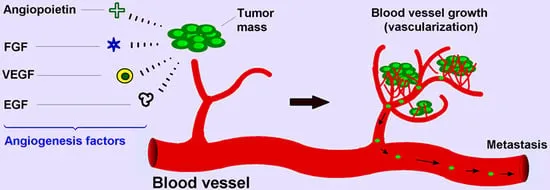
Tumor angiogenesis US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Tumor angiogenesis. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Tumor angiogenesis US Medical PG Question 1: A research team develops a new monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitor for advanced melanoma that has shown promise in animal studies as well as high efficacy and low toxicity in early phase human clinical trials. The research team would now like to compare this drug to existing standard of care immunotherapy for advanced melanoma. The research team decides to conduct a non-randomized study where the novel drug will be offered to patients who are deemed to be at risk for toxicity with the current standard of care immunotherapy, while patients without such risk factors will receive the standard treatment. Which of the following best describes the level of evidence that this study can offer?
- A. Level 1
- B. Level 3 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 5
- D. Level 4
- E. Level 2
Tumor angiogenesis Explanation: ***Level 3***
- A **non-randomized controlled trial** like the one described, where patient assignment to treatment groups is based on specific characteristics (risk of toxicity), falls into Level 3 evidence.
- This level typically includes **non-randomized controlled trials** and **well-designed cohort studies** with comparison groups, which are prone to selection bias and confounding.
- The study compares two treatments but lacks randomization, making it Level 3 evidence.
*Level 1*
- Level 1 evidence is the **highest level of evidence**, derived from **systematic reviews and meta-analyses** of multiple well-designed randomized controlled trials or large, high-quality randomized controlled trials.
- The described study is explicitly stated as non-randomized, ruling out Level 1.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence involves at least one **well-designed randomized controlled trial** (RCT) or **systematic reviews** of randomized trials.
- The current study is *non-randomized*, which means it cannot be classified as Level 2 evidence, as randomization is a key criterion for this level.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence includes **case series**, **case-control studies**, and **poorly designed cohort or case-control studies**.
- While the study is non-randomized, it is a controlled comparative trial rather than a case series or retrospective case-control study, placing it at Level 3.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, typically consisting of **expert opinion** without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research, or animal studies.
- While the drug was initially tested in animal studies, the current human comparative study offers a higher level of evidence than expert opinion or preclinical data.
Tumor angiogenesis US Medical PG Question 2: A patient with HCC and a long history of alcohol dependence and chronic hepatitis C has been using the mTOR inhibitor sirolimus 100 mg for cancer treatment. Her cancer has shown a partial response. She also has a history of hypertension and poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by diabetic retinopathy. Current medications include enalapril and insulin. She asks her oncologist and hepatologist if she could try everolimus for its purported survival benefit in treating HCC. Based on clinical considerations, which of the following statements is most accurate?
- A. The patient should start everolimus 50 mg because of the survival benefit relative to sirolimus 100 mg
- B. The patient is not a good candidate for everolimus due to her history of hypertension
- C. The patient should start everolimus 100 mg because of the survival benefit relative to sirolimus 100 mg
- D. The patient should start everolimus 50 mg because of her history of alcohol use disorder and hepatitis C
- E. The patient is not a good candidate for everolimus due to her history of diabetes (Correct Answer)
Tumor angiogenesis Explanation: ***The patient is not a good candidate for Noxbinle due to her history of diabetes***
- The current medication is sirolimus, an **mTOR inhibitor** and its successor everolimus, also an mTOR inhibitor, is not beneficial for this patient due to her **poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus**.
- mTOR inhibitors, including everolimus, are known to **worsen hyperglycemia** and **accelerate the progression of diabetes**, making it contraindicated in patients with already complicated diabetes.
*The patient should start everolimus 50 mg because of the survival benefit relative to sirolimus 100 mg*
- There is **no established evidence** that everolimus at any dose offers a superior survival benefit compared to sirolimus in HCC, particularly after a partial response to sirolimus.
- **Switching mTOR inhibitors** without a compelling clinical reason, especially with existing comorbidities, is not standard practice.
*The patient is not a good candidate for everolimus due to her history of hypertension*
- While mTOR inhibitors can contribute to **hypertension**, this patient is already on **enalapril** for her existing hypertension.
- Her **poorly controlled diabetes** presents a more direct and severe contraindication due to the metabolic side effects of everolimus.
*The patient should start everolimus 100 mg because of the survival benefit relative to sirolimus 100 mg*
- No clinical data supports a **superior survival benefit** of everolimus 100 mg over sirolimus 100 mg in HCC.
- Given the patient's existing **poorly controlled diabetes**, increasing the dose of an mTOR inhibitor or switching to an equivalent dose of another would heighten the risk of severe metabolic complications.
*The patient should start everolimus 50 mg because of her history of alcohol use disorder and hepatitis C*
- The patient's history of alcohol dependence and chronic hepatitis C are **risk factors for HCC** but do not directly contraindicate a specific dose of everolimus more than her diabetes.
- While liver impairment due to these conditions might influence dosing of various medications, the **primary concern for everolimus** in this case remains the uncontrolled diabetes.
Tumor angiogenesis US Medical PG Question 3: A 61-year-old man with hypertension and hyperlipidemia comes to the physician for a 4-month history of recurrent episodes of retrosternal chest pain, shortness of breath, dizziness, and nausea. The episodes usually start after physical activity and subside within minutes of resting. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 40 years. He is 176 cm (5 ft 9 in) tall and weighs 95 kg (209 lb); BMI is 30 kg/m2. His blood pressure is 160/100 mm Hg. Coronary angiography shows an atherosclerotic lesion with stenosis of the left anterior descending artery. Compared to normal healthy coronary arteries, increased levels of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) are found in this lesion. Which of the following is the most likely effect of this factor?
- A. Calcification of the atherosclerotic plaque core
- B. Invasion of T-cells through the disrupted endothelium
- C. Increased expression of vascular cell-adhesion molecules
- D. Ingestion of cholesterol by mature monocytes
- E. Intimal migration of smooth muscle cells (Correct Answer)
Tumor angiogenesis Explanation: ***Intimal migration of smooth muscle cells***
- **PDGF** is a potent **mitogen** and **chemotactic factor** for smooth muscle cells, promoting their migration from the tunica media into the intima during atherogenesis.
- This migration is a crucial step in the formation of the **fibrous cap**, contributing to plaque growth and stability.
*Calcification of the atherosclerotic plaque core*
- While calcification does occur in advanced atherosclerotic plaques, it is primarily driven by mechanisms involving **osteoblast-like differentiation** of vascular cells and deposition of **calcium phosphate**, not directly by PDGF.
- PDGF's primary role is in **cellular proliferation** and **migration**, particularly of smooth muscle cells.
*Invasion of T-cells through the disrupted endothelium*
- **T-cell invasion** into the arterial wall is an important inflammatory process in atherosclerosis, but it is primarily mediated by **chemokines** like MCP-1 and adhesion molecules, not directly by PDGF.
- PDGF typically acts on mesenchymal cells (like smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts) rather than immune cells in this context.
*Increased expression of vascular cell-adhesion molecules*
- **Expression of adhesion molecules** (e.g., VCAM-1, ICAM-1) is crucial for the recruitment of inflammatory cells, but this process is mainly driven by **pro-inflammatory cytokines** like TNF-α and IL-1, not PDGF.
- While there might be indirect effects, PDGF's direct role is not primarily in promoting adhesion molecule expression.
*Ingestion of cholesterol by mature monocytes*
- **Ingestion of cholesterol** by **macrophages** (which mature from monocytes) leads to the formation of **foam cells**, a hallmark of early atherosclerosis.
- This process is largely driven by oxidized LDL uptake, often facilitated by scavenger receptors, rather than directly by PDGF.
Tumor angiogenesis US Medical PG Question 4: A 62-year-old woman presents to her oncologist to discuss the chemotherapy options for her newly diagnosed breast cancer. During the meeting, they discuss a drug that inhibits the breakdown of mitotic spindles in cells. Her oncologist explains that this will be more toxic to cancer cells because those cells are dividing more rapidly. Which of the following side effects is closely associated with the use of this chemotherapeutic agent?
- A. Photosensitivity
- B. Peripheral neuropathy (Correct Answer)
- C. Paralytic ileus
- D. Hemorrhagic cystitis
- E. Pulmonary fibrosis
Tumor angiogenesis Explanation: ***Peripheral neuropathy***
- Drugs that inhibit the breakdown of **mitotic spindles** are **microtubule-targeting agents** (e.g., **taxanes** like paclitaxel/docetaxel, **vinca alkaloids** like vincristine/vinblastine).
- These agents interfere with **microtubule function** in neurons, leading to **axonal damage** and **peripheral neuropathy**.
- This is the **most characteristic and common dose-limiting toxicity** of microtubule inhibitors, affecting sensory and motor nerves (numbness, tingling, weakness in extremities).
*Photosensitivity*
- **Photosensitivity** is a common adverse effect associated with certain chemotherapeutic agents like **fluorouracil** (5-FU) or **methotrexate**, but is not linked to microtubule inhibitors.
- It involves an increased sensitivity to UV light, often manifesting as a rash or exaggerated sunburn.
*Paralytic ileus*
- **Paralytic ileus** can occur with **vinca alkaloids** (especially vincristine) due to autonomic neuropathy affecting the **enteric nervous system**.
- However, this is **less common** than peripheral neuropathy and occurs more specifically with vincristine rather than taxanes.
- **Peripheral neuropathy** is the more pervasive, dose-limiting, and universally characteristic side effect across all microtubule inhibitors.
*Hemorrhagic cystitis*
- **Hemorrhagic cystitis** is a classic side effect of **alkylating agents** like **cyclophosphamide** and **ifosfamide**, which produce the toxic metabolite **acrolein**.
- It is prevented/managed with **mesna**, which inactivates acrolein.
- Not associated with microtubule inhibitors.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- **Pulmonary fibrosis** is a known side effect of certain chemotherapeutic drugs, most notably **bleomycin** and **busulfan**.
- This adverse effect is not associated with agents that target **mitotic spindle breakdown**.
Tumor angiogenesis US Medical PG Question 5: A 66-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of constipation and streaks of blood in his stool. He has had a 10-kg (22-lb) weight loss during this period. Colonoscopy shows an exophytic tumor in the sigmoid colon. A CT scan of the abdomen shows liver metastases and enlarged mesenteric and para-aortic lymph nodes. A diagnosis of stage IV colorectal cancer is made, and palliative chemotherapy is initiated. The chemotherapy regimen includes a monoclonal antibody that inhibits tumor growth by preventing ligand binding to a protein directly responsible for epithelial cell proliferation and organogenesis. Which of the following proteins is most likely inhibited by this drug?
- A. VEGF
- B. TNF-α
- C. EGFR (Correct Answer)
- D. ALK
- E. CD52
Tumor angiogenesis Explanation: ***EGFR***
- The description of a monoclonal antibody preventing ligand binding to a protein responsible for **epithelial cell proliferation** and organogenesis strongly points to the **epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)**.
- EGFR is highly expressed in many colorectal cancers and its activation by ligands like EGF promotes cell growth, survival, and metastasis. Inhibiting it reduces tumor progression.
*VEGF*
- **Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)** is primarily involved in **angiogenesis**, the formation of new blood vessels.
- While anti-VEGF therapies (e.g., bevacizumab) are used in colorectal cancer, their mechanism is inhibiting blood supply to the tumor, not directly blocking a receptor responsible for epithelial cell proliferation as described.
*TNF-α*
- **Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)** is a **cytokine** primarily involved in inflammation and immune responses.
- Antibodies against TNF-α (e.g., infliximab) are used in inflammatory conditions like Crohn's disease, not typically as targeted therapy for colorectal cancer directly inhibiting epithelial proliferation.
*ALK*
- **Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)** is a **receptor tyrosine kinase** often implicated in lung cancer and lymphomas.
- ALK rearrangements lead to oncogenic fusion proteins, but it is not a primary target for widespread epithelial cell proliferation in colorectal cancer.
*CD52*
- **CD52** is a glycoprotein found on the surface of various immune cells, including lymphocytes.
- Antibodies targeting CD52 (e.g., alemtuzumab) are used in certain leukemias and lymphomas to deplete these cells, not for inhibiting epithelial cell proliferation in solid tumors.
Tumor angiogenesis US Medical PG Question 6: A 62-year-old man seeks evaluation at a local walk-in clinic for mid-low back pain of several weeks. He has tried different rehabilitation therapies and medications with no improvement. He was prescribed some pain medications and sent home last week, but the patient presents today with difficulty walking and worsening of his back pain. He was referred to the ER, where he was examined and found to have hypoesthesia from T12 to S4–S5, significant muscle weakness in both lower limbs, and reduced knee and ankle deep tendon reflexes. A hypotonic anal sphincter with conserved deep anal pressure was demonstrated on digital rectal examination, as well as a multinodular, asymmetric prostate. Imaging studies showed multiple sclerotic bone lesions along the spine. Subsequently, a prostate core biopsy was obtained which confirmed the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Which of the following characteristics would you expect in the specimen?
- A. Well-formed glands with an increase in interglandular stroma
- B. Fat invasion
- C. Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia
- D. Small, closely-packed, well-formed glands
- E. Perineural invasion (Correct Answer)
Tumor angiogenesis Explanation: ***Perineural invasion***
- **Perineural invasion** is a common finding in prostate adenocarcinoma, indicating that cancer cells have invaded the nerves surrounding the prostatic glands. This feature is often associated with a higher Gleason score and increased likelihood of extraprostatic extension and metastasis.
- While not visible on gross examination, its presence on biopsy can influence staging and treatment decisions for prostate cancer, particularly regarding the risk of recurrence and spread to other tissues.
*Well-formed glands with an increase in interglandular stroma*
- This description is more indicative of **benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)**, a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate, characterized by an increase in both glandular and stromal components.
- In BPH, the glands typically remain well-formed, and the stroma often proliferates, but these features do not represent malignancy.
*Fat invasion*
- **Fat invasion** is not a typical characteristic of prostate cancer within the prostate gland itself, as the prostate is not primarily composed of fat.
- While prostate cancer can invade periprostatic fatty tissue if it extends beyond the prostatic capsule, fat invasion within the biopsy specimen from the prostate proper is not a diagnostic feature of adenocarcinoma.
*Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia*
- **Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN)** is a pre-malignant lesion where the prostatic ductal and acinar cells show cytologic atypia but remain confined within the basement membrane.
- While PIN (especially high-grade PIN) can be associated with prostate cancer and may precede its development, it is not cancer itself and is not the definitive diagnosis in this case where prostate cancer has been confirmed.
*Small, closely-packed, well-formed glands*
- This description could represent a **low-grade prostate adenocarcinoma** (Gleason pattern 3), where the glands are still relatively well-formed but are more numerous and crowded than in benign tissue.
- However, compared to perineural invasion, which is a more definitive sign of aggressive behavior and advanced disease in a patient presenting with metastatic features (sclerotic bone lesions, neurologic symptoms), this histological finding alone is less specific for the advanced cancer described.
Tumor angiogenesis US Medical PG Question 7: A 6-year-old girl is brought to the physician for pain and increasing swelling over her scalp for 1 month. She has not had any trauma to the area. There is no family or personal history of serious illness. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows a 3-cm solitary, tender mass over the right parietal bone. X-ray of the skull shows a solitary osteolytic lesion. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.9 g/dL
Leukocyte count 7300/mm3
Serum
Na+ 136 mEq/L
K+ 3.7 mEq/L
Cl- 103 mEq/L
Ca2+ 9.1 mg/dL
Glucose 71 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Giant-cell tumor of bone
- B. Langerhans cell histiocytosis (Correct Answer)
- C. Ewing sarcoma
- D. Multiple myeloma
- E. Aneurysmal bone cyst
Tumor angiogenesis Explanation: ***Langerhans cell histiocytosis***
- The presentation of a **solitary osteolytic skull lesion** in a child, especially with pain and swelling, is highly suggestive of **Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH)**.
- LCH can manifest as **eosinophilic granuloma**, which is a localized form primarily affecting bone, often the skull, and commonly presents in children.
*Giant-cell tumor of bone*
- This tumor typically occurs in **young adults (20s-40s)**, not children, and most commonly affects the **epiphysis of long bones**, such as the distal femur or proximal tibia.
- While it can be lytic, its demographic and usual location are inconsistent with this case.
*Ewing sarcoma*
- Ewing sarcoma also presents in children and young adults with bone pain and swelling, but it often involves the **diaphysis of long bones** or the pelvis.
- Radiographically, it is classically described as an **"onion-skin" periosteal reaction** or a permeative lesion, which is not indicated here.
*Multiple myeloma*
- This is a malignancy of **plasma cells** almost exclusively seen in **older adults**, typically over 60 years of age.
- It presents with widespread **punched-out lytic lesions** in the skull, vertebrae, and other bones, along with systemic symptoms like anemia and renal dysfunction.
*Aneurysmal bone cyst*
- An aneurysmal bone cyst is a benign, expansile, lytic bone lesion that can occur in children and often causes pain and swelling.
- However, it typically presents as an **eccentric, expansile lesion** with a thin rim of periosteal new bone formation, and more often affects the metaphysis of long bones or vertebrae, rather than a purely lytic lesion in the parietal bone without trauma.
Tumor angiogenesis US Medical PG Question 8: A 70-year-old man comes to the physician because of right-sided back pain, red urine, and weight loss for the last 4 months. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 40 years. A CT scan of the abdomen shows a large right-sided renal mass. Biopsy of the mass shows polygonal clear cells filled with lipids. Which of the following features is necessary to determine the tumor grade in this patient?
- A. Invasion of surrounding structures
- B. Response to chemotherapy
- C. Nuclear pleomorphism and nucleolar prominence (Correct Answer)
- D. Involvement of regional lymph nodes
- E. Size of malignant proliferation
Tumor angiogenesis Explanation: ***Nuclear pleomorphism and nucleolar prominence***
- The **Fuhrman nuclear grading system** (and newer WHO/ISUP grading system) for renal cell carcinoma is based on **nuclear morphologic features**: nuclear size, nuclear contour irregularity, and most importantly, **nucleolar prominence**.
- **Grade 1**: Small uniform nuclei with inconspicuous nucleoli
- **Grade 2**: Slightly irregular nuclei with small nucleoli visible at 400× magnification
- **Grade 3**: Moderately irregular nuclei with prominent nucleoli visible at 100× magnification
- **Grade 4**: Marked nuclear pleomorphism, multilobated nuclei, and prominent nucleoli
- Higher nuclear grades correlate with more aggressive tumor behavior and worse prognosis.
*Invasion of surrounding structures*
- This feature is crucial for **tumor staging (T stage)**, specifically T3 disease when perinephric fat, renal vein, or IVC is invaded, and T4 when beyond Gerota's fascia.
- **Invasion** determines surgical approach and prognosis related to local spread but does not define histological grade.
*Response to chemotherapy*
- **Response to chemotherapy** is evaluated after treatment and is not a feature used for grading at diagnosis.
- Clear cell RCC is **chemoresistant**; treatment typically involves targeted therapy (VEGF inhibitors, mTOR inhibitors) or immunotherapy, not traditional chemotherapy.
*Involvement of regional lymph nodes*
- **Lymph node involvement** is a component of **tumor staging (N stage)**: N0 (no nodes), N1 (regional nodes positive).
- It indicates metastatic spread and significantly worsens prognosis but does not contribute to **histological grade**, which assesses cellular differentiation.
*Size of malignant proliferation*
- **Tumor size** is the primary criterion for **T staging**: T1a (≤4 cm), T1b (>4-7 cm), T2a (>7-10 cm), T2b (>10 cm), all confined to kidney.
- Size is a prognostic factor but does not determine **histological grade**, which is based exclusively on nuclear microscopic features.
Tumor angiogenesis US Medical PG Question 9: A 61-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office complaining of morning headaches of 6 weeks duration. A head MRI reveals a likely metastasis of unknown origin in the supratentorial region of the brain. On biopsy, the neoplastic mass is shown to have a mutation in BRAF, a protein kinase, in which a glutamic acid is substituted for valine at position 600 of the protein. Where did this metastasis most likely originate?
- A. Stomach
- B. Skin (Correct Answer)
- C. Breast
- D. Brain
- E. Bone
Tumor angiogenesis Explanation: ***Skin***
- A brain metastasis with a **V600E BRAF mutation** is highly suggestive of **melanoma**, a type of skin cancer.
- Melanoma frequently metastasizes to the **brain**, and the BRAF V600E mutation is a common and actionable target in advanced melanoma.
*Stomach*
- Stomach cancers (gastric adenocarcinomas) less commonly metastasize to the brain compared to melanoma.
- While BRAF mutations can occur in gastric cancer, the **V600E mutation** is not typically a defining feature of gastric cancer metastases to the brain.
*Breast*
- Breast cancer can metastasize to the brain, but the presence of a **BRAF V600E mutation** is not a characteristic genetic alteration for breast cancer.
- Common mutations in breast cancer include those in **ER, PR, and HER2** receptors or **PIK3CA**, not BRAF V600E.
*Brain*
- The question states the mass is a **metastasis of unknown origin**, implying it did not originate in the brain itself.
- Primary brain tumors like **gliomas** would not be described as metastases and have a different mutational spectrum.
*Bone*
- Bone cancers (sarcomas) or metastases to the bone usually do not present with a **BRAF V600E mutation** as their primary driver for brain metastasis.
- While various cancers can metastasize to bone, the specific mutation points away from a bone origin.
Tumor angiogenesis US Medical PG Question 10: A 31-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 4-week history of worsening headache, nausea, and vomiting. The headache is worse at night. Fundoscopic examination shows swelling of the optic discs. A CT scan of the brain shows a heterogeneous, hyperintense, intraventricular mass. The patient undergoes surgical excision of the mass. Pathologic examination of the surgical specimen confirms that the tumor is of neuronal origin. The cells in this specimen are most likely to stain positive for which of the following immunohistochemical markers?
- A. Synaptophysin (Correct Answer)
- B. S-100
- C. Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- D. Cytokeratin
- E. Desmin
Tumor angiogenesis Explanation: ***Synaptophysin***
- This marker is characteristic of **neuronal and neuroendocrine differentiation**, strongly supporting the diagnosis of a tumor of neuronal origin.
- Tumors like **gangliogliomas** and **central neurocytomas**, which are neuronal tumors, typically stain positive for synaptophysin.
*S-100*
- S-100 protein is a marker typically associated with cells of **glial**, **Schwann cell**, or **melanocytic** origin.
- While some neuronal tumors can show focal S-100 positivity, it is not the primary or most specific marker for neuronal differentiation.
*Glial fibrillary acidic protein*
- **GFAP** is the canonical marker for **astrocytes and other glial cells**, indicating a glial rather than neuronal origin for the tumor.
- An intraventricular mass of neuronal origin would not primarily stain for GFAP.
*Cytokeratin*
- **Cytokeratins** are intermediate filament proteins exclusively found in **epithelial cells** and are markers for carcinomas.
- They are not expressed in cells of neuronal origin, making this option incorrect.
*Desmin*
- **Desmin** is an intermediate filament protein found in **muscle cells** (smooth, skeletal, and cardiac).
- Its presence indicates a myogenic origin, which is inconsistent with a tumor described as being of neuronal origin.
More Tumor angiogenesis US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.