been especially irritable. She has a history of depression, which was diagnosed 4 years ago and is currently being treated with sertraline. She denies any recent fever, trauma, infections, travel, weakness, or sensory changes. She was adopted so is unsure of her family history. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for her symptoms?
- A. Frontotemporal lobe degeneration
- B. Presence of misfolded proteins in the brain
- C. Development of intracellular eosinophilic inclusions
- D. CAG triplet expansion on chromosome 4 (Correct Answer)
- E. GAA triplet expansion on chromosome 9
Alzheimer's disease pathology Explanation: ***CAG triplet expansion on chromosome 4***
- The patient's symptoms of **chorea** (uncontrolled writhing movements) and **irritability** (psychiatric changes) are classic manifestations of **Huntington's disease**.
- **Huntington's disease** is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disorder caused by a **CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion** on **chromosome 4** in the *HTT* gene.
*Frontotemporal lobe degeneration*
- **Frontotemporal dementia** typically presents with prominent behavioral changes (disinhibition, apathy) or language difficulties (aphasia), but **chorea** is not a characteristic feature.
- While psychiatric symptoms can occur, the specific motor dysfunction described points away from isolated frontotemporal degeneration.
*Presence of misfolded proteins in the brain*
- While **Huntington's disease** does involve misfolded huntingtin protein, this answer choice is too general and could apply to many neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's (beta-amyloid, tau) or Parkinson's (alpha-synuclein).
- It does not specify the unique genetic basis directly responsible for the observed symptoms in this case.
*Development of intracellular eosinophilic inclusions*
- **Intracellular eosinophilic inclusions**, specifically **Lewy bodies**, are characteristic of **Parkinson's disease** and **Lewy body dementia**.
- These conditions primarily present with parkinsonism or dementia, not the prominent choreiform movements seen in this patient.
*GAA triplet expansion on chromosome 9*
- A **GAA triplet expansion on chromosome 9** is the genetic cause of **Friedreich's ataxia**, an autosomal recessive disorder.
- Friedreich's ataxia typically presents with progressive **ataxia**, dysarthria, and loss of proprioception, not chorea or prominent psychiatric changes like irritability.
Alzheimer's disease pathology US Medical PG Question 4: A 1-week-old baby is brought to the pediatrician’s office for a routine checkup. On examination, she is observed to have microcephaly with a prominent occiput. She also has clenched fists and rocker-bottom feet with prominent calcanei. A cardiac murmur is evident on auscultation. Based on the clinical findings, a diagnosis of nondisjunction of chromosome 18 is suspected. The pediatrician orders a karyotype for confirmation. He goes on to explain to the mother that her child will face severe growth difficulties. Even if her daughter progresses beyond a few months, she will not be able to reach developmental milestones at the appropriate age. In addition to the above, which of the following is most likely a consequence of this genetic disturbance?
- A. Supravalvular aortic stenosis
- B. Alzheimer’s disease
- C. Macroglossia
- D. Cutis aplasia
- E. Death within the first year of life (Correct Answer)
Alzheimer's disease pathology Explanation: ***Death within the first year of life***
- This patient has Trisomy 18, also known as Edwards syndrome, which is characterized by a high mortality rate, with **90-95% of affected infants dying within the first year** due to severe congenital anomalies, especially cardiac defects.
- **Rocker-bottom feet**, **clenched fists with overlapping fingers**, **microcephaly with a prominent occiput**, and **congenital heart defects** (such as ventricular septal defects or patent ductus arteriosus) are classic features of Trisomy 18.
*Cutis aplasia*
- **Cutis aplasia** (a congenital absence of skin) is a characteristic symptom of **Trisomy 13 (Patau syndrome)**, not Trisomy 18.
- While both are chromosomal abnormalities, their specific phenotypic presentations differ, making cutis aplasia less likely in this case.
*Macroglossia*
- **Macroglossia** (an enlarged tongue) is a common feature of **Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)**.
- It is not typically associated with Trisomy 18, which presents with distinct facial and oral features.
*Alzheimer’s disease*
- Individuals with **Down syndrome (Trisomy 21)** have an increased risk of developing **early-onset Alzheimer's disease**, often by middle age.
- This is due to the triplication of the **APP gene**, located on chromosome 21, which is involved in amyloid-beta plaque formation.
*Supravalvular aortic stenosis*
- **Supravalvular aortic stenosis** (narrowing of the aorta above the aortic valve) is a characteristic cardiac finding in **Williams syndrome**, a microdeletion syndrome involving chromosome 7.
- Williams syndrome is also associated with elfin facies, intellectual disability, and a friendly personality, none of which align with this patient's presentation.
Alzheimer's disease pathology US Medical PG Question 5: A 65-year-old man was picked up by the security personnel for voiding urine and defecating at an inappropriate place in the community. On questioning, he was making offensive remarks and behaving inappropriately. On physical examination, the physician observed signs of cognitive impairment and amnesia. Initial urine drug screen is negative for any drugs of abuse. Which is the most likely pathological finding present in this patient?
- A. Drug abuse
- B. Amyloid plaques
- C. Lewy bodies
- D. Pick bodies (Correct Answer)
- E. PrPSC Sheets
Alzheimer's disease pathology Explanation: ***Pick bodies***
- The patient presents with **disinhibition** (inappropriate voiding, defecating in public), **offensive remarks**, and **inappropriate behavior**, which are hallmarks of **frontotemporal dementia (FTD)**, specifically the behavioral variant.
- **Pick bodies** are aggregates of **tau protein** found in neurons of the frontal and temporal lobes, characteristic of Pick's disease, a subtype of FTD.
- Behavioral variant FTD characteristically presents with **personality changes**, **loss of social awareness**, and **executive dysfunction** before significant memory impairment.
*Drug abuse*
- While drug abuse can lead to inappropriate behavior and neuropsychiatric symptoms, the **negative urine drug screen** makes this diagnosis unlikely.
- Drug abuse typically doesn't present with the progressive cognitive decline and specific behavioral pattern seen here.
*Amyloid plaques*
- **Amyloid plaques** (along with neurofibrillary tangles) are characteristic pathological findings in **Alzheimer's disease**, which typically presents with **memory impairment** as the predominant initial symptom.
- Although Alzheimer's disease can lead to behavioral changes in later stages, the **prominent early disinhibition** and preserved memory (relative to behavioral changes) are more typical of FTD than Alzheimer's.
*Lewy bodies*
- **Lewy bodies** are associated with **dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB)** and **Parkinson's disease dementia**.
- DLB is characterized by **fluctuating cognition**, **visual hallucinations**, and **parkinsonism** (rigidity, bradykinesia), which are not the predominant features in this patient's presentation.
*PrPSC Sheets*
- **PrPSC sheets** refer to the misfolded prion protein found in **prion diseases** such as Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD).
- CJD typically manifests with **rapidly progressive dementia** (over weeks to months), **myoclonus**, and **cerebellar signs**, with a much faster progression than the clinical picture suggested here.
Alzheimer's disease pathology US Medical PG Question 6: An 81-year-old woman presents to your office accompanied by her husband. She has been doing well except for occasional word finding difficulty. Her husband is concerned that her memory is worsening over the past year. Recently, she got lost twice on her way home from her daughter’s house, was unable to remember her neighbor’s name, and could not pay the bills like she usually did. She has a history of hypertension and arthritis. She has no significant family history. Her medications include a daily multivitamin, hydrochlorothiazide, and ibuprofen as needed. Physical exam is unremarkable. Which of the following is associated with an increased risk of this patient’s disease?
- A. Presenilin-2
- B. ApoE2
- C. ApoE4 (Correct Answer)
- D. Female gender
- E. Advanced age (>85 years)
Alzheimer's disease pathology Explanation: ***Correct: ApoE4***
- The patient's symptoms (progressive memory loss, getting lost on familiar routes, difficulty with routine tasks like paying bills) in an 81-year-old suggest **Alzheimer's disease**.
- The **ApoE4 allele** is a well-established genetic risk factor for **late-onset Alzheimer's disease**, significantly increasing the likelihood (3-fold increased risk for one allele, 12-fold for two alleles) and often lowering the age of onset.
- ApoE4 is the **most specific and discriminating risk factor** among the options provided.
*Incorrect: Presenilin-2*
- **Presenilin-2** mutations are associated with **early-onset familial Alzheimer's disease**, which typically manifests before age 65 and often has a strong family history.
- This patient is 81 years old and has no significant family history, making early-onset familial AD unlikely.
*Incorrect: ApoE2*
- The **ApoE2 allele** is actually associated with a **decreased risk** of Alzheimer's disease.
- It is thought to be protective due to its more efficient clearance of amyloid beta peptides from the brain.
*Incorrect: Female gender*
- While **female gender** is indeed a risk factor for Alzheimer's disease (women have approximately 2:1 higher lifetime risk even after adjusting for longevity), it is less specific than ApoE4 as a discriminating answer.
- All patients have a biological sex, but only some carry the ApoE4 allele, making ApoE4 a more useful clinical and epidemiological marker.
*Incorrect: Advanced age (>85 years)*
- **Advanced age** is actually the strongest non-modifiable risk factor for Alzheimer's disease, with incidence doubling every 5 years after age 65.
- However, in the context of this question, **ApoE4 is the better answer** because it represents a specific genetic risk factor that can be tested and is directly associated with disease pathogenesis, whereas advanced age is a universal demographic factor that applies to all individuals who live long enough.
Alzheimer's disease pathology US Medical PG Question 7: A 68-year-old man is brought to the physician by his wife because she is concerned about his speech being irregular. Specifically, she says that over the last 8 months, her husband has been saying increasingly nonsensical statements at home. In addition, he is no longer able to perform basic verbal tasks such as ordering from a menu or giving directions even though he was an English teacher prior to retirement. She also reports that he has recently started attempting to kiss strangers and urinate in public. Finally, she has also noticed that he has been frequently binge eating sweets even though he was previously very conscientious about his health. When asked about these activities, the patient does not have insight into his symptoms. Which of the following would most likely be seen in this patient?
- A. Intracellular hyperphosphorylated tau proteins
- B. Alpha-synuclein
- C. Large intracellular vacuoles
- D. Perivascular inflammation
- E. Hyperphosphorylated tau inclusion bodies (Correct Answer)
Alzheimer's disease pathology Explanation: ***Hyperphosphorylated tau inclusion bodies***
- The patient's symptoms of **disinhibition** (kissing strangers, public urination), **personality changes** (binge eating sweets), and **progressive language dysfunction** are characteristic of **frontotemporal dementia (FTD)**.
- FTD has heterogeneous pathology: approximately **40-50% of cases** involve **tau pathology** (forming Pick bodies and neurofibrillary tangles), while 50-60% show **TDP-43 pathology**.
- The term **"inclusion bodies"** specifically refers to the aggregated, pathological deposits visible microscopically, making this the most precise answer.
- Tau pathology is particularly associated with **Pick's disease**, a subtype of FTD characterized by **Pick bodies** (spherical tau inclusions).
*Intracellular hyperphosphorylated tau proteins*
- This describes the **same pathological process** as the correct answer but is **less specific**.
- While technically accurate for tau-positive FTD cases, the term lacks the specificity of "inclusion bodies," which denotes the characteristic aggregated form seen on microscopy.
- In pathology, precision matters: stating "inclusion bodies" indicates you recognize the specific morphological finding.
*Alpha-synuclein*
- **Alpha-synuclein** aggregates (Lewy bodies) are characteristic of **Lewy body dementia** and **Parkinson's disease dementia**.
- These conditions typically present with **fluctuating cognition**, **visual hallucinations**, **parkinsonism**, and **REM sleep behavior disorder**.
- The prominent behavioral disinhibition and language dysfunction without parkinsonian features point away from synucleinopathies.
*Large intracellular vacuoles*
- **Spongiform change** (vacuolation) with prion protein accumulation is pathognomonic for **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD)**.
- CJD presents with **rapidly progressive dementia** (weeks to months), **myoclonus**, **ataxia**, and periodic sharp waves on EEG.
- The **gradual 8-month progression** and absence of myoclonus make prion disease unlikely.
*Perivascular inflammation*
- **Perivascular lymphocytic infiltration** indicates **inflammatory or infectious CNS disease**, such as **vasculitis** or **viral encephalitis**.
- This patient's **chronic, insidious progression** over 8 months without acute features argues against an inflammatory process.
Alzheimer's disease pathology US Medical PG Question 8: A 69-year-old man is brought to clinic by his daughter for poor memory. She states that over the past two years his memory has been slowly declining though he has been able to take care of himself, pay his own rent, and manage his finances. However, two months ago she noticed a sharp decline in his cognitive functioning as well as his gait. Then one month ago, she noticed a similar decline in his functioning again that came on suddenly. The patient has a past medical history of diabetes mellitus type II, hypertension, obesity, and dyslipidemia. Current medications include hydrochlorothiazide, lisinopril, metformin, and glipizide. His blood pressure is 165/95 mmHg, pulse is 82/minute, he is afebrile, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Cardiac exam reveals a crescendo-decrescendo murmur heard in the left upper sternal border that radiates to the carotids. Abdominal exam is benign, and neurologic exam reveals an unsteady gait. Which of the following findings is associated with the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Neurofibrillary tangles and hyperphosphorylated tau
- B. Fronto-temporal degeneration
- C. Diffuse, subtle atrophy of the brain, subtle ventricular enlargement
- D. Lewy bodies found on biopsy
- E. Multiple lacunar infarcts (Correct Answer)
Alzheimer's disease pathology Explanation: ***Multiple lacunar infarcts***
- The patient's history of **stepwise decline** in cognitive function, vascular risk factors (hypertension, diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia), and unsteadiness of gait are highly suggestive of **vascular dementia**. Multiple lacunar infarcts are the pathological hallmark of this condition.
- The **crescendo-decrescendo murmur** radiating to the carotids indicates **aortic stenosis**, which although not directly causing the dementia, is another sign of widespread vascular disease in an elderly patient.
*Neurofibrillary tangles and hyperphosphorylated tau*
- These are the characteristic pathological findings in **Alzheimer's disease**, which typically presents with a **gradual and progressive decline** rather than the stepwise deterioration described here.
- While Alzheimer's is common, the sudden, repeated declines strongly point away from its typical insidious progression.
*Fronto-temporal degeneration*
- This is the pathological basis for **frontotemporal dementia**, which usually presents with early and prominent changes in **personality, behavior, or language**, rather than memory being the primary initial symptom.
- The patient's primary symptom is memory decline, and the sudden, stepwise deterioration is not typical for frontotemporal dementia.
*Diffuse, subtle atrophy of the brain, subtle ventricular enlargement*
- While cortical atrophy and ventricular enlargement can be seen in various neurodegenerative conditions, they are **non-specific findings** and do not explain the distinct **stepwise decline** pattern.
- These findings might be present in many types of dementia, but they do not specifically point to the underlying cause as clearly as the stepwise decline points to vascular issues.
*Lewy bodies found on biopsy*
- This is characteristic of **Lewy body dementia**, which typically presents with a **fluctuating cognitive function**, **visual hallucinations**, and **parkinsonism**.
- While there is an unsteady gait, the history does not mention hallucinations or other motor features typical of Parkinsonism, and the predominant pattern is stepwise decline rather than fluctuation.
Alzheimer's disease pathology US Medical PG Question 9: A 28-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 1-year history of intermittent buzzing in both her ears. She says she sometimes has episodes of mild dizziness which resolve spontaneously. She has a 15-year history of type 1 diabetes mellitus and episodes of low back pain. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Current medications include insulin and aspirin. She works as a trombonist for a symphony orchestra. Her vital signs are within normal limits. On otoscopic examination, the tympanic membrane appears normal. Bone conduction is greater than air conduction in both ears. Weber test shows no lateralization. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Presbycusis
- B. Diabetic otopathy
- C. Drug-induced ototoxicity
- D. Otosclerosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Endolymphatic hydrops
Alzheimer's disease pathology Explanation: ***Otosclerosis***
- The combination of **conductive hearing loss** (**bone conduction > air conduction**), **intermittent buzzing (tinnitus)**, and mild dizziness in a young adult is characteristic of otosclerosis. The normal tympanic membrane further supports this diagnosis as it indicates no external or middle ear infection/perforation.
- **Weber test shows no lateralization** because the conductive hearing loss is **symmetric and bilateral**, meaning both ears are equally affected.
*Presbycusis*
- This is an age-related **sensorineural hearing loss** that typically affects older individuals, usually over 50-60 years old, not a 28-year-old.
- Presbycusis usually presents with **air conduction > bone conduction** (sensorineural pattern) and affects high frequencies first, not conductive hearing loss.
*Diabetic otopathy*
- While patients with long-standing diabetes can develop hearing loss, it is typically a **sensorineural hearing loss** due to microvascular damage, not conductive hearing loss.
- The symptoms in diabetic otopathy usually involve high-frequency hearing loss and are not typically associated with bone conduction exceeding air conduction.
*Drug-induced ototoxicity*
- **Aspirin** can cause tinnitus and sensorineural hearing loss, but the presented case demonstrates **conductive hearing loss** (bone conduction > air conduction).
- Aspirin ototoxicity typically causes reversible sensorineural hearing loss and tinnitus, not the conductive pattern seen here.
*Endolymphatic hydrops*
- Also known as **Meniere's disease**, this condition causes episodic **vertigo, tinnitus, and sensorineural hearing loss**.
- The hearing loss is typically **sensorineural** and often fluctuating, while this patient presents with signs of **conductive hearing loss**.
Alzheimer's disease pathology US Medical PG Question 10: A 56-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with several episodes in which she felt "dizzy." She has had these symptoms on and off for the past year and can recall no clear exacerbating factor or time of day when her symptoms occur. She has a perpetual sensation of fullness in her ear but otherwise has no symptoms currently. Her temperature is 97.6°F (36.4°C), blood pressure is 122/77 mmHg, pulse is 85/min, respirations are 13/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Cardiopulmonary exam is unremarkable. The patient's gait is stable. Which of the following is also likely to be found in this patient?
- A. Gradually improving symptoms
- B. Conductive hearing loss
- C. Positional vertigo
- D. Sensorineural hearing loss (Correct Answer)
- E. Vertical nystagmus
Alzheimer's disease pathology Explanation: ***Sensorineural hearing loss***
- The sensation of **aural fullness**, recurrent dizzy spells without clear triggers, and the episodic nature of symptoms are classic for **Ménière's disease**.
- **Ménière's disease** is characterized by the triad of **vertigo**, **tinnitus**, and **sensorineural hearing loss**, often accompanied by ear fullness.
*Gradually improving symptoms*
- **Ménière's disease** is a chronic, progressive condition, and symptoms typically **fluctuate** in severity and can worsen over time, rather than gradually improving.
- While periods of remission can occur, the underlying pathology does make a steady improvement unlikely without intervention.
*Conductive hearing loss*
- **Conductive hearing loss** results from problems with sound transmission to the inner ear, such as **earwax** or **ossicular chain dysfunction**.
- **Ménière's disease** specifically affects the inner ear (cochlea and vestibular system), leading to **sensorineural hearing loss** due to endolymphatic hydrops.
*Positional vertigo*
- **Positional vertigo** suggests conditions like **Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)**, where vertigo is triggered by specific head movements due to otolith displacement.
- In this patient, the vertigo is described as recurrent and "on and off" without "clear exacerbating factor," which is less consistent with positional vertigo.
*Vertical nystagmus*
- **Vertical nystagmus** is typically indicative of **central vestibular lesions** or brainstem dysfunction.
- The symptoms presented, including aural fullness and episodic dizziness, point towards a **peripheral vestibular disorder** like Ménière's disease, which usually causes horizontal or rotatory nystagmus during acute attacks.
More Alzheimer's disease pathology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.