Neuropathology

On this page
🧠 The Neuropathology Command Center: Decoding Brain Disease Architecture
The brain's architectural failures-from misfolded proteins choking neurons to diagnostic patterns that separate Alzheimer's from frontotemporal dementia-demand precision thinking that bridges microscope and bedside. You'll master how protein aggregation pathways drive disease, recognize the quantitative criteria that distinguish overlapping pathologies, and deploy evidence-based frameworks that transform neuropathological findings into targeted interventions. This lesson builds your command of the molecular machinery, diagnostic discrimination skills, and systems-level integration needed to decode complex brain diseases with confidence and clinical impact.
Cellular Architecture: The Neural Foundation
The nervous system's unique cellular organization creates specific vulnerability patterns that define neuropathological processes:
- Neurons: Post-mitotic cells with limited regenerative capacity
- Gray matter concentration: 86 billion neurons in human brain
- Metabolic demand: 20% of total body glucose consumption
- Vulnerability: Hypoxia tolerance <4 minutes before irreversible damage
- Glial Cells: Support network comprising 50% of brain volume
- Astrocytes: Blood-brain barrier maintenance, 10:1 astrocyte-to-neuron ratio
- Oligodendrocytes: Myelin production, 1 cell myelinates 40+ axons
- Microglia: CNS immune surveillance, activation within 30 minutes of injury
📌 Remember: GOAN - Glia Outnumber, Astrocytes Nurture (Glial cells outnumber neurons, astrocytes provide metabolic support and maintain BBB integrity)
Pathological Response Patterns
Neural tissue responds to injury through stereotyped patterns that form the foundation of neuropathological diagnosis:
| Response Type | Timeline | Cellular Changes | Clinical Significance | Reversibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute Neuronal Injury | 0-24 hours | Chromatolysis, nuclear pyknosis | Stroke, trauma assessment | Potentially reversible |
| Chronic Neuronal Loss | Weeks-months | Gliosis, tissue atrophy | Neurodegenerative diseases | Irreversible |
| Demyelination | Days-weeks | Myelin loss, axon preservation | MS, inflammatory disorders | Potentially reversible |
| Wallerian Degeneration | 2-4 weeks | Distal axon breakdown | Peripheral nerve injury | Requires regeneration |
| Reactive Gliosis | 48-72 hours | Astrocyte proliferation | Universal injury response | Permanent scarring |
Vascular Vulnerability Zones
The brain's vascular architecture creates watershed territories where pathology preferentially develops:
- Border Zone Infarcts: Junction areas between major arterial territories
- ACA-MCA watershed: Parasagittal frontal-parietal cortex
- MCA-PCA watershed: Posterior temporal-occipital junction
- Hypoperfusion threshold: <20 mL/100g/min cerebral blood flow
- Deep Watershed Areas: Periventricular white matter
- Vulnerable to chronic hypoperfusion in elderly
- Leukoaraiosis development with >65 years age progression
💡 Master This: Watershed infarcts occur at cerebral blood flow <20 mL/100g/min, creating characteristic "string of pearls" pattern on imaging-essential for recognizing hypoperfusion injury patterns.

Understanding these foundational concepts establishes the framework for recognizing how specific disease processes exploit neural vulnerabilities, setting the stage for exploring the molecular mechanisms that drive neuropathological changes.
🧠 The Neuropathology Command Center: Decoding Brain Disease Architecture
⚙️ Molecular Machinery Malfunction: Protein Aggregation Pathways
Protein Aggregation Cascade Mechanisms
The protein aggregation process follows predictable stages with specific therapeutic windows:
- Nucleation Phase: Lag time 10-20 years before clinical symptoms
- Critical oligomer size: 6-12 protein units for pathological activity
- Seeding concentration: <1% misfolded protein can initiate cascade
- Propagation Phase: Exponential growth over 2-5 years
- Prion-like spreading: Cell-to-cell transmission via synaptic connections
- Doubling time: 6-12 months for aggregate burden
- Saturation Phase: Clinical symptom onset with >30% neuronal loss
📌 Remember: NIPS - Nucleation (20 years), Initiation (seeding), Propagation (2-5 years), Symptoms (30% loss)

Disease-Specific Protein Signatures
| Disease | Primary Protein | Aggregate Type | Location | Onset Age | Progression Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alzheimer's | Aβ42 + Tau | Plaques + Tangles | Hippocampus → Cortex | 65-75 years | 8-10 years |
| Parkinson's | α-Synuclein | Lewy Bodies | Substantia Nigra → Cortex | 55-65 years | 15-20 years |
| Huntington's | Huntingtin | Nuclear Inclusions | Striatum → Cortex | 35-45 years | 15-25 years |
| ALS | TDP-43/SOD1 | Cytoplasmic Inclusions | Motor Cortex + Spinal Cord | 50-60 years | 2-5 years |
| Frontotemporal | Tau/TDP-43 | Pick Bodies/Inclusions | Frontal/Temporal Cortex | 45-65 years | 6-8 years |
Cellular Defense System Failures
Neural cells employ multiple quality control mechanisms that become overwhelmed in neurodegenerative diseases:
- Ubiquitin-Proteasome System: Degrades 80% of cellular proteins
- Capacity: 1-2% of total cellular protein per hour
- Failure threshold: >150% normal protein load overwhelms system
- Age-related decline: 40% reduction in proteasome activity by age 70
- Autophagy-Lysosome Pathway: Bulk protein and organelle clearance
- Basal autophagy: 2-3% cellular volume recycled daily
- Stress response: 10-fold increase in autophagosome formation
- Lysosomal pH: 4.5-5.0 required for optimal enzyme function
💡 Master This: Proteasome capacity decreases 40% by age 70, while protein damage increases 200%-creating the "perfect storm" for aggregate accumulation in aging brains.
These molecular mechanisms establish the foundation for understanding how protein aggregation patterns create distinct clinical phenotypes, leading us to explore the diagnostic frameworks that distinguish between different neurodegenerative processes.
⚙️ Molecular Machinery Malfunction: Protein Aggregation Pathways
🎯 Pattern Recognition Arsenal: Diagnostic Discrimination Frameworks
Morphological Pattern Recognition Matrix
- Cellular Patterns: Size, shape, and staining characteristics
- Neuronal loss: >30% reduction for clinical significance
- Gliosis patterns: Fibrillary vs. protoplasmic astrocyte predominance
- Inflammatory infiltrates: Perivascular vs. parenchymal distribution
- Tissue Architecture: Laminar organization and connectivity
- Cortical lamination: 6-layer preservation vs. selective vulnerability
- White matter integrity: Myelin preservation vs. axonal loss
- Vascular changes: Amyloid angiopathy vs. hyaline arteriopathy
📌 Remember: MAGIC - Morphology, Architecture, Gliosis, Inflammation, Clinical correlation (systematic evaluation sequence for neuropathological diagnosis)
"See This, Think That" Clinical Correlations
Temporal Lobe Patterns:
- Hippocampal sclerosis + memory loss → Temporal lobe epilepsy (80% association)
- Asymmetric atrophy + language dysfunction → Primary progressive aphasia (90% left hemisphere)
- Bilateral atrophy + episodic memory loss → Alzheimer's disease (95% hippocampal involvement)
Brainstem Patterns:
- Substantia nigra depigmentation + movement disorder → Parkinson's disease (>70% neuronal loss)
- Pontine atrophy + cerebellar signs → Multiple system atrophy (MSA-C subtype)
- Medullary involvement + respiratory dysfunction → Progressive supranuclear palsy (brainstem variant)
Cortical Distribution Patterns:
- Frontal predominance + behavioral changes → Frontotemporal dementia (Pick's disease)
- Parietal predominance + visuospatial deficits → Posterior cortical atrophy (Alzheimer's variant)
- Occipital involvement + visual symptoms → Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (Heidenhain variant)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Hippocampal sclerosis affects CA1 and subiculum in 95% of cases, while CA3 preservation distinguishes it from global hypoxic injury-critical for epilepsy surgery planning.
Rapid Screening Decision Trees
Diagnostic Confidence Thresholds:
- >90% confidence: 3+ pathognomonic features present
- 70-90% confidence: 2 major + 2 minor criteria met
- <70% confidence: Requires additional testing or tissue confirmation
💡 Master This: Age of onset <40 years shifts differential toward genetic causes (85% probability), while >65 years favors sporadic neurodegenerative diseases (75% probability)-fundamental triage principle.
These pattern recognition frameworks provide the foundation for systematic differential diagnosis, preparing us to explore the quantitative criteria that distinguish between similar neuropathological entities.
🎯 Pattern Recognition Arsenal: Diagnostic Discrimination Frameworks
🔬 Microscopic Battlefield Analysis: Quantitative Pathological Criteria
Standardized Quantitative Assessment Criteria
| Parameter | Normal Range | Mild Pathology | Moderate Pathology | Severe Pathology | Clinical Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neuronal Density | 200-400/mm² | 150-200/mm² | 100-150/mm² | <100/mm² | <150/mm² symptomatic |
| Amyloid Plaques | 0-2/mm² | 3-10/mm² | 11-25/mm² | >25/mm² | >15/mm² diagnostic |
| Neurofibrillary Tangles | 0-1/mm² | 2-5/mm² | 6-15/mm² | >15/mm² | >10/mm² significant |
| Lewy Bodies | 0/mm² | 1-3/mm² | 4-10/mm² | >10/mm² | >5/mm² diagnostic |
| Microglial Activation | 5-10% | 15-25% | 30-50% | >50% | >30% inflammatory |
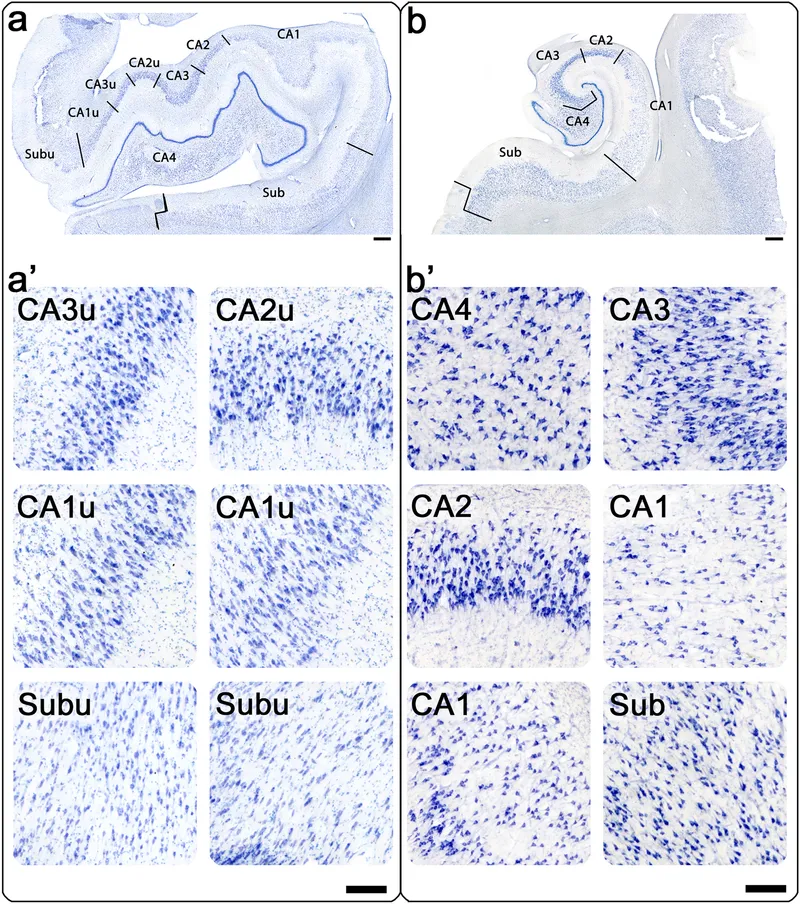
Disease-Specific Quantitative Signatures
Alzheimer's Disease Staging (Braak Criteria):
- Stage I-II: Entorhinal cortex involvement, <5 tangles/mm²
- Stage III-IV: Hippocampal spread, 10-20 tangles/mm²
- Stage V-VI: Neocortical involvement, >25 tangles/mm²
- Clinical correlation: Stages I-II asymptomatic, III-IV mild cognitive impairment, V-VI dementia
Parkinson's Disease Progression (Braak α-synuclein):
- Stage 1: Medulla oblongata, dorsal motor nucleus
- Stage 2: Pontine tegmentum, locus coeruleus
- Stage 3: Midbrain, substantia nigra (>70% neuronal loss for symptoms)
- Stage 4: Temporal mesocortex, cognitive symptoms emerge
- Stage 5-6: Neocortical involvement, dementia development
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Substantia nigra neuronal loss >70% correlates with motor symptom onset in Parkinson's disease, while >50% loss may remain asymptomatic-explaining the "preclinical phase".
Inflammatory Response Quantification
Microglial Activation Patterns:
- Resting microglia: Ramified morphology, small cell body
- Activated microglia: Amoeboid shape, enlarged cell body
- Quantification: Iba1+ cell density and morphological index
- Activation threshold: >30% activated microglia indicates significant neuroinflammation
Astrocytic Response Grading:
- Grade 1: Mild hypertrophy, preserved processes
- Grade 2: Moderate enlargement, process thickening
- Grade 3: Severe hypertrophy, gemistocytic morphology
- Grade 4: Fibrillary gliosis, scar formation
💡 Master This: Microglial activation >30% precedes neuronal loss by 6-12 months, providing a therapeutic window for anti-inflammatory interventions before irreversible damage occurs.
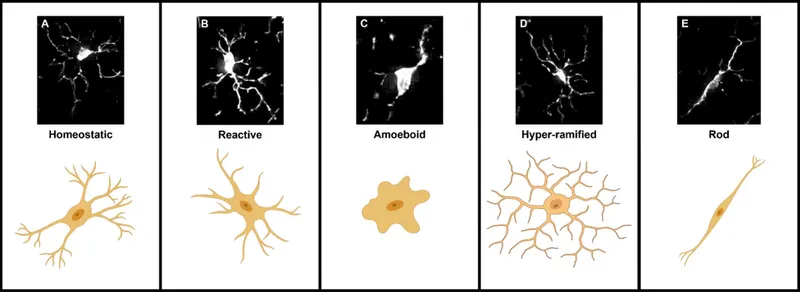
Protein Aggregate Burden Assessment
Standardized Scoring Systems:
- CERAD Neuritic Plaques: None (0), Sparse (1), Moderate (2), Frequent (3)
- Braak Neurofibrillary Tangles: Stages 0-VI based on anatomical distribution
- McKeith Lewy Body Score: None, Mild, Moderate, Severe in specific brain regions
Quantitative Thresholds for Diagnosis:
- Alzheimer's: CERAD ≥2 + Braak ≥IV + appropriate clinical syndrome
- Parkinson's: Lewy bodies in substantia nigra + >70% neuronal loss
- Dementia with Lewy Bodies: Limbic/neocortical Lewy bodies + cognitive symptoms
These quantitative frameworks establish objective criteria for neuropathological diagnosis, setting the foundation for exploring evidence-based treatment algorithms that target specific pathological processes.
🔬 Microscopic Battlefield Analysis: Quantitative Pathological Criteria
⚕️ Therapeutic Targeting Algorithms: Evidence-Based Intervention Strategies
Molecular Target-Specific Treatment Algorithms
Anti-Amyloid Therapy Protocols:
- Aducanumab: 10 mg/kg IV monthly, 38% plaque reduction at 78 weeks
- Lecanemab: 10 mg/kg IV biweekly, 27% clinical decline reduction
- ARIA monitoring: MRI at weeks 5, 9, 14, then every 6 months
- Efficacy threshold: >20% amyloid reduction for clinical benefit
Tau-Targeting Strategies:
- Passive immunotherapy: Monthly IV infusions, CSF tau reduction >30%
- Active vaccination: Quarterly injections, antibody titer >1:1000
- Small molecule inhibitors: Daily oral dosing, brain penetration >10%
📌 Remember: ARIA - Amyloid-Related Imaging Abnormalities (monitor at weeks 5, 9, 14, then every 6 months for anti-amyloid therapies)
Evidence-Based Treatment Outcomes
| Intervention | Target Population | Primary Endpoint | Success Rate | Monitoring Frequency | Cost-Effectiveness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anti-Amyloid mAb | Early AD | CDR-SB reduction | 27-38% | Monthly MRI × 4 | $56,000/QALY |
| Tau Immunotherapy | Mild-Moderate AD | Tau PET reduction | 15-25% | Quarterly CSF | Under study |
| Deep Brain Stimulation | Advanced PD | UPDRS improvement | 65-75% | 3-month visits | $35,000/QALY |
| Gene Therapy | Genetic ALS | Survival extension | 40-60% | Monthly labs | $125,000/QALY |
| Immunomodulation | MS | Relapse reduction | 70-85% | 6-month MRI | $45,000/QALY |
Personalized Treatment Selection Criteria
Biomarker-Guided Therapy Selection:
- CSF Aβ42/40 ratio <0.89: Anti-amyloid therapy candidate
- CSF p-tau >25 pg/mL: Tau-targeting intervention
- Neurofilament light >40 pg/mL: Neuroprotective strategy priority
- APOE4 homozygous: Increased ARIA risk, modified dosing
Clinical Staging for Intervention Timing:
- Preclinical (biomarker positive, cognitively normal): Prevention trials
- Prodromal (MCI + biomarkers): Disease-modifying therapy
- Mild dementia (CDR 0.5-1.0): Combination approaches
- Moderate-severe (CDR >1.0): Symptomatic management
💡 Master This: APOE4 homozygotes have 15-fold increased ARIA risk with anti-amyloid therapy, requiring dose reduction and enhanced monitoring-genetic testing essential before treatment initiation.
Combination Therapy Strategies
Multi-Target Approaches:
- Anti-amyloid + tau therapy: Synergistic effect in 30-40% patients
- Immunomodulation + neuroprotection: Additive benefit for inflammatory conditions
- Symptomatic + disease-modifying: Quality of life + progression slowing
Monitoring Protocol Integration:
- Baseline assessment: Comprehensive biomarker panel + imaging
- Early monitoring (0-6 months): Safety parameters + target engagement
- Efficacy assessment (6-18 months): Clinical outcomes + biomarker response
- Long-term follow-up (>18 months): Sustained benefit + progression monitoring
These evidence-based treatment algorithms provide the framework for implementing targeted neuropathological interventions, leading us to explore how multiple pathological processes interact in complex clinical presentations.
⚕️ Therapeutic Targeting Algorithms: Evidence-Based Intervention Strategies
🌐 Systems Integration Matrix: Multi-Pathology Convergence Patterns
Multi-Pathology Interaction Networks
Primary-Secondary Pathology Cascades:
- Alzheimer's → Vascular pathology: Amyloid angiopathy in 85% of AD cases
- CAA severity correlates with cognitive decline rate (r=0.72)
- Microhemorrhage risk: 15-fold increase with severe CAA
- Treatment implications: Anti-amyloid therapy contraindicated with >4 microbleeds
- Parkinson's → Alzheimer's pathology: Lewy body dementia development
- Dual pathology in 60% of advanced PD cases
- Cognitive decline acceleration: 2.5-fold faster with mixed pathology
- Cholinesterase inhibitor response: Enhanced efficacy in dual pathology
Inflammatory Amplification Circuits:
- Protein aggregates → Microglial activation → Enhanced aggregation
- Neuronal death → Damage-associated molecular patterns → Chronic inflammation
- Blood-brain barrier disruption → Peripheral immune infiltration → Tissue damage
📌 Remember: CAMP - Cerebral Amyloid angiopathy, Mixed pathology, Peripheral inflammation (convergence patterns in complex neuropathology)
Convergence Zone Vulnerabilities
| Brain Region | Primary Vulnerability | Secondary Pathology | Convergence Rate | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hippocampus | Alzheimer's tau | Vascular + TDP-43 | 75% | Memory + executive |
| Substantia Nigra | α-Synuclein | Tau + inflammation | 60% | Motor + cognitive |
| Frontal Cortex | FTD pathology | Alzheimer's + vascular | 45% | Behavioral + executive |
| Brainstem | Multiple pathologies | Vascular + protein | 80% | Autonomic + motor |
| White Matter | Vascular disease | Protein deposits | 90% | Processing speed |
Cutting-Edge Research Integration
Emerging Pathological Mechanisms:
- Prion-like spreading: Cell-to-cell transmission of misfolded proteins
- Tau spreading rate: 1-2 brain regions per year in AD progression
- α-Synuclein propagation: Braak staging reflects anatomical connectivity
- Therapeutic target: Intercellular transfer inhibition
- Glymphatic system dysfunction: Protein clearance failure
- Sleep disruption reduces glymphatic flow by 60%
- Aging decreases clearance efficiency by 40%
- AQP4 polarization loss in 80% of AD cases
Precision Medicine Applications:
- Polygenic risk scores: >100 genetic variants for AD susceptibility
- Biomarker panels: Multi-analyte prediction models with >85% accuracy
- Imaging signatures: Multi-modal patterns for differential diagnosis
💡 Master This: Glymphatic dysfunction reduces protein clearance by 40-60% with aging and sleep disruption, creating a "perfect storm" for aggregate accumulation-sleep optimization becomes a therapeutic intervention.
Therapeutic Integration Strategies
Multi-Target Combination Approaches:
- Protein aggregation + inflammation: Anti-amyloid + microglial modulation
- Vascular + neurodegenerative: Cardiovascular optimization + neuroprotection
- Metabolic + protein pathology: Insulin sensitization + aggregate clearance
Personalized Medicine Algorithms:
- Genetic profiling: APOE status + polygenic risk for treatment selection
- Biomarker stratification: CSF/plasma panels for pathway targeting
- Imaging phenotyping: Multi-modal signatures for precision therapy
Systems-Level Monitoring:
- Multi-domain assessment: Cognitive + motor + behavioral + autonomic
- Biomarker trajectories: Longitudinal patterns for treatment response
- Network connectivity: Functional MRI for circuit-based interventions
These systems integration concepts establish the foundation for developing comprehensive clinical mastery tools that synthesize complex neuropathological knowledge into practical diagnostic and therapeutic frameworks.
🌐 Systems Integration Matrix: Multi-Pathology Convergence Patterns
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid-Fire Diagnostic Tools
Essential Neuropathology Quick-Reference Matrix
| Clinical Presentation | Key Pathological Feature | Diagnostic Threshold | Treatment Priority | Prognosis Marker |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Progressive memory loss | Hippocampal tau tangles | Braak Stage ≥IV | Anti-amyloid therapy | MMSE decline 3-4/year |
| Asymmetric tremor | Substantia nigra Lewy bodies | >70% neuronal loss | Dopamine replacement | Hoehn-Yahr progression |
| Behavioral disinhibition | Frontal Pick bodies | Tau-positive inclusions | Behavioral management | Survival 6-8 years |
| Rapid cognitive decline | Spongiform changes | PrP immunostaining | Supportive care | Death 6-12 months |
| Fluctuating cognition | Cortical Lewy bodies | Limbic/neocortical | Cholinesterase inhibitors | Faster decline than AD |
High-Yield Diagnostic Discriminators
Age-Based Probability Shifts:
- <40 years: Genetic causes 85%, metabolic 10%, inflammatory 5%
- 40-65 years: Early neurodegenerative 60%, genetic 25%, vascular 15%
- >65 years: Alzheimer's 40%, vascular 25%, mixed pathology 20%, other 15%
Anatomical Distribution Signatures:
- Hippocampal predominance: Alzheimer's disease (95% sensitivity)
- Asymmetric frontal atrophy: Frontotemporal dementia (90% specificity)
- Brainstem involvement: Progressive supranuclear palsy (85% diagnostic)
- Striatal changes: Huntington's disease (pathognomonic)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Hippocampal volume loss >15% combined with CSF tau >400 pg/mL provides >90% diagnostic accuracy for Alzheimer's disease in appropriate clinical context.
Rapid Assessment Protocols
30-Second Neuropathology Screen:
- Age + onset pattern → Genetic vs. sporadic
- Distribution + symmetry → Focal vs. diffuse
- Progression rate → Acute vs. chronic
- Associated features → Pure vs. mixed pathology
Critical Decision Points:
- Tissue biopsy indicated: Atypical presentation + treatment implications
- Genetic testing priority: Early onset + family history
- Biomarker assessment: Diagnostic uncertainty + therapeutic candidates
- Imaging requirements: Differential diagnosis + progression monitoring
💡 Master This: Rapid progression (>4 MMSE points/year) shifts differential toward prion disease, autoimmune encephalitis, or malignancy-requiring urgent evaluation and tissue confirmation.
Evidence-Based Clinical Commandments
The Neuropathology Ten:
- Age <40 = genetic until proven otherwise
- Rapid decline = rule out treatable causes first
- Asymmetric presentation = focal pathology likely
- Mixed symptoms = multiple pathologies probable
- Family history = genetic testing indicated
- Treatment response = confirms suspected pathology
- Biomarker discordance = mixed or atypical disease
- Imaging-pathology mismatch = reconsider diagnosis
- Plateau progression = vascular component likely
- Early behavioral changes = frontotemporal spectrum
Understanding these rapid mastery tools transforms complex neuropathological knowledge into immediate clinical decision-making capabilities, enabling precise diagnosis and optimal therapeutic interventions across the spectrum of neurodegenerative diseases.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid-Fire Diagnostic Tools
Practice Questions: Neuropathology
Test your understanding with these related questions
A group of neurologists develop a new blood test for Alzheimer's. They are optimistic about the test, as they have found that for any given patient, the test repeatedly produces very similar results. However, they find that the new test results are not necessarily consistent with the gold standard of diagnosis. How would this new test most accurately be described?













