Paraneoplastic syndromes US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Paraneoplastic syndromes. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Paraneoplastic syndromes US Medical PG Question 1: A 74-year-old man presents to the physician with a painful lesion over his right lower limb which began 2 days ago. He says that the lesion began with pain and severe tenderness in the area. The next day, the size of the lesion increased and it became erythematous. He also mentions that a similar lesion had appeared over his left lower limb 3 weeks earlier, but it disappeared after a few days of taking over the counter analgesics. There is no history of trauma, and the man does not have any known medical conditions. On physical examination, the physician notes a cordlike tender area with erythema and edema. There are no signs suggestive of deep vein thrombosis or varicose veins. Which of the following malignancies is most commonly associated with the lesion described in the patient?
- A. Malignant melanoma
- B. Basal cell carcinoma
- C. Multiple myeloma
- D. Adenocarcinoma of pancreas (Correct Answer)
- E. Squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck
Paraneoplastic syndromes Explanation: ***Adenocarcinoma of pancreas***
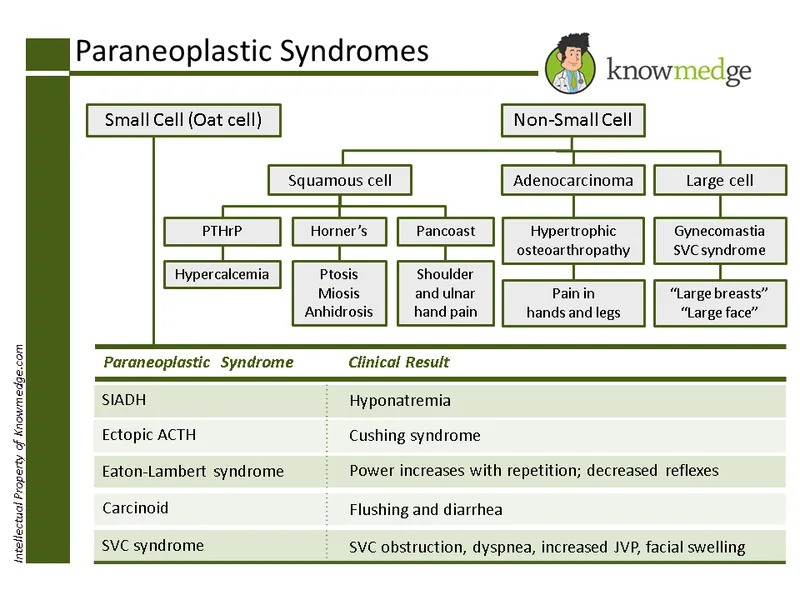
- The patient's presentation of a migratory, tender, cord-like lesion with erythema and edema, known as **Trousseau's Syndrome**, is a classic paraneoplastic phenomenon.
- **Trousseau's Syndrome**, or migratory thrombophlebitis, is most commonly associated with **adenocarcinomas**, particularly those of the **pancreas**, lung, gastrointestinal tract, and prostate.
*Malignant melanoma*
- While melanoma can metastasize widely, it is not typically associated with **migratory thrombophlebitis** as a paraneoplastic syndrome.
- Melanoma presents primarily as a **skin lesion** with characteristic changes in size, color, or shape, not thrombotic episodes.
*Basal cell carcinoma*
- This is a **slow-growing, localized skin cancer** that rarely metastasizes and is not associated with paraneoplastic syndromes like Trousseau's.
- It typically presents as a **pearly nodule** or an ulcerating lesion on sun-exposed areas.
*Multiple myeloma*
- Multiple myeloma is a **plasma cell malignancy** primarily affecting bone marrow, leading to bone lesions, renal failure, and hypercalcemia.
- While it can cause hypercoagulability, it less commonly presents with **Trousseau's Syndrome** compared to adenocarcinomas.
*Squamous cell carcinoma of head and neck*
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck is a malignancy strongly associated with **smoking and alcohol use**.
- It is not a common cause of **migratory thrombophlebitis** as a paraneoplastic syndrome, although other paraneoplastic syndromes can occur.
Paraneoplastic syndromes US Medical PG Question 2: A 61-year-old man presents to the urgent care clinic complaining of cough and unintentional weight loss over the past 3 months. He works as a computer engineer, and he informs you that he has been having to meet several deadlines recently and has been under significant stress. His medical history is significant for gout, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, diabetes mellitus type 2, and pulmonary histoplasmosis 10 years ago. He currently smokes 2 packs of cigarettes/day, drinks a 6-pack of beer/day, and he endorses a past history of cocaine use back in the early 2000s but currently denies any drug use. The vital signs include: temperature 36.7°C (98.0°F), blood pressure 126/74 mm Hg, heart rate 87/min, and respiratory rate 18/min. His physical examination shows minimal bibasilar rales, but otherwise clear lungs on auscultation, grade 2/6 holosystolic murmur, and a benign abdominal physical examination. However, on routine lab testing, you notice that his sodium is 127 mEq/L. His chest X-ray is shown in the picture. Which of the following is the most likely underlying diagnosis?
- A. Large cell lung cancer
- B. Squamous cell carcinoma
- C. Non-small cell lung cancer
- D. Adenocarcinoma
- E. Small cell lung cancer (Correct Answer)
Paraneoplastic syndromes Explanation: ***Small cell lung cancer***
- The patient's presentation with **cough**, **unintentional weight loss**, **hyponatremia (Na 127 mEq/L)**, and a significant smoking history (2 packs/day) are highly suggestive of **small cell lung cancer (SCLC)**.
- SCLC is **strongly associated with paraneoplastic syndromes**, particularly **syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH)**, which causes **euvolemic hyponatremia** - the key diagnostic clue in this case.
- The chest x-ray findings would typically show a **central mass** with **mediastinal widening**, characteristic of SCLC.
- SCLC accounts for approximately 15% of lung cancers but has the strongest association with paraneoplastic SIADH.
*Large cell lung cancer*
- While strongly associated with smoking, **large cell carcinoma** more commonly presents as a **peripheral mass** and is **less frequently associated with paraneoplastic syndromes like SIADH**.
- It's a diagnosis of exclusion and less likely to cause prominent hyponatremia compared to SCLC.
*Squamous cell carcinoma*
- **Squamous cell carcinoma** often presents with **hemoptysis** and can cause **hypercalcemia** (not hyponatremia) due to paraneoplastic **PTHrP secretion**.
- While it's centrally located and linked to smoking, **hyponatremia from SIADH is much less common** than in SCLC.
*Non-small cell lung cancer*
- This is a broad category that includes adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma. While specific types within NSCLC can cause various symptoms, the highly characteristic presentation of **cough, weight loss, and hyponatremia (suggesting SIADH)** in a heavy smoker points more specifically to SCLC.
- This option is too general; the clinical picture allows for a more specific diagnosis.
*Adenocarcinoma*
- **Adenocarcinoma** is typically a **peripheral lung cancer** and is the most common type in non-smokers, though it can occur in smokers.
- It is **less commonly associated with paraneoplastic hyponatremia (SIADH)** compared to small cell lung cancer.
- Would not typically present with the prominent hyponatremia seen in this patient.
Paraneoplastic syndromes US Medical PG Question 3: A 61-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 1-week history of dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and repeated falls. Neurologic examination shows past-pointing on a finger-nose test. She has a broad-based gait. Ophthalmologic exam shows rhythmic leftward movement of the globes. A serum antibody assay is positive for anti-Yo antibodies directed at proteins expressed by Purkinje cells. This patient's condition is most likely associated with which of the following tumors?
- A. Small cell lung cancer
- B. Breast cancer (Correct Answer)
- C. Neuroblastoma
- D. Ovarian teratoma
- E. Thymoma
Paraneoplastic syndromes Explanation: ***Breast cancer***
- **Anti-Yo antibodies**, also known as anti-Purkinje cell cytoplasmic antibodies type 1 (PCA-1), are strongly associated with **paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration** that most commonly occurs in patients with **breast or gynecological cancers** (particularly ovarian carcinoma).
- The patient's symptoms of **dizziness, nausea, vomiting, repeated falls, past-pointing, broad-based gait**, and **nystagmus** are classic signs of cerebellar dysfunction, which is consistent with paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration.
*Small cell lung cancer*
- Small cell lung cancer is more commonly associated with other paraneoplastic syndromes and antibodies, such as **Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (anti-voltage-gated calcium channel antibodies)** or **paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis/sensory neuronopathy (anti-Hu antibodies)**.
- While it can cause paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration, it is not the most frequent tumor type associated with **anti-Yo antibodies**.
*Neuroblastoma*
- Neuroblastoma is typically found in **children** and is associated with **opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome (anti-Ri antibodies)**, not anti-Yo antibodies or cerebellar degeneration in an adult.
- This patient is a 61-year-old woman, making neuroblastoma highly unlikely.
*Ovarian teratoma*
- Ovarian **teratoma** is strongly associated with **anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis**, which presents with psychiatric symptoms, seizures, and dyskinesias, different from the cerebellar signs seen here.
- Anti-Yo antibodies are associated with **ovarian carcinoma** (epithelial ovarian cancer), not teratomas. The distinction between teratoma and carcinoma is important in paraneoplastic syndromes.
*Thymoma*
- Thymoma is classically linked to **myasthenia gravis (anti-acetylcholine receptor antibodies)**, which causes fluctuating muscle weakness, not cerebellar dysfunction.
- It is not associated with **anti-Yo antibodies** or paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration.
Paraneoplastic syndromes US Medical PG Question 4: A 59-year-old woman comes to the physician because of upper extremity weakness and fatigue for the past 4 months. She has had difficulty combing her hair and lifting objects. She has also had difficulty rising from her bed in the mornings for 2 months. Over the past month, she started using over-the-counter mouth rinses for dry mouth. She has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes daily for 40 years. Examination shows decreased deep tendon reflexes. Repetitive muscle tapping shows increased reflex activity. There are no fasciculations or muscle atrophy. A low-dose CT scan of the chest shows a 3-cm mass with heterogeneous calcifications in the center of the right lung. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism responsible for this patient’s current symptoms?
- A. Metastasis
- B. Infection
- C. Invasion
- D. Autoimmunity (Correct Answer)
- E. Inflammation
Paraneoplastic syndromes Explanation: ***Autoimmunity***
- The patient's symptoms of **proximal muscle weakness**, fatigue, difficulty rising from bed, and a lung mass with **heterogeneous calcifications** (suggesting lung cancer in a heavy smoker) are highly indicative of **Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS)**, a **paraneoplastic autoimmune disorder** strongly associated with **small cell lung cancer** (60% of cases).
- LEMS is caused by **autoantibodies against presynaptic P/Q-type voltage-gated calcium channels** at the neuromuscular junction, leading to **impaired acetylcholine release** and muscle weakness. The **dry mouth** (autonomic dysfunction), **decreased reflexes that improve with repetitive muscle tapping** (post-tetanic potentiation), and absence of fasciculations or atrophy are characteristic features that distinguish LEMS from other neuromuscular disorders.
*Metastasis*
- While lung cancer can metastasize to various sites, including bone and brain, muscle weakness of this type and presentation is **unlikely to be directly caused by muscle metastases** in the absence of significant muscle atrophy or focal lesions.
- Furthermore, the specific neurological findings like **increased reflex activity with repetitive muscle tapping** (post-tetanic potentiation) and dry mouth point away from direct metastatic involvement as the primary mechanism for the muscle weakness.
*Infection*
- An infection would typically present with a more **acute onset** of symptoms, fever, or other signs of systemic inflammation, which are not described here.
- While some infections can cause muscle weakness (e.g., botulism, tetanus), the chronic nature, association with a lung mass, and specific neurological examination findings make infection a less likely primary cause.
*Invasion*
- Direct invasion of the tumor into nerves or muscles would typically cause more **focal or asymmetric weakness**, pain, or sensory deficits.
- The **generalized, proximal weakness** and the unique electrophysiological findings (repetitive muscle tapping improves reflexes) are not characteristic of direct tumor invasion.
*Inflammation*
- While some inflammatory myopathies (e.g., polymyositis or dermatomyositis) cause proximal muscle weakness, they typically present with **elevated muscle enzymes** and may have different clinical features (e.g., rash in dermatomyositis).
- The combination of a lung mass, dry mouth, and the specific neurological findings of LEMS points to a **paraneoplastic autoimmune process** rather than a primary inflammatory myopathy.
Paraneoplastic syndromes US Medical PG Question 5: A 39-year-old female presents with confusion. Her husband reports that she doesn't know where she is and cannot remember the date. She was recently diagnosed with small cell lung cancer. Vital signs are T 37C, HR 80, BP 120/80 mmHg, RR 14, and O2 sat 99% on room air. She is not orthostatic. Physical examination reveals moist mucous membranes and normal capillary refill. A basic metabolic profile reveals that serum sodium is 129. Regarding this patient's illness, which of the following is true?
- A. Urinary osmolarity will be < 100, and another potential cause of this disorder is excessive water drinking
- B. Urinary sodium will be > 20 and another potential cause of this disorder is renal failure
- C. Urinary sodium will be > 20 and fractional excretion of sodium will be >1%
- D. Urinary osmolarity will be > 100, and this illness will not correct with normal saline infusion (Correct Answer)
- E. Urinary sodium will be < 10, and fractional excretion of sodium will be <1%
Paraneoplastic syndromes Explanation: ***Urinary osmolarity will be > 100, and this illness will not correct with normal saline infusion***
- The patient's **hyponatremia** in the context of **small cell lung cancer** (a known cause of SIADH), euvolemia (normal vital signs, moist mucous membranes, normal capillary refill), suggests **SIADH**. In SIADH, **ADH** is inappropriately elevated, leading to water retention, dilute serum, and concentrated urine, so **urinary osmolarity will be > 100 mOsm/kg** (typically > 300 mOsm/kg).
- Since SIADH involves excess free water retention due to inappropriate ADH secretion and not volume depletion, administering **normal saline (0.9%)** can actually worsen the hyponatremia by providing additional free water without addressing the underlying ADH excess. The appropriate treatment for symptomatic SIADH is **hypertonic saline (3%)**, fluid restriction, and addressing the underlying cause.
*Urinary osmolarity will be < 100, and another potential cause of this disorder is excessive water drinking*
- In SIADH, the presence of inappropriately high ADH leads to increased water reabsorption in the collecting ducts, resulting in **concentrated urine**; therefore, **urinary osmolarity will be > 100 mOsm/kg**, not < 100.
- **Urinary osmolarity < 100 mOsm/kg** with hyponatremia suggests **primary polydipsia** (excessive water drinking), where ADH is appropriately suppressed and the kidneys produce maximally dilute urine. While polydipsia can cause hyponatremia, it is not consistent with the clinical picture of SIADH, where ADH is elevated and urine is concentrated.
*Urinary sodium will be > 20 and another potential cause of this disorder is renal failure*
- In SIADH, the kidneys continue to excrete sodium due to the expanded extracellular fluid volume even in the setting of hyponatremia, leading to a **urinary sodium concentration > 20 mEq/L** ✓.
- While **renal failure** can cause hyponatremia due to impaired free water excretion, it typically presents with volume overload, elevated BUN/creatinine, and other findings not seen in this euvolemic patient with SIADH. Renal failure is not a typical "other cause" when discussing SIADH specifically.
*Urinary sodium will be > 20 and fractional excretion of sodium will be >1%*
- In SIADH, the body experiences perceived volume expansion, causing natriuresis despite low serum sodium, resulting in **urinary sodium > 20 mEq/L** ✓.
- The **fractional excretion of sodium (FENa)** is typically **>1%** (usually 1-2%) in SIADH because the kidneys appropriately excrete sodium in response to the perceived volume expansion ✓. While this option is medically accurate for SIADH, it doesn't address the critical clinical point about treatment (that normal saline is contraindicated) and the urinary osmolarity, which are more defining diagnostic and therapeutic characteristics.
*Urinary sodium will be < 10, and fractional excretion of sodium will be <1%*
- **Urinary sodium < 10 mEq/L** and **FENa < 1%** typically indicate **hypovolemic hyponatremia** with effective arterial blood volume depletion (e.g., dehydration, heart failure, cirrhosis), where the kidneys are avidly conserving sodium and water.
- This is **not consistent with SIADH**, which presents as **euvolemic hyponatremia** where the urine is concentrated (not maximally dilute) and sodium continues to be excreted, making these values incompatible with the diagnosis.
Paraneoplastic syndromes US Medical PG Question 6: A 51-year-old woman comes to the physician because of swelling of her legs for 4 months. She first noticed the changes on the left leg, followed by the right leg. Sometimes her legs are itchy. She has a 1-month history of hoarseness. She returned from a trip to Mexico 8 months ago. She has a history of hypertension, constipation, and coronary artery disease. She works as a teacher at a primary school. Her mother had type-2 diabetes mellitus. She smoked one-half pack of cigarettes daily for 6 years but stopped smoking 11 years ago. She drinks one glass of wine daily and occasionally more on the weekend. Current medications include aspirin, bisoprolol, and atorvastatin. She is 165 cm (5 ft 5 in) tall and weighs 82 kg (181 lb); BMI is 30.1 kg/m2. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows bilateral pretibial non-pitting edema. The skin is indurated, cool, and dry. Peripheral pulses are palpated bilaterally. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. The patient is at increased risk for which of the following conditions?
- A. Cardiovascular complications
- B. Respiratory depression
- C. Hypothermia
- D. Cognitive impairment
- E. Myxedema coma (Correct Answer)
Paraneoplastic syndromes Explanation: ***Myxedema coma***
- The patient's symptoms of **non-pitting pretibial edema**, **hoarseness**, **cold and dry skin**, along with **constipation** and elevated BMI (30.1), are highly suggestive of **severe hypothyroidism**
- **Myxedema coma** is a life-threatening endocrine emergency representing the most severe manifestation of untreated hypothyroidism
- This patient with undiagnosed/untreated hypothyroidism is at highest risk for progression to myxedema coma, particularly if exposed to precipitating factors (infection, cold exposure, medications, surgery)
- Myxedema coma has high mortality (20-50%) and requires urgent recognition and treatment
*Cardiovascular complications*
- While hypothyroidism increases cardiovascular risk (bradycardia, pericardial effusion, heart failure), these are chronic complications
- The patient already has coronary artery disease, but the question asks about increased risk given the current presentation of severe hypothyroidism
- Myxedema coma represents a more immediate and life-threatening risk
*Respiratory depression*
- Respiratory depression can occur in severe hypothyroidism due to decreased respiratory drive and respiratory muscle weakness
- However, respiratory depression is typically a **feature of myxedema coma** rather than a separate entity
- Myxedema coma is the more comprehensive and critical diagnosis
*Hypothermia*
- Hypothermia is common in severe hypothyroidism due to decreased metabolic rate
- However, hypothermia is an **associated finding** of myxedema coma, not a separate complication
- Myxedema coma encompasses hypothermia along with altered mental status, cardiovascular collapse, and other systemic manifestations
*Cognitive impairment*
- Cognitive impairment (slowed thinking, memory problems, depression) can occur in chronic hypothyroidism
- This is a less acute and less life-threatening manifestation compared to the severe metabolic decompensation of myxedema coma
- Altered mental status in myxedema coma is more severe than chronic cognitive impairment
Paraneoplastic syndromes US Medical PG Question 7: A 31-year-old man comes to the physician because of worsening abdominal pain, an inability to concentrate at work, and a general lack of motivation over the past several months. He has a history of spontaneous passage of two kidney stones. His father and uncle underwent thyroidectomy before the age of 35 for thyroid cancer. Physical examination shows diffuse tenderness over the abdomen. Serum studies show:
Na+ 142 mEq/L
K+ 3.7 mEq/L
Glucose 131 mg/dL
Ca2+ 12.3 mg/dL
Albumin 4.1 g/dL
Parathyroid hormone 850 pg/mL
Further evaluation is most likely to show elevated levels of which of the following?
- A. Serum aldosterone to renin ratio
- B. Serum prolactin
- C. Urine metanephrines (Correct Answer)
- D. Urine 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid
- E. Midnight salivary cortisol
Paraneoplastic syndromes Explanation: ***Urine metanephrines***
- The patient's presentation with **hypercalcemia** (Ca2+ 12.3 mg/dL) and **elevated PTH** (850 pg/mL) indicates **hyperparathyroidism**.
- The family history of **thyroidectomy for thyroid cancer before age 35** (medullary thyroid cancer) along with hyperparathyroidism points towards **Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2 (MEN2)**. MEN2 syndromes often include **pheochromocytoma**, which is diagnosed by elevated **urine metanephrines**.
*Serum aldosterone to renin ratio*
- This ratio is used to screen for **primary hyperaldosteronism**, which presents with **hypertension and hypokalemia**.
- The patient's blood pressure is not mentioned as elevated, and his **potassium (3.7 mEq/L) is within normal limits**, making primary hyperaldosteronism less likely.
*Serum prolactin*
- Elevated serum prolactin levels indicate **hyperprolactinemia**, which is a feature of **MEN1 (Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 1)**.
- While MEN1 also includes hyperparathyroidism, the family history of **early-onset thyroid cancer** (suggesting medullary thyroid cancer, not typically seen in MEN1) points more strongly to MEN2.
*Urine 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid*
- Elevated levels of **5-HIAA in urine** are indicative of a **carcinoid tumor**, which secretes serotonin.
- Carcinoid tumors are not typically associated with the constellation of symptoms and family history presented, particularly hyperparathyroidism and early-onset medullary thyroid cancer.
*Midnight salivary cortisol*
- This test is used to diagnose **Cushing's syndrome**, which is characterized by elevated cortisol levels and symptoms like central obesity, moon facies, and striae.
- The patient's symptoms are not consistent with Cushing's syndrome, and the laboratory findings (hypercalcemia, elevated PTH) point to a different endocrine disorder.
Paraneoplastic syndromes US Medical PG Question 8: A lung mass of a 50 pack-year smoker is biopsied. If ADH levels were grossly increased, what would most likely be the histologic appearance of this mass?
- A. Layered squamous cells with keratin pearls
- B. Pleomorphic giant cells with leukocyte fragments in cytoplasm
- C. Hyperplasia of mucin producing glandular tissue
- D. Tall columnar cells bordering the alveolar septum
- E. Sheets of small round cells with hyperchromatic nuclei (Correct Answer)
Paraneoplastic syndromes Explanation: ***Sheets of small round cells with hyperchromatic nuclei***
- Grossly increased **ADH levels** in a smoker suggest **syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH)**, which is commonly associated with **small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC)**.
- SCLC is characterized histologically by sheets of **small (lymphocyte-like) cells** with scant cytoplasm and **hyperchromatic nuclei**.
*Layered squamous cells with keratin pearls*
- This description corresponds to **squamous cell carcinoma**, which is associated with smoking but typically causes **hypercalcemia** due to parathyroid hormone-related peptide (PTHrP) production, not elevated ADH.
- Key histological features are **keratin pearls** and **intercellular bridges**.
*Pleomorphic giant cells with leukocyte fragments in cytoplasm*
- This describes **large cell carcinoma**, which is a diagnosis of exclusion and does not typically manifest with paraneoplastic SIADH.
- **Large cell carcinoma** is characterized by large, anaplastic cells without differentiation towards squamous, glandular, or small cell features.
*Hyperplasia of mucin producing glandular tissue*
- This appearance is characteristic of **adenocarcinoma**, which often arises in non-smokers and is not typically associated with SIADH.
- **Adenocarcinoma** exhibits glandular differentiation and often produces mucin.
*Tall columnar cells bordering the alveolar septum*
- This refers to **lepidic growth pattern** often seen in some subtypes of **adenocarcinoma (e.g., adenocarcinoma in situ or minimally invasive adenocarcinoma)**.
- While it is a type of lung cancer, it is not primarily associated with SIADH as a paraneoplastic syndrome.
Paraneoplastic syndromes US Medical PG Question 9: A 54-year-old man comes to the emergency department for nausea and vomiting for the past 2 days. The patient reports that he felt tired and weak for the past week without any obvious precipitating factors. Past medical history is significant for hypertension controlled with hydrochlorothiazide. He denies diarrhea, changes in diet, recent surgery, vision changes, or skin pigmentation but endorses a 10-lb weight loss, headaches, fatigue, and a chronic cough for 2 years. He smokes 2 packs per day for the past 20 years but denies alcohol use. Physical examination demonstrates generalized weakness with no peripheral edema. Laboratory tests are shown below:
Serum:
Na+: 120 mEq/L
Cl-: 97 mEq/L
K+: 3.4 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
Ca2+: 10 mg/dL
Osmolality: 260 mOsm/L
Urine:
Na+: 25 mEq/L
Osmolality: 285 mOsm/L
Specific gravity: 1.007
What is the most likely finding in this patient?
- A. Antibodies against presynaptic calcium channels
- B. Pituitary hypertrophy
- C. Chromogranin positive mass in the lung (Correct Answer)
- D. Venous congestion at the liver
- E. Orphan Annie eyes and psammoma bodies in the thyroid
Paraneoplastic syndromes Explanation: ***Chromogranin positive mass in the lung***
- The patient presents with **hyponatremia**, **low serum osmolality (260 mOsm/L)**, and **inappropriately high urine osmolality (285 mOsm/L)** and urine sodium (25 mEq/L), which are characteristic findings of the **Syndrome of Inappropriate Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH)**.
- While **hydrochlorothiazide can cause hyponatremia**, the patient's **20-pack-year smoking history**, **chronic cough for 2 years**, **weight loss**, and **fatigue** strongly suggest an underlying malignancy rather than simple medication effect.
- The most likely cause of SIADH in this patient is **small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC)**, which is a **neuroendocrine tumor** that commonly secretes ADH ectopically and stains positive for **chromogranin A**, a neuroendocrine marker.
- SCLC is the most common malignancy associated with SIADH and frequently presents with paraneoplastic syndromes in heavy smokers.
*Antibodies against presynaptic calcium channels*
- This finding is characteristic of **Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome (LEMS)**, which is a paraneoplastic syndrome associated with small cell lung cancer caused by antibodies against voltage-gated calcium channels.
- While LEMS can occur in patients with SCLC, the presented symptoms and laboratory findings (specifically euvolemic hyponatremia consistent with SIADH) point more directly to **ectopic ADH secretion** from the tumor rather than a neuromuscular disorder.
- LEMS typically presents with proximal muscle weakness that improves with repeated use, which is not described in this patient.
*Pituitary hypertrophy*
- **Pituitary adenomas** can cause various endocrine abnormalities, but they do not typically cause SIADH.
- SIADH from pituitary pathology is rare and would not explain the **pulmonary symptoms** (chronic cough) or the patient's **significant smoking history**.
- This does not fit the overall clinical picture as well as small cell lung carcinoma.
*Venous congestion at the liver*
- **Hepatic venous congestion** occurs in conditions like right-sided heart failure, constrictive pericarditis, or Budd-Chiari syndrome.
- The patient has **no signs of volume overload** (no peripheral edema, and exam shows generalized weakness only).
- While heart failure can cause hyponatremia, it typically presents with hypervolemic hyponatremia with signs of fluid overload, which is absent in this case.
*Orphan Annie eyes and psammoma bodies in the thyroid*
- These are characteristic histological features of **papillary thyroid carcinoma**.
- There is **no clinical evidence** of thyroid pathology (e.g., thyroid nodule, neck mass, dysphagia, hoarseness) in this patient.
- Papillary thyroid carcinoma is not associated with SIADH or the paraneoplastic syndromes seen in this case.
Paraneoplastic syndromes US Medical PG Question 10: An obese 63-year-old man comes to the physician because of 3 episodes of red urine over the past week. He has also had recurrent headaches and intermittent blurry vision during the past month. He has benign prostatic hyperplasia. He works as an attendant at a gas station. The patient has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for the last 40 years. He does not drink alcohol. Current medications include tamsulosin. His temperature is 37.4°C (99.4°F), pulse is 90/min, and blood pressure is 152/95 mm Hg. Examination shows a flushed face. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no abnormalities. The abdomen is soft and non-tender. Digital rectal examination shows an enlarged prostate with no nodules. Urinalysis shows:
Blood 3+
Glucose negative
Protein negative
WBC 1-2/hpf
RBC 40-45/hpf
RBC casts none
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Nephrolithiasis
- B. Renal cell carcinoma (Correct Answer)
- C. Transitional cell bladder carcinoma
- D. IgA nephropathy
- E. Renal oncocytoma
Paraneoplastic syndromes Explanation: ***Correct: Renal cell carcinoma***
- This patient presents with **painless gross hematuria**, a common initial symptom of renal cell carcinoma, especially concerning in a long-term **smoker** with hypertension.
- The constellation of **headaches, blurry vision, and flushed face** could indicate paraneoplastic syndromes associated with RCC, such as **erythrocytosis (polycythemia)** causing facial flushing and hyperviscosity symptoms, or **hypertension due to renin secretion** by the tumor.
- RCC is strongly associated with **smoking** (major risk factor) and **obesity**.
*Incorrect: Nephrolithiasis*
- While nephrolithiasis can cause hematuria, it is typically associated with **severe, colicky flank pain** radiating to the groin, which is absent in this patient.
- The patient's other symptoms like headaches, blurry vision, and flushed face are not characteristic of nephrolithiasis.
*Incorrect: Transitional cell bladder carcinoma*
- Bladder cancer often presents with **painless gross hematuria**, similar to RCC.
- However, the additional symptoms of **headaches, blurry vision, flushed face, and hypertension in a long-term smoker** point more strongly towards a renal mass with **paraneoplastic effects** (polycythemia, renin secretion) rather than solely bladder involvement.
- Urothelial carcinoma is also associated with smoking but does not typically cause these systemic paraneoplastic manifestations.
*Incorrect: IgA nephropathy*
- IgA nephropathy is characterized by recurrent episodes of **gross hematuria**, often following an upper respiratory or gastrointestinal infection (synpharyngitic hematuria).
- Urinalysis would typically show **dysmorphic RBCs and RBC casts** (indicating glomerular bleeding), which are **absent** here.
- The non-glomerular hematuria pattern (no casts, no proteinuria) argues against this diagnosis.
*Incorrect: Renal oncocytoma*
- Renal oncocytomas are **benign renal tumors** that are often asymptomatic and discovered incidentally on imaging.
- While they can cause hematuria, they are **rarely associated with systemic symptoms** like headaches, blurry vision, hypertension, or flushed face.
- Unlike RCC, oncocytomas do **not produce paraneoplastic syndromes** (no erythropoietin or renin secretion).
More Paraneoplastic syndromes US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.