DNA repair genes and cancer US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for DNA repair genes and cancer. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
DNA repair genes and cancer US Medical PG Question 1: A 33-year-old woman comes to the physician 1 week after noticing a lump in her right breast. Fifteen years ago, she was diagnosed with osteosarcoma of her left distal femur. Her father died of an adrenocortical carcinoma at the age of 41 years. Examination shows a 2-cm, firm, immobile mass in the lower outer quadrant of the right breast. A core needle biopsy of the mass shows adenocarcinoma. Genetic analysis in this patient is most likely to show a defect in which of the following genes?
- A. BRCA1
- B. KRAS
- C. TP53 (Correct Answer)
- D. Rb
- E. PTEN
DNA repair genes and cancer Explanation: ***TP53***
- This patient's presentation with **early-onset breast cancer**, a history of **osteosarcoma** at a young age, and a father's death from **adrenocortical carcinoma** at 41 years strongly suggests **Li-Fraumeni syndrome**.
- Li-Fraumeni syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder caused by a germline mutation in the **tumor suppressor gene TP53**, increasing the risk for multiple primary cancers at a young age.
*BRCA1*
- While **BRCA1 mutations** are associated with an increased risk of breast and ovarian cancer, they are not typically linked to osteosarcoma or adrenocortical carcinoma.
- The constellation of cancers in this patient is more indicative of Li-Fraumeni syndrome than solely a BRCA1-related cancer syndrome.
*KRAS*
- **KRAS** is an oncogene commonly mutated in several cancers, including pancreatic, colorectal, and lung cancer, but is not primarily associated with either Li-Fraumeni syndrome or the specific tumors seen in this family history.
- Mutations in KRAS are typically somatic mutations acquired during a person's lifetime, not germline mutations causing inherited cancer syndromes like the one suggested here.
*Rb*
- Mutations in the **retinoblastoma (Rb) gene** are associated with retinoblastoma and an increased risk of osteosarcoma, but not typically with adrenocortical carcinoma or breast cancer as part of a classic inherited syndrome.
- The combination of breast cancer, osteosarcoma, and adrenocortical carcinoma points more specifically to TP53.
*PTEN*
- **PTEN mutations** are associated with Cowden syndrome, which increases the risk for breast cancer, thyroid cancer, and endometrial cancer, along with benign growths.
- However, Cowden syndrome does not typically include osteosarcoma or adrenocortical carcinoma as prominent features, making PTEN less likely than TP53 for this specific family history.
DNA repair genes and cancer US Medical PG Question 2: An investigator studying the molecular characteristics of various malignant cell lines collects tissue samples from several families with a known mutation in the TP53 tumor suppressor gene. Immunohistochemical testing performed on one of the cell samples stains positive for desmin. This sample was most likely obtained from which of the following neoplasms?
- A. Squamous cell carcinoma
- B. Rhabdomyosarcoma (Correct Answer)
- C. Prostate cancer
- D. Endometrial carcinoma
- E. Melanoma
DNA repair genes and cancer Explanation: ***Rhabdomyosarcoma***
- **Desmin** is an intermediate filament present in **muscle cells**, and its positive staining is a definitive marker for tumors of muscle origin
- A **rhabdomyosarcoma** is a malignant tumor of **skeletal muscle** differentiation, thus explaining the positive desmin staining.
*Squamous cell carcinoma*
- **Squamous cell carcinomas** are epithelial tumors that typically stain positive for **cytokeratin**, not desmin, as they originate from epithelial cells.
- They are characterized by features such as **intercellular bridges** and **keratinization**.
*Prostate cancer*
- **Prostate cancer** is an adenocarcinoma, meaning it's derived from glandular epithelial cells, and would stain positive for markers like **PSA (prostate-specific antigen)**, not desmin.
- This tumor type is characterized by glandular differentiation.
*Endometrial carcinoma*
- **Endometrial carcinomas** are adenocarcinomas of the uterine lining, derived from glandular epithelial cells, and would express **cytokeratins**, not desmin.
- Histologically, they show glandular structures and atypical endometrial cells.
*Melanoma*
- **Melanomas** are malignant tumors of melanocytes and would stain positive for markers such as **S-100**, **HMB-45**, and **Mart-1**, not desmin.
- These tumors originate from neural crest cells and are not muscle-derived.
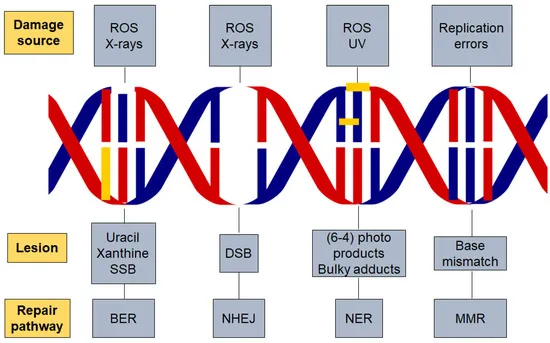
DNA repair genes and cancer US Medical PG Question 3: While performing a Western blot, a graduate student spilled a small amount of the radiolabeled antibody on her left forearm. Although very little harm was done to the skin, the radiation did cause minor damage to the DNA of the exposed skin by severing covalent bonds between the nitrogenous bases and the deoxyribose sugar, leaving several apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. Damaged cells would most likely repair these sites by which of the following mechanisms?
- A. Nucleotide excision repair
- B. Nonhomologous end joining repair
- C. Homologous recombination
- D. Mismatch repair
- E. Base excision repair (Correct Answer)
DNA repair genes and cancer Explanation: **Base excision repair**
- This mechanism is specifically involved in correcting **single-base DNA damage** or **modified bases**, such as **apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites**.
- It involves removing the damaged base by a **DNA glycosylase**, creating an AP site, which is then processed by an **AP endonuclease** to cleave the phosphodiester backbone, followed by DNA polymerase and ligase.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- Primarily repairs **bulky DNA lesions**, such as **thymine dimers** caused by UV radiation, or damage from chemical adducts that distort the DNA helix.
- It involves excising a larger oligonucleotide containing the damage, not just a single base.
*Nonhomologous end joining repair*
- This pathway is used to repair **double-strand DNA breaks**, where both strands of the DNA molecule are broken.
- It is a "quick-and-dirty" repair mechanism that ligates the broken ends together, often leading to small insertions or deletions.
*Homologous recombination*
- A repair mechanism for **double-strand DNA breaks** that uses a homologous DNA template (e.g., sister chromatid) to accurately repair the break.
- This process is highly accurate but occurs only when a homologous template is available, typically during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle.
*Mismatch repair*
- Corrects **base-pair mismatches** and **small insertions/deletions** that occur during DNA replication, which were not corrected by DNA polymerase proofreading.
- It targets newly synthesized DNA strands based on methylation patterns in the parental strand.
DNA repair genes and cancer US Medical PG Question 4: A 35-year-old woman, gravida 2, para 2, comes to the physician with intermenstrual bleeding and heavy menses for the past 4 months. She does not take any medications. Her father died of colon cancer at the age of 42 years. A curettage sample shows dysplastic tall, columnar, cells in the endometrium without intervening stroma. Germline sequencing shows a mutation in the MLH1 gene. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of neoplasia in this patient?
- A. Inability to excise bulky DNA adducts
- B. Defective checkpoint control transitions
- C. Impaired repair of deaminated DNA bases
- D. Accumulation of double-stranded DNA breaks
- E. Instability of short tandem DNA repeats (Correct Answer)
DNA repair genes and cancer Explanation: ***Instability of short tandem DNA repeats***
- The presence of a **germline mutation in the MLH1 gene**, combined with a family history of early-onset colon cancer (father died at 42), is highly indicative of **Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer or HNPCC)**.
- Lynch syndrome is caused by defects in **DNA mismatch repair (MMR) genes**, such as MLH1, which leads to microsatellite instability (MSI) where **short tandem DNA repeats** accumulate mutations due to inefficient repair.
*Inability to excise bulky DNA adducts*
- This mechanism is characteristic of defects in **nucleotide excision repair (NER)**, often seen in conditions like **xeroderma pigmentosum**, which is typically associated with skin cancers due to UV-induced DNA damage.
- The patient's presentation and MLH1 mutation point specifically to microsatellite instability, not bulky adduct repair.
*Defective checkpoint control transitions*
- Defects in cell cycle checkpoint control lead to uncontrolled cell proliferation and genomic instability, but this is a general mechanism in many cancers and not directly linked to MLH1 or microsatellite instability in the specific way that mismatch repair defects are.
- Mutations in genes like **p53** or **Rb** are classic examples of defective checkpoint controls, which is not the primary defect described by an MLH1 mutation.
*Impaired repair of deaminated DNA bases*
- This refers to defects in **base excision repair (BER)**, which is responsible for correcting small lesions like deaminated bases.
- While critical for DNA integrity, BER defects are not the primary mechanism behind Lynch syndrome and MLH1 mutations, which are specifically involved in correcting errors during DNA replication.
*Accumulation of double-stranded DNA breaks*
- This is typically associated with defects in **homologous recombination** or **non-homologous end-joining pathways**, often seen in conditions like **BRCA1/2 mutations** leading to breast and ovarian cancers.
- MLH1 mutations primarily affect mismatch repair and do not directly lead to an accumulation of double-stranded breaks.
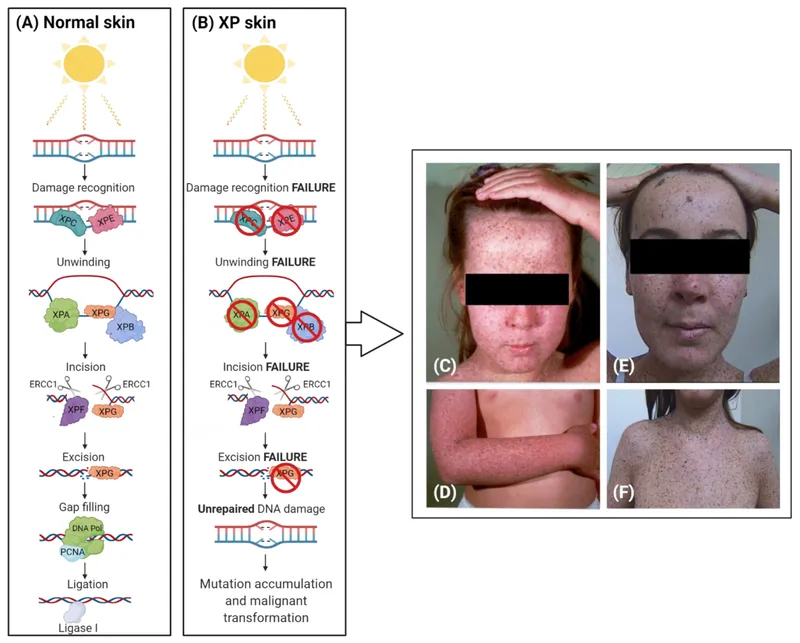
DNA repair genes and cancer US Medical PG Question 5: A 5-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother because of a 1-month history of a painful ulcer on her face. She has developed painful sunburns in the past with minimal UV exposure. Examination of the skin shows a 2-cm ulcerated nodule on the left cheek. There are scaly, hyperpigmented papules and plaques over the skin of the entire body. Ophthalmologic examination shows decreased visual acuity, clouded corneas, and limbal injection. Examination of a biopsy specimen from the facial lesion shows poorly-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Impairment of which of the following proteins is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Rb nuclear protein
- B. Base-specific glycosylase
- C. Excision endonuclease (Correct Answer)
- D. ATM serine/threonine kinase
- E. DNA helicase
DNA repair genes and cancer Explanation: ***Excision endonuclease***
- This patient's presentation with **painful sunburns**, **early-onset squamous cell carcinoma** on the face, and **ocular abnormalities (clouded corneas, decreased visual acuity)** is highly suggestive of **xeroderma pigmentosum (XP)**.
- XP is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by a defect in **nucleotide excision repair (NER)**, which is responsible for removing DNA damage primarily induced by **UV radiation**. **Excision endonucleases** are key enzymes in the initiation phase of NER, recognizing and excising the damaged DNA segment.
*Rb nuclear protein*
- The **Rb nuclear protein** is a tumor suppressor involved in cell cycle regulation (G1/S checkpoint).
- Impairment of Rb is associated with **retinoblastoma** and several other cancers, but not typically with this specific constellation of light sensitivity, skin cancer, and ocular damage seen in XP.
*Base-specific glycosylase*
- **Base-specific glycosylases** are involved in **base excision repair (BER)**, which primarily corrects small, non-helix-distorting base lesions (e.g., deaminated or alkylated bases).
- While important for DNA repair, defects in BER would not explain the extreme UV sensitivity and subsequent skin cancers characteristic of xeroderma pigmentosum, as these are primarily linked to UV-induced pyrimidine dimers.
*ATM serine/threonine kinase*
- **ATM (ataxia-telangiectasia mutated) kinase** is a critical protein involved in initiating the cellular response to **DNA double-strand breaks**.
- Defects in ATM cause **ataxia-telangiectasia**, characterized by cerebellar ataxia, immunodeficiency, and a predisposition to lymphoid malignancies, but not the specific skin and eye findings of XP.
*DNA helicase*
- **DNA helicases** are enzymes that unwind DNA and are involved in various DNA processes, including replication, recombination, and repair.
- While critical for many functions, a general defect in **DNA helicase** would lead to a broader range of severe developmental and cellular defects, and is not specifically linked to the clinical phenotype of xeroderma pigmentosum which results from specific NER pathway defects.
DNA repair genes and cancer US Medical PG Question 6: An investigator is studying DNA repair processes in an experimental animal. The investigator inactivates a gene encoding a protein that physiologically excises nucleotides from damaged, bulky, helix-distorting DNA strands. A patient with a similar defect in this gene is most likely to present with which of the following findings?
- A. Ataxic gait and facial telangiectasias
- B. Malignant breast and ovarian growths
- C. Leukocoria and a painful bone mass
- D. Colorectal and endometrial cancers
- E. Dry skin and increased photosensitivity (Correct Answer)
DNA repair genes and cancer Explanation: ***Dry skin and increased photosensitivity***
- The description of excising **nucleotides from damaged, bulky, helix-distorting DNA strands** points to a defect in **Nucleotide Excision Repair (NER)**.
- Patients with defects in NER, such as those with **xeroderma pigmentosum**, are highly susceptible to UV-induced DNA damage, leading to **dry skin, increased photosensitivity**, and a high risk of skin cancers.
*Ataxic gait and facial telangiectasias*
- This constellation of symptoms is characteristic of **ataxia-telangiectasia**, a disorder caused by mutations in the **ATM gene**, which is involved in **DNA double-strand break repair**.
- While a DNA repair defect, it's not primarily linked to the excision of bulky, helix-distorting DNA strands.
*Malignant breast and ovarian growths*
- These cancers are commonly associated with mutations in the **BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes**, which play crucial roles in **homologous recombination repair of DNA double-strand breaks**.
- This type of repair is distinct from the excision of bulky, helix-distorting DNA strands described in the question.
*Leukocoria and a painful bone mass*
- **Leukocoria** can indicate **retinoblastoma**, linked to mutations in the **RB1 tumor suppressor gene**, which regulates the cell cycle but isn't primarily a DNA repair gene.
- A painful bone mass could suggest **osteosarcoma**, which is sometimes seen in retinoblastoma patients but not directly related to the specific DNA repair defect described.
*Colorectal and endometrial cancers*
- These cancers are hallmarks of **Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer - HNPCC)**, which is caused by defects in **Mismatch Repair (MMR)** genes (e.g., MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, PMS2).
- Mismatch repair corrects errors that arise during DNA replication, which is different from excising bulky, helix-distorting DNA damage.
DNA repair genes and cancer US Medical PG Question 7: A 58-year-old male undergoes a surveillance colonoscopy in which a 2 cm adenoma is identified and removed. Had this adenoma not been excised, the patient would have been at risk of progression to carcinoma. Which of the following is the final mutational step in the progression from adenoma to carcinoma?
- A. p53 inactivation (Correct Answer)
- B. APC mutation
- C. COX-2 overexpression
- D. SMAD 2/4 loss
- E. K-ras mutation
DNA repair genes and cancer Explanation: ***p53 inactivation***
- **p53 loss of function** is typically the final genetic event in the **adenoma-to-carcinoma sequence**, facilitating unrestricted cell growth and preventing apoptosis in dysplastic cells.
- The **p53 tumor suppressor gene** normally checkpoints cell division and induces programmed cell death, making its inactivation critical for malignant transformation.
*APC mutation*
- **APC (adenomatous polyposis coli) mutation** is often the **initiating event** in colorectal adenoma formation, leading to aberrant crypt foci and polyp formation.
- While critical for early tumor genesis, it does not represent the final step in progression to invasive carcinoma.
*COX-2 overexpression*
- **Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) overexpression** leads to increased prostaglandin production, which can promote cell proliferation, angiogenesis, and inhibit apoptosis.
- It is an important factor in tumor growth and progression but occurs earlier in the sequence and is not the terminal mutational step for carcinoma.
*SMAD 2/4 loss*
- **SMAD 2/4 loss of function** disrupts the **TGF-β signaling pathway**, which normally inhibits cell growth and promotes differentiation.
- This event typically occurs in the late adenoma stage, contributing to dysplasia, but **p53 inactivation** is considered the final critical step for full malignant transformation.
*K-ras mutation*
- **K-ras mutation** is a well-known event in the **adenoma-to-carcinoma sequence**, occurring earlier than p53 inactivation, usually in intermediate-sized adenomas.
- It leads to constitutive activation of the RAS/MAPK pathway, promoting cell growth and survival, but generally before full malignant transformation.
DNA repair genes and cancer US Medical PG Question 8: A 10-year-old boy is brought by his mother to his pediatrician for "skin growths." His mother reports that she started noticing small lumps arising from the patient's lips and eyelids several months ago. She also notes that he seems to suffer from frequent constipation and appears "weaker" than many of his peers. The boy's past medical history is unremarkable. His father and paternal grandmother have a history of medullary thyroid carcinoma. His height and weight are in the 85th and 45th percentiles, respectively. His temperature is 99°F (37.1°C), blood pressure is 110/65 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, and respirations are 18/min. On examination, he has an elongated face with protruding lips. There are numerous sessile painless nodules on the patient's lips, tongue, and eyelids. This patient's condition is most strongly associated with a mutation in which of the following genes?
- A. NF1
- B. MEN1
- C. RET (Correct Answer)
- D. NF2
- E. c-KIT
DNA repair genes and cancer Explanation: ***RET***
- The constellation of **skin growths** on the lips and eyelids (neuromas), **constipation** (ganglioneuromatosis), and a family history of **medullary thyroid carcinoma** (MTC) strongly suggests **Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2B (MEN2B)**.
- MEN2B is caused by a germline mutation in the **RET proto-oncogene**, which is a receptor tyrosine kinase involved in cell growth and differentiation.
*NF1*
- Mutations in the **NF1 gene** cause **Neurofibromatosis type 1**, characterized by **café-au-lait spots**, neurofibromas (subcutaneous, not typically mucosal), iris Lisch nodules, and optic pathway gliomas.
- While it involves skin growths (neurofibromas), the specific mucosal neuromas, elongated facies, and family history of MTC are not typical features.
*MEN1*
- **MEN1 syndrome** is caused by mutations in the **MEN1 gene** and is associated with tumors of the **parathyroid**, **anterior pituitary**, and **pancreatic islet cells** (the 3 Ps).
- This patient's presentation of mucosal neuromas and medullary thyroid carcinoma is not characteristic of MEN1.
*NF2*
- Mutations in the **NF2 gene** cause **Neurofibromatosis type 2**, classically characterized by **bilateral vestibular schwannomas**, meningiomas, and ependymomas.
- Skin manifestations are less prominent and different from what is described, and MTC is not associated.
*c-KIT*
- Mutations in the **c-KIT gene** are primarily associated with **gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST)** and certain types of mastocytosis.
- It is not linked to the constellation of mucosal neuromas, elongated facies, or medullary thyroid carcinoma seen in this patient.
DNA repair genes and cancer US Medical PG Question 9: A 61-year-old Caucasian male presents to your office complaining of morning headaches of 6 weeks duration. A head MRI reveals a likely metastasis of unknown origin in the supratentorial region of the brain. On biopsy, the neoplastic mass is shown to have a mutation in BRAF, a protein kinase, in which a glutamic acid is substituted for valine at position 600 of the protein. Where did this metastasis most likely originate?
- A. Stomach
- B. Skin (Correct Answer)
- C. Breast
- D. Brain
- E. Bone
DNA repair genes and cancer Explanation: ***Skin***
- A brain metastasis with a **V600E BRAF mutation** is highly suggestive of **melanoma**, a type of skin cancer.
- Melanoma frequently metastasizes to the **brain**, and the BRAF V600E mutation is a common and actionable target in advanced melanoma.
*Stomach*
- Stomach cancers (gastric adenocarcinomas) less commonly metastasize to the brain compared to melanoma.
- While BRAF mutations can occur in gastric cancer, the **V600E mutation** is not typically a defining feature of gastric cancer metastases to the brain.
*Breast*
- Breast cancer can metastasize to the brain, but the presence of a **BRAF V600E mutation** is not a characteristic genetic alteration for breast cancer.
- Common mutations in breast cancer include those in **ER, PR, and HER2** receptors or **PIK3CA**, not BRAF V600E.
*Brain*
- The question states the mass is a **metastasis of unknown origin**, implying it did not originate in the brain itself.
- Primary brain tumors like **gliomas** would not be described as metastases and have a different mutational spectrum.
*Bone*
- Bone cancers (sarcomas) or metastases to the bone usually do not present with a **BRAF V600E mutation** as their primary driver for brain metastasis.
- While various cancers can metastasize to bone, the specific mutation points away from a bone origin.
DNA repair genes and cancer US Medical PG Question 10: A 74-year-old retired female teacher is referred to the endocrinology clinic. She is very concerned about a large mass in her neck that has progressively enlarged over the past 2 weeks. She also reports a 15 pound weight loss over the last 3 months. She now has hoarseness and difficulty swallowing her food, giving her a sensation that food gets stuck in her windpipe when she swallows. There is no pain associated with swallowing. Her speech is monotonous. No other gait or language articulation problems are noted. Testing for cranial nerve lesions is unremarkable. On palpation, a large, fixed and non-tender mass in the thyroid is noted. Cervical lymph nodes are palpable bilaterally. The patient is urgently scheduled for an ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration to guide management. Which of the following is the most likely gene mutation to be found in this mass?
- A. Activating mutation of the Ras protooncogene
- B. Inactivating mutation of the p53 tumor suppressor gene (Correct Answer)
- C. RET/PTC rearrangement
- D. BRAF mutation
- E. RET gene mutation
DNA repair genes and cancer Explanation: ***Inactivating mutation of the p53 tumor suppressor gene***
- The patient's presentation with a **rapidly enlarging, fixed, non-tender thyroid mass**, *hoarseness*, *dysphagia*, *weight loss*, and *palpable cervical lymph nodes* is highly suggestive of **anaplastic thyroid carcinoma (ATC)**, an aggressive malignancy.
- Inactivating mutations of the **p53 tumor suppressor gene** are frequently associated with the development and progression of ATC, contributing to its uncontrolled growth and poor prognosis.
*Activating mutation of the Ras protooncogene*
- **Ras mutations** are more commonly found in *follicular thyroid carcinoma* and *follicular variants of papillary thyroid carcinoma*.
- While they can indicate malignancy, they are not typically the primary genetic driver for the highly aggressive features seen in anaplastic carcinoma.
*RET/PTC rearrangement*
- **RET/PTC rearrangements** are characteristic genetic alterations found in **papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC)**.
- PTC typically presents with a *slower growth rate* and *less aggressive features* compared to the rapid progression described in the patient.
*BRAF mutation*
- The **BRAF V600E mutation** is the most common genetic alteration in **papillary thyroid carcinoma (PTC)**, especially the conventional and tall-cell variants.
- While it indicates a more aggressive subset of PTC, it is generally not the primary mutation associated with the extremely aggressive and rapidly progressing features of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma.
*RET gene mutation*
- **Germline RET mutations** are primarily associated with **medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC)**, often occurring as part of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 2 (MEN2).
- The clinical presentation with a *rapidly growing, fixed mass* and *compressive symptoms* is less typical for MTC, which can also be aggressive but usually presents differently.
More DNA repair genes and cancer US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.